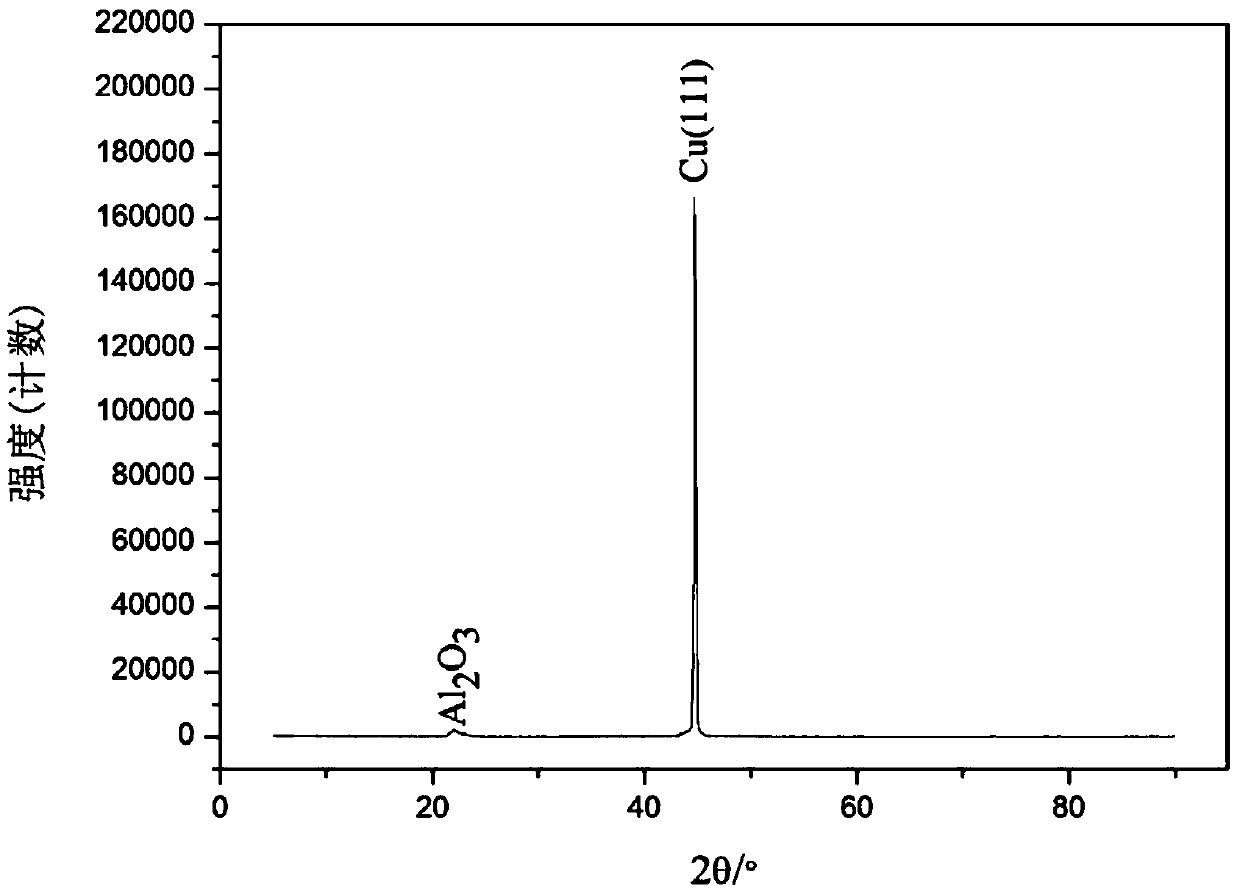
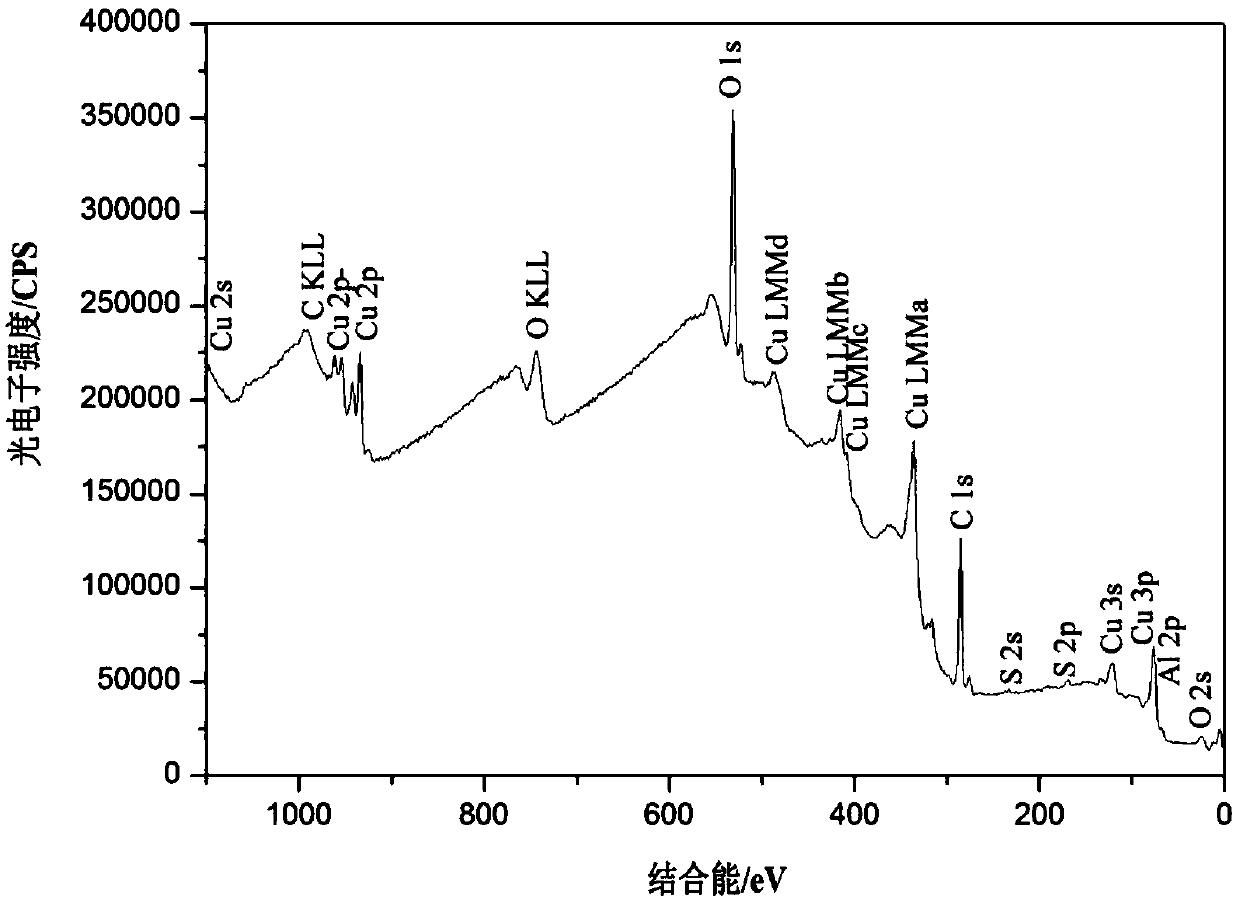
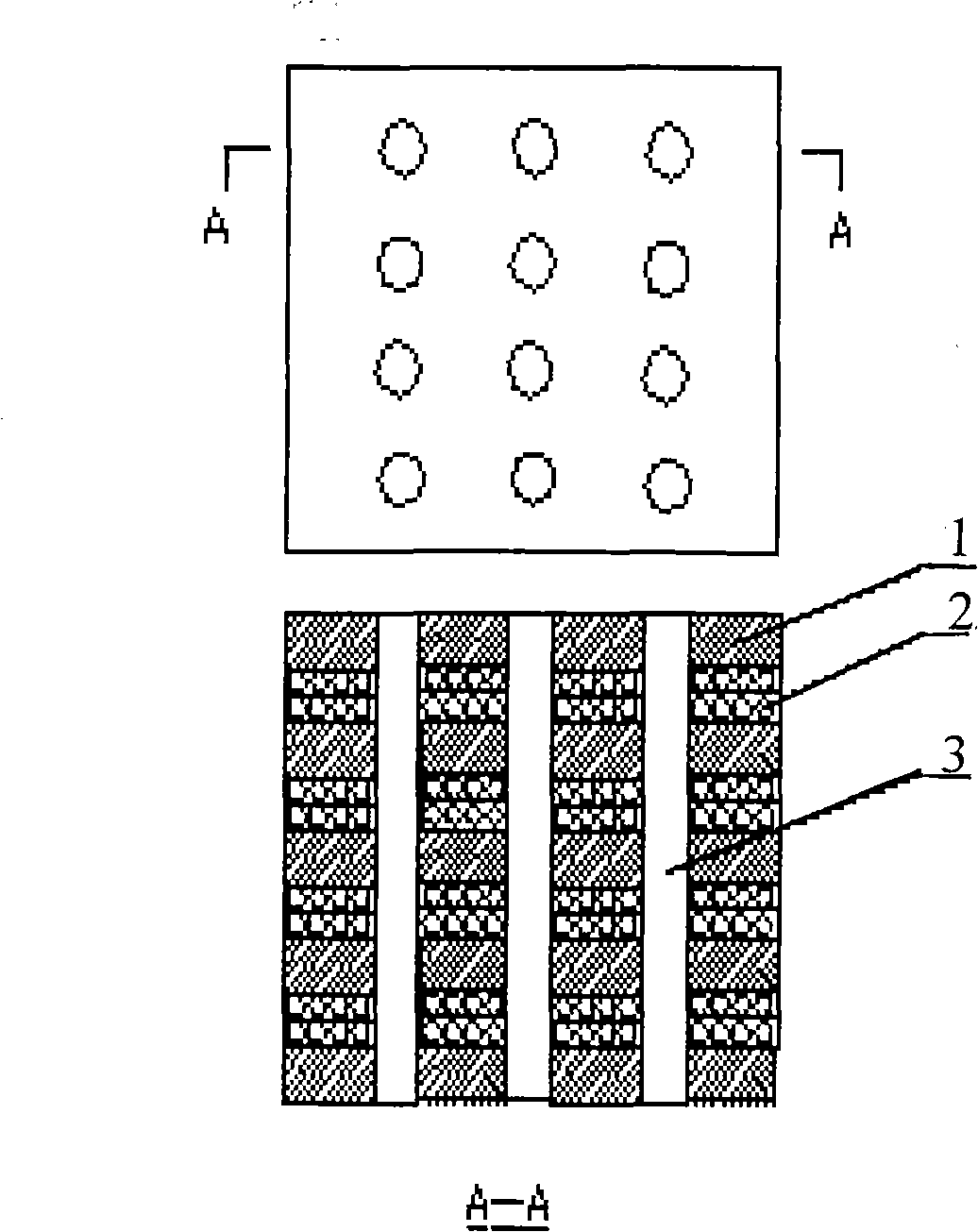
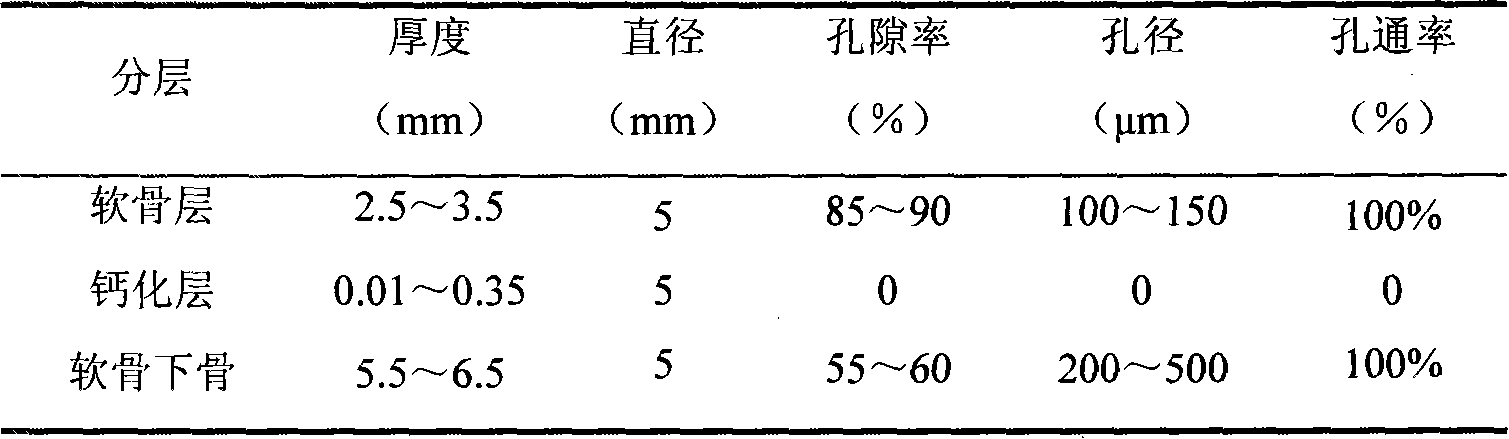
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Osteoblast adhesion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hydroxyapatite coated nanostructured titanium surfaces
InactiveUS20090035722A1Improve adhesionPromote accumulationDental implantsImpression capsOsteoblast adhesionApatite
Nanotubular structured titanium (Ti) substrates have been coated with nanoparticulate hydroxyapatite (nano-HA). The nano-HA surface is highly adherent to the nanotubular Ti surface and is free of microparticles. The nano-HA coated nanotubular Ti surface promotes osteoblast cell adhesion and is particularly suitable for orthopedic and dental implants where deposition of osteoblasts and other proteins is important in bone formation.
Owner:METASCAPE
Method for preparing integrated frame fabrication of cartilage of tissue-engineered bone having function interface
InactiveCN101032430AAchieve mechanical strengthGood biocompatibilityBone implantCartilage cellsOsteoblast adhesion
The present invention discloses process of preparing integral bionic tissue engineering bone-cartilage rack with functional interface. The process includes the first establishment of CAD model of the integral bone-cartilage rack by means of bionic principle; preparing collagen / chitosan and collagen / hydroxyapatite micro polymer powder; converting the CAD model into fast forming file input into a 3D printing fast forming machine, spreading the powder with one powder spreader, spraying pentanedial adhesive selectively on the spread powder for adhering and eliminating excessive powder to obtain the integral bionic tissue engineering bone-cartilage rack with functional interface. The present invention has excellent biocompatibility, controllable cartilage rack degrading speed and mechanical strength and other advantages.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Artificial bone with porous laminated structure and passages and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101766843AControllable degradation rateGood biocompatibilityBone implantOsteoblast adhesionOrthopedic department
The invention relates to an artificial bone with a porous laminated structure and passages, which belongs to the technical field of biomedical materials. The artificial bone is alternately laminated and formed by compact layers and porous layers which are made of calcium phosphate base biological ceramic materials, and in addition, passages for conveying cells and body fluid are arranged in the direction which forms a set angle with the laminated layers. The preparation method comprises the following step: mixing powder such as hydroxylapatite, beta-tricalcium phosphate and the like through using deionized water as medium to be prepared into pulp. A three-dimensional gel laminated forming system is adopted for preparing ceramic blanks formed by the compact layers, the porous layers and the passages, and then the ceramic blanks are sintered at a high temperature for preparing the artificial bone. The invention has the characteristics that the artificial bone has high mechanical strength, has the porous structure with the effects of osteoplast adhesion, propagation, growth and vascularization, can be used as the artificial bone, can also be used as a bone tissue engineering support frame, and has wide application prospects in clinics in the orthopedics department.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing micro-nano composite structure on surface of titanium substrate
InactiveCN105624763AImprove bindingPromote growthSurface reaction electrolytic coatingLaser beam welding apparatusMicro nanoOsteoblast adhesion
The invention discloses a method for preparing a continuous gentle micro-nano structure on a titanium substrate from the outside to the inside through femtosecond laser processing and then anodizing. The method comprises the three steps of polishing, femtosecond laser processing and anodizing. The continuous gentle micro-nano structure prepared through the method is good in repeatability, high in stability and controllable in size and has excellent mechanical properties and biological properties. Due to the fact that the continuous gentle micro-nano structure is formed by partially converting an implantation material and no obvious separatrix exists between the structure and the substrate, the combination strength of the structure and the titanium substrate is high; in addition, the continuous gentle concave pit structure is more approximate a natural bone structure, and osteoblast adhesion growing is facilitated.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method for wettability controllable porous structure of titanium and titanium alloy surface
InactiveCN102345134AImprove bindingAchieve freedom of controlChemical vapor deposition coatingOsteoblast adhesionTitanium alloy
The invention discloses a preparation method for a wettability controllable porous structure of a titanium and titanium alloy surface, and belongs to the technical field of surface modification of biological implant materials. The method comprises the following steps of: performing roughening treatment on the titanium and titanium alloy surface by using a sand-blast, large-grit and acid-etch method (SLA) to prepare a super-hydrophilic surface with a micron-nano double-microcosmic pore structure; preparing a titanium oxide thin film with hydrophilic performance by using a plasma oxidation process, wherein osteoblast adhesion and proliferation experiments show that the surface prepared by the process method has excellent bioactivity; and finally, forming a hydrophobic surface on a rough titanium oxide surface by using a molecular self-assembly method and realizing mutual switching between hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity of the surface by using plasma treatment and ultraviolet irradiation. The hydrophilicity of the surface of an implant is obviously improved in the aspects of stability, durability and the like; and the binding force of the metal implant material and a surface coating can be obviously improved while the bioactivity of the titanium and titanium alloy surface is guaranteed.
Owner:蔺增
Enhanced bonding layers on titanium materials
The present invention provides a dense-coverage, adherent phosphorous-based coating on the native oxide surface of a material. Disclosed phosphorous-based coatings include phosphate and organo-phosphonate coatings. The present invention also provides further derivatization of the phosphorous-based coatings to yield dense surface coverage of chemically reactive coatings and osteoblast adhesion-promoting and proliferation-promoting coatings on the native oxide surface of a titanium material.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Enhanced bonding layers on titanium materials
The present invention provides a dense-coverage, adherent phosphorous-based coating on the native oxide surface of a material. Disclosed phosphorous-based coatings include phosphate and organo-phosphonate coatings. The present invention also provides further derivatization of the phosphorous-based coatings to yield dense surface coverage of chemically reactive coatings and osteoblast adhesion-promoting and proliferation-promoting coatings on the native oxide surface of a titanium material.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Bone defect repairing material, preparation method and applications thereof
The invention relates to a bone defect repairing material. The bone defect repairing material comprises a bacteria cellulose membrane, a biologic ceramic material and cellulase, wherein the biologic ceramic material is deposited on a microfiber surface of the bacteria cellulose membrane, and the cellulase is dispersed in the bacteria cellulose membrane and can degrade the bacteria cellulose membrane. When the bone defect repairing material is implanted into bone defect positions, as osteoblasts are attached on the microfiber surface of the bacteria cellulose membrane for growing and the ceramic material is deposited on the microfiber surface of the bacteria cellulose membrane, the osteoblasts growing on the ceramic material deposited on the microfiber surface are wrapped easily, and an intact bone organization is formed by the osteoblasts combining with collagen generated from the osteoblasts. The cellulose membrane is degraded gradually by the cellulase embedded, leaving no residues. Glucose as a degraded product does no harm to cells, and the glucose can support osteocyte copying and growing as nutrients. Furthermore, the invention also relates to a preparation method for the bone defect repairing material and applications of the bone defect repairing material.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Metallic nanoparticles as orthopedic biomaterial
ActiveUS7824462B2Increase roughnessHeavy metal active ingredientsNanotechOsteoblast adhesionSurface roughness
A composition for use as a prosthetic biomaterial and associated method. The biomaterial exhibits cytocompatibility, mechanical functionality and osteoblast adhesion between the implant and interfacing surface. The biomaterial is metallic, has a grain size less than about 500 nanometers and has a surface roughness of less than about 800 nm rms.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
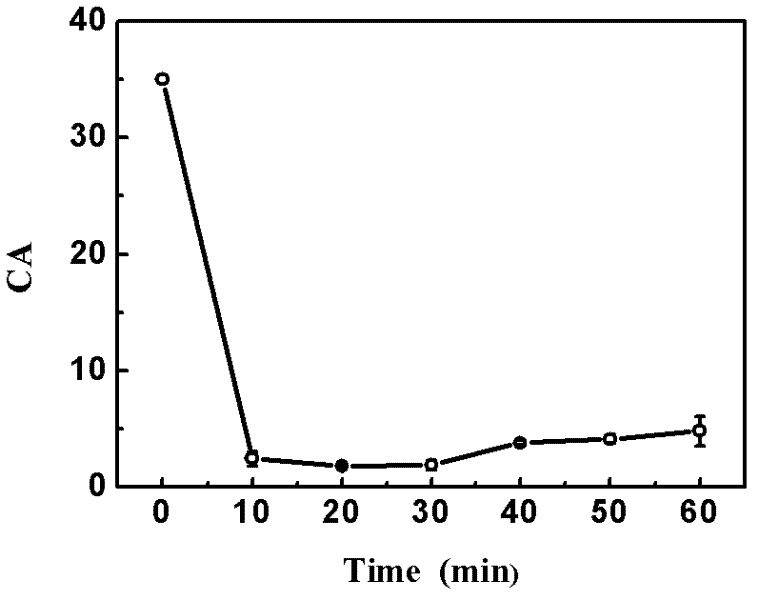
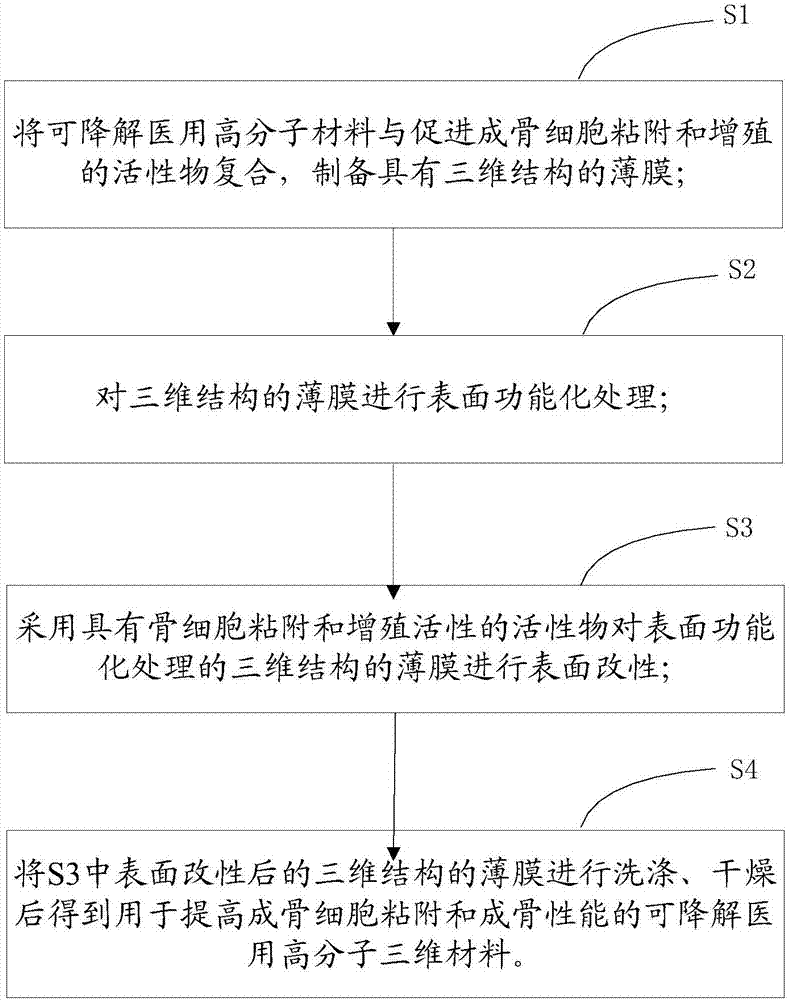
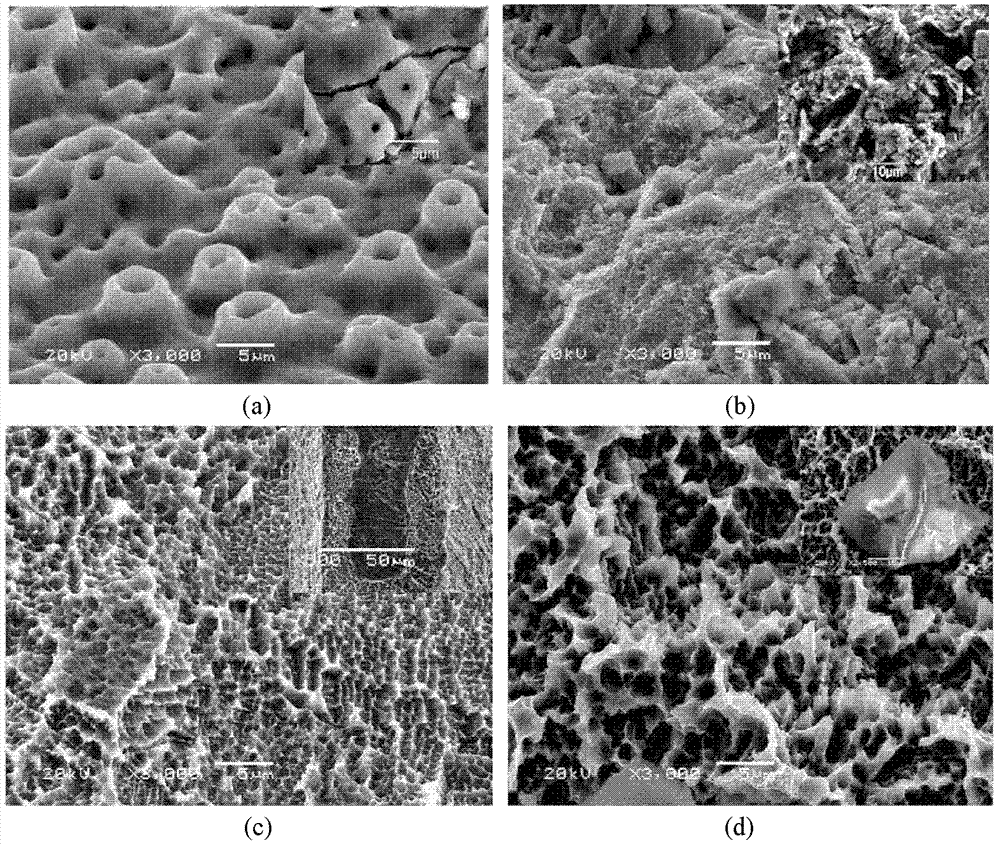
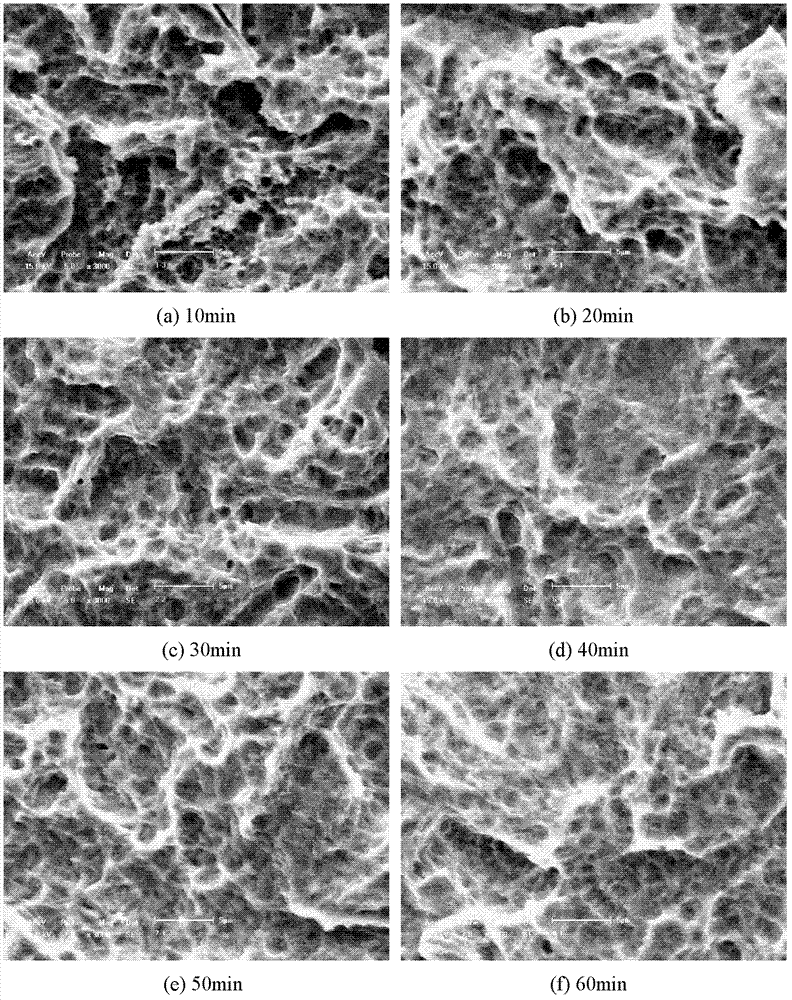
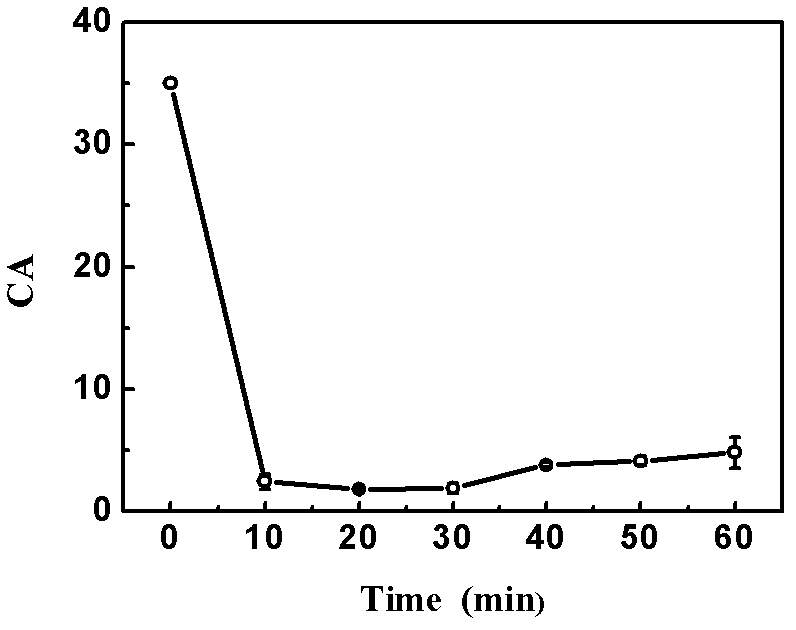
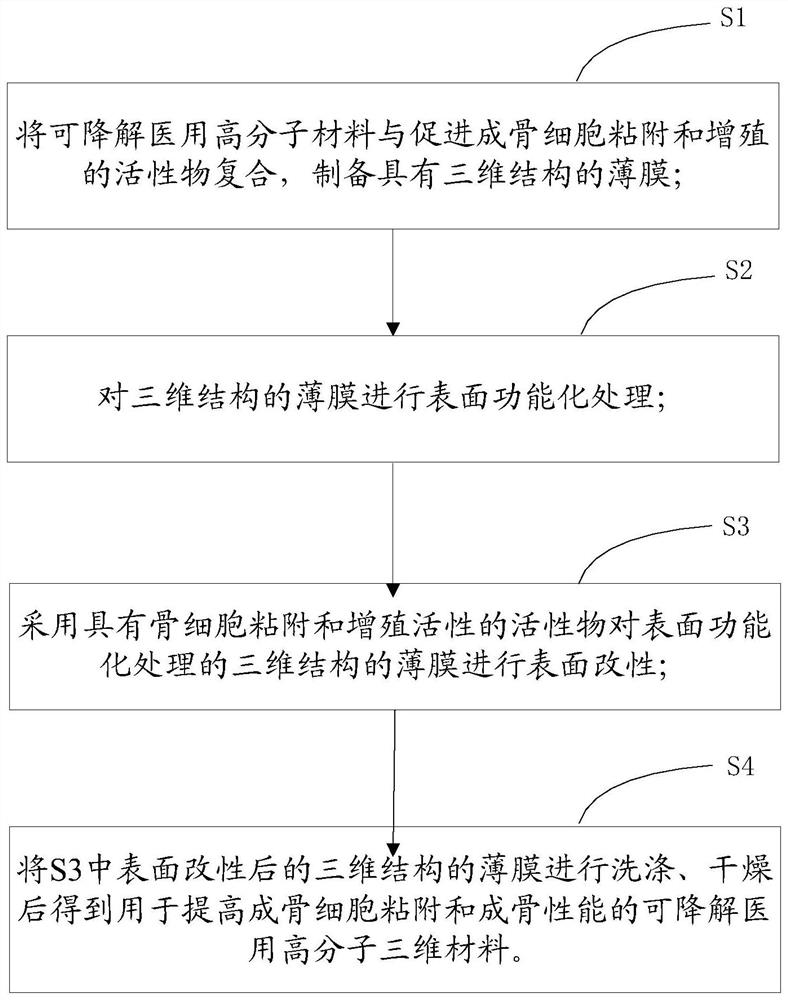
Preparation method of degradable medical macromolecular three-dimensional material for improving osteoblast adhesion and osteogenic property
ActiveCN107213529AGood osteogenic propertiesNo toxicitySurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismHigh concentrationOsteoblast adhesion
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SUZHOU UNIV
Enhanced bonding layers on titanium materials
The present invention provides a dense-coverage, adherent phosphorous-based coating on the native oxide surface of a material. Disclosed phosphorous-based coatings include phosphate and organo-phosphonate coatings. The present invention also provides further derivatization of the phosphorous-based coatings to yield dense surface coverage of chemically reactive coatings and osteoblast adhesion-promoting and proliferation-promoting coatings on the native oxide surface of a titanium material.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Preparation method of good-biocompatibility, enzyme-responsive and antibacterial titanium material
InactiveCN108310471AEasy to operateImprove controllabilitySurface reaction electrolytic coatingTissue regenerationOsteoblast adhesionTio2 nanotube
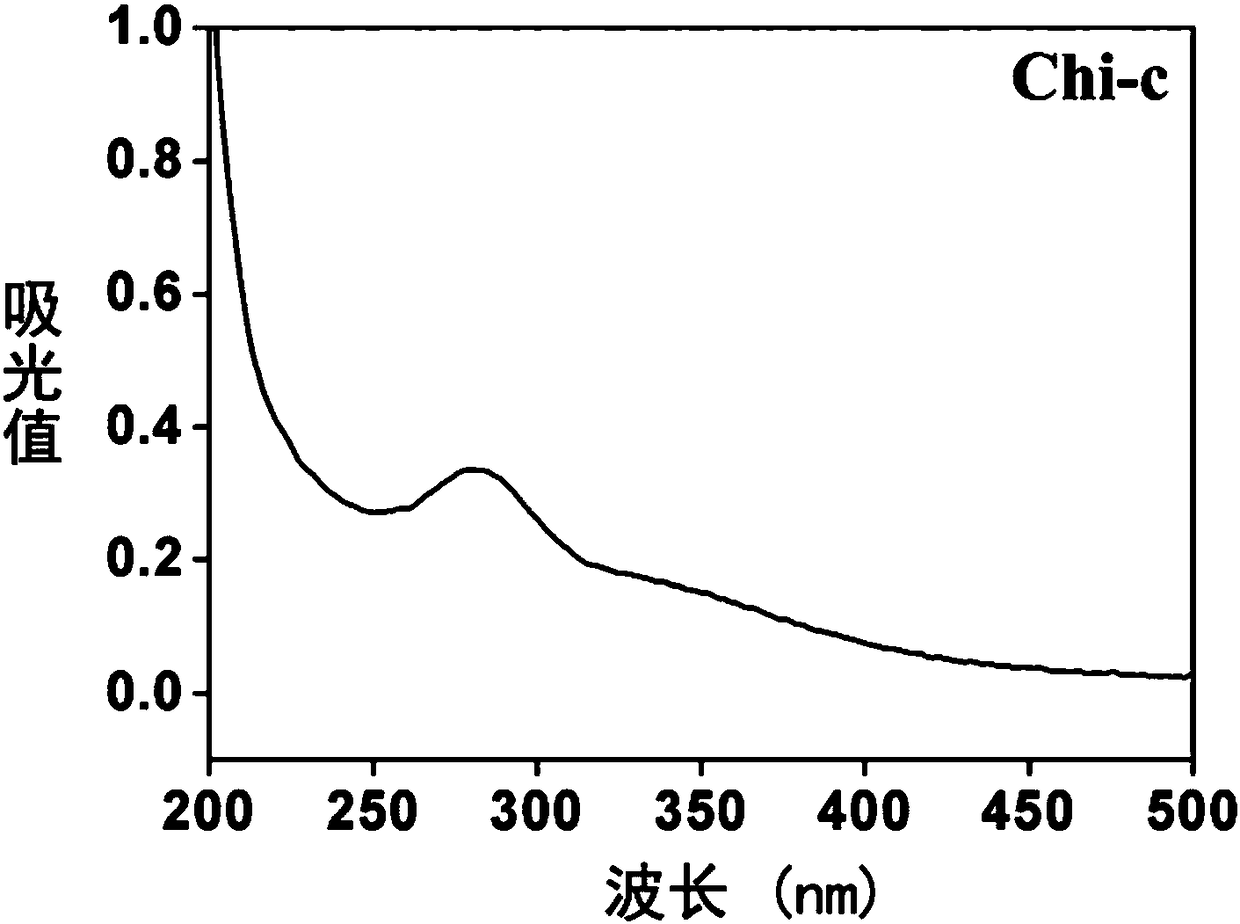
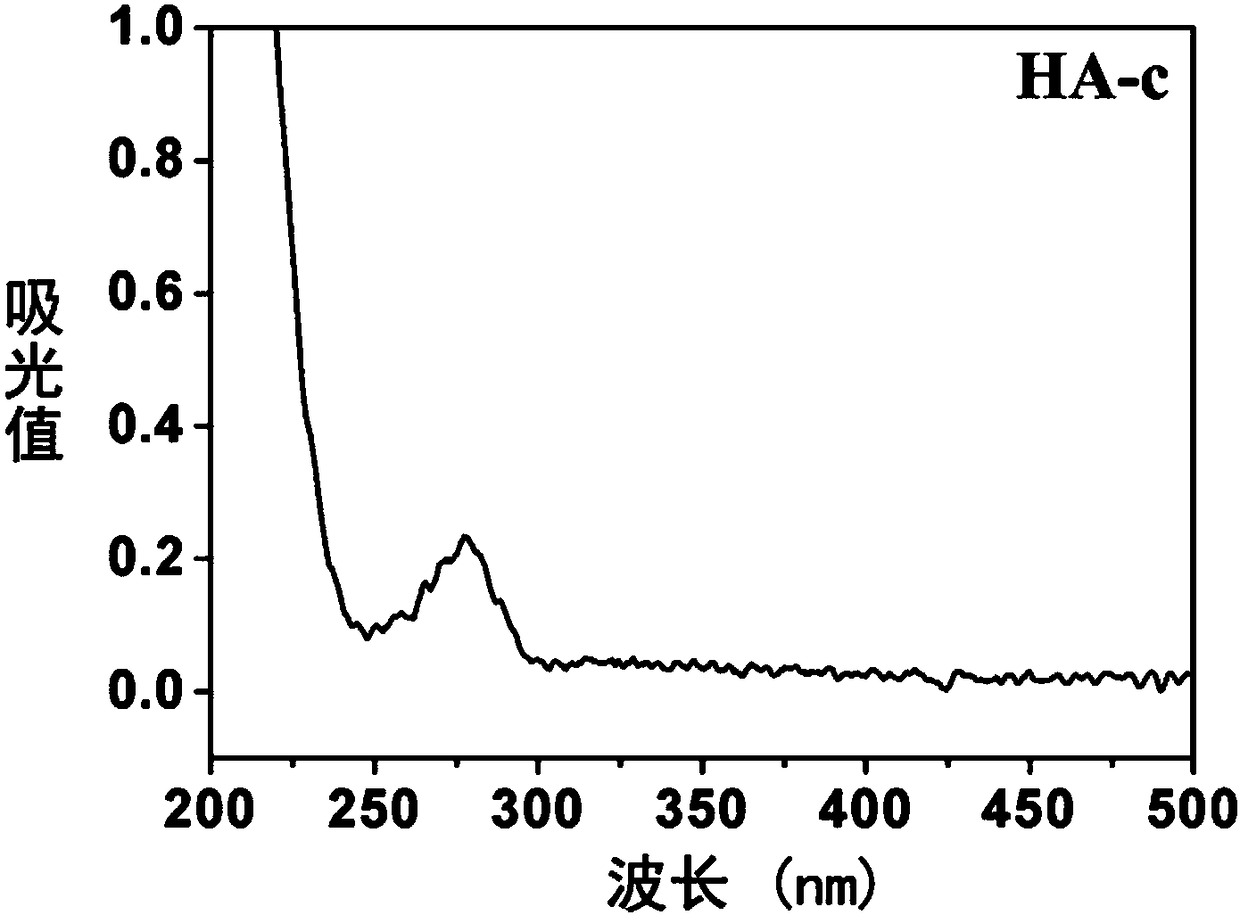
The invention discloses a preparation method of a good-biocompatibility, enzyme-responsive and antibacterial titanium material. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, constructing a uniform titanium dioxide nanotube on the surface of a titanium material by an anodic oxidation method, and using the uniform titanium dioxide nanotube as an antibiotic-loaded medicine storage reservoir; secondly, modifying hyaluronic acid and chitosan by using dopamine and dihydrocaffeic acid respectively to synthesize catechol-functionalized hyaluronic acid and chitosan, which are named as HA-c and Chi-c and used as a polyelectrolyte anion and a polyelectrolyte cation respectively; constructing a catechol-functionalized polyelectrolyte multilayer film on the surfaceof the antibiotic-loaded titanium dioxide nanotube by using the HA-c and the Chi-c by a layer-by-layer self-assembly technology. By the preparation method, biological coating with dual functions of promoting adhesion and differentiation of osteoblasts and achieving a bacterial responsive antibacterial property is constructed on the surface of the titanium material, and a titanium-based implant isendowed with good antibacterial and osteogenic properties.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Metallic nanoparticles as orthopedic biomaterial
ActiveUS20060204538A1Improve adhesionMaintain compatibilityHeavy metal active ingredientsNanotechOsteoblast adhesionNanoparticle
A composition for use as a prosthetic biomaterial and associated method. The biomaterial exhibits cytocompatibility, mechanical functionality and osteoblast adhesion between the implant and interfacing surface. The biomaterial is metallic, has a grain size less than about 500 nanometers and has a surface roughness of less than about 800 nm rms.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method for surface inclusions detection, enhancement of endothelial and osteoblast cells adhesion and proliferation, sterilization of electropolished and magnetoelectropolished nitinol surfaces
InactiveUS20120093944A1Enhancement of endothelialEnhancement of osteoblast cell adhesionSuture equipmentsInorganic active ingredientsOsteoblast adhesionElectrolysis
The method for surface inclusions detection, enhancement of endothelial and osteoblast cells adhesion and proliferation and sterilization of electropolished and magnetoelectropolished Nitinol implantable medical device surfaces uses an aqueous solution of chemical compounds containing halogenous oxyanions as hypochlorite (ClO−) and hypobromite (BrO−) preferentially 6% sodium hypochlorite (NaClO).
Owner:ROKICKI MARGARET
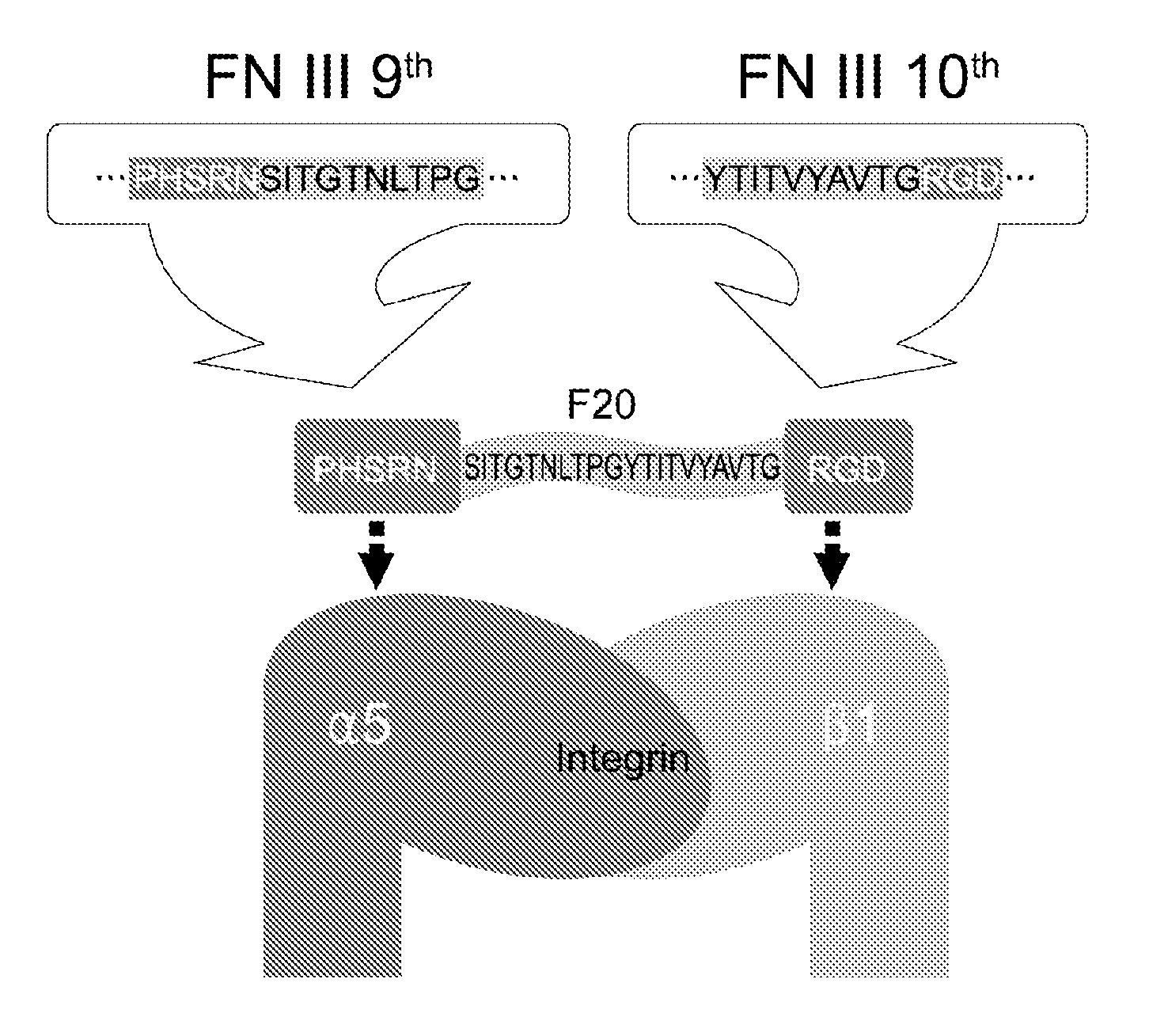
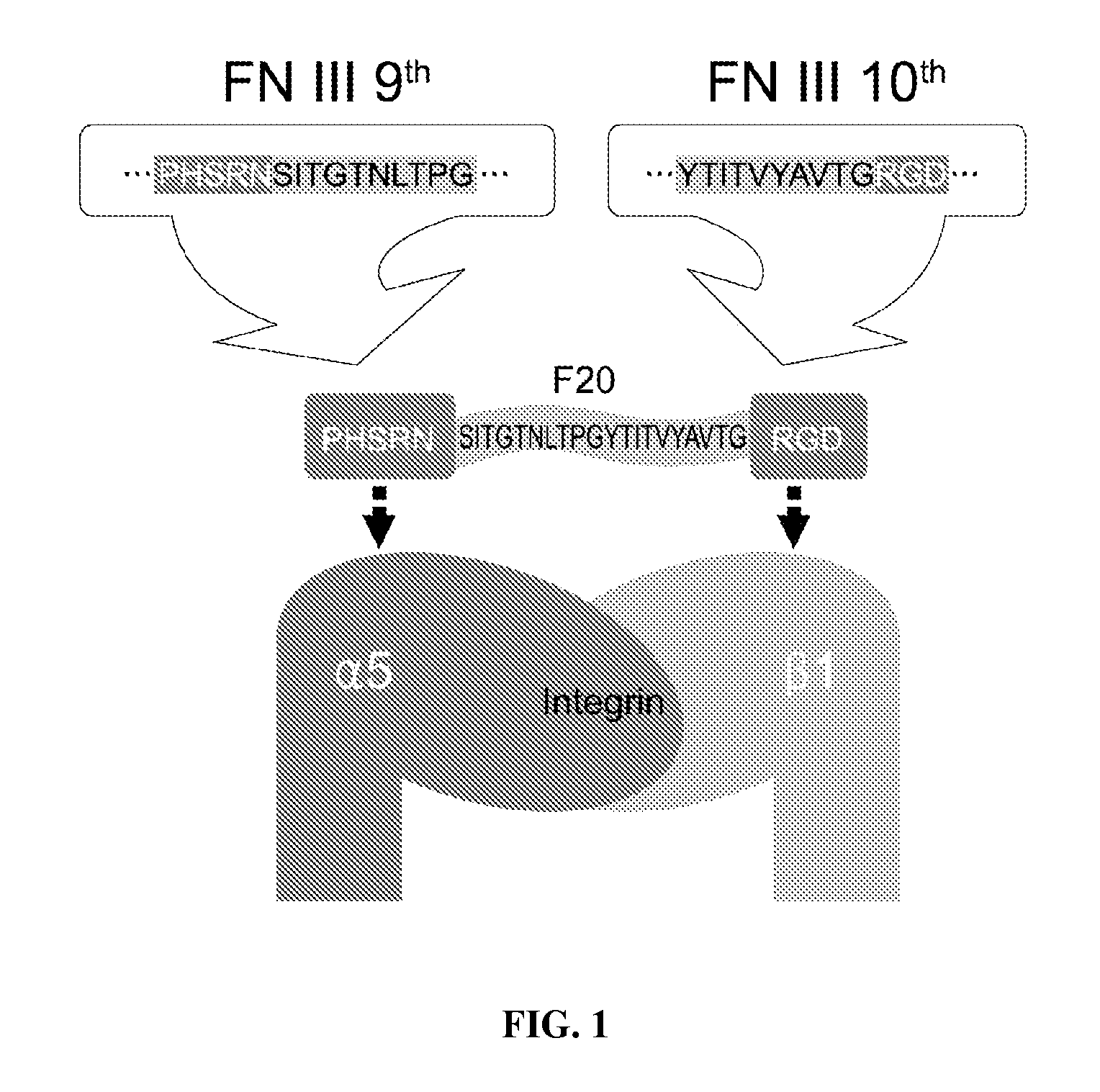
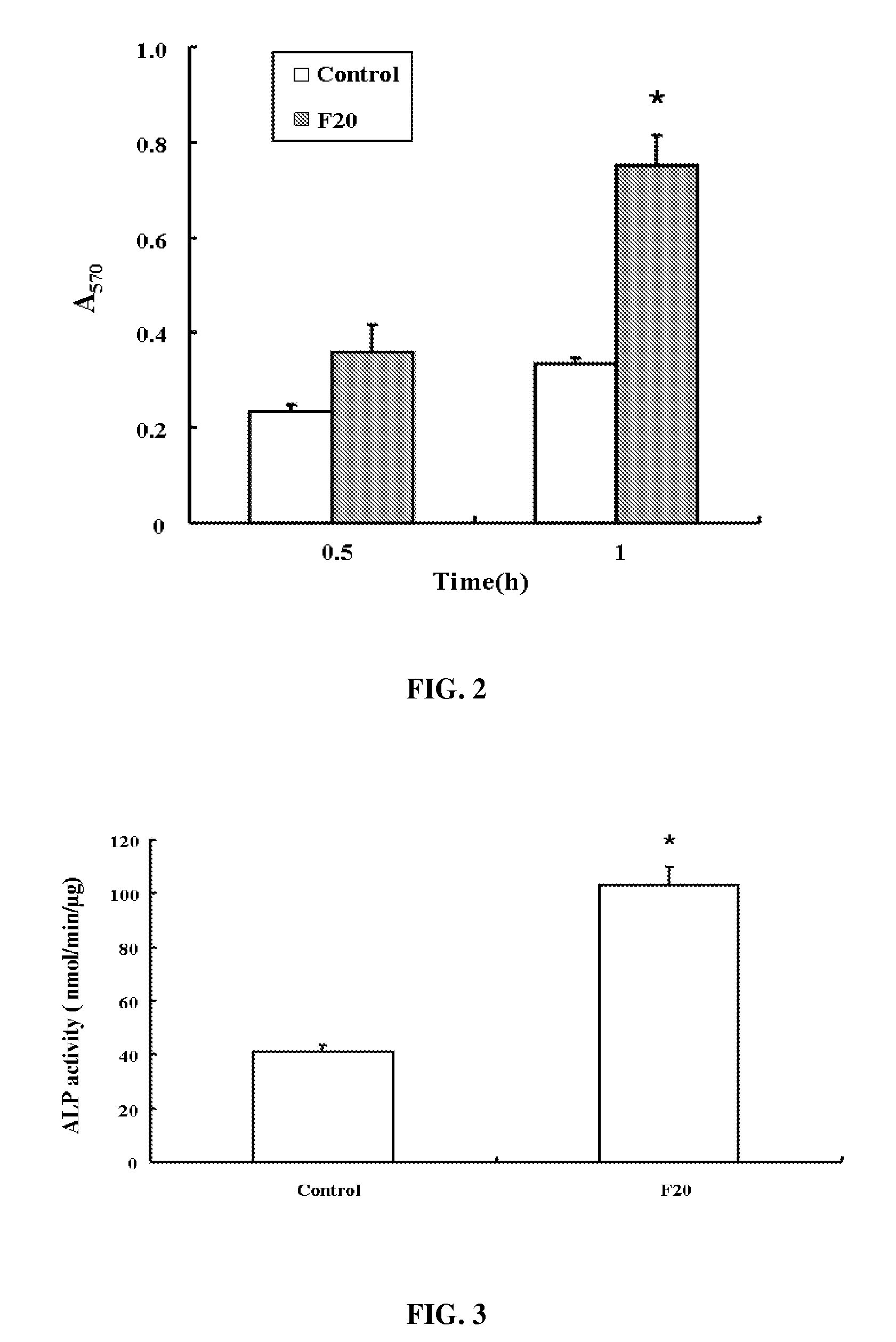
Composition of bone formation with PHSRN-RGD containing oligopeptide
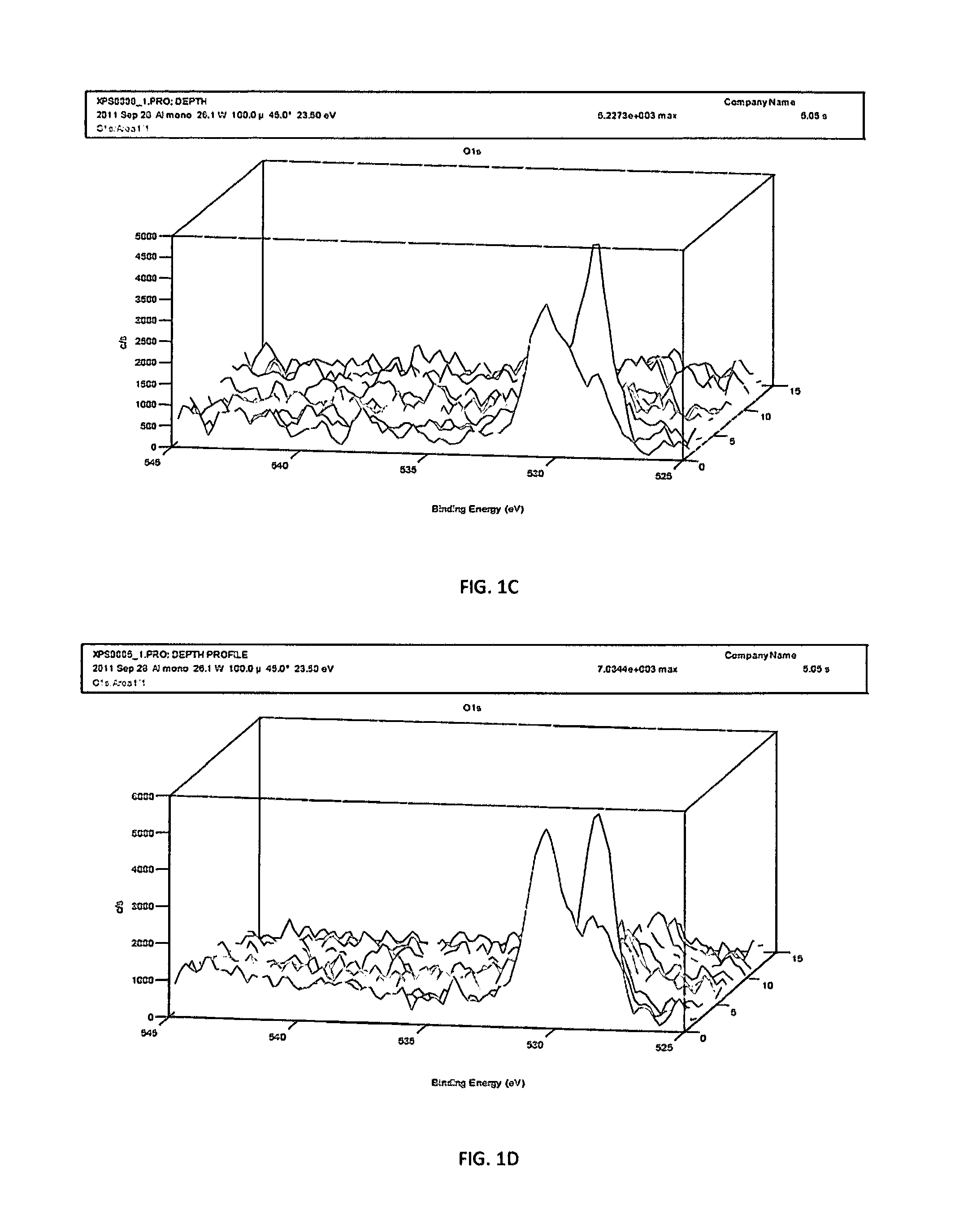
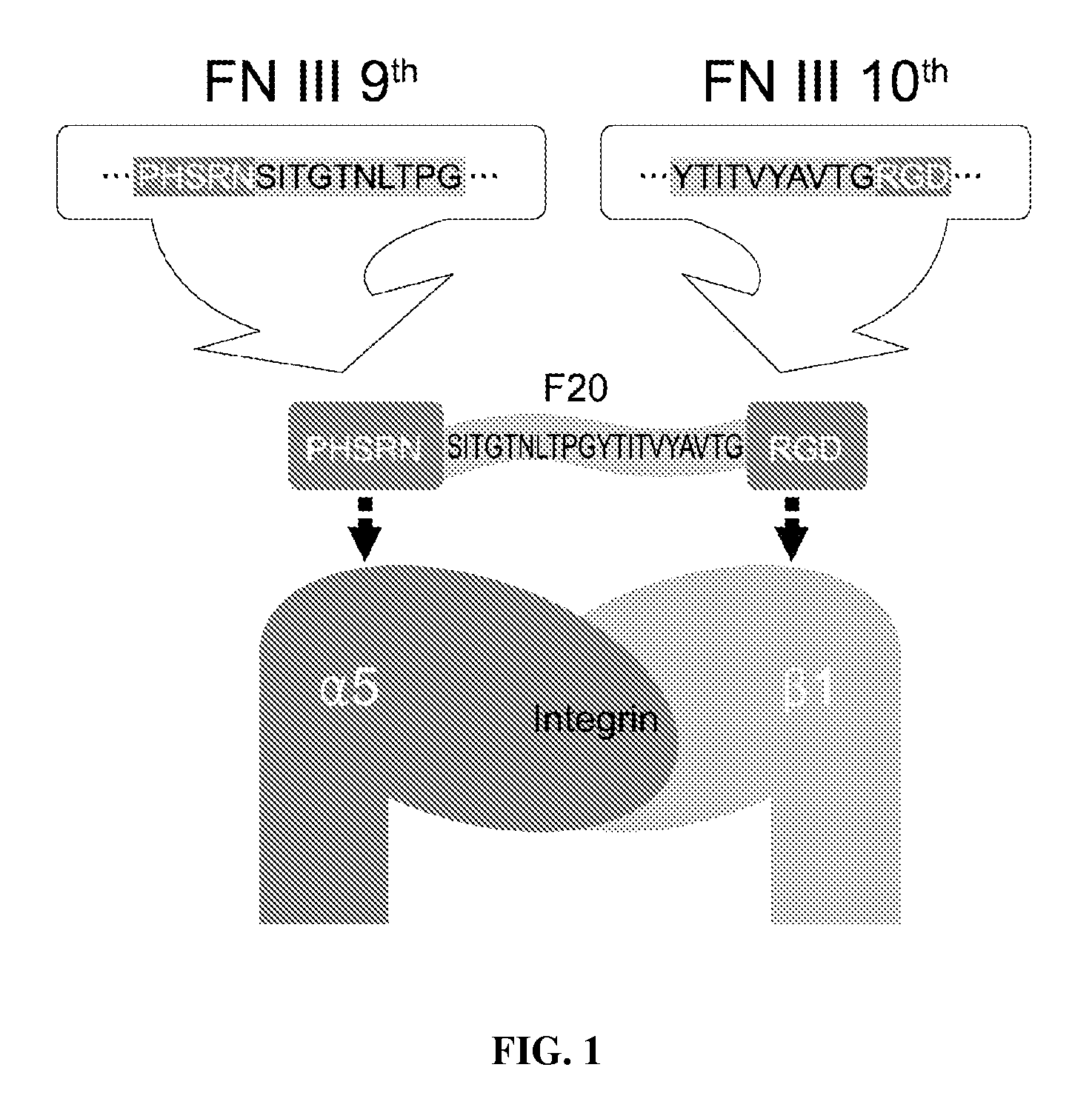
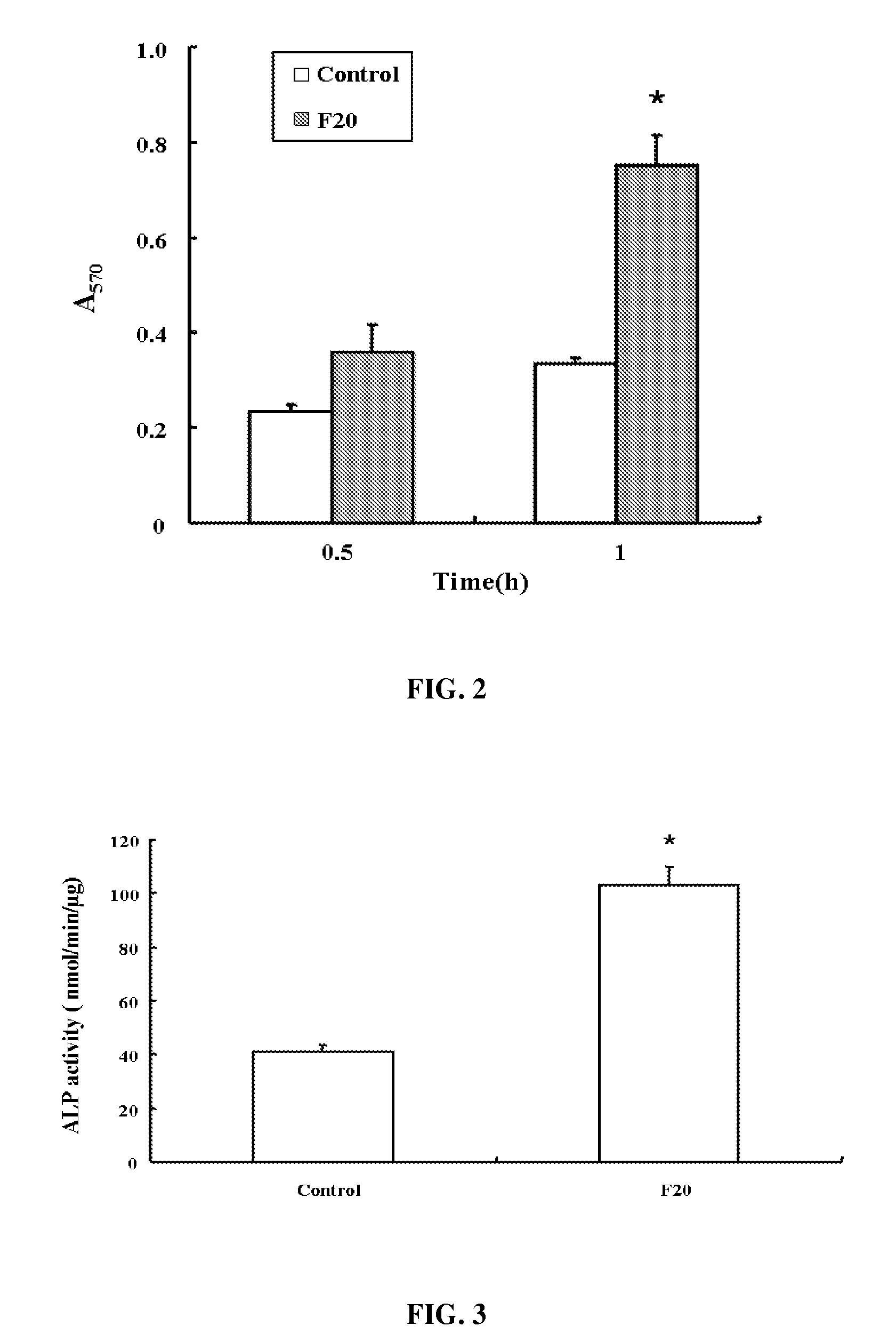
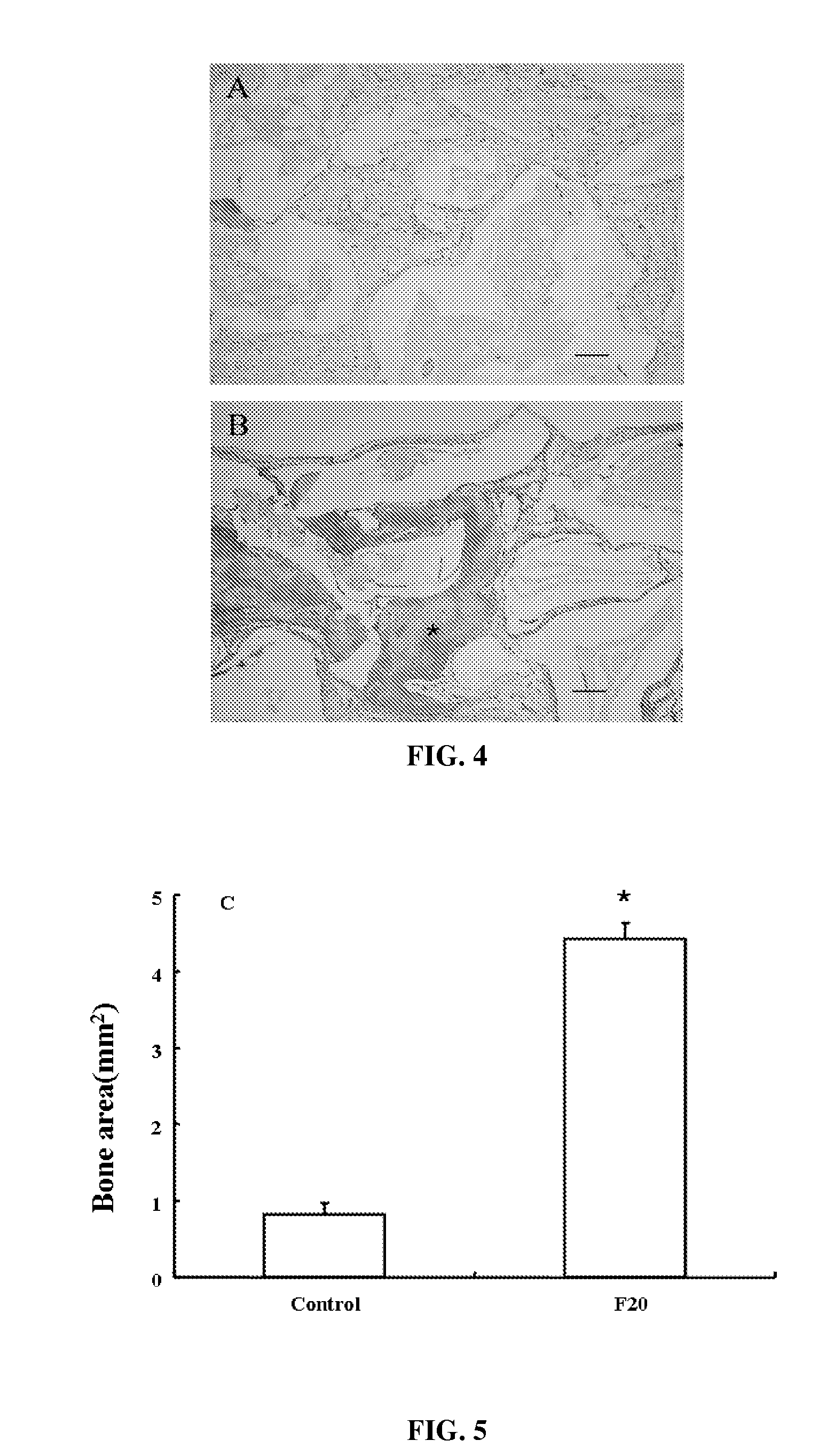
InactiveUS7897722B2Connective tissue peptidesIn-vivo radioactive preparationsOsteoblast adhesionBone tissue
A PHSRN-RGD-containing oligopeptide and a composition for promoting bone formation, which contains such oligopeptide as an effective ingredient. The oligopeptide promotes osteoblastic cell adhesion and differentiation and enhances bone regenerative ability, so that the inventive oligopeptide can be effectively used in regenerative treatment of bone tissue and periodontal tissue.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Composition of bone formation with phsrn-rgd containing oligopeptide
InactiveUS20090010988A1Connective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsOsteoblast adhesionBone tissue
A PHSRN-RGD-containing oligopeptide and a composition for promoting bone formation, which contains such oligopeptide as an effective ingredient. The oligopeptide promotes osteoblastic cell adhesion and differentiation and enhances bone regenerative ability, so that the inventive oligopeptide can be effectively used in regenerative treatment of bone tissue and periodontal tissue.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Fusion peptide capable of promoting osteoblast adhesion and osteogenic differentiation as well as preparation method and application of fusion peptide
ActiveCN105504069AInfluence of self-assembly abilityStabilizes the β-sheet structurePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsOsteoblast adhesionOsseous Cell
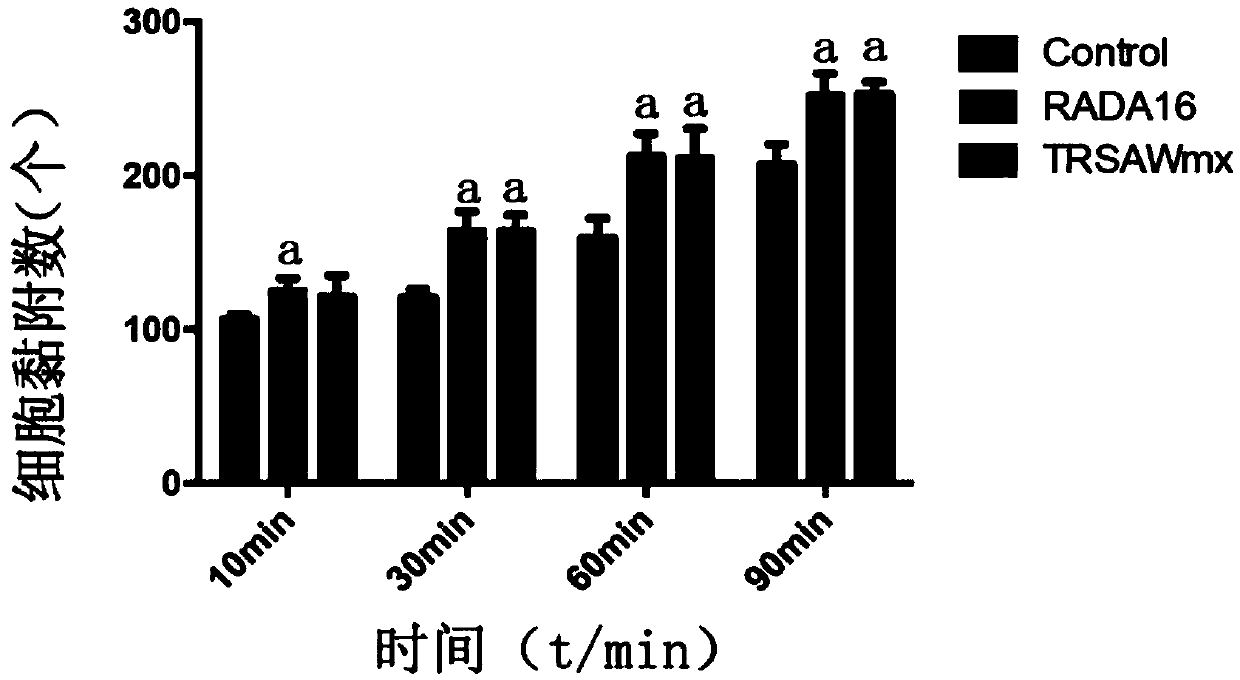
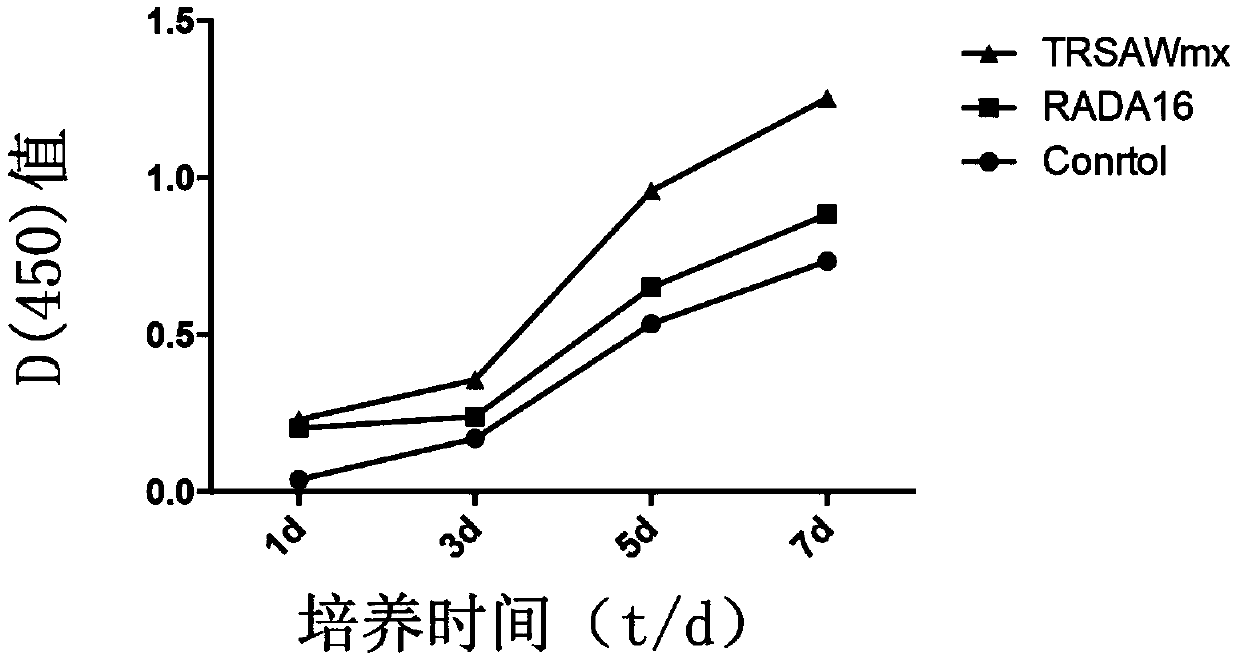
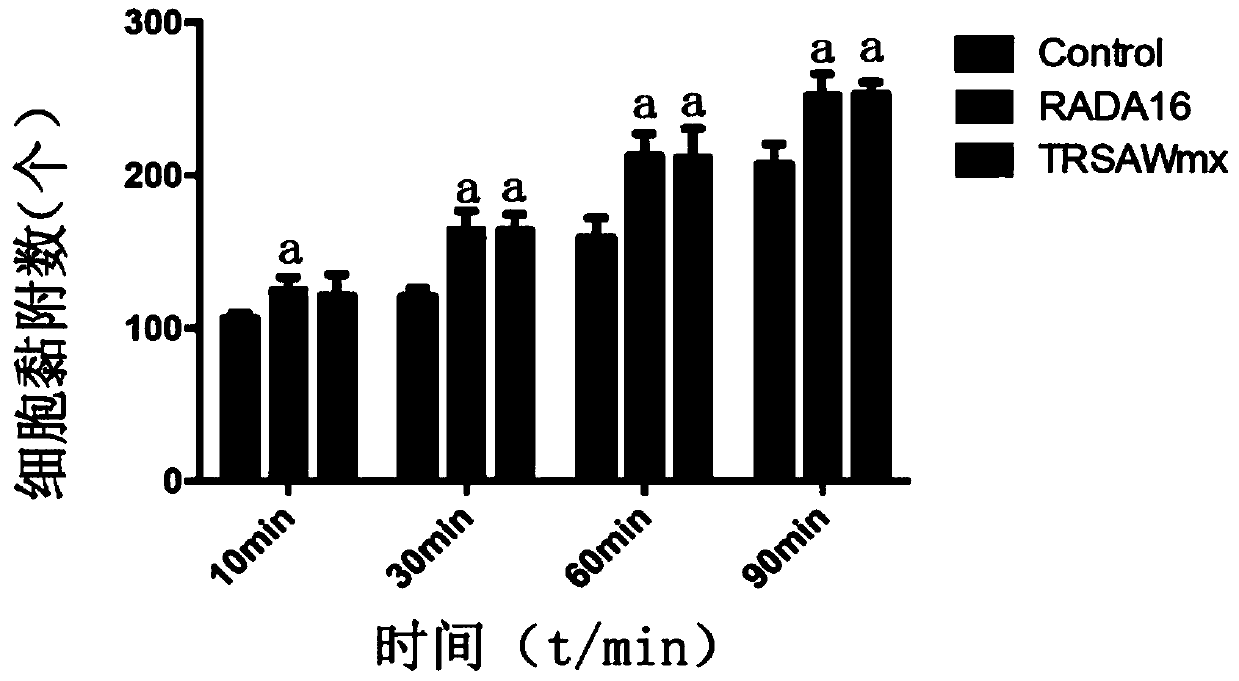
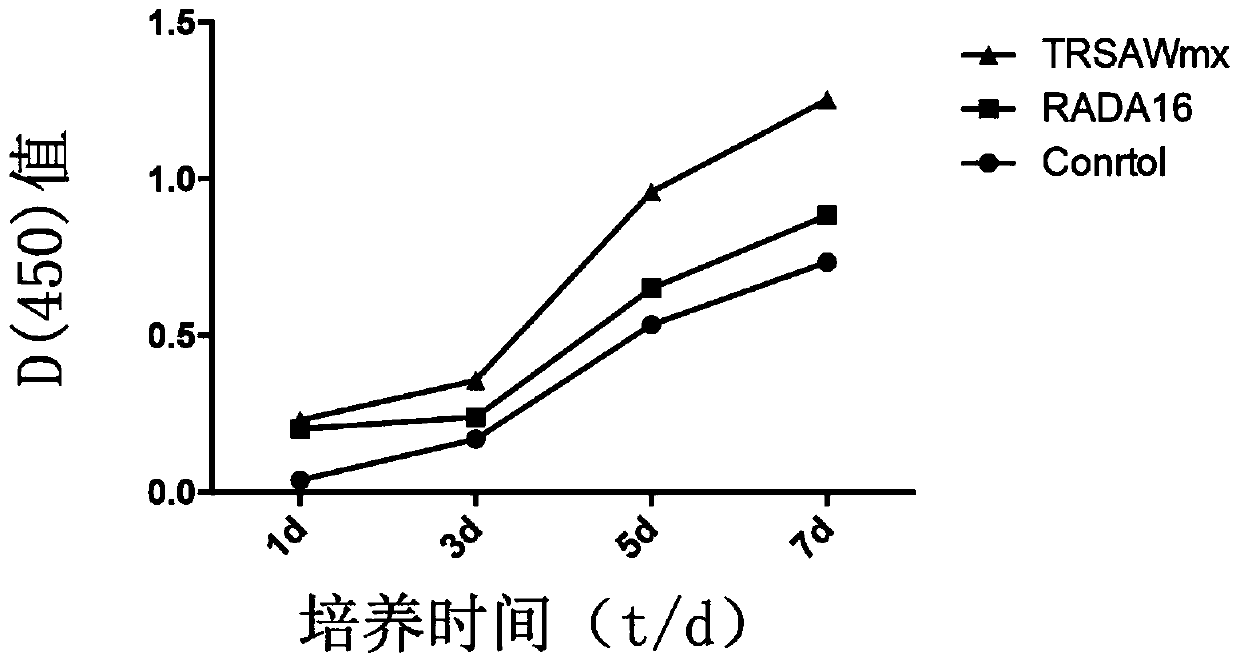
The invention provides a fusion peptide capable of promoting osteoblast adhesion and osteogenic differentiation as well as a preparation method and application of the fusion peptide. The fusion peptide comprises an RADA16-I peptide and an osteostatin (TRSAW) peptide coupled at the C end of the RADA16-I peptide sequence, wherein the amino acid sequence of the RADA16-I peptide is shown as SEQ ID NO:1 in the specification. The invention further provides a medicine composition comprising the fusion peptide. The fusion peptide provided by the invention not only can promote MC3T3-E1 osteocyte adhesion and proliferation, but also can promote osteogenic differentiation, and further has a good application prospect.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Method for surface inclusions detection, enhancement of endothelial and osteoblast cells adhesion and proliferation, sterilization of electropolished and magnetoelectropolished nitinol surfaces
InactiveUS9017489B2Improve cell adhesionEnhanced corrosion behaviorSuture equipmentsInorganic active ingredientsOsteoblast adhesionElectrolysis
Owner:ROKICKI MARGARET
3D printing titanium alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112999414ASatisfy AdhesionFulfil requirementsAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyAcid etchingOsteoblast adhesion
The invention belongs to the field of titanium alloys, and relates to a 3D printing titanium alloy and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the 3D printing titanium alloy comprises the steps: subjecting titanium alloy powder to 3D printing, and then sequentially subjecting an obtained 3D printing titanium alloy body to cleaning and oil removal, sand blasting treatment, high-pressure washing, first-time surface hydrophilic treatment, first-time acid etching treatment, second-time surface hydrophilic treatment and second-time acid etching treatment. By adopting the method provided by the invention, a composite structure of a macroscopic bone trabecula structure and a microcosmic multi-stage micron hole structure can be obtained on the surface of the 3D printing titanium alloy, so that the requirements of osteoblast adhesion and osteogenesis promotion are met, and free powder particles and semi-molten particle residues in a porous layer and a grid structure on the surface of the 3D printing titanium alloy can be effectively removed, and particulate matter and impurity components are prevented from remaining on the surface of the 3D printing titanium alloy.
Owner:DABO MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +1
Preparation method for wettability controllable porous structure of titanium and titanium alloy surface
InactiveCN102345134BAchieve freedom of controlImprove timelinessChemical vapor deposition coatingOsteoblast adhesionTitanium alloy
The invention discloses a preparation method for a wettability controllable porous structure of a titanium and titanium alloy surface, and belongs to the technical field of surface modification of biological implant materials. The method comprises the following steps of: performing roughening treatment on the titanium and titanium alloy surface by using a sand-blast, large-grit and acid-etch method (SLA) to prepare a super-hydrophilic surface with a micron-nano double-microcosmic pore structure; preparing a titanium oxide thin film with hydrophilic performance by using a plasma oxidation process, wherein osteoblast adhesion and proliferation experiments show that the surface prepared by the process method has excellent bioactivity; and finally, forming a hydrophobic surface on a rough titanium oxide surface by using a molecular self-assembly method and realizing mutual switching between hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity of the surface by using plasma treatment and ultraviolet irradiation. The hydrophilicity of the surface of an implant is obviously improved in the aspects of stability, durability and the like; and the binding force of the metal implant material and a surface coating can be obviously improved while the bioactivity of the titanium and titanium alloy surface is guaranteed.
Owner:蔺增
A preparation method of degradable medical polymer three-dimensional material for improving osteoblast adhesion and osteogenic performance
ActiveCN107213529BGood osteogenic propertiesNo toxicitySurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismOsteoblast adhesionHigh concentration
The invention provides a method for preparing a degradable medical polymer three-dimensional material for improving osteoblast adhesion and osteogenic performance. Compound the proliferating active substance to prepare a three-dimensional structure film; perform surface functionalization on the three-dimensional structure film; use active substances with bone cell adhesion and proliferation activity to modify the surface of the surface functionalized three-dimensional structure film ; Washing and drying the surface-modified film with three-dimensional structure to obtain the product. Compared with the existing technology, the degradable medical polymer three-dimensional material prepared by the above method for improving the adhesion and osteogenic performance of osteoblasts can maintain the mechanical properties and structure, and the body can be realized by mixing modification and surface modification methods. The combination of low-concentration persistent expression and high-concentration short-term expression of osteogenic active substances on the surface can significantly improve the adhesion and three-dimensional growth of osteoblasts.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SUZHOU UNIV
Application of a titanium implant storage solution containing vitamin c
ActiveCN111588506BImprove adhesionPromote proliferationDental implantsMetallic material coating processesOsteoblast adhesionVitamin C
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV +1
Biomechanical mandible scaffold and preparation method of micro-nano hierarchical permeable titanium-niobium surface
PendingCN111437439AConform to biomechanical characteristicsReduce stress shieldingBone implantVacuum evaporation coatingOsteoblast adhesionBiomechanics
The invention discloses a biomechanical mandible scaffold and a preparation method of a micro-nano hierarchical permeable titanium-niobium surface. The material of the mandible scaffold has a gradientstructure, and the mandible scaffold comprises an alloy matrix and a porous surface, wherein the alloy matrix is a titanium-niobium-based beta-series alloy material and the porous surface is a micro-nano hierarchical permeable titanium-niobium surface. The biomechanical mandible scaffold has the high-strength and low-modulus alloy matrix and the porous surface, the modulus is further reduced through the porous structure, the morphology beneficial to osteoblast adhesion is formed, and the constructed mandible scaffold better conforms to biomechanical characteristics and has surface osteogenicactivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Bone defect repairing material, preparation method and applications thereof
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Fusion peptide promoting osteoblast adhesion and osteogenic differentiation, preparation method and application
ActiveCN105504069BReduce the impact of self-assembly abilityStabilizes the β-sheet structurePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsOsteoblast adhesionOsseous Cell
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
A kind of bionic ternary ion-doped hydroxyapatite bioceramic powder material and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN108164263BLow costEasy to operateTissue regenerationProsthesisOsteoblast adhesionPhysical chemistry
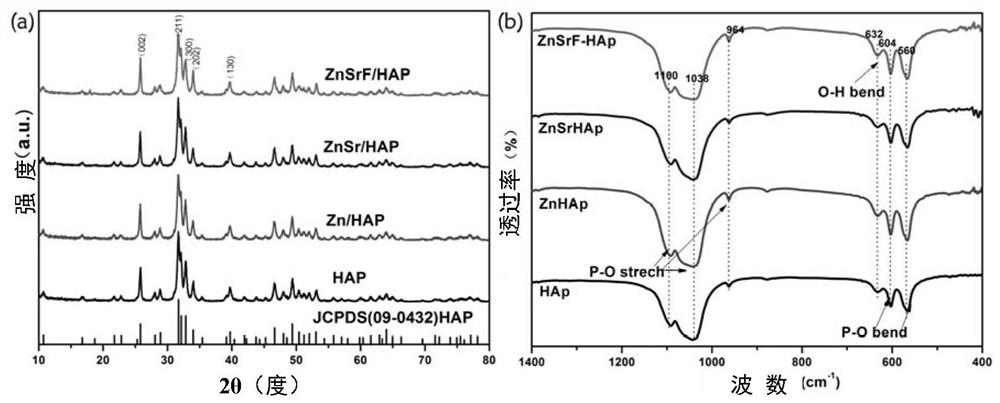
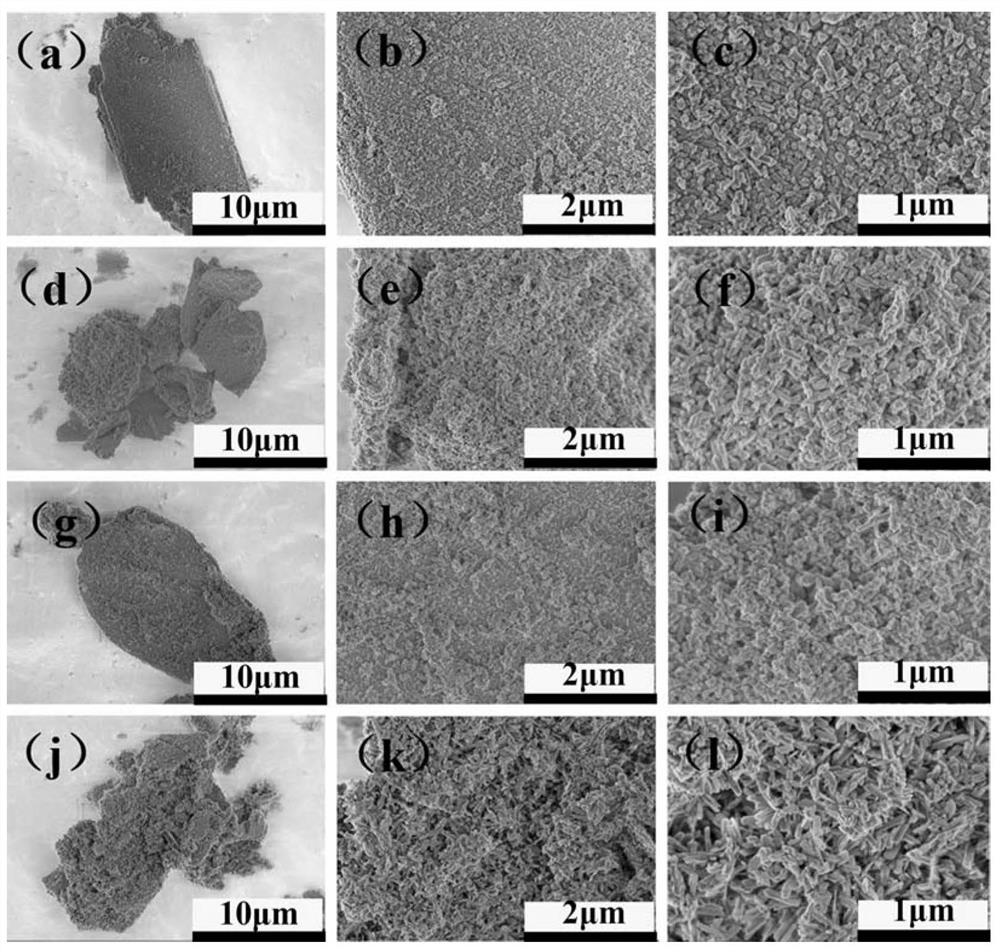
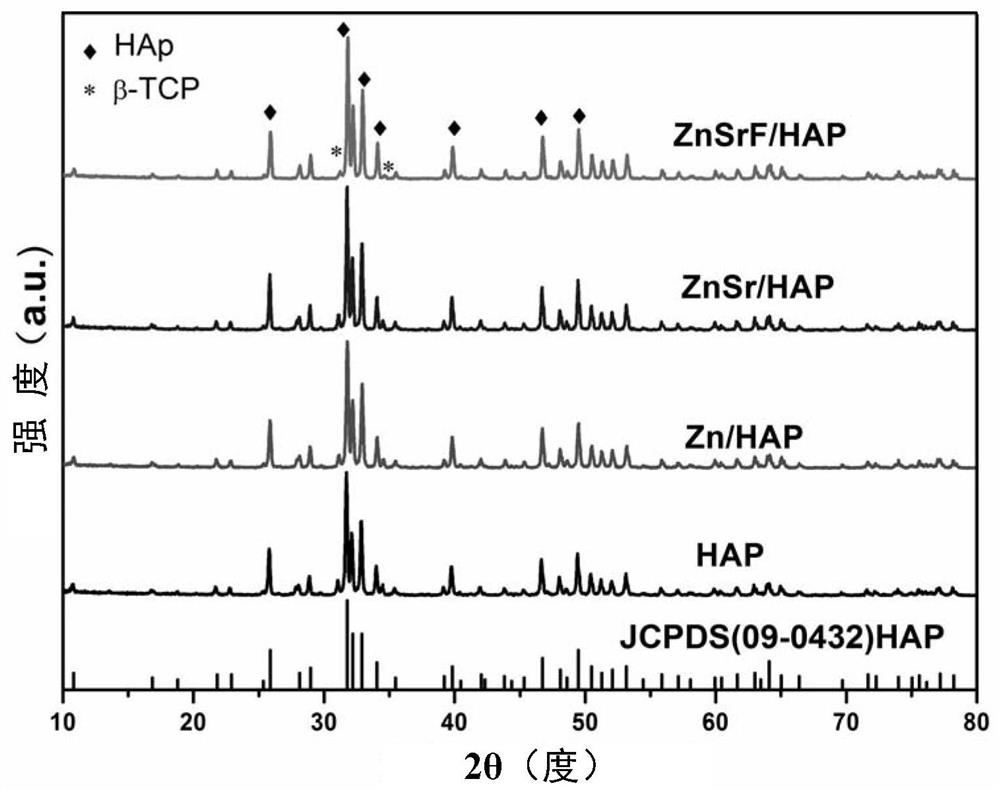
The invention provides a biomimetic ternary ion-doped hydroxyapatite bioceramic powder material, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The chemical formula of the biomimetic ternary ion-doped hydroxyapatite bioceramic powder material is Ca10-a-bZnaSrb(PO4)6(OH)2-cFc, wherein a is not less than 0.004 and not more than 0.006, b is not less than 0.005 and not more than 0.007, and c isnot less than 0.04 and not more than 0.08. The material promotes biomineralization and osteoblast adhesion, so the material has great application values in the field of hard tissue repairing materials.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of cu/paa composite film and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN106637310BControl loadAntibacterialSurgerySurface reaction electrolytic coatingOsteoblast adhesionAlternating current
The invention relates to a Cu / porous anodic alumina (PAA) composite membrane as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The composite membrane has a structure that nano-Cu is evenly distributed in a PAA porous structure by means of alternate current (AC) deposition. The preparation method comprises the steps of carrying out barrier layer thinning and pore broadening pretreatment on PAA; adding the PAA subjected to the pretreatment into electro-deposition liquid, and carrying out external AC deposition to obtain the Cu / PAA composite membrane. The method provided by the invention is simple and efficient in operation and convenient to popularize; the prepared composite membrane has antibacterial property and osteoblast adhesion proliferation promoting ability at the same time, thus being expected to come into use as a surface coating of an artificially implanted material.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Artificial bone with porous laminated structure and passages and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101766843BControllable degradation rateGood biocompatibilityBone implantOsteoblast adhesionHydroxylapatite
The invention relates to an artificial bone with a porous laminated structure and passages, which belongs to the technical field of biomedical materials. The artificial bone is alternately laminated and formed by compact layers and porous layers which are made of calcium phosphate base biological ceramic materials, and in addition, passages for conveying cells and body fluid are arranged in the direction which forms a set angle with the laminated layers. The preparation method comprises the following step: mixing powder such as hydroxylapatite, beta-tricalcium phosphate and the like through using deionized water as medium to be prepared into pulp. A three-dimensional gel laminated forming system is adopted for preparing ceramic blanks formed by the compact layers, the porous layers and the passages, and then the ceramic blanks are sintered at a high temperature for preparing the artificial bone. The invention has the characteristics that the artificial bone has high mechanical strength, has the porous structure with the effects of osteoplast adhesion, propagation, growth and vascularization, can be used as the artificial bone, can also be used as a bone tissue engineering support frame, and has wide application prospects in clinics in the orthopedics department.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing integrated frame of cartilage of tissue-engineered bone having function interface
InactiveCN101032430BAchieve mechanical strengthGood biocompatibilityBone implantOsteoblast adhesionCartilage cells
The present invention discloses process of preparing integral bionic tissue engineering bone-cartilage rack with functional interface. The process includes the first establishment of CAD model of the integral bone-cartilage rack by means of bionic principle; preparing collagen / chitosan and collagen / hydroxyapatite micro polymer powder; converting the CAD model into fast forming file input into a 3D printing fast forming machine, spreading the powder with one powder spreader, spraying pentanedial adhesive selectively on the spread powder for adhering and eliminating excessive powder to obtain the integral bionic tissue engineering bone-cartilage rack with functional interface. The present invention has excellent biocompatibility, controllable cartilage rack degrading speed and mechanical strength and other advantages.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
A kind of 3D printing titanium alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112999414BMicrostructure reduction or disappearanceEfficient removalAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyAcid etching3d print
The invention belongs to the field of titanium alloys, and relates to a 3D printing titanium alloy and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the 3D printing titanium alloy includes: 3D printing the titanium alloy powder, and then sequentially performing cleaning and degreasing, sandblasting, high pressure washing, first surface hydrophilic treatment, first The second acid etching treatment, the second surface hydrophilic treatment and the second acid etching treatment. The method provided by the invention can not only obtain a composite structure of macroscopic bone trabecular structure and microscopic multi-level micro-hole structure on the surface of 3D printed titanium alloy to meet the requirements of osteoblast adhesion and osteogenesis, but also can 3D printed titanium alloy. The porous layer on the surface of the alloy and the free powder particles and semi-molten particle residues in the mesh structure are effectively removed to prevent particles and impurities from remaining on the surface of the 3D printed titanium alloy.
Owner:DABO MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com