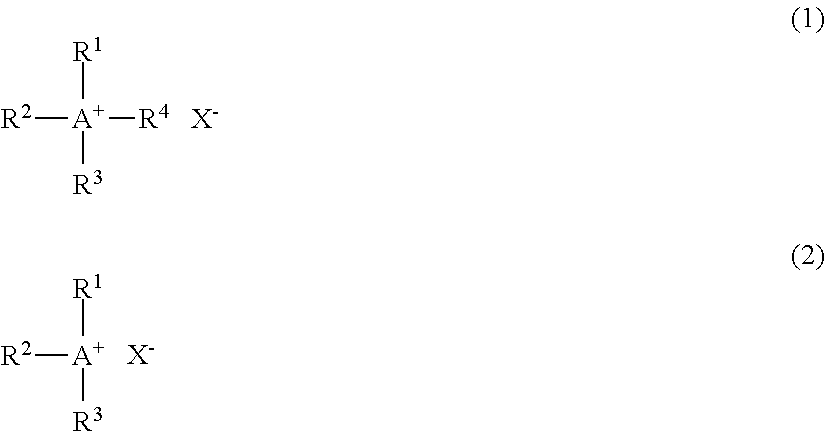Patents
Literature
48 results about "Hypobromite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The hypobromite ion, also called alkaline bromine water, is BrO⁻. Bromine is in the +1 oxidation state. Hypobromite is the bromine compound analogous to hypochlorites found in common bleaches, and in immune cells. In many ways, hypobromite functions in the same manner as hypochlorite, and is also used as a germicide and antiparasitic in both industrial applications, and in the immune system.
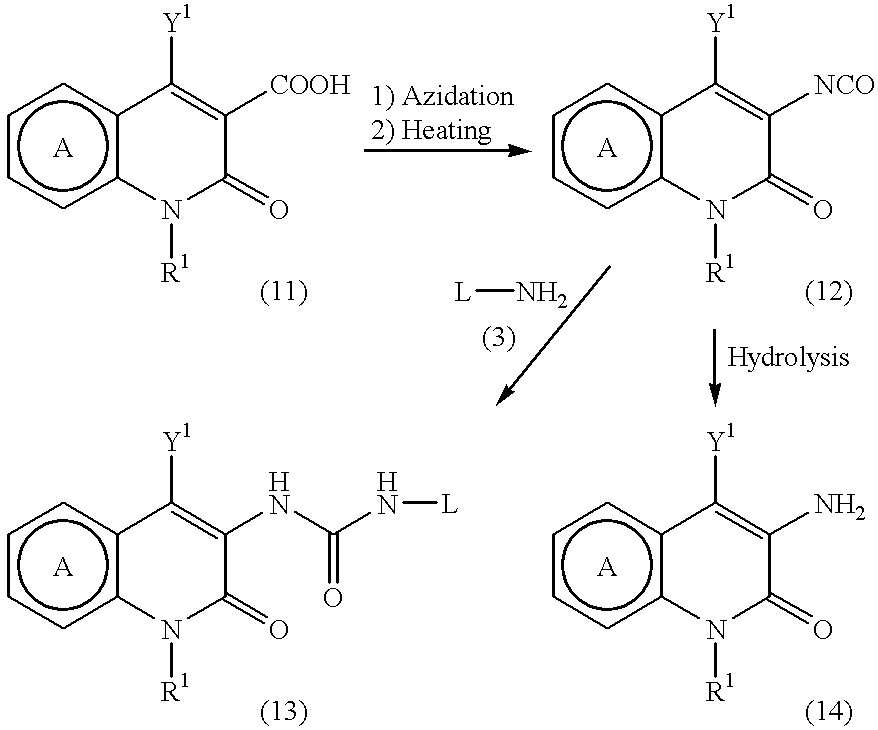
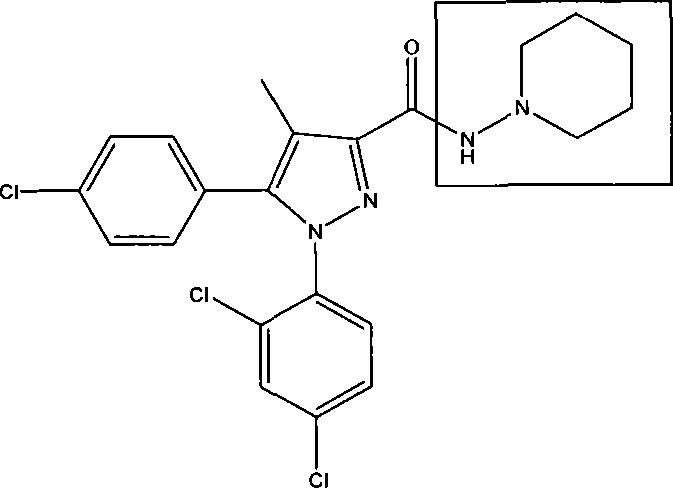
Pyridone derivatives and process for preparing the same
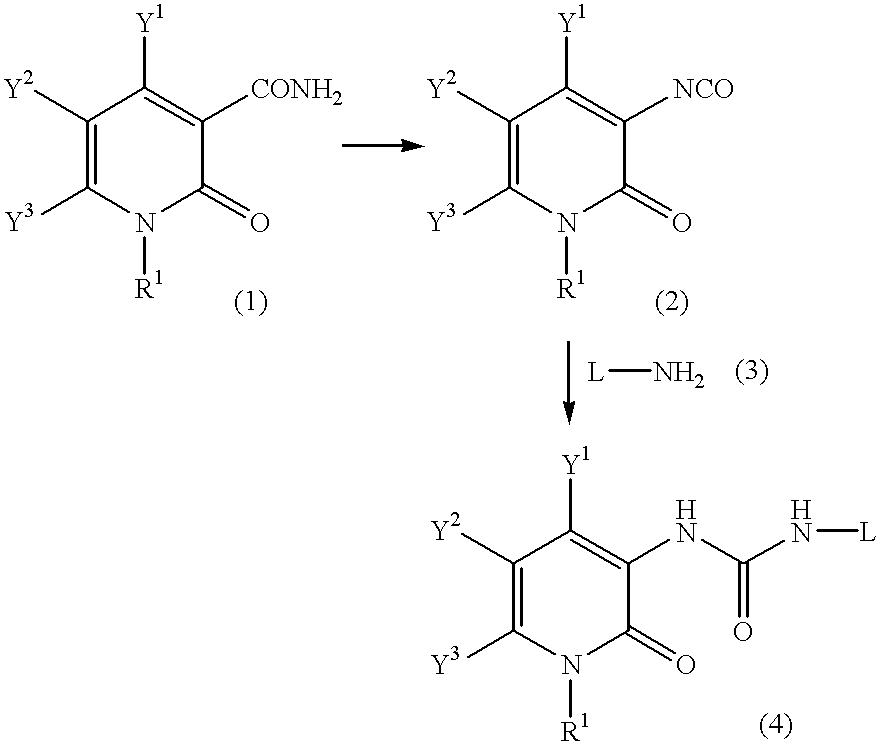
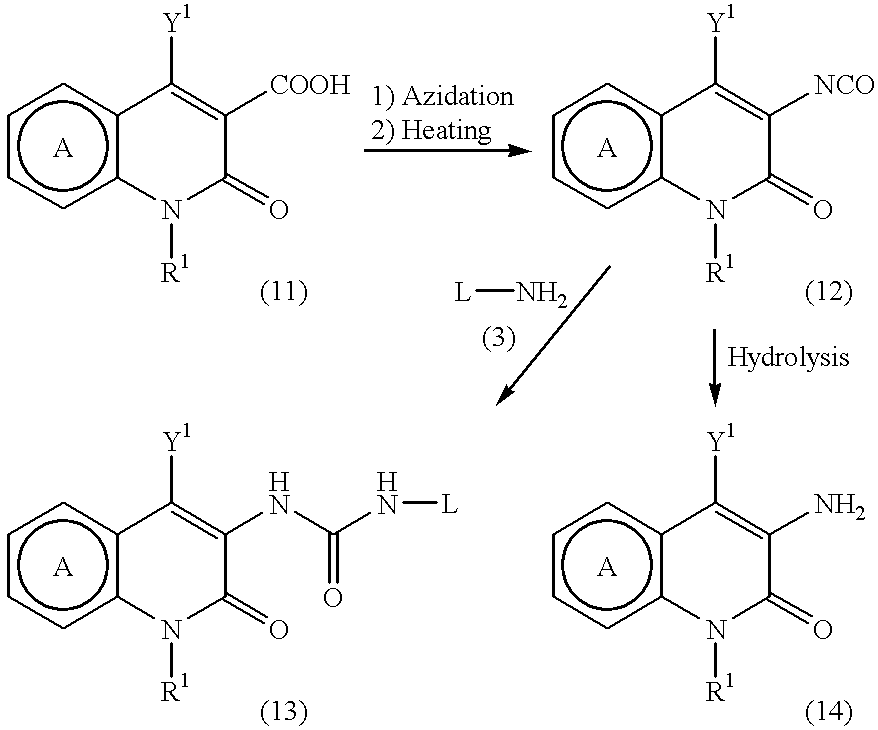
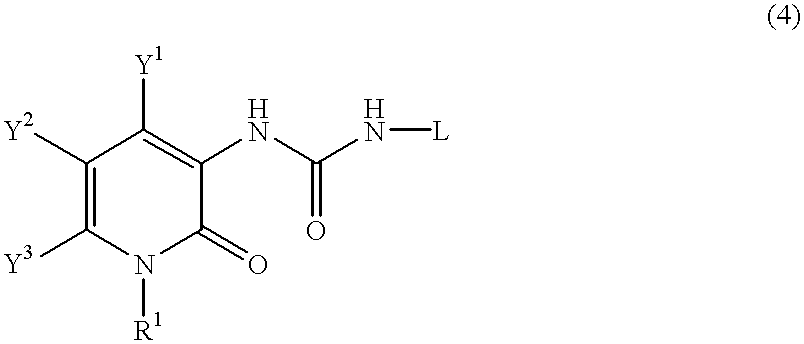
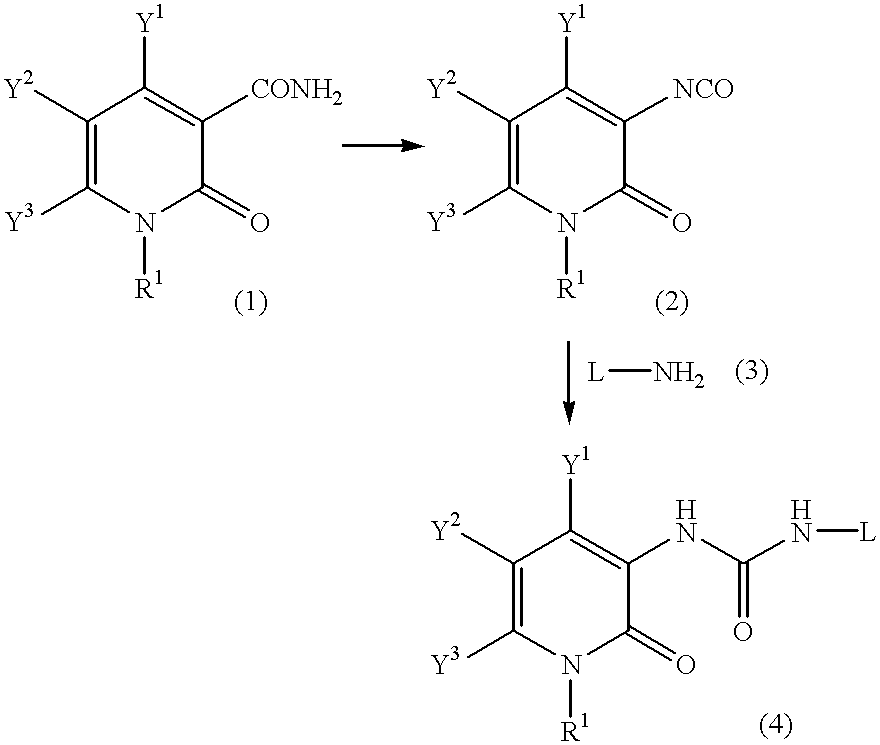
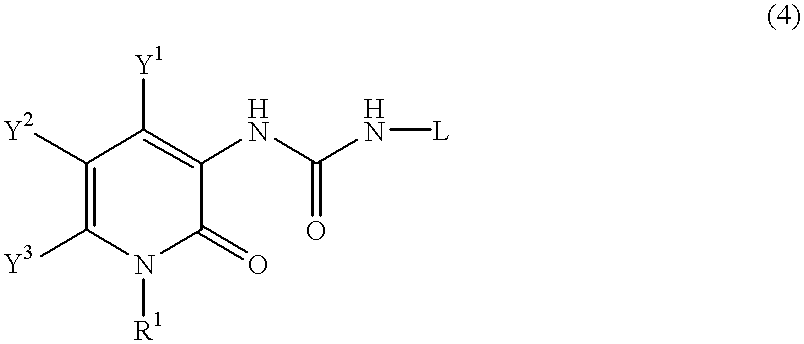
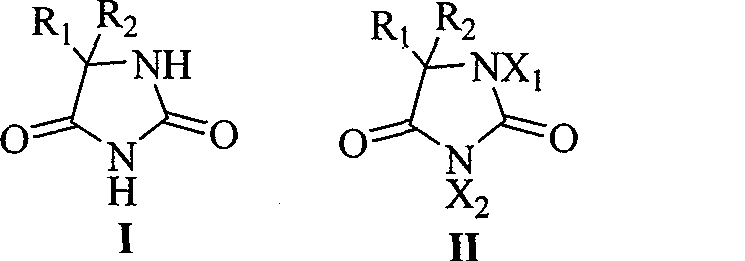
A process for preparing a pyridone derivative (4), which comprises reacting the compound (1) with a hypochlorite or a hypobromite or with lead tetraacetate to give the compound (2), and reacting the compound (2) with the compound (3). Said process is preferably especially from the standpoint of safety. wherein R1 is hydrogen, alkyl, substituted alkyl, etc.; Y1 is hydrogen, alky, substituted alky, etc.; Y2 and Y3 are indenpently hydrogen, halogen, etc.; and L is alkyl, substituted alkyl, etc.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
Pyridone derivatives and process for preparing the same
InactiveUS6452008B2Potent ACAT inhibitory activityProcess stabilityOrganic chemistryHalogenHypochlorite
A process for preparing a pyridone derivative (4), which comprises reacting the compound (1) with a hypochlorite or a hypobromite or with lead tetraacetate to give the compound (2), and reacting the compound (2) with the compound (3). Said process is preferably especially from the standpoint of safety.wherein R1 is hydrogen, alkyl, substituted alkyl, etc.; Y1 is hydrogen, alky, substituted alky, etc.; Y2 and Y3 are indenpently hydrogen, halogen, etc.; and L is alkyl, substituted alkyl, etc.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
Preparation method of amino pyridine bromide compound
InactiveCN101704781ASimple processLow equipment requirementsOrganic chemistryOrganic synthesisSodium hydroxide
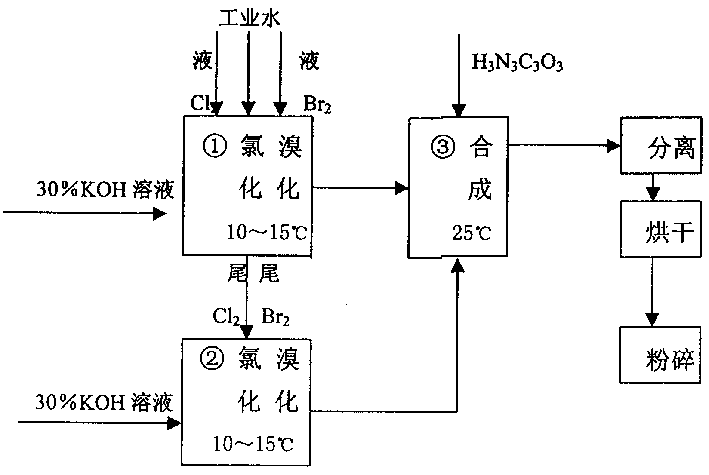
The invention discloses a preparation method of an amino pyridine bromide compound, relating to the field of organic synthesis. The amino pyridine bromide compound takes pyridine bromide formamide as raw material, and is prepared according to the following formula of Hofmann degradation reaction which comprising the following steps of: (1) dropping liquid bromine into alkali liquid with the concentration of 2.0-4.0 mol / L at -5-0 DEG C, reacting for 1.0 hour to obtain sodium hypobromite or potassium hypobromite, wherein the alkali is sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide or sodium methoxide; (2) adding the pyridine bromide formamide with the general foumula I to the hypobromite solution at room temperature for dissolving, raising temperature to 50-80 DEG C, reacting for 0.5-2 hours, decreasing temperature to 0 DEG C for separating out solids, and filtrating to obtain crude products; extracting the filtrate with an organic solvent, removing the solvent, and merging the crude products; re-crystallizing by using petroleum ether, and drying to obtain amino pyridine bromide. Wherein, the mole ratio of the general formula I to the alkali is 1:4-8, the mole ratio of the general formula I to water is 1:80-160, and the mole ratio of the general formula I to the liquid bromine is 1:1-2; and the organic solvent is dichloromethane, chloroform or normal hexane. The invention has the advantages of one-step reaction, simple process, low requirement on equipment, and high product purity, and the yield coefficient is around 50 percent.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Portable bio-chemical decontaminant system and method of using the same
InactiveUS20080241276A1Simplified logisticsEffective relatively quicklyBiocideCellsChlorine dioxideHypobromite
The present invention relates to a portable bio-chemical decontaminant system and methods of using the same. Specifically, the present invention provides a portable bio-chemical decontaminant system that is rapidly effective across a broad range of chemical and biological weapons agents. The disclosed portable bio-chemical decontaminant system electrochemically generates a decontaminant solution at the point of use obviating the need to transport corrosive or reactive chemicals, and dramatically simplifies the logistics of delivering an effective bio-chemical decontaminant system to wherever it may be needed. The portable bio-chemical decontaminant system electrochemically generates chlorine dioxide and hypobromite.
Owner:TDA RES
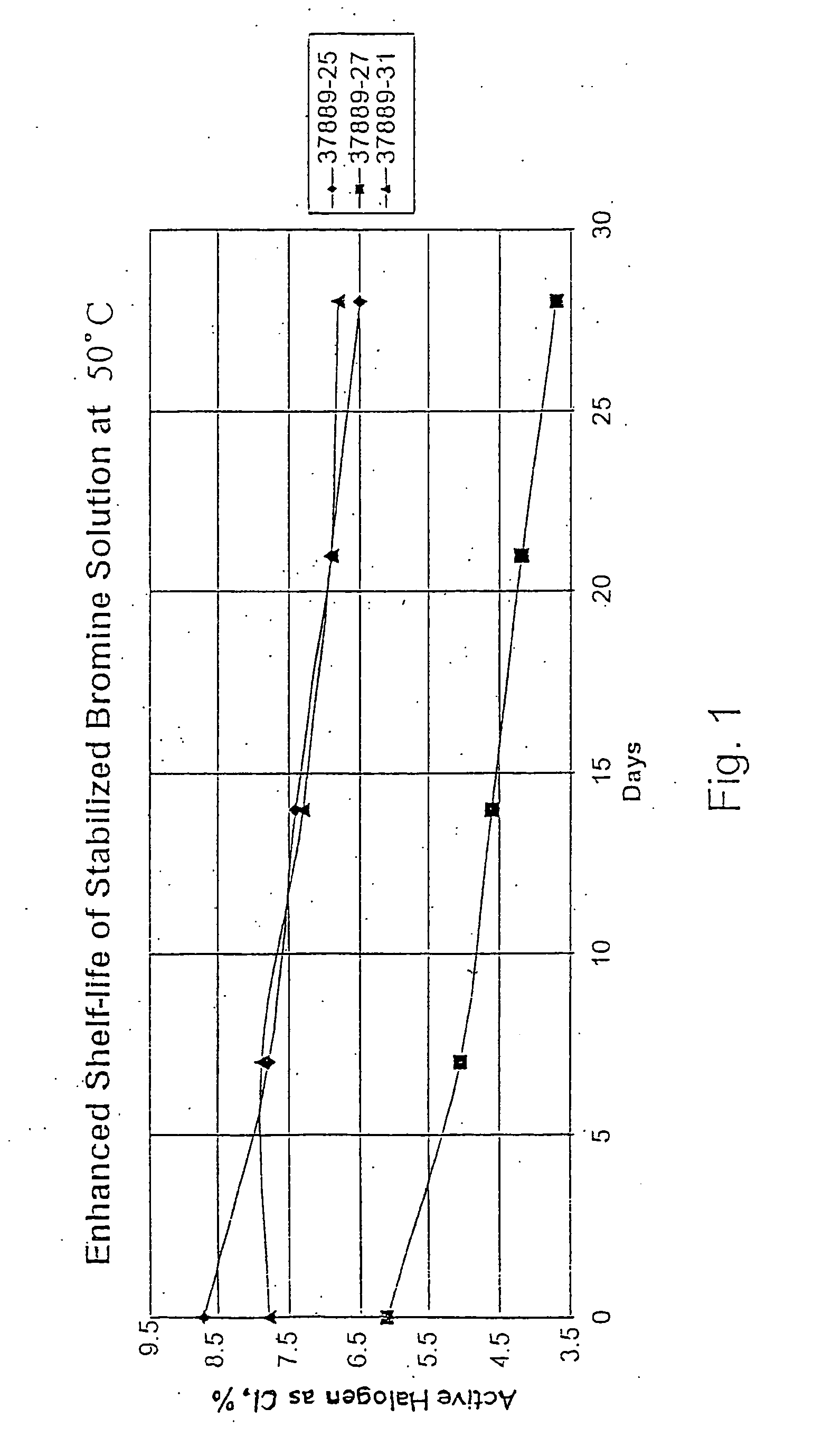
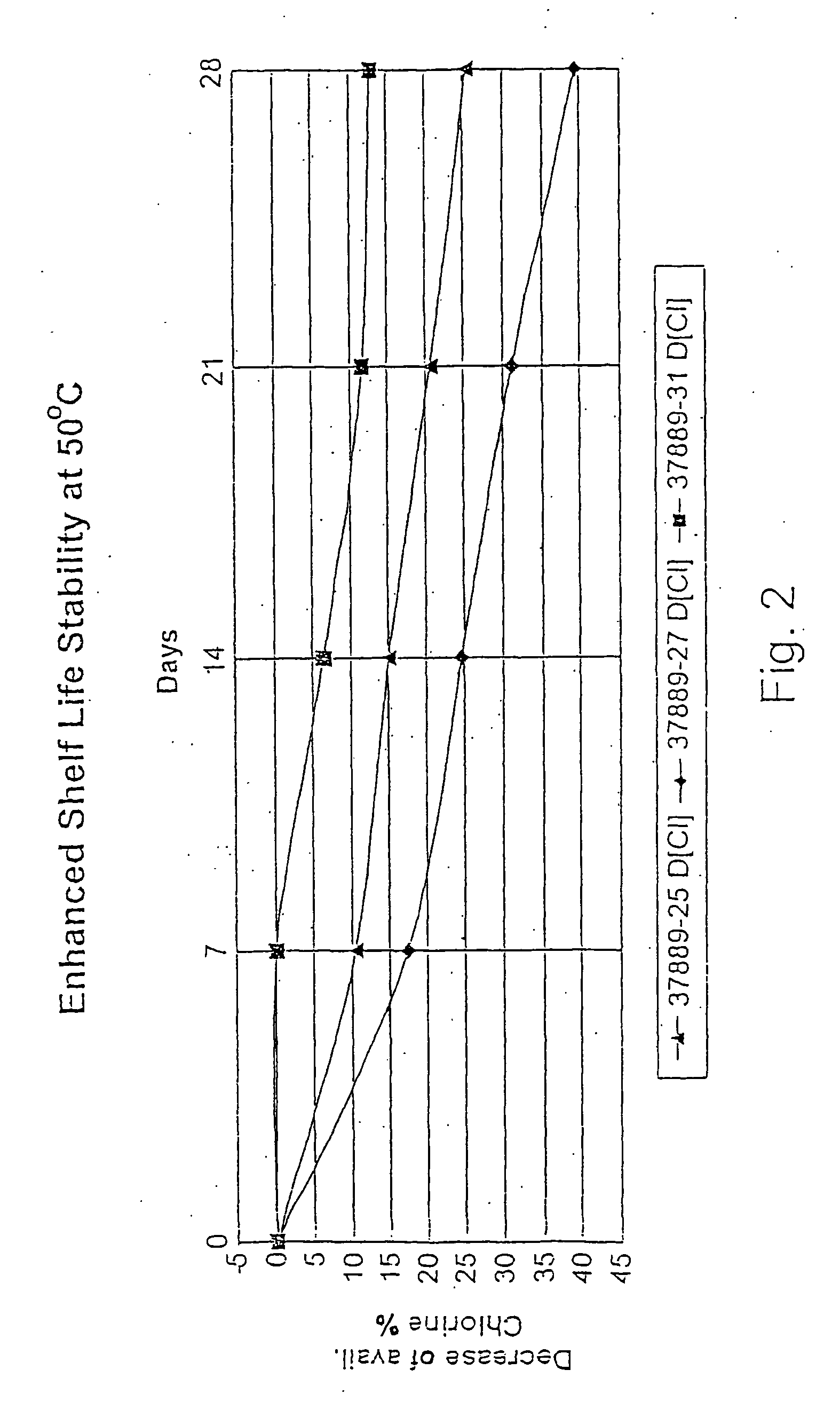
Process for the preparation of concentrated solutions of stabilized hypobromites
The invention is a process for the preparation of stabilized aqueous solutions of alkali hypobromites, which comprises reacting a concentrated alkali hydroxide aqueous solution with bromine, allowing the mixture to react, adding to the reaction product, which is a non-stabilized solution, an aqueous solution of a sulfamic compound, such as sodium sulfamate, and thus forming stabilized alkali hypobromite solution. This solution can be further stabilized by the addition of a sulfamate solution. The temperatures of all the above stages are comprised between −5 and +10° C.
Owner:BROMINE COMPOUNDS
Cmp of noble metals
InactiveCN1813038ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolishing compositions with abrasivesHypochloriteHalogen
The invention provides a method of polishing a substrate comprising (i) contacting a substrate comprising a noble metal layer with a chemical-mechanical polishing system comprising (a) a polishing component, (b) an oxidizing agent, and (c) a liquid carrier, and (ii) abrading at least a portion of the noble metal layer to polish the substrate. The polishing component is selected from the group consisting of an abrasive, a polishing pad, or a combination thereof, and the oxidizing agent is selected from the group consisting of bromates, bromites, hypobromites, chlorates, chlorites, hypochlorites, perchlorates, iodates, hypoiodites, periodates, peroxyacetic acid, organo-halo-oxy compounds, salts thereof, and combinations thereof. The chemical-mechanical polishing system has a pH of 9 or less, and the oxidizing agent does not produce a substantial amount of elemental halogen. The invention also provides a method of polishing a substrate comprising a noble metal layer and a second layer using the aforementioned polishing system that further comprises a stopping compound.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
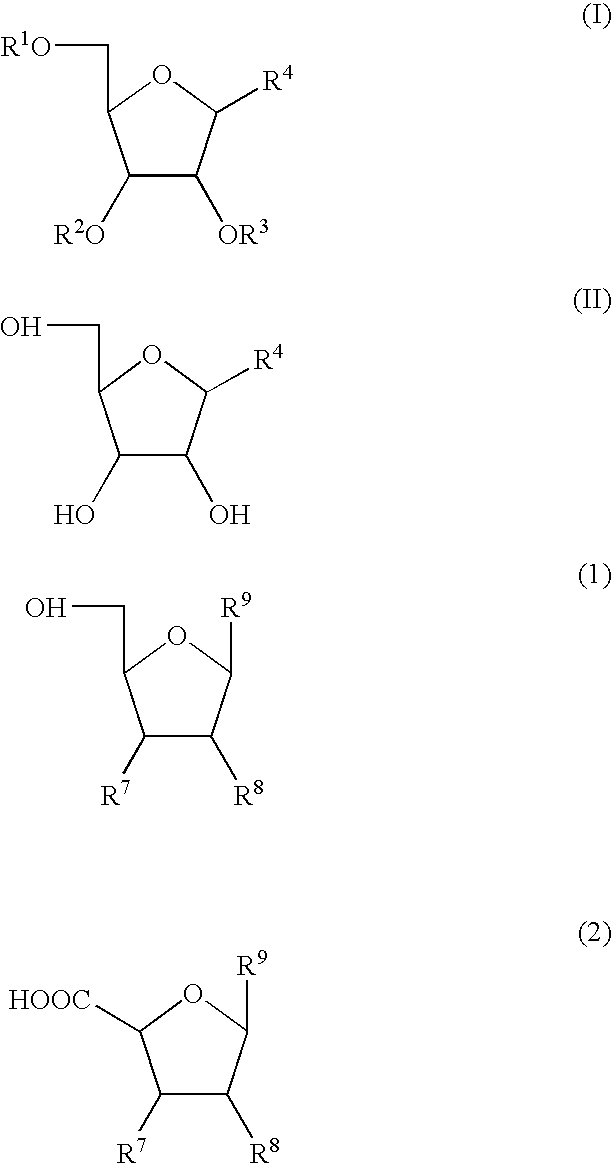
Processes for production of nucleosides
InactiveUS20060014944A1Reaction control is easyImprove securitySugar derivativesAminosugarsHypochloriteOrganic solvent
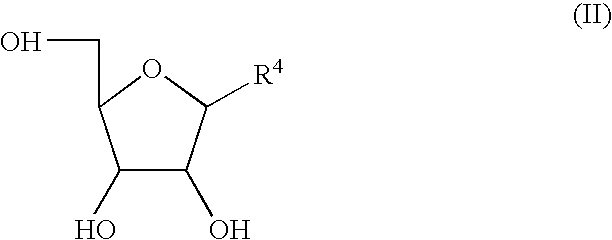
Nucleoside compounds represented by formula (II) may be prepared by subjecting a 2′,3′,5′-triacyloxynucleoside compound represented by formula (I) to deacylation using alkali metal hydroxide in a 0.01- to 0.5-fold amount in a molar ratio relative to the moles of the 2′,3′,5′-triacyloxynucleoside compound. The production method of the nucleoside compound of formula (II) suppresses the formation of by-products, and the products amy be used for the production of nucleoside derivatives. In addition, oxidation of a nucleoside compound represented by formula (1) in the presence of a 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxy catalyst, and hypochlorite or hypobromite, while adjusting pH to fall within 5 to 9, and further, extracting a nucleoside-carboxylic acid compound represented by the formula (2) into an organic solvent under acidic conditions, back-extracting the compound from the organic solvent into an aqueous alkali solution, and neutralizing the aqueous alkali solution by adding an acid thereto affords highly pure crystals of the compound of formula (2) or a salt thereof. wherein each symbol is as defined in the Description.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for surface inclusions detection, enhancement of endothelial and osteoblast cells adhesion and proliferation, sterilization of electropolished and magnetoelectropolished nitinol surfaces
InactiveUS20120093944A1Enhancement of endothelialEnhancement of osteoblast cell adhesionSuture equipmentsInorganic active ingredientsOsteoblast adhesionElectrolysis
The method for surface inclusions detection, enhancement of endothelial and osteoblast cells adhesion and proliferation and sterilization of electropolished and magnetoelectropolished Nitinol implantable medical device surfaces uses an aqueous solution of chemical compounds containing halogenous oxyanions as hypochlorite (ClO−) and hypobromite (BrO−) preferentially 6% sodium hypochlorite (NaClO).
Owner:ROKICKI MARGARET
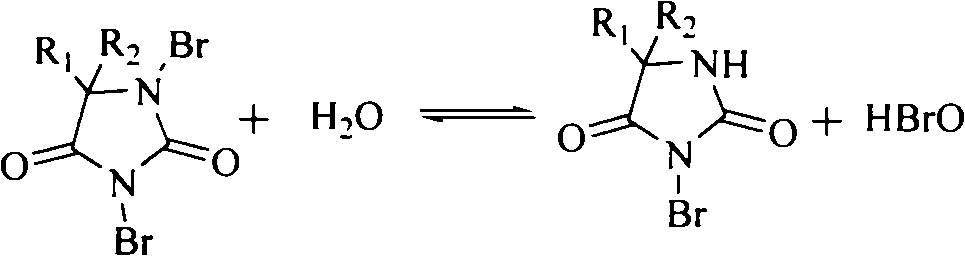
Electrochemical synthesis method for preparing halogenated hydantoin
InactiveCN101775613AReduce usageDoes not affect product qualityElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic productionHypochloriteHydantoin derivatives
The invention relates to an improved synthesis method for hydantoin bromo and for preparing dibromohydantoin or bromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin. The method comprises the following steps of: taking various hydantoins as raw materials, dissolving the hydantoins and the corresponding amount of bromide in 0.2g / mL saturation chlorate solution, electrolyzing the bromide solution and obtaining the corresponding hypobromite, generating hypobromous acid under the condition of addition of acid, further performing bromo reaction to the hydantoin, adjusting the bromide equivalent according to demand and synthesizing the corresponding dibromohydantoin or bromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin. Reaction liquid can be repeated and used, and the reaction yield can reach more than 95%. The invention has the advantages of easy obtainment of raw materials by low cost, low production cost, simple post treatment, high yield, good purity and repetitive recycle of the mother liquid. By utilizing the electrolysis process, the process is simple, and the equipment has low requirement, safe operation and no toxicity or stimulation.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
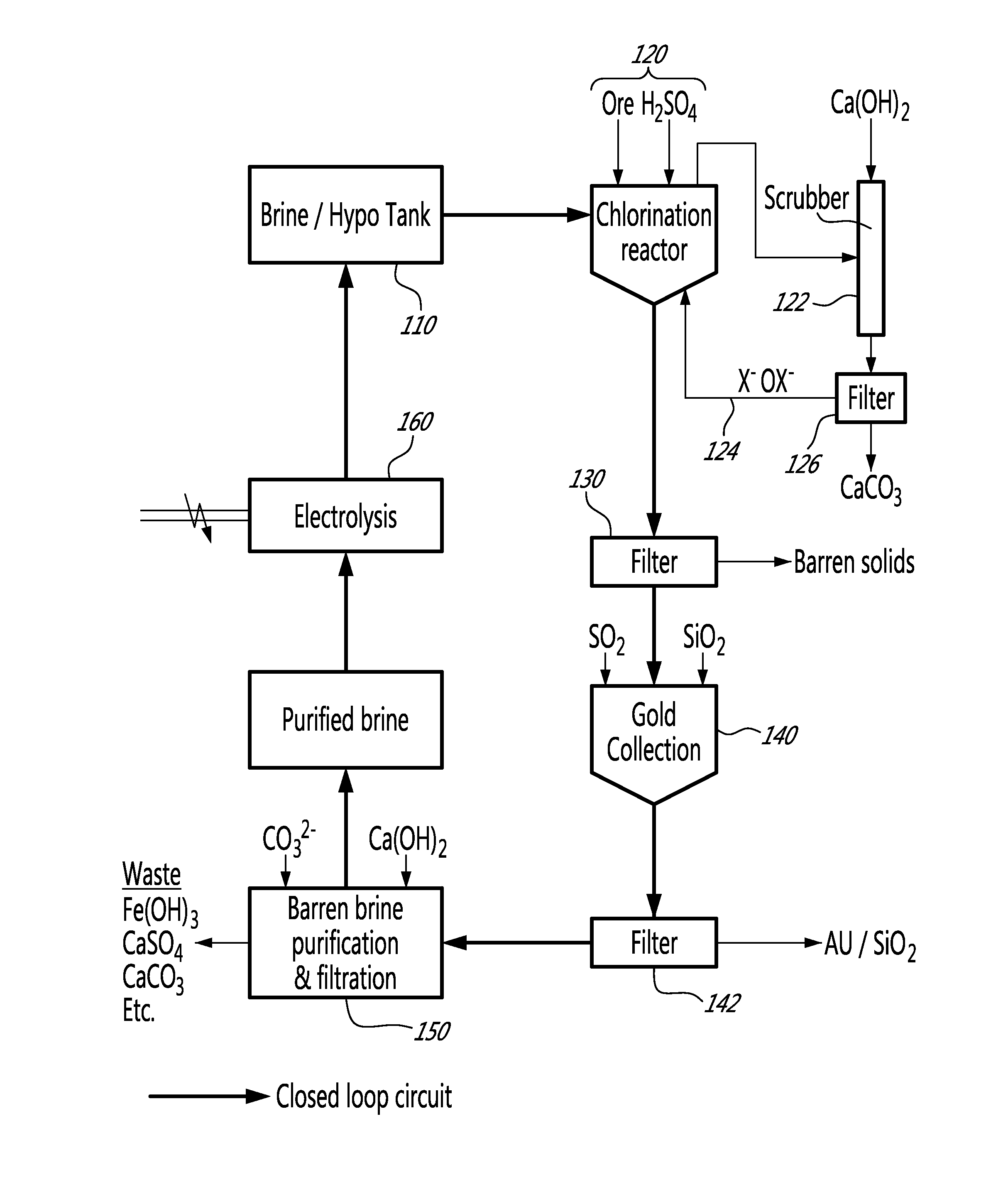
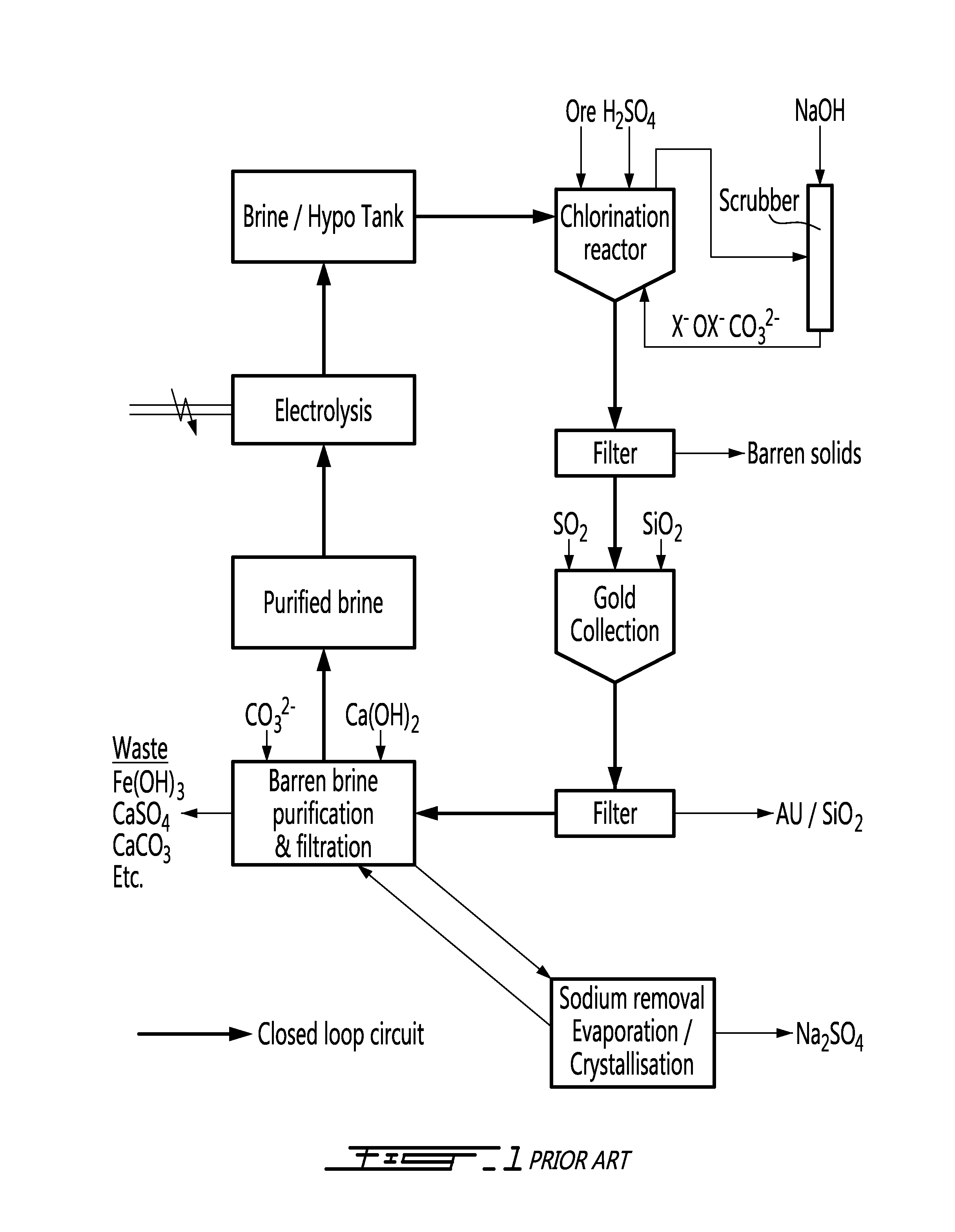
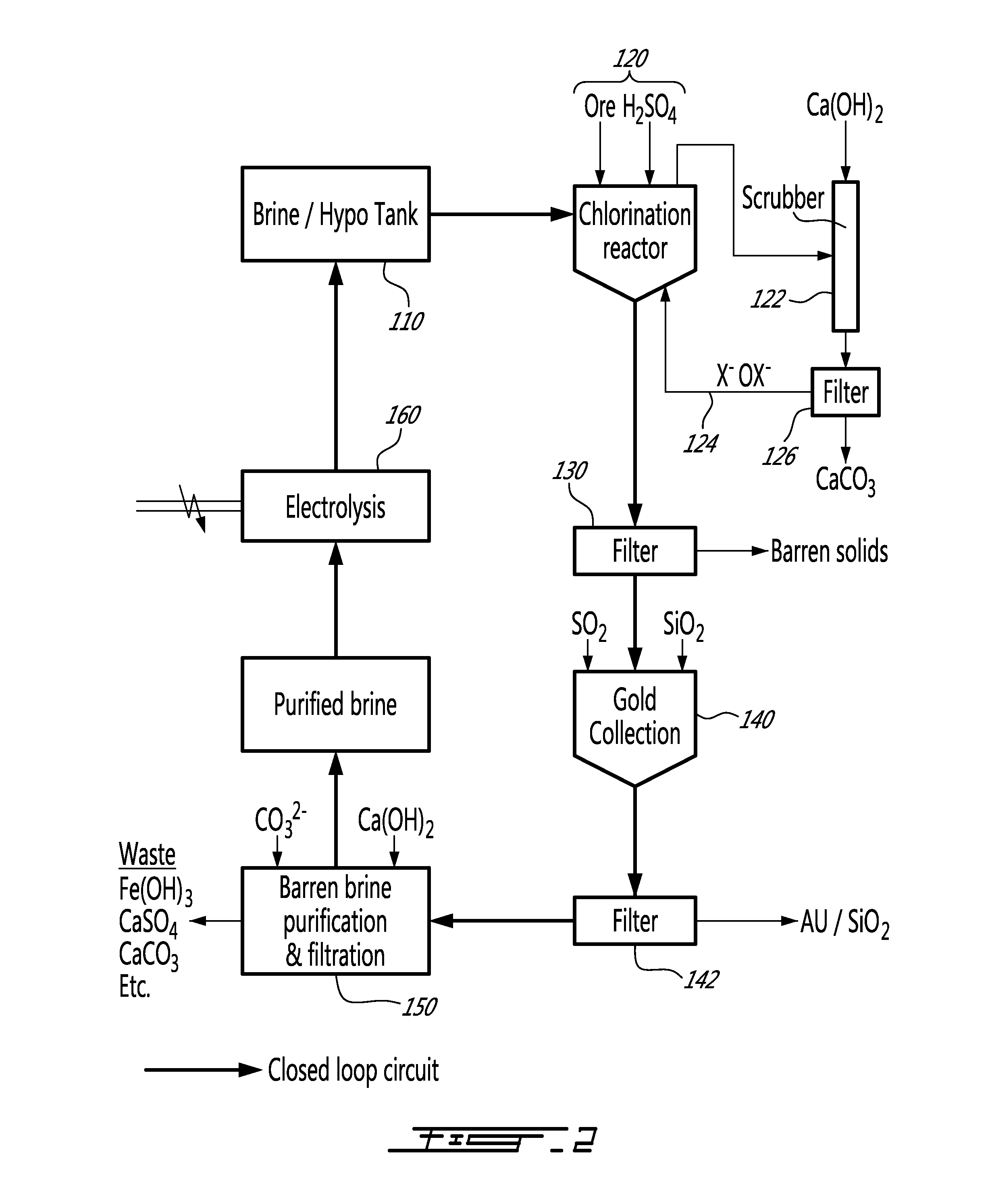
Closed loop method for gold and silver extraction by halogens
A method for extracting precious metals from a polymetallic ore, comprising a) generating hypochlorites from a salt brine; b) chlorination of the ore using hypochlorites under acidic conditions; c) filtering to collect a pregnant solution and treating the pregnant solution for collection of precious metals; d) filtering to separate the precious metals and a barren brine; e) purifying the barren brine; and f) recycling halogens from the purified brine in the form of hypohalites formed by electrolysis of the purified brine, and comprising hypochlorite and hypobromite; step b) further comprising scrubbing excess halogens using calcium hydroxide; treating the pregnant solution in step c) comprises reducing an oxydo reduction potential of the pregnant solution and using calcium hydroxide for neutralization; and step e) comprising increasing the pH of the barren brine by addition of calcium hydroxide.
Owner:DUNDEE SUSTAINABLE TECH
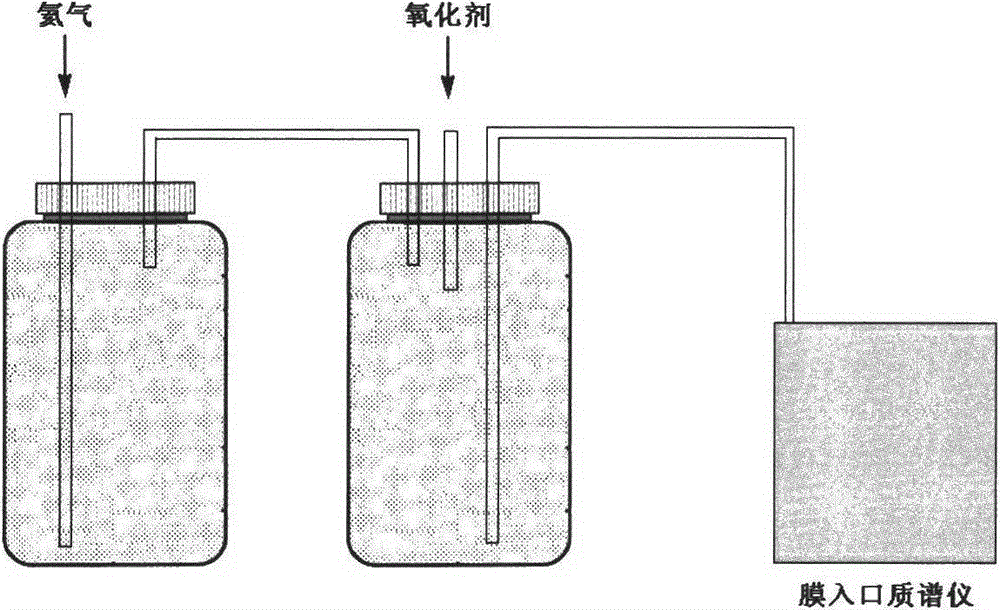
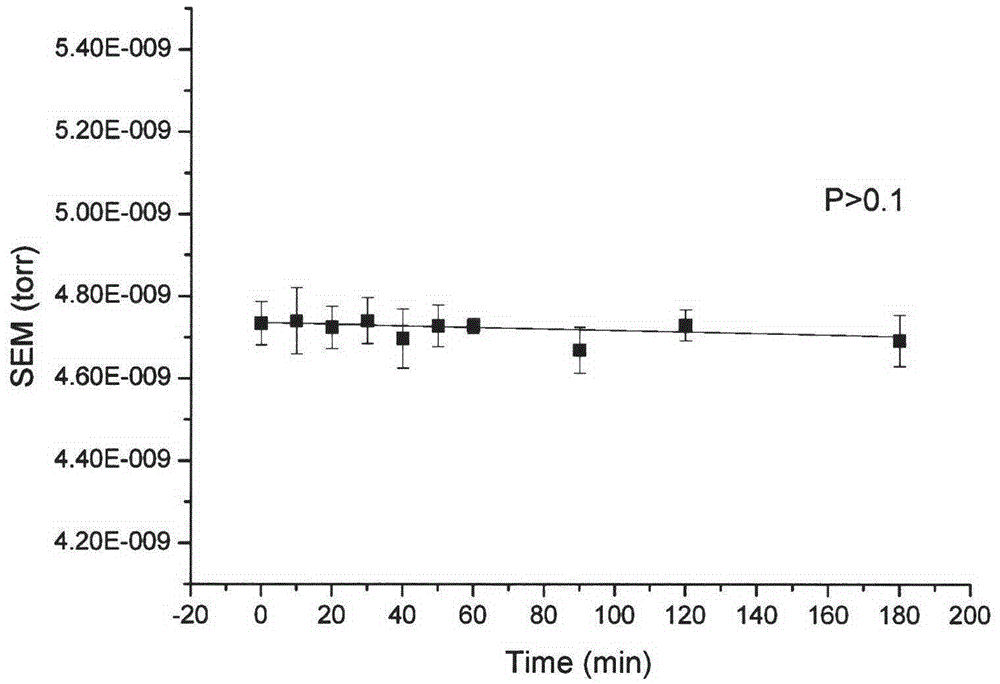
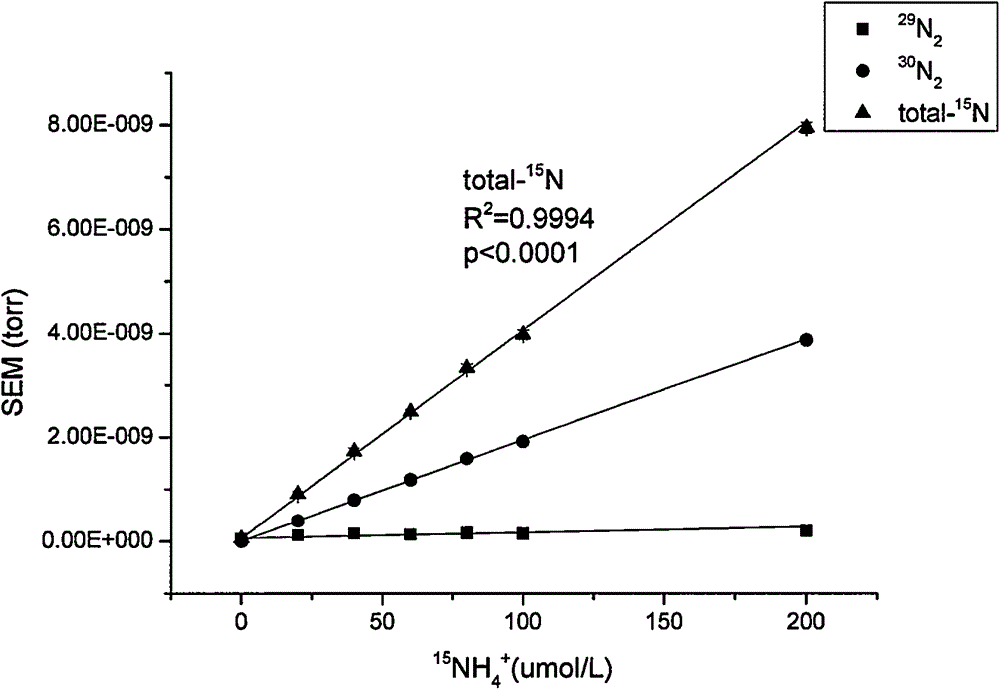
Membrane entrance mass spectrometer based method for analyzing content of dissolved nitrogen isotope
ActiveCN104422729ALow cost of analysisShort analysis timeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass analyzerIsotope
A membrane entrance mass spectrometer based method for analyzing content of dissolved nitrogen isotope comprises the following steps: 1, introducing helium into the liquid to be tested for 20 min to remove nitrogen dissolved in water; 2, adding an oxidant iodine hypobromite solution in the liquid to be tested with nitrogen removed to oxidize ammonia nitrogen into nitrogen; 3, determining a standard curve through a standard sample membrane entrance mass spectrometer; 4, measuring the liquid to be tested from the step 2 by the membrane entrance mass spectrometer, and calculating the content of nitrogen isotope in the ammonia nitrogen liquid; 5, removing the original ammonia nitrogen in the liquid to be tested treated in the step 2 by magnesium oxide, acidifying with sulfuric acid, then reducing nitrate to ammonia nitrogen by zinc powder, and then use the above step 2 to step 4 to obtain the content of nitrate nitrogen isotope in the solution. The method provided by the invention can fast and accurately measure and analyze the content of dissolved nitrogen isotope, and is conducive to promoting the application of nitrogen isotope tracer technique.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Bromide reduction process in liquid solutions
InactiveUS20060110312A1Increase supplyReduced effectivenessHypochlorous acidBromine oxygen compoundsPotassiumPh dependent
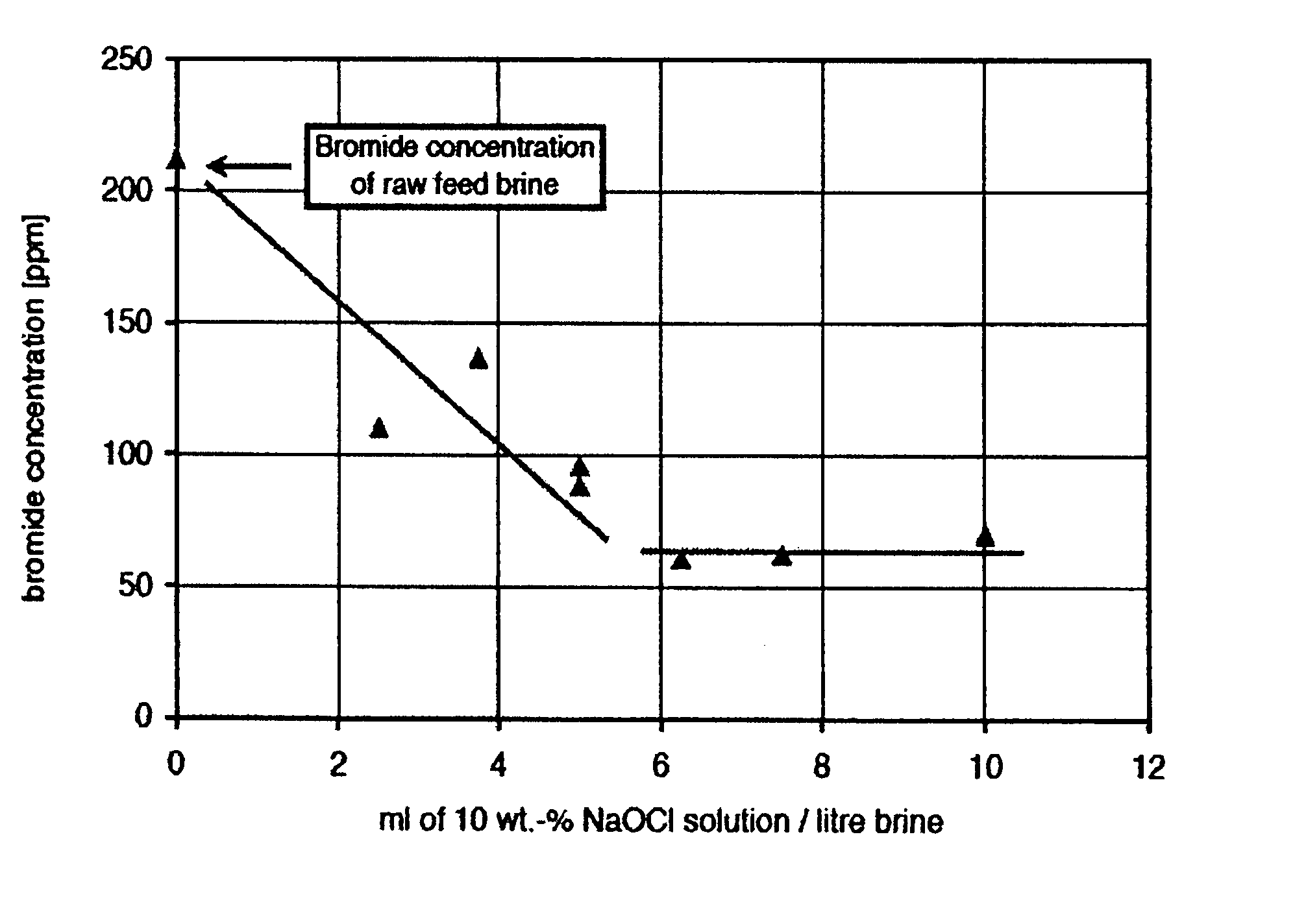
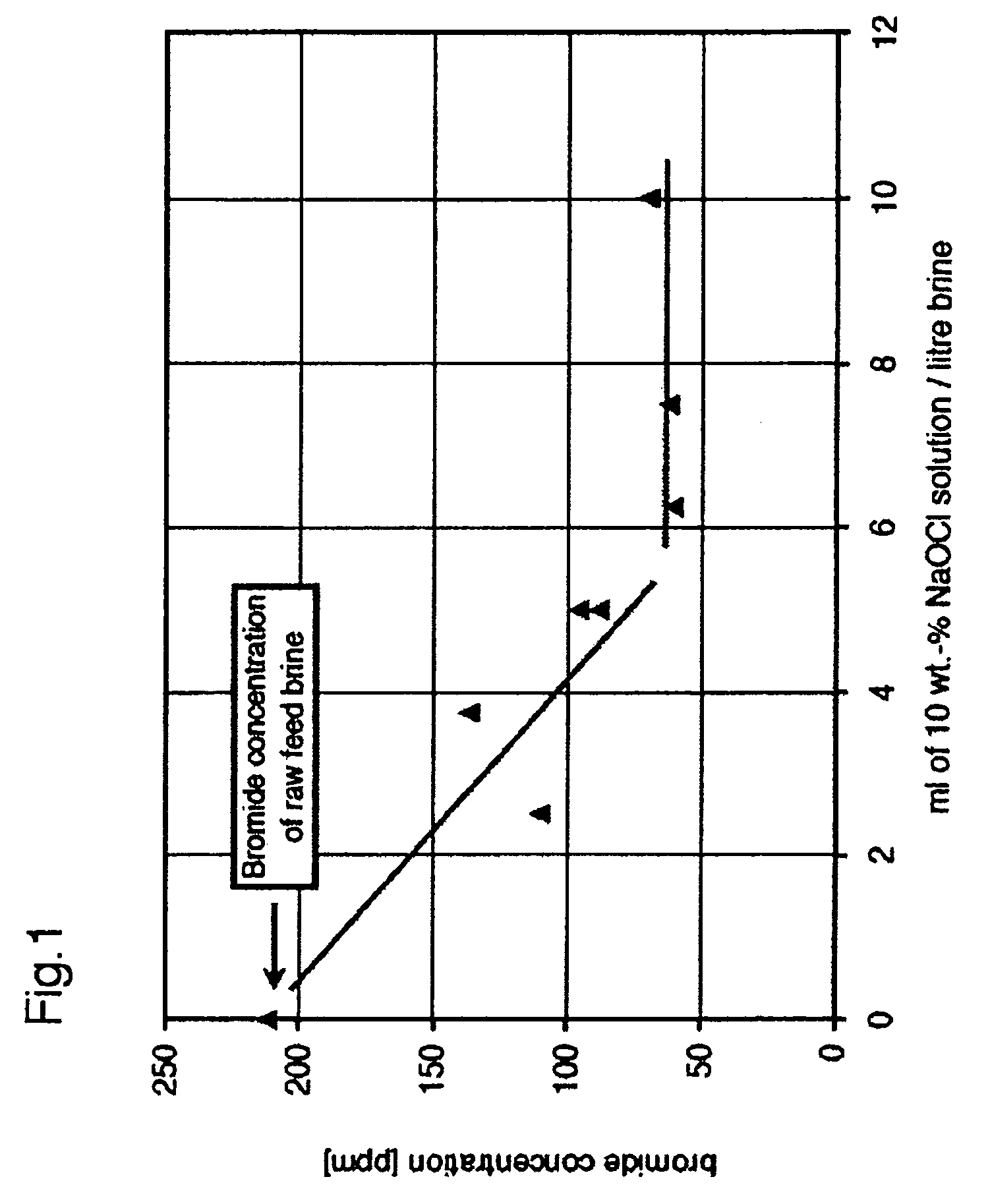
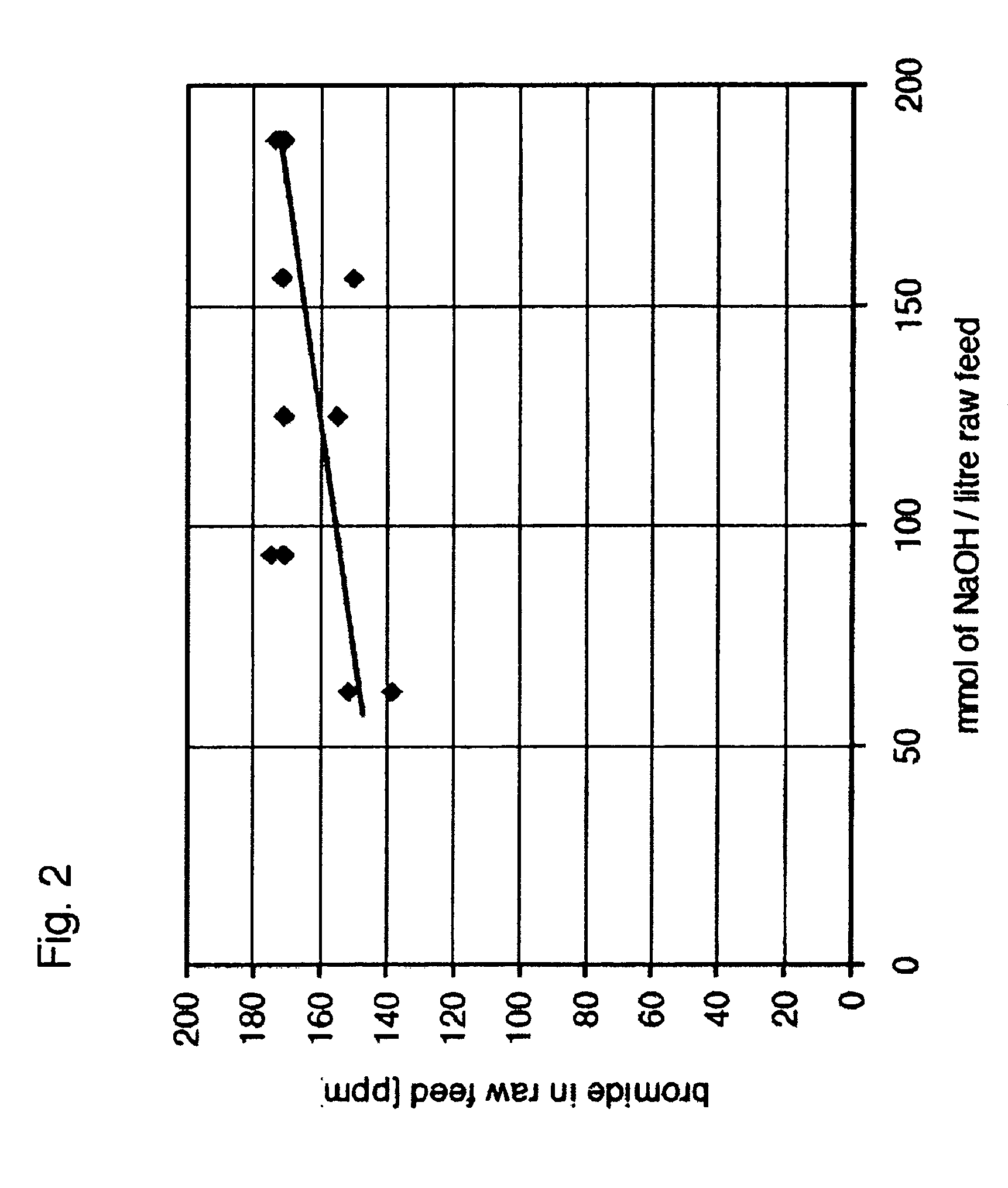
The invention provides a method for reducing bromine levels in brine solutions such as potassium chloride brine solutions. Bromide in solution is converted to hypobromite by the addition of an oxidant such as sodium hypochlorite. Hypobromite is precipitated by the addition of a metal cation such as magnesium under conditions of basic pH. The process is pH dependent such that the most efficient removal of bromine is achieved at a sodium hydroxide concentration of 90-200 mM. The pH optimum is also temperature dependent such that increased temperature lowers the optimal pH for bromide removal. The invention further provides a bromine-reduced potassium chloride product, suitable for uses in industrial applications. By the method of the invention bromine levels in a potassium chloride feed stock can be reduced by 97% or more.
Owner:IMC GLOBAL
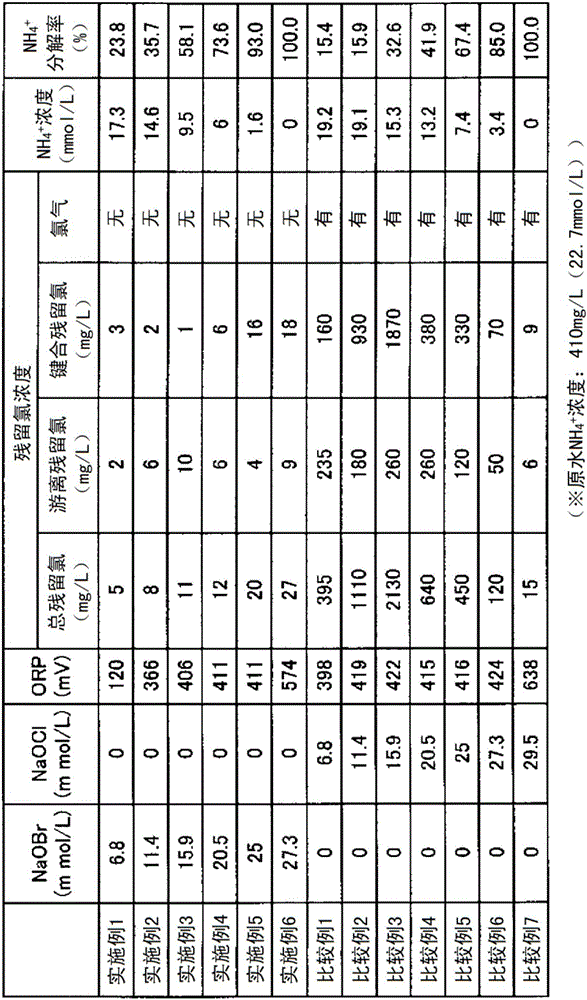
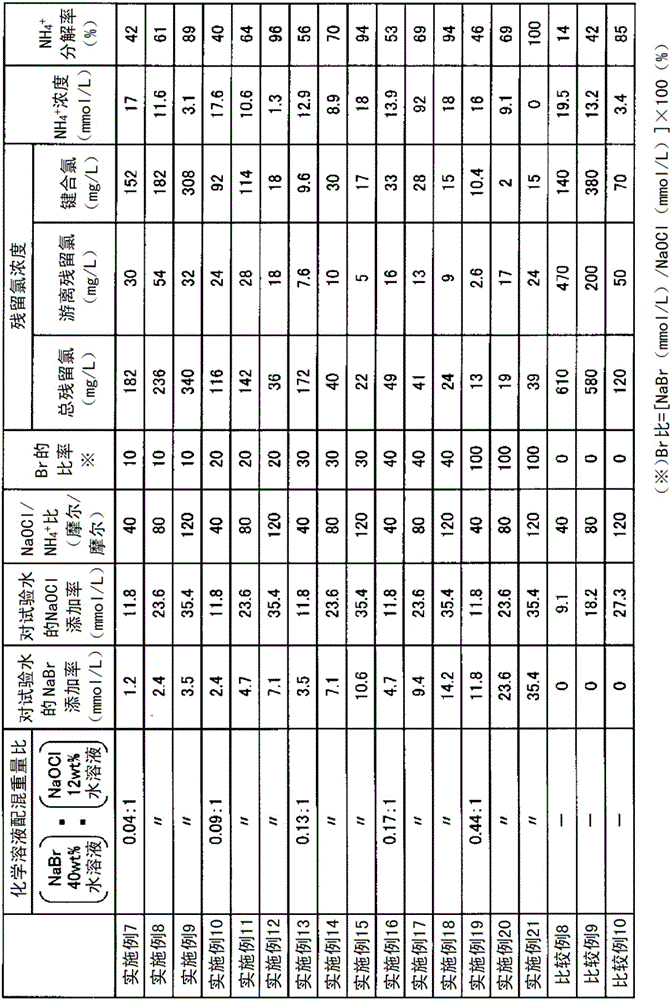
Method for treating wastewater containing cyanogen and ammonia
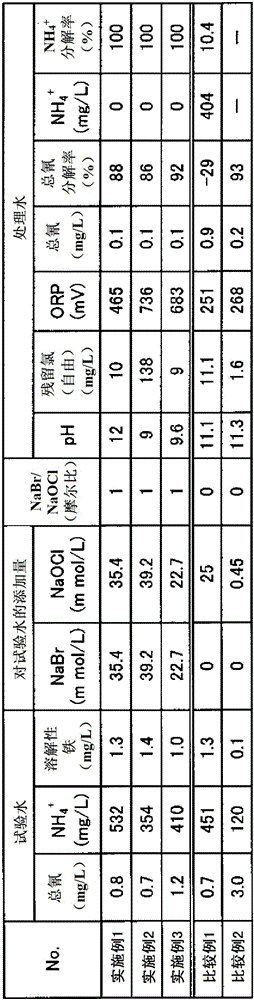
ActiveCN106232531ABromine oxygen compoundsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationSolubilityChemical solution
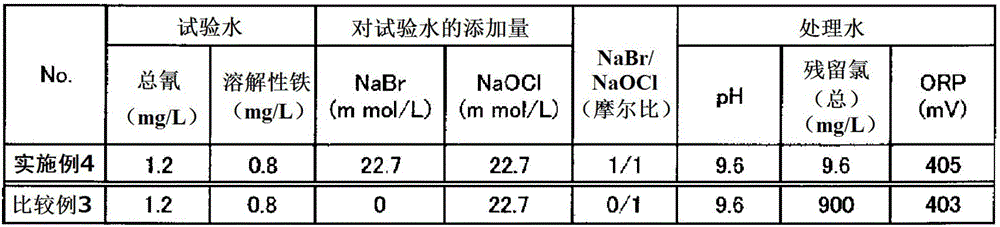
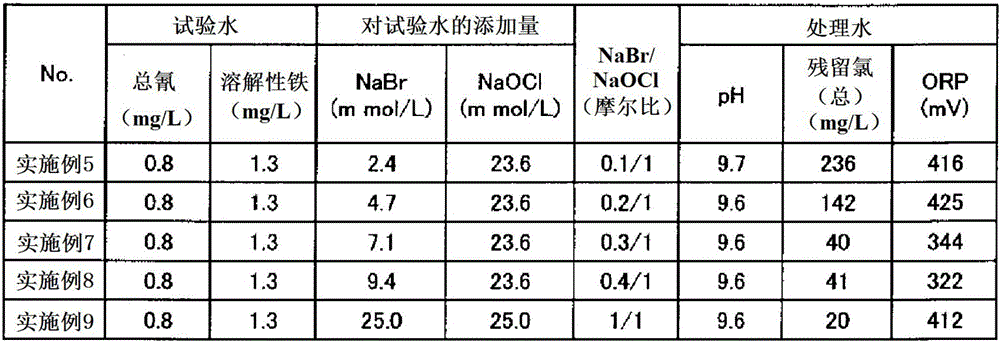
Provided is a method for treating water containing cyanogen and ammonia with which cyanogen and ammonia are sufficiently decomposed even in cases where the concentration of soluble iron is high. This method for treating wastewater containing cyanogen and ammonia involves a step for oxidizing and decomposing cyanogen and ammonia by adding a chemical solution including hypobromous acid and / or hypochlorous acid to wastewater containing cyanogen and ammonia. A solution in which hypobromous acid and / or a hypobromite have / has been produced by mixing a bromide aqueous solution and a hypochlorite aqueous solution is added to wastewater containing cyanogen and ammonia. A sodium bromide aqueous solution and a sodium hypochlorite aqueous solution are mixed and added at an equimolar ratio or such that sodium hypochlorite is excessive.
Owner:KURITA WATER INDUSTRIES LTD
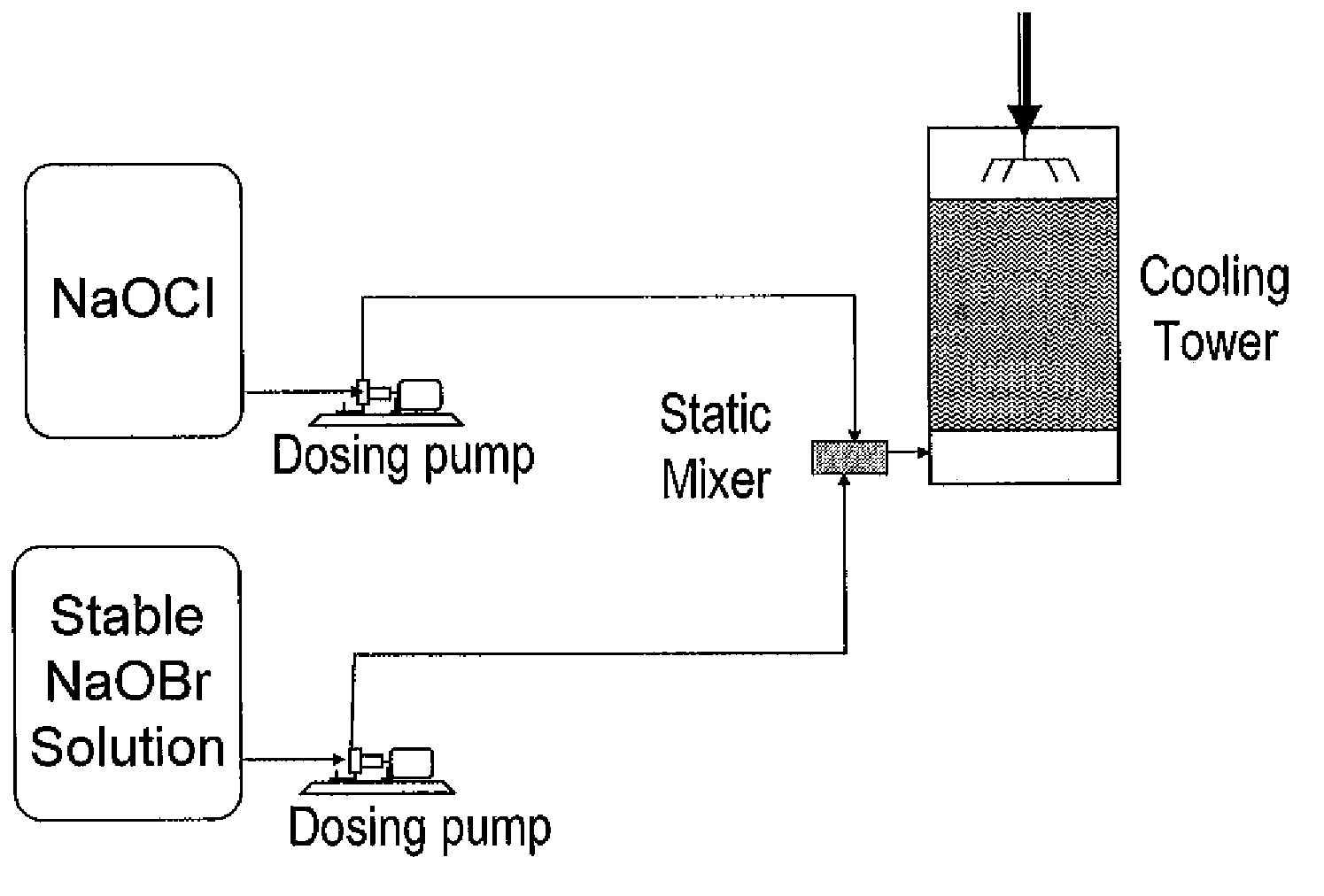
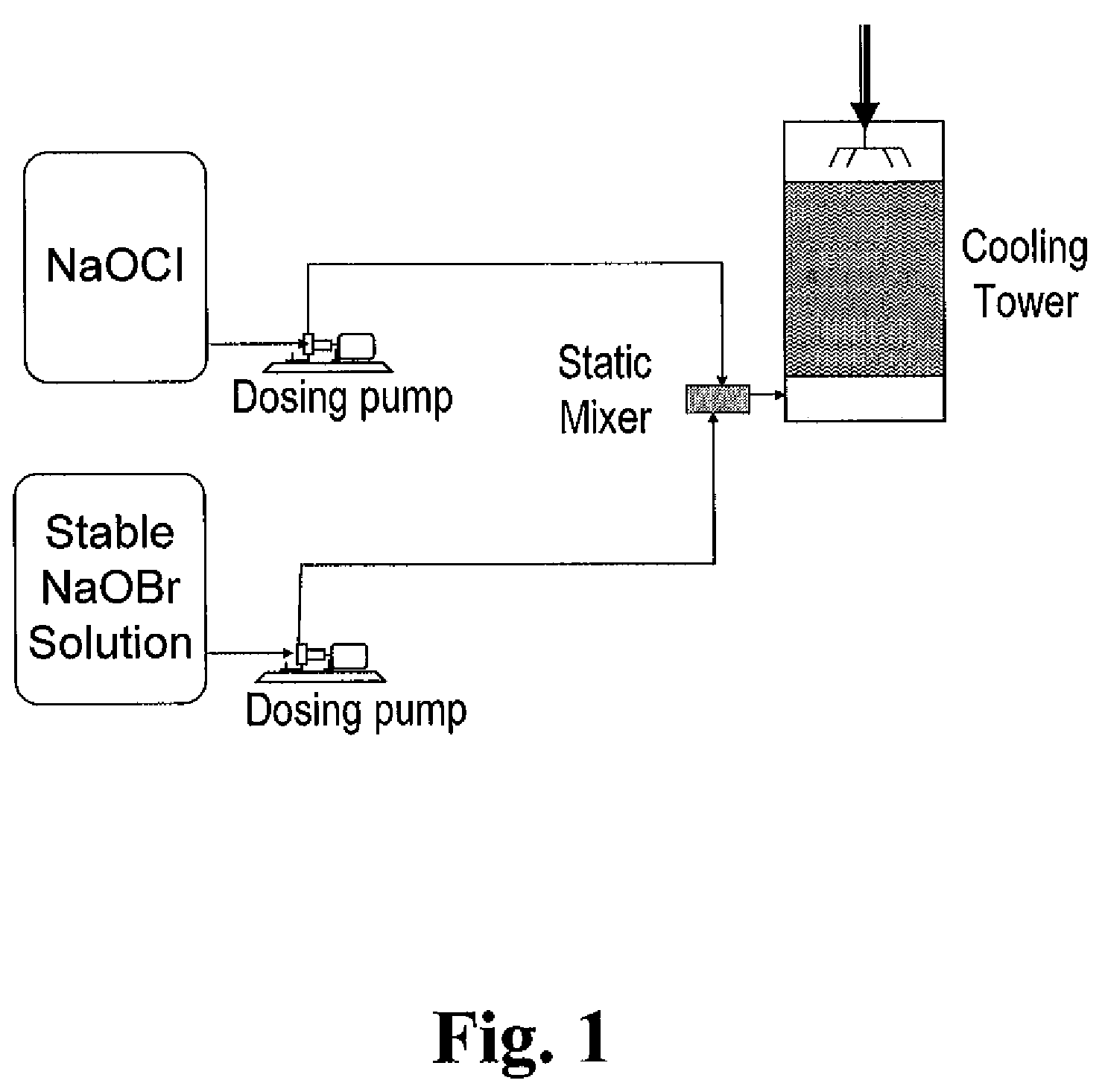
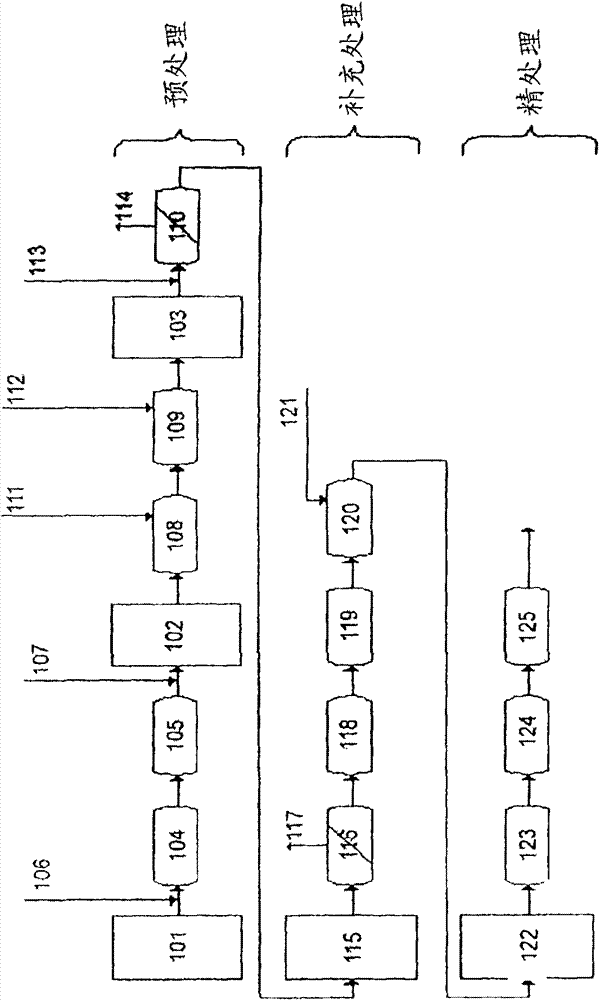
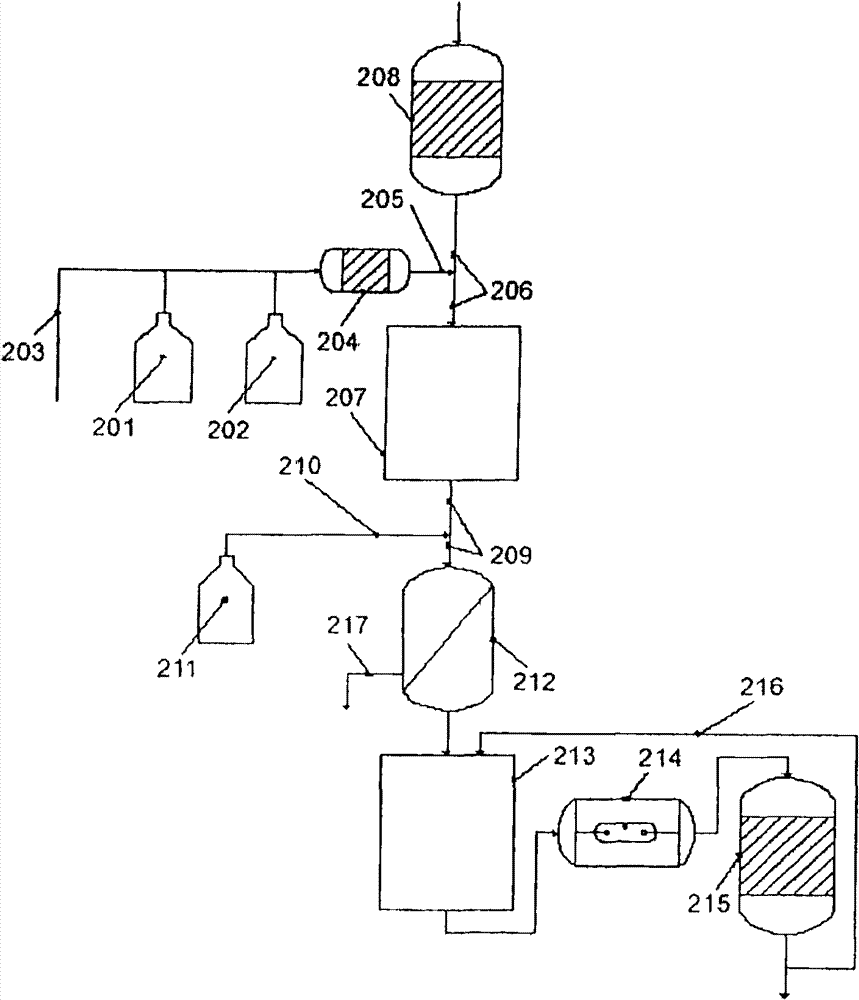
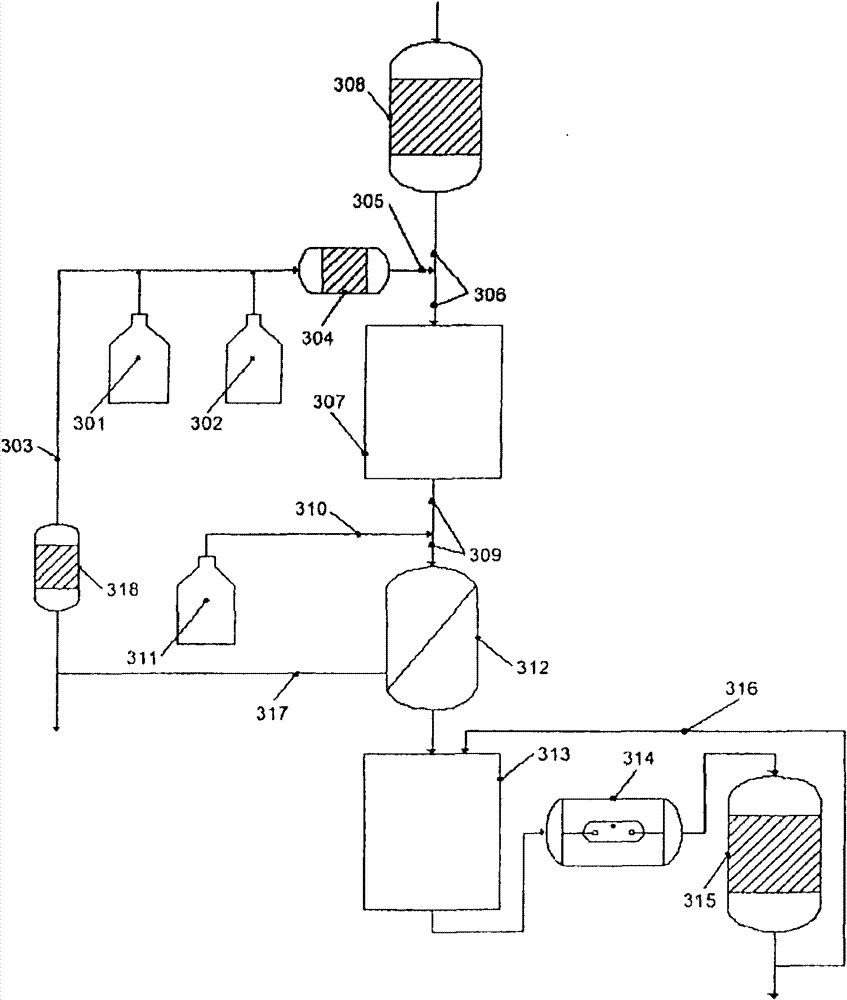
Treatment of water with hypobromite solution
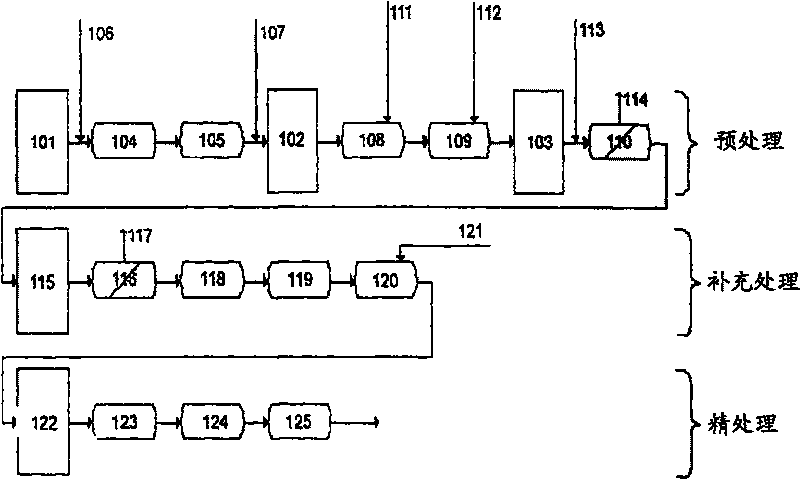
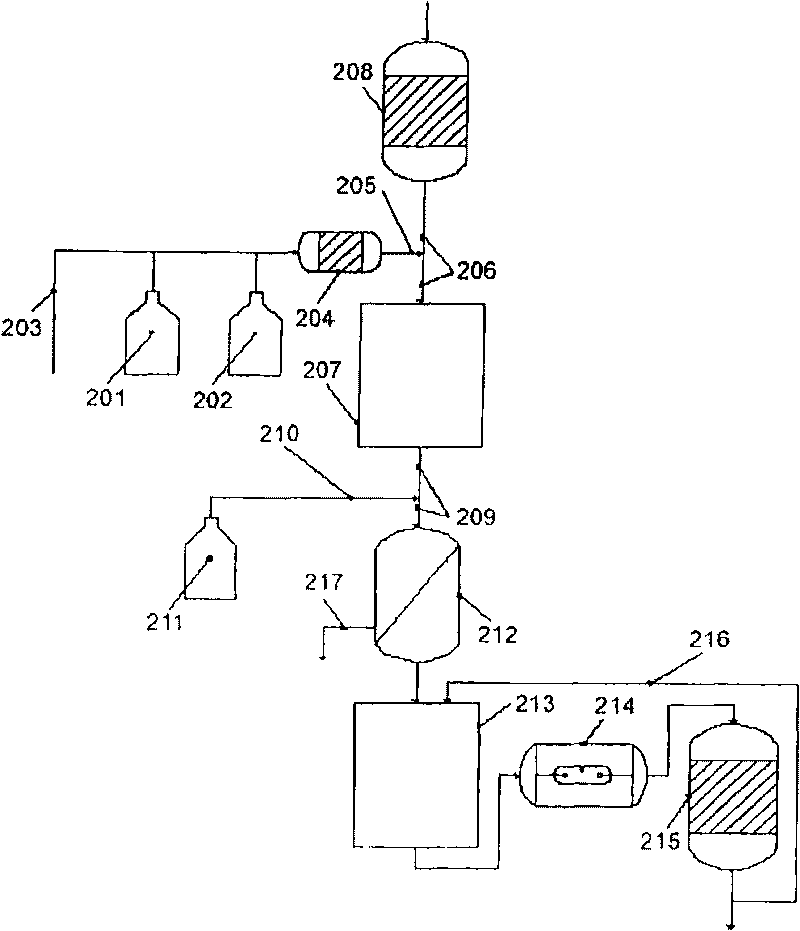
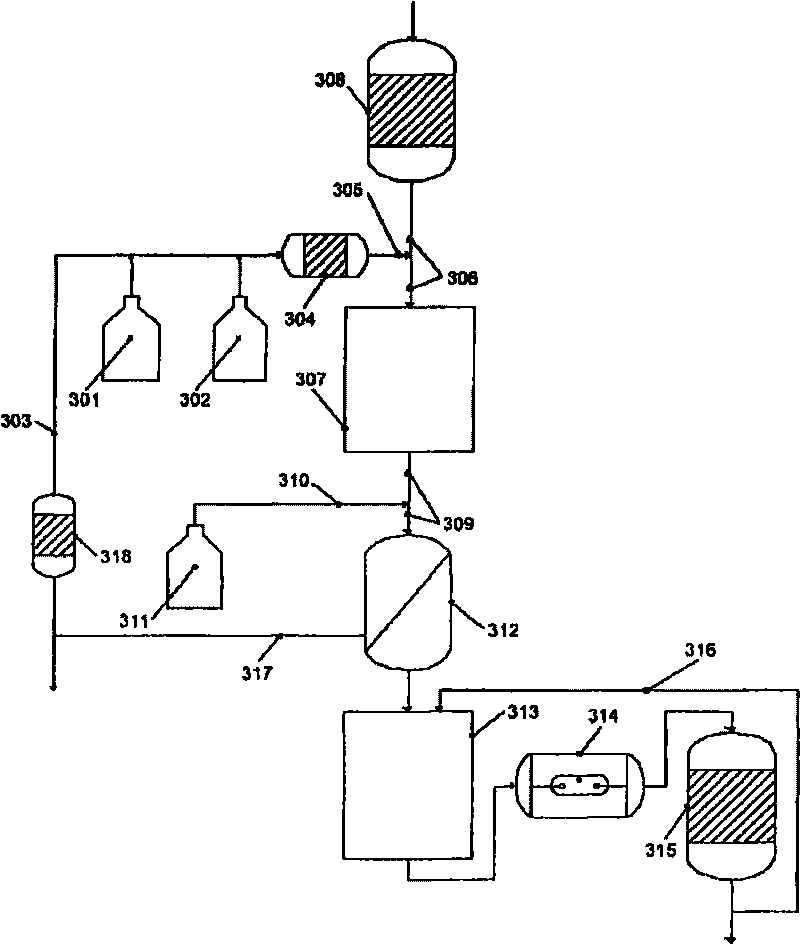
ActiveCN101720307AEasy to understandWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsWater treatment systemHypobromite
A process is described for treating water, in particular for producing ultrapure water, in which a water stream is passed through a plurality of treatment stages in which inorganic and / or organic species which are present in the water are separated off, wherein an aqueous hypobromite solution is added to the water stream in at least one of the stages. Furthermore, a water treatment system for carrying out such a process is described, comprising one or more means for separating off inorganic and / or organic species from a water stream, characterized by at least one device for generating hypobromite solution, which device is connected to the water stream via at least one hypobromite feed line.
Owner:クリストウォーターテクノロジーアクチェンゲゼルシャフト
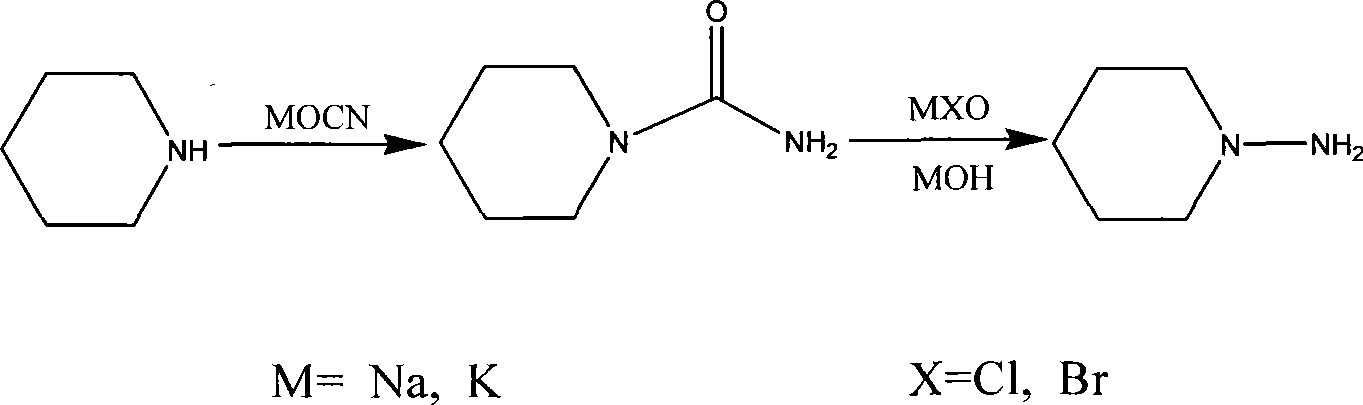
Method for producing N-amido piperidine hydrochlorate
InactiveCN101220009AShort reaction timeMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryHypochloriteHypobromite
The invention relates to a preparation method for N-aminopiperidine hydrochloride, particularly relating to a method for synthesizing N-aminopiperidine hydrochloride by piperidine, which is characterized in that the following steps are adopted: a piperidine reacts with a cyanate under an acidic condition to derive an N-carbamoyl piperidine; the N-carbamoyl piperidine reacts with a hypochlorite or hypobromite under a basic condition; after the N-carbamoyl piperidine is rearranged by Hoffman and treated by hydrochloric, the N-aminopiperidine hydrochloride is derived. In the preparation method of the invention, the reaction time of each step is short, the reaction condition is mild (normal temperature and normal pressure reaction at most of the time), the after-treatment is quite easy and a column chromatography is not needed; the method of the invention is a simple operated, economical, practical and safe synthetic method with a yield of more than 60 percent.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Method for surface inclusions detection, enhancement of endothelial and osteoblast cells adhesion and proliferation, sterilization of electropolished and magnetoelectropolished nitinol surfaces
InactiveUS9017489B2Improve cell adhesionEnhanced corrosion behaviorSuture equipmentsInorganic active ingredientsOsteoblast adhesionElectrolysis
Owner:ROKICKI MARGARET
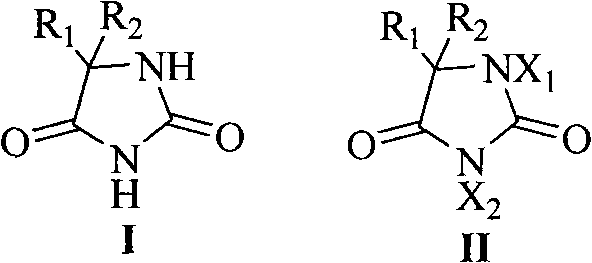
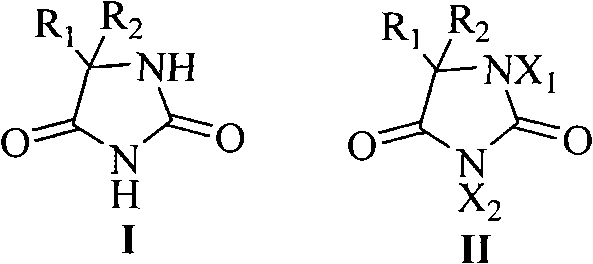
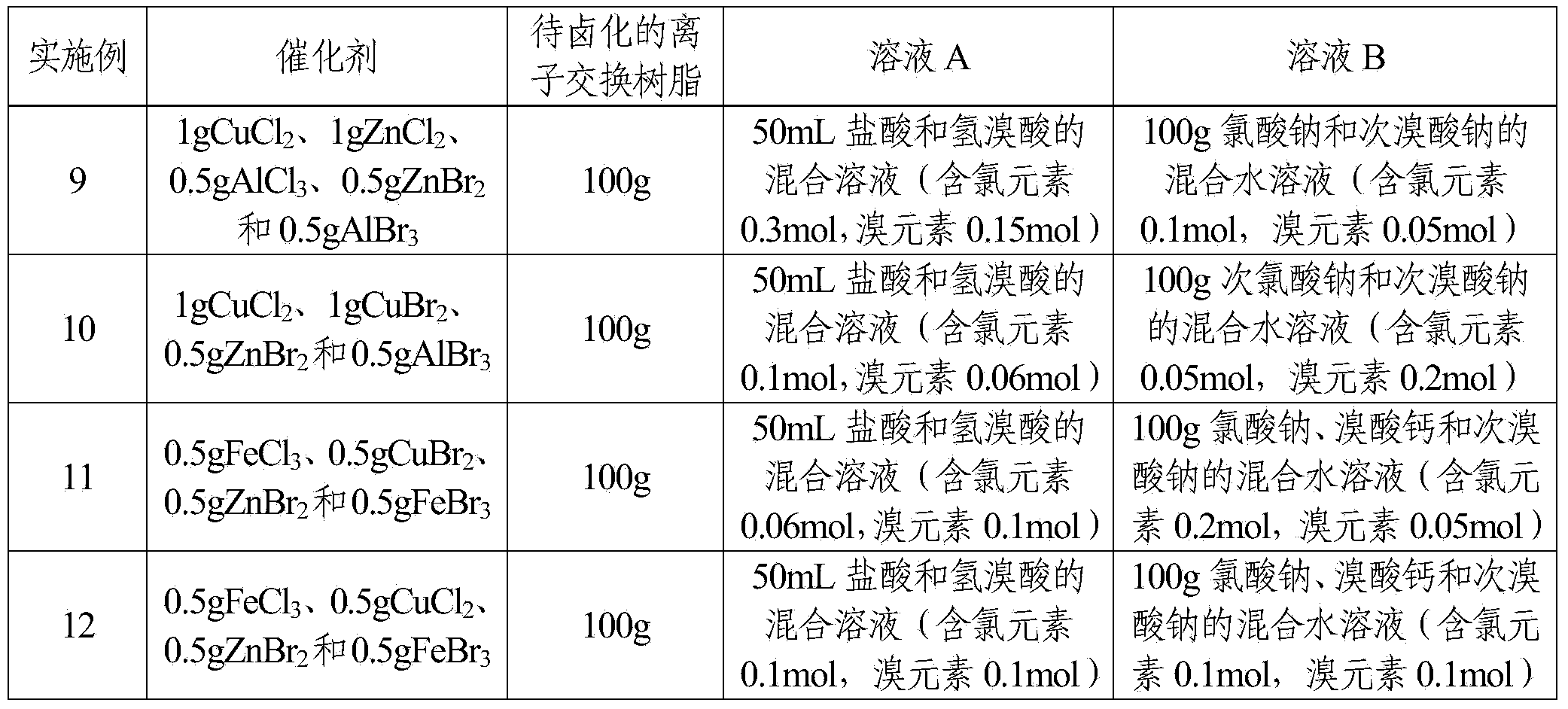
Reaction system for halogenating ion exchange resins and halogenation method of ion exchange resins
ActiveCN103965498AThere is no security riskSimple processOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHypochloriteIon exchange
The invention discloses a reaction system for halogenating ion exchange resins. The reaction system comprises a catalyst and a halogenating agent, wherein the catalyst is chloride and / or bromide; the mass of the catalyst accounts for 0.1%-5% of the mass of ion exchange resin to be halogenated; the halogenating agent comprises a solution A and a solution B, the solution A is hydrochloric acid of which the concentration is 0.1mol / L-12mol / L and / or hydrobromic acid of which the concentration is 0.1mol / L-12mol / L, the solute of the solution B is one or more hypochlorite, chlorate, perchlorate, hypobromite, bromate and perbromate. Furthermore, the invention also discloses a halogenation method of ion exchange resins. According to the reaction system for halogenating ion exchange resins disclosed by the invention, low-toxic salts and acids are adopted as halogen sources instead of chlorine and bromine with high toxicity, and all materials in the operation are liquid or solid and thus the potential safety hazard of toxic gas leakage is avoided and the reaction system is safer.
Owner:XIAN ORIGIN CHEM TECH
Potassium chlorobromo isocyanurate and its production process and application
InactiveCN1389460AEasy to useChemically stableBiocideOrganic chemistryHypobromitePotassium hypochlorite
Owner:李宝林 +1
Process for the preparation of concentrated solutions of stabilized hypobromites
The invention provides stabilized concentrated aqueous solutions of alkali hypobromites, as well as a process for the preparation of said stabilized concentrated solutions at low temperatures, comprising reacting a concentrated alkali hydroxide aqueous solution with bromine, adding to the non-stabilized reaction product an aqueous solution of a sulfamic compound to stabilize the hypobromite, and oxidizing bromide to produce additional hypobromite.
Owner:BROMINE COMPOUNDS
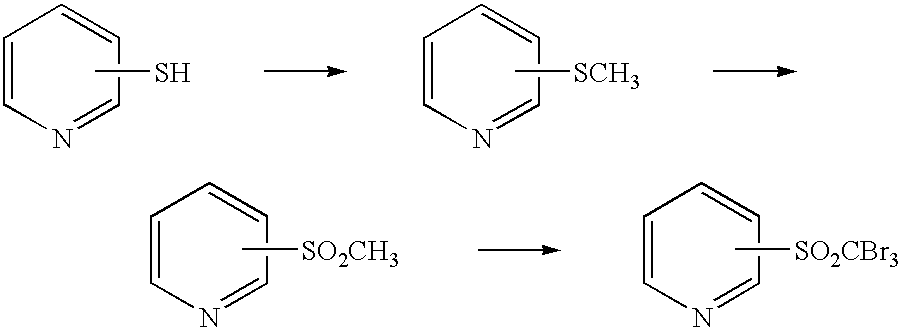
Process for preparing tribromomethylsulfonylpyridine
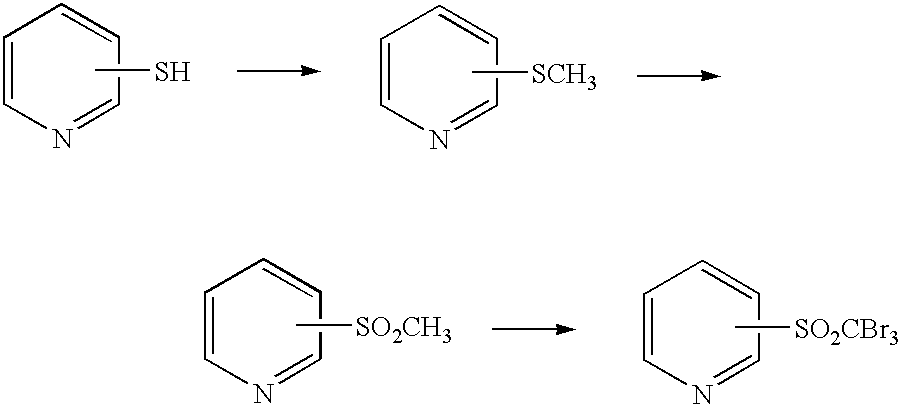
The present invention provides a process for preparing a tribromomethylsulfonylpyridine, which comprises reacting a methylthiopyridine and a hypobromite in the presence of a base and water in a heterogeneous system. According to the present invention, it is possible to prepare a tribromomethylsulfonylpyridine industrially advantageously, and with high yield and high purity.
Owner:SUMITOMO SEIKA CHEM CO LTD
Electrochemical synthesis method for preparing halogenated hydantoin
InactiveCN101775613BReduce usageAccurate judgmentElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic productionHypobromous acidElectrolysis
The invention relates to an improved synthesis method for hydantoin bromo and for preparing dibromohydantoin or bromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin. The method comprises the following steps of: taking various hydantoins as raw materials, dissolving the hydantoins and the corresponding amount of bromide in 0.2g / mL saturation chlorate solution, electrolyzing the bromide solution and obtaining the corresponding hypobromite, generating hypobromous acid under the condition of addition of acid, further performing bromo reaction to the hydantoin, adjusting the bromide equivalent according to demand and synthesizing the corresponding dibromohydantoin or bromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin. Reaction liquid can be repeated and used, and the reaction yield can reach more than 95%. The invention has the advantages of easy obtainment of raw materials by low cost, low production cost, simple post treatment, high yield, good purity and repetitive recycle of the mother liquid. By utilizing the electrolysis process, the process is simple, and the equipment has low requirement, safe operation and no toxicity or stimulation.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
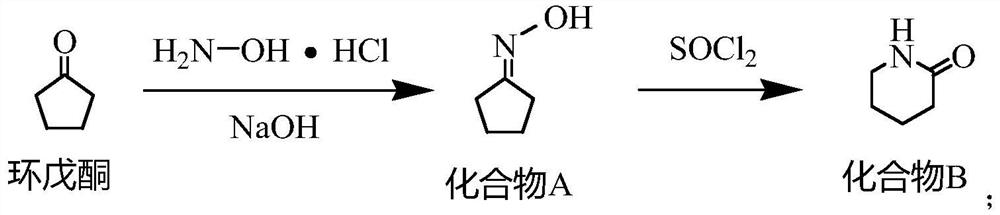
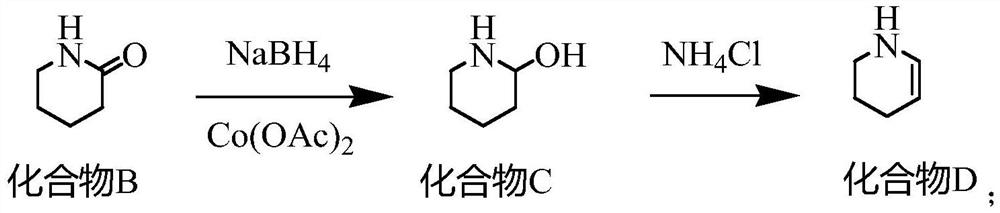
Synthesis method of 2, 3-dichloropyridine
ActiveCN111620812AEasy to operateQuality improvementOrganic chemistryBeckmann rearrangementHydroxylamine
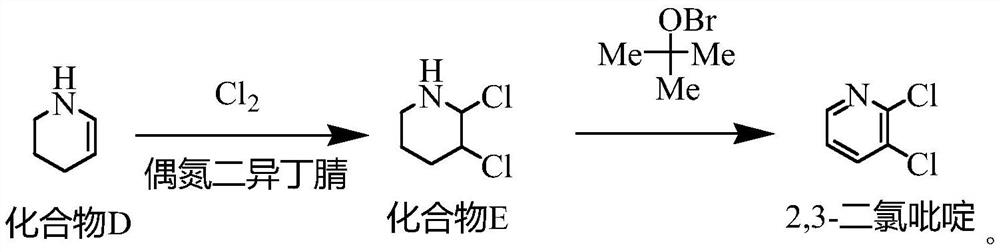
The invention provides a synthesis method of 2, 3-dichloropyridine, which comprises the following steps: reacting cyclopentanone with hydroxylamine hydrochloride, and taking sodium hydroxide as an acid-binding agent to obtain a compound A; carrying out Beckmann rearrangement reaction on the compound A under the action of thionyl chloride to obtain a compound B; reacting the compound B with sodiumborohydride under the catalysis of cobalt acetate to obtain a compound C; reacting the compound C under the catalysis of ammonium chloride to obtain a compound D; reacting the compound D with chlorineunder the action of azodiisobutyronitrile to obtain a compound E; and reacting the compound E with tert-butyl hypobromite to obtain 2, 3-dichloropyridine. The method is simple in operation steps, theused reaction raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, the total molar yield is 68.88%, the purity of the produced 2, 3-dichloropyridine is 98.0% or above, the product quality is good, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG WANYE CHEM IND CO LTD
Rapid high-selectivity hypobromous acid fluorescence probe, and preparation method and application thereof
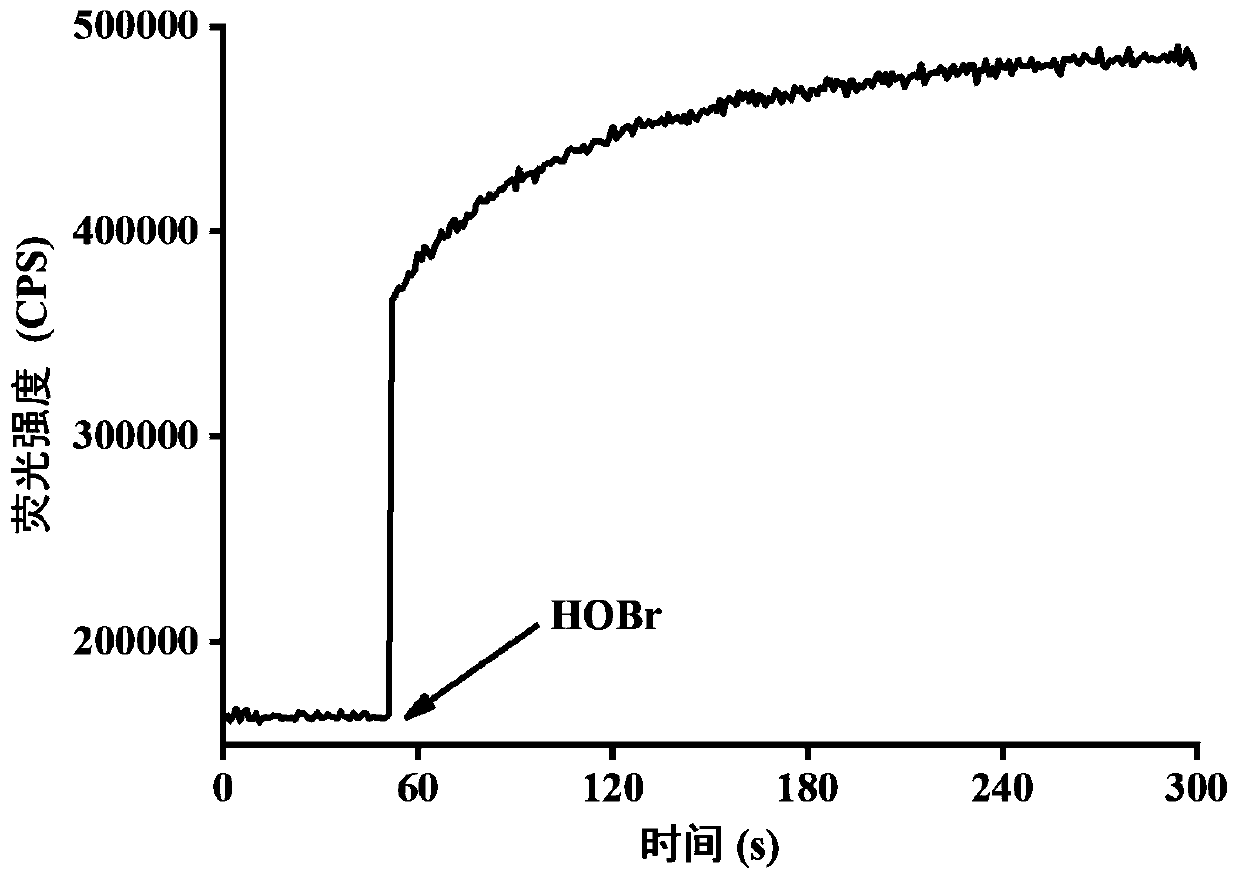
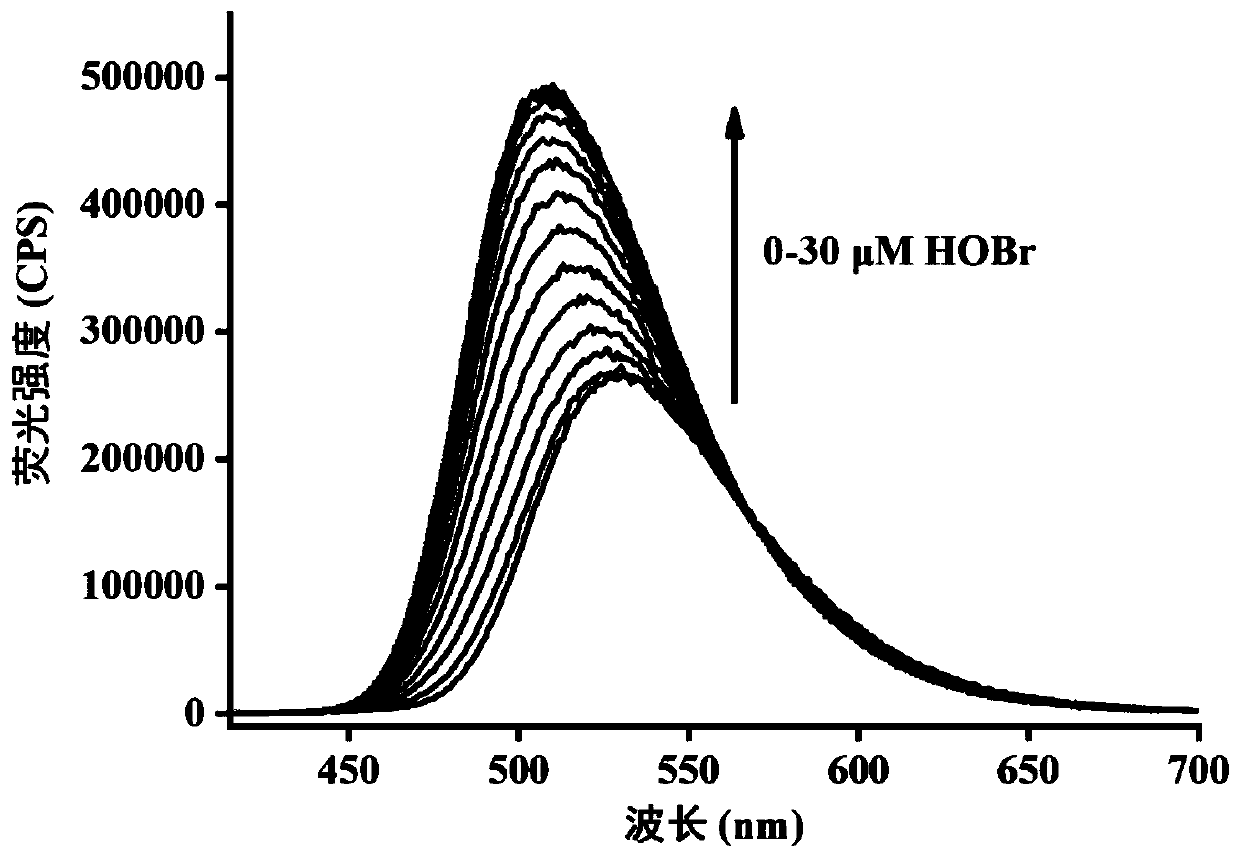
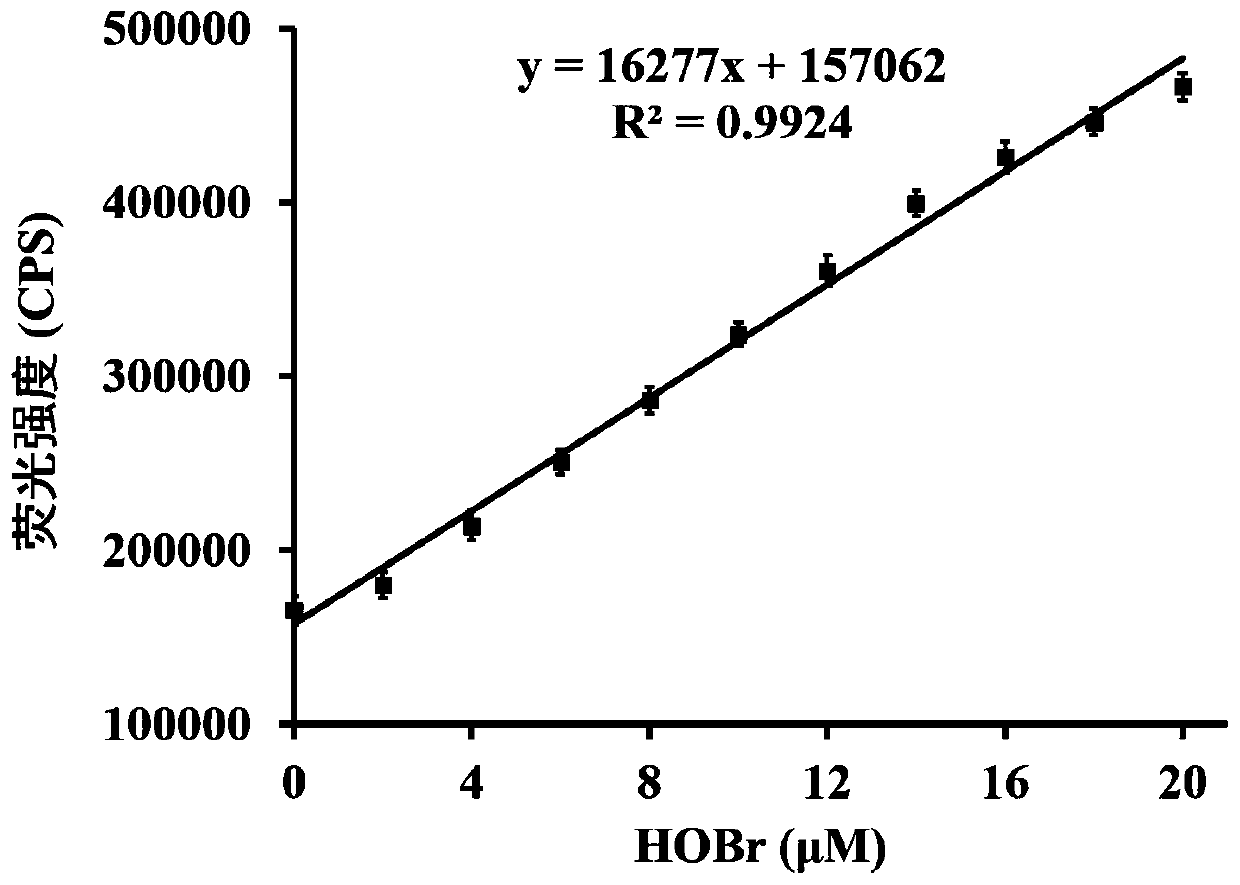
ActiveCN110878085AHigh selectivityImprove anti-interference abilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesHypobromous acid
The invention relates to a rapid high-selectivity hypobromous acid fluorescence probe, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The fluorescence probe is a 1-(2-aminoethyl)piperidine compound, and can be used for measuring, detecting or screening hypobromite and carrying out living cell fluorescence imaging as a hypobromite fluorescence probe. The probe can realize at least one of high-selectivity identification of hypobromite, rapid response to hypobromite, ultra-sensitive analysis of hypobromite and detection of hypobromite under physiological level conditions, and also has the advantages of strong anti-interference capability, simplicity in synthesis, and stable properties.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
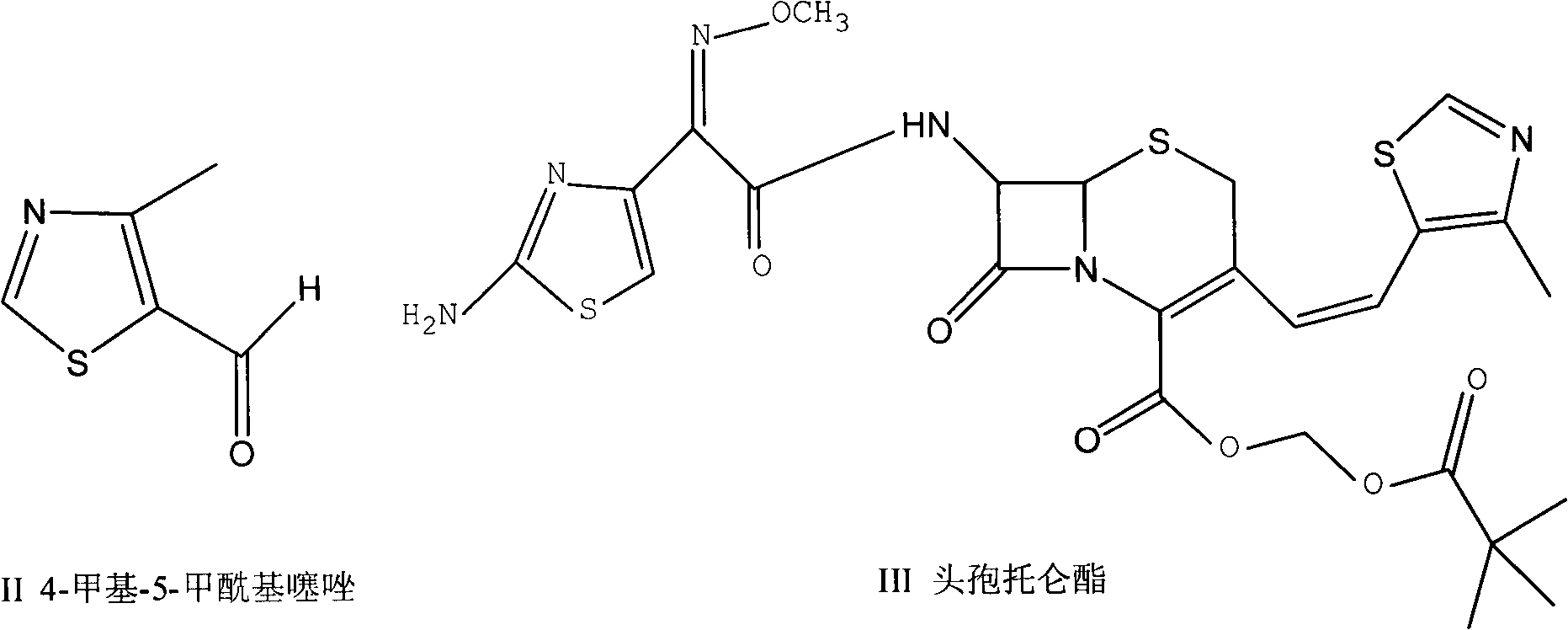
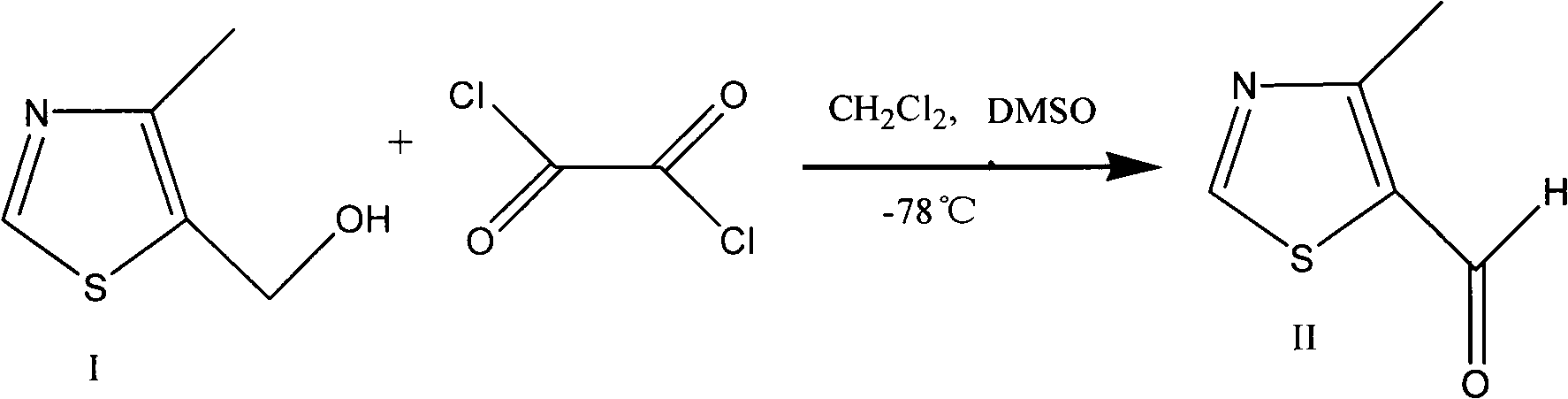
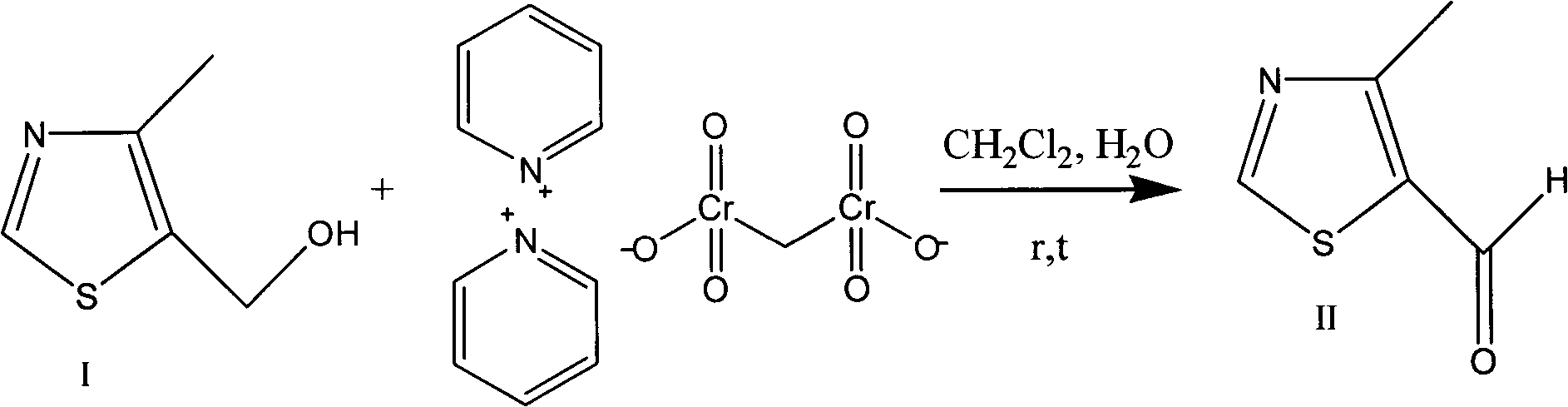
Preparation method of 4-alkyl-5-formoxyl thiazole or 5-formoxyl thiazole
InactiveCN103030604ALow costImprove protectionOrganic chemistryAlkaline earth metalReaction temperature
The invention provides a preparation method of 4-alkyl-5-formoxyl thiazole or 5-formoxyl thiazole shown by a formula II, which comprises the following step of: in mixed phase formed by organic solvent and a water solution with the pH value of 7-9, enabling a compound shown by a formula I to have oxidation reaction with oxidizing agent under the conditions that catalyst exists and the reaction temperature is 0-40 DEG C to generate a compound shown by the formula II, wherein R1 is H or linear chain or branched chain alkyl group of C1-C3, the oxidizing agent is hypochlorite or hypobromite of alkaline-earth metal or alkaline metal, and the catalyst is 2, 2, 6, 6-tetramethyl piperidine 1-oxy-free radical (Tempo) and derivatives of the 2, 2, 6, 6-tetramethyl piperidine 1-oxy-free radical (Tempo). The method is mild in reaction conditions, low in price of raw materials, easy in obtaining of raw materials and smaller in reaction molar volume, does not need KBr for catalysis, and is simple in aftertreatment, thus being suitable for industrial production and environment-friendly; and the method can be used for producing 4-methyl-5-formoxyl thiazole which is high in yield and purity and is a key intermediate of cefditoren pivoxil.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +1
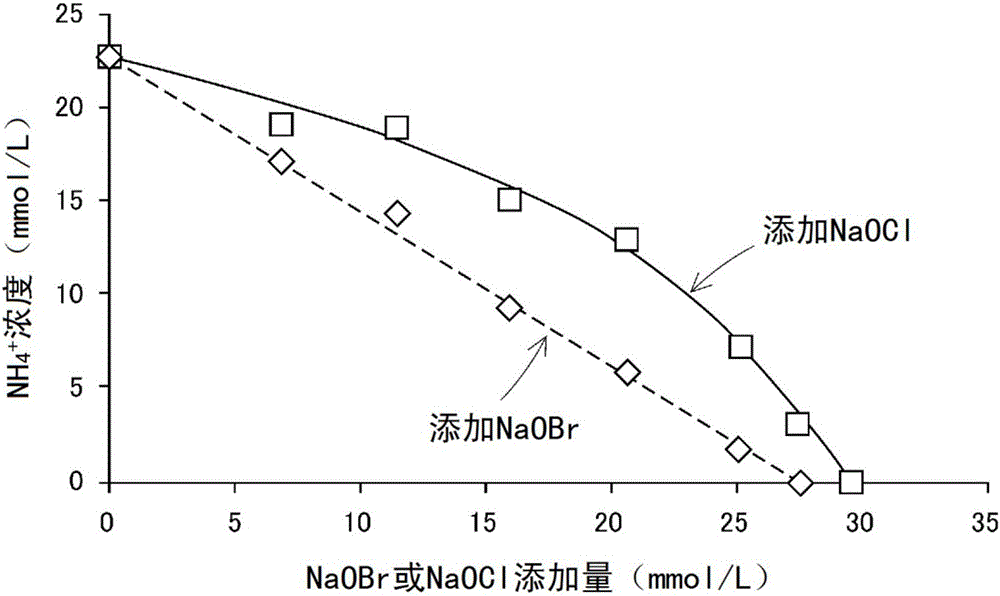
Method for treating wastewater containing ammonia
ActiveCN106232532AQuick breakdownPromote decompositionWater/sewage treatment by oxidationHigh concentrationHypobromous acid
Provided is a method for treating ammonia-containing water in which the generation of hazardous gas is prevented even at the time of decomposing high concentrations of ammonia, and that is also suitable for partially decomposing ammonia. This method for treating wastewater containing ammonia involves a step for oxidizing and decomposing ammonia by adding a chemical solution including hypobromous acid and / or hypochlorous acid to wastewater containing ammonia. A solution in which hypobromous acid and / or a hypobromite have / has been produced by mixing a bromide aqueous solution and a hypochlorite aqueous solution is added to wastewater containing ammonia. A sodium bromide aqueous solution and a sodium hypochlorite aqueous solution are mixed and added at an equimolar ratio or such that sodium hypochlorite is excessive.
Owner:KURITA WATER INDUSTRIES LTD
Process for preparing tribromomethylsulfonylpyridine
The present invention provides a process for preparing a tribromomethylsulfonylpyridine, which comprises reacting a methylthiopyridine and a hypobromite in the presence of a base and water in a heterogeneous system. According to the present invention, it is possible to prepare a tribromomethylsulfonylpyridine industrially advantageously, and with high yield and high purity.
Owner:SUMITOMO SEIKA CHEM CO LTD
Semiconductor treatment liquid
PendingUS20220328320A1Sufficient rateHigh yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHypobromiteHalogen
Provided are: a semiconductor treatment liquid containing a hypobromite ion, in which the concentration of the hypobromite ion is 0.1 μmol / L or more and less than 0.001 mol / L; a RuO4 gas generation inhibitor containing an onium salt composed of an onium ion and a bromine-containing ion, in which the hypobromite ion concentration is 0.1 μmol / L or more and less than 0.001 mol / L; and a method of producing a halogen oxyacid, the method including allowing a bromine salt, an organic alkali, and a halogen to react with each other to obtain the halogen oxyacid.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
Water treatment agent composition, method for producing water treatment agent composition, and water treatment method
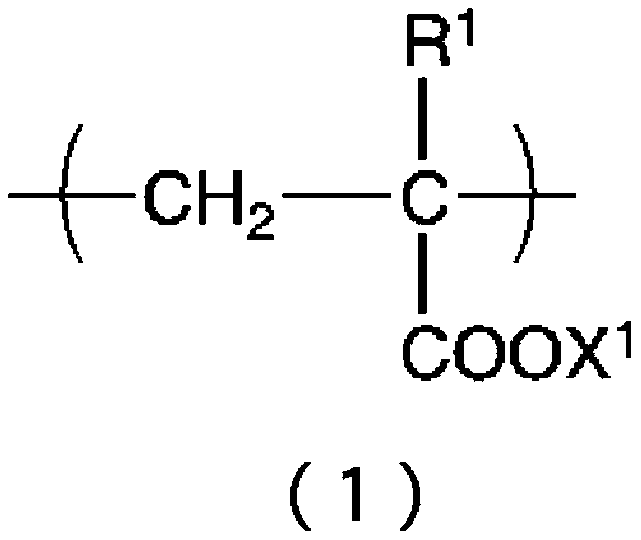
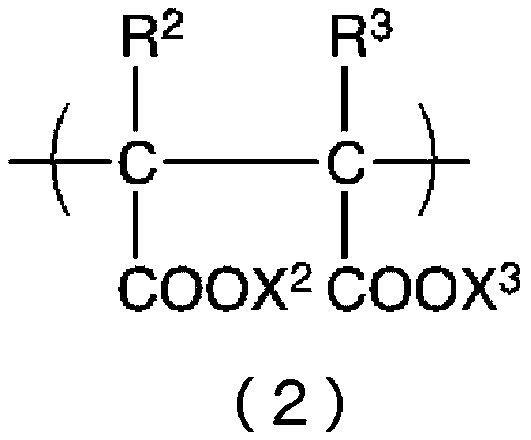
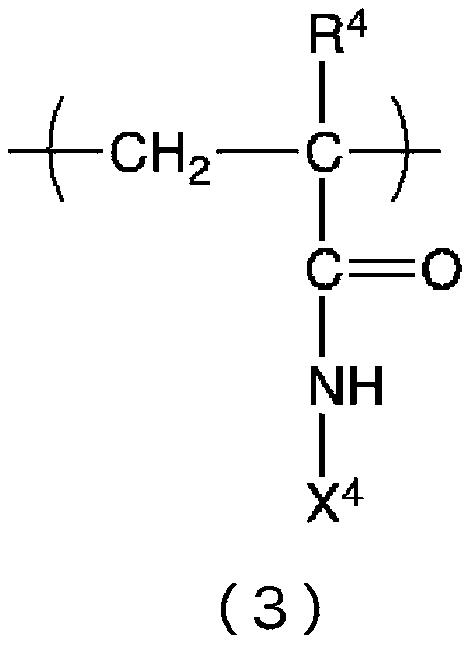
ActiveCN107249332BReduced sludge control performanceReduce oxidative powerBiocideFungicidesCarboxyl radicalSludge
Owner:ORGANO CORP
Process for the preparation of concentrated solutions of stabilized hypobromites
The invention is a process for the preparation of stabilized aqueous solutions of alkali hypobromites at low temperatures, which comprises reacting a concentrated alkali hydroxide aqueous solution with bromine, and adding to the reaction product, which is a non-stabilized solution, an aqueous solution of a sulfamic compound, such as sodium sulfamate, thus forming a stabilized alkali hypobromite solution.
Owner:BROMINE COMPOUNDS
Treatment of water with hypobromite solution
ActiveCN101720307BEasy to understandWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsHypobromiteWater treatment system
A process of producing ultrapure water includes passing a water stream through a plurality of treatment stages in which inorganic and organic species which are present in the water are separated from the water stream; and adding an aqueous hypobromite solution to the water stream in at least one of the stages.
Owner:クリストウォーターテクノロジーアクチェンゲゼルシャフト
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com