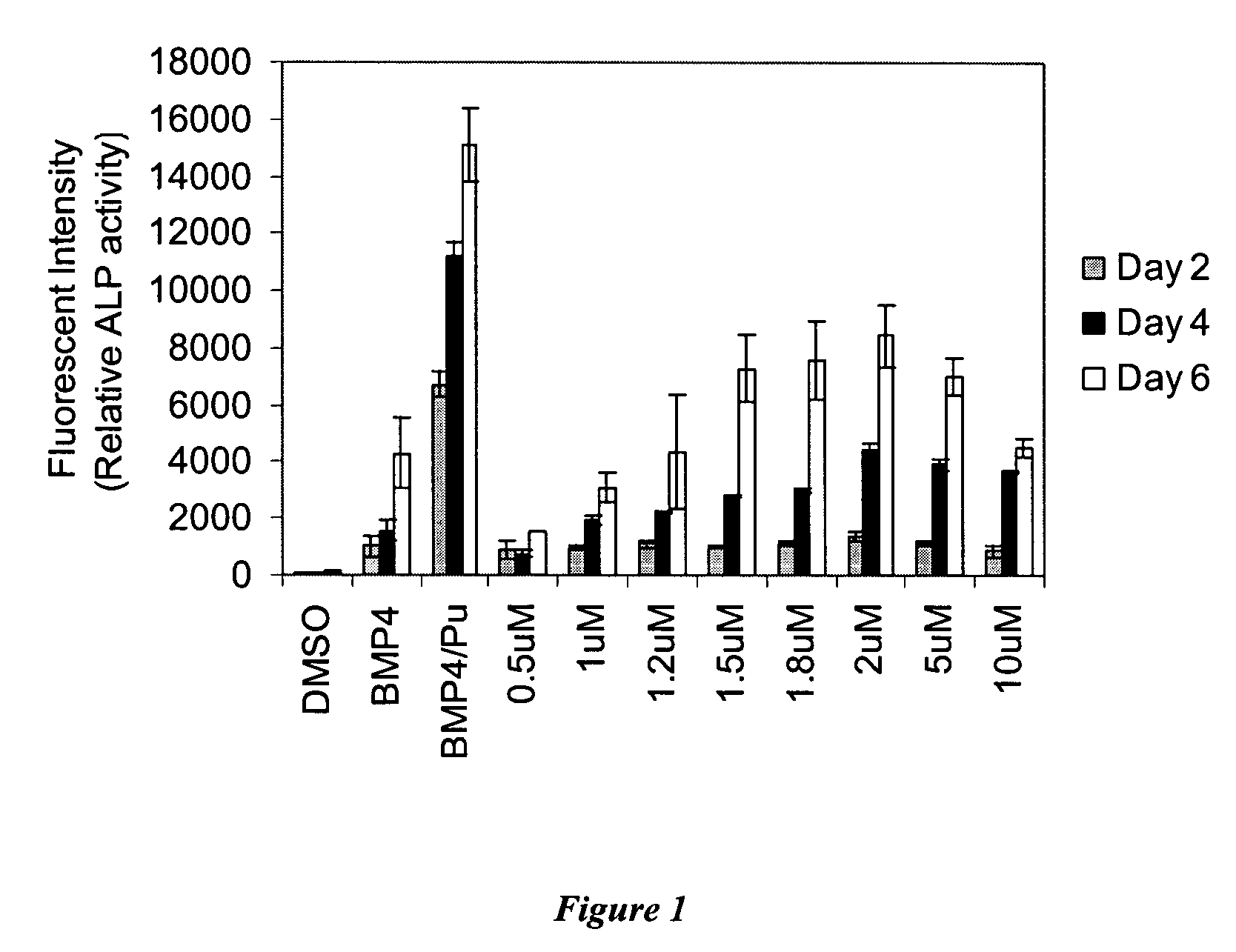
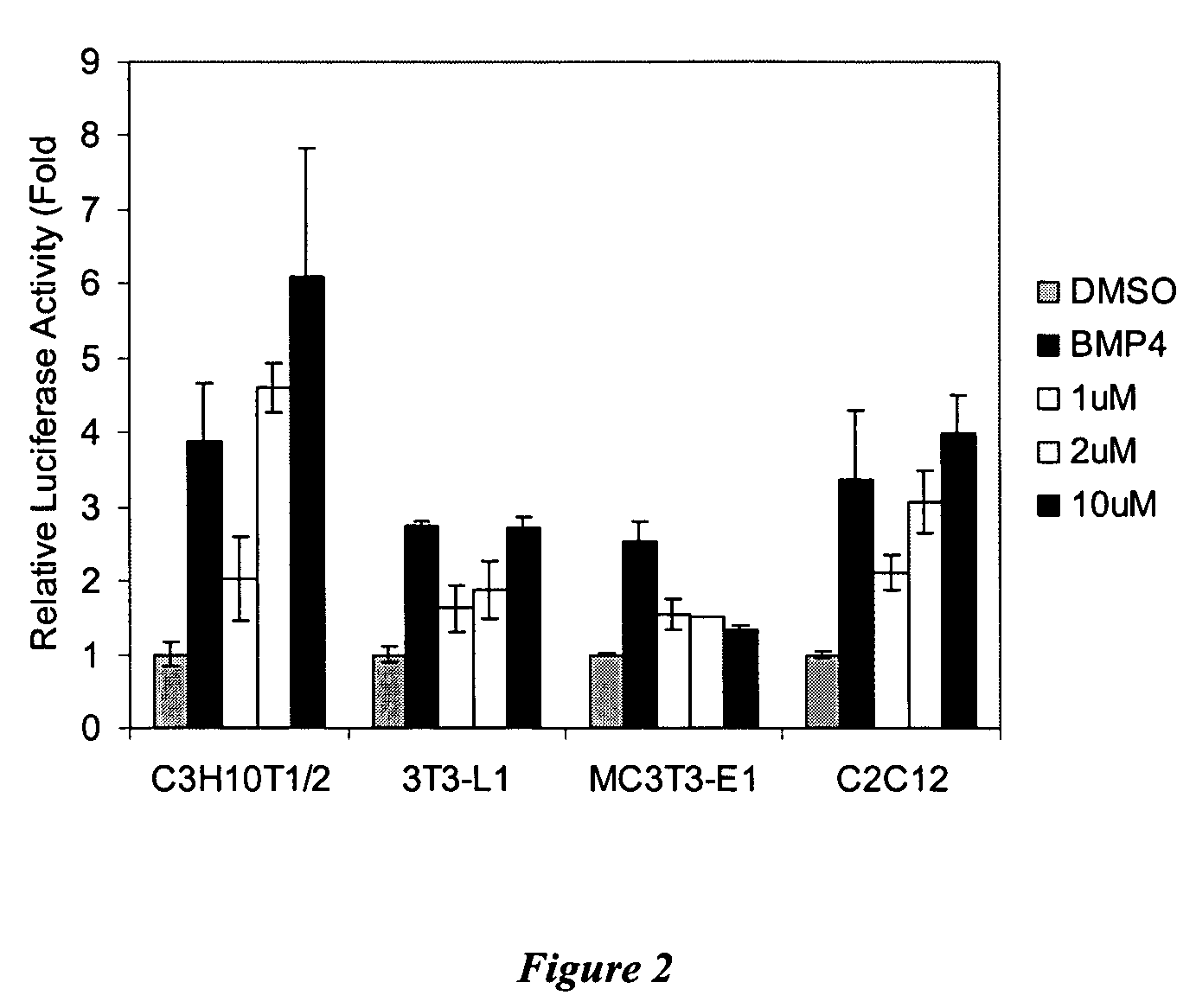
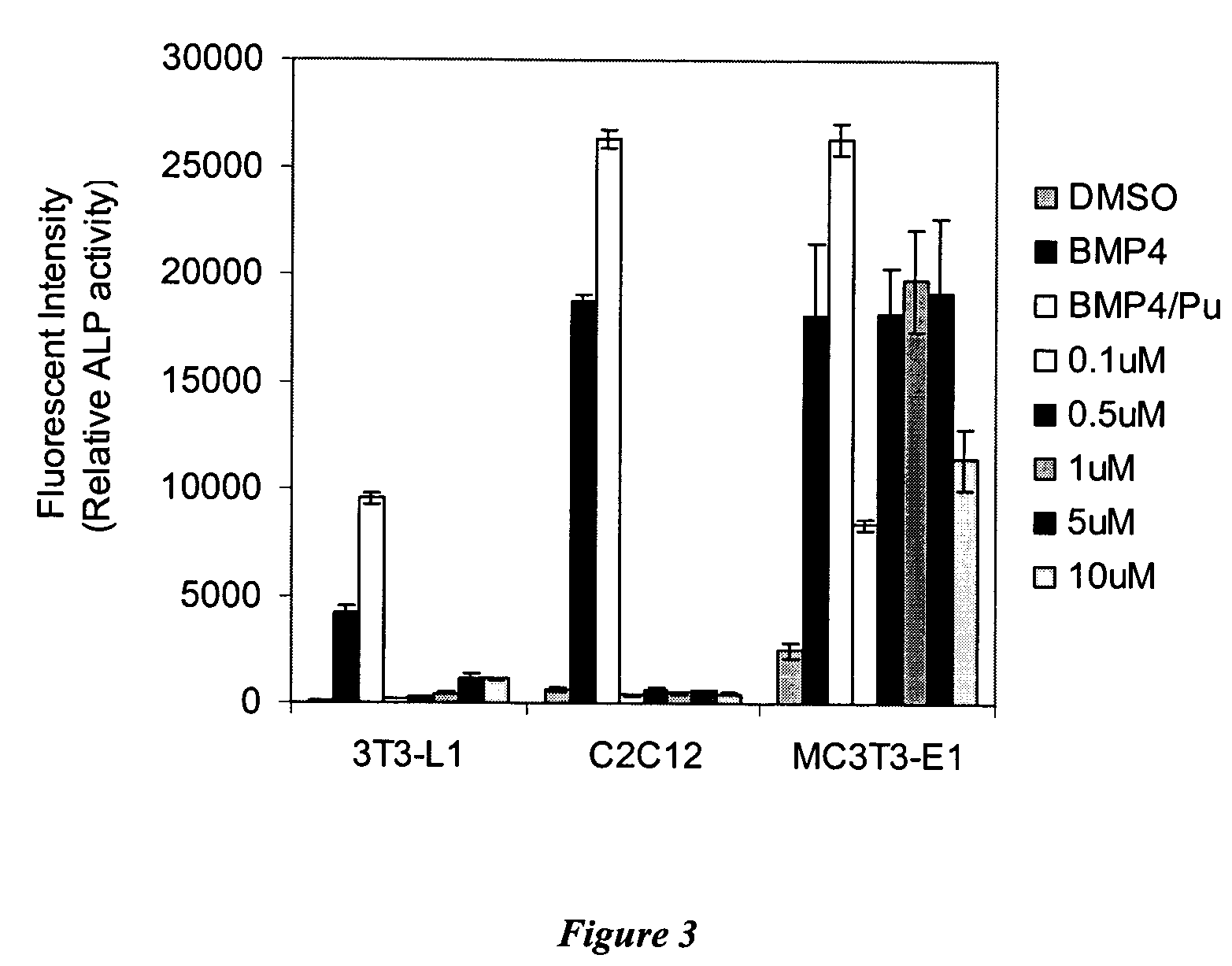
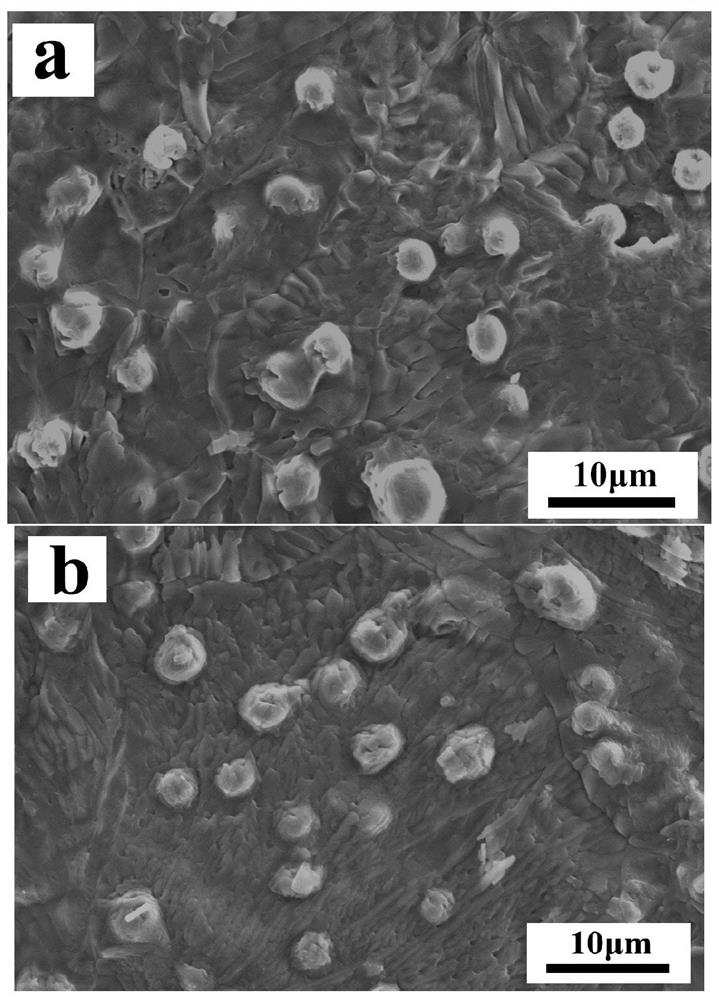
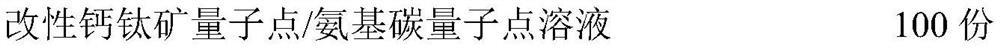Patents
Literature
296 results about "Osteoblast cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Osteoblasts are cells in bone marrow that contribute to the production of new bone. Osteoclasts are cells that break down old bone cells to make way for osteoblasts to stimulate new bone growth.
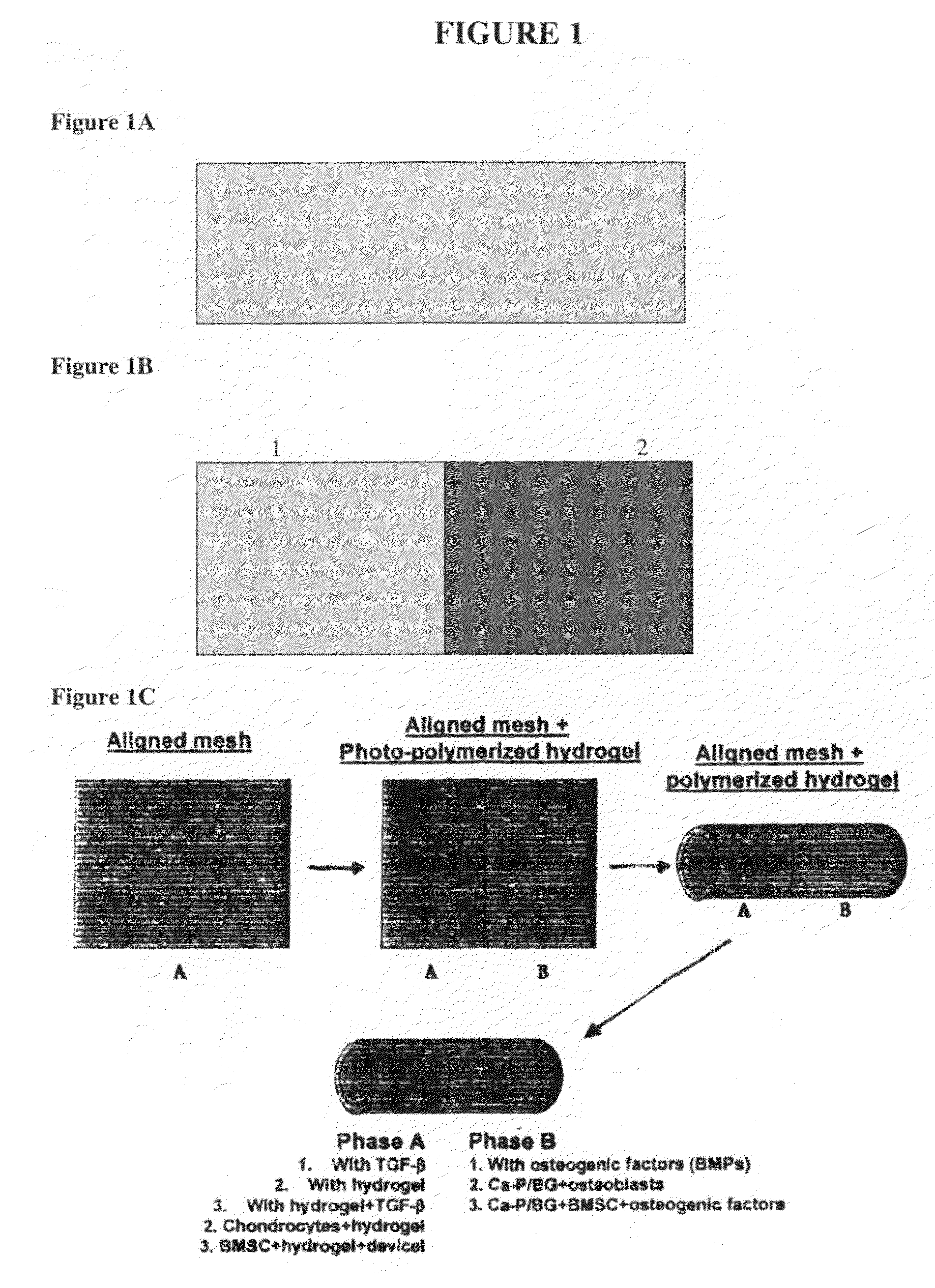
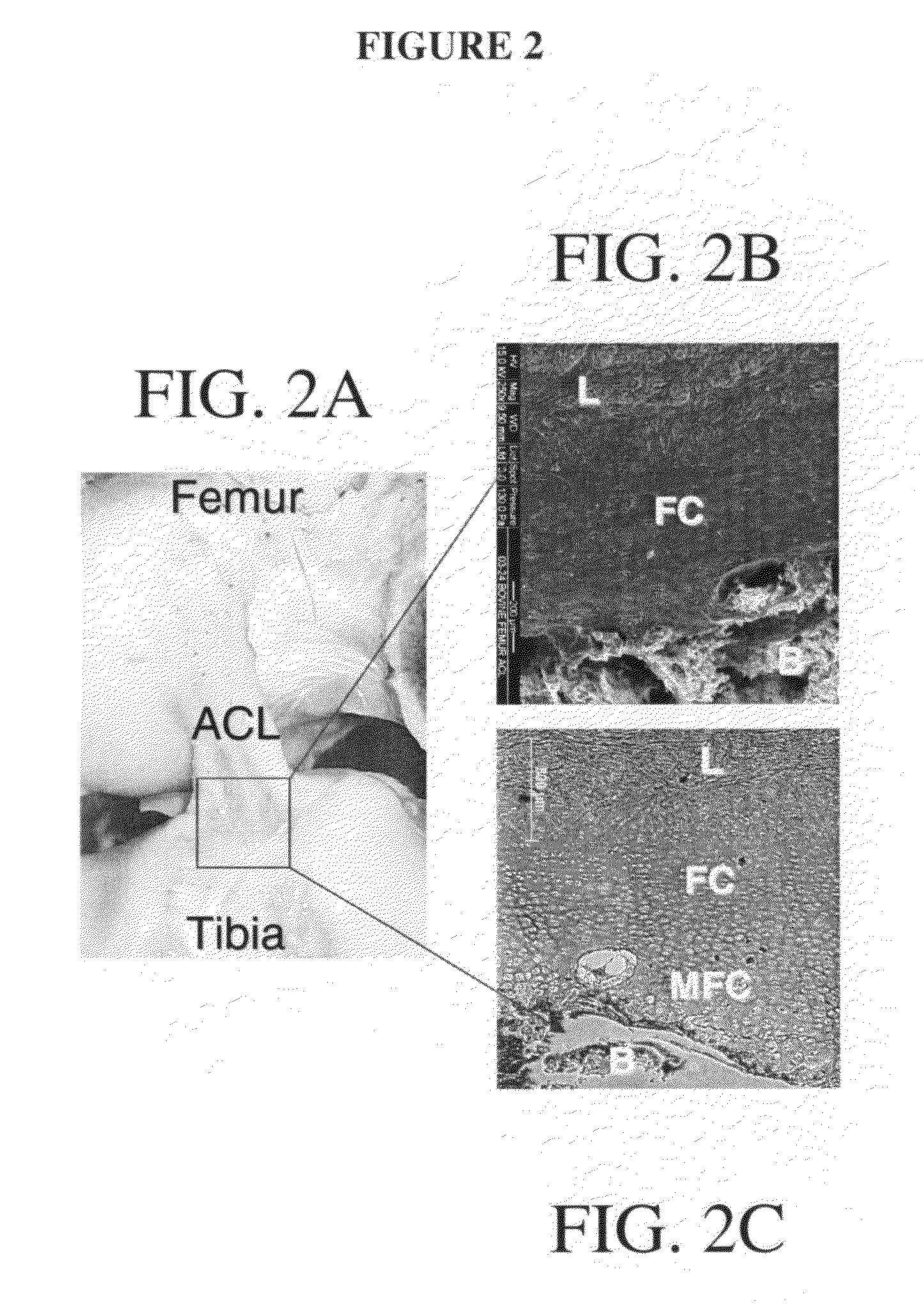
Graft collar and scaffold apparatuses for musculoskeletal tissue engineering and related methods
This application describes apparatuses and methods for musculoskeletal tissue engineering. Specifically, graft collar and scaffold apparatuses are provided for promoting fixation of musculoskeletal soft tissue to bone.This application provides for graft collars comprising biopolymer mesh and / or polymer-fiber mesh for fixing tendon to bone. In one aspect, the graft collar comprises more than one region, wherein the regions can comprise different materials configured to promote integration of and the regeneration of the interfacial region between tendon and bone.This application also provides for scaffold apparatuses and methods for fixing musculoskeletal soft tissue to bone. The scaffold apparatus is multiphasic, preferably triphasic, and each phase is configured promote growth and proliferation of a different cell and its associated tissue. In one aspect, the scaffold apparatus is triphasic, with phases comprising materials to promote growth and proliferation of fibroblasts, chondroblasts, and osteoblasts. In addition, an apparatus comprising two portions, each of said portion being the scaffold apparatus described above is provided, wherein each of said portion encases one end of a soft tissue graft. Further, a triphasic interference screw is provided.This application further provides apparatuses and methods for inducing formation of fibrocartilage comprising wrapping a graft collar with polymer-fiber mesh configured to apply compression to the graft collar. In another aspect, the polymer-fiber is applied directly to the graft to apply compression to the graft.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Hydroxyapatite coated nanostructured titanium surfaces
InactiveUS20090035722A1Improve adhesionPromote accumulationDental implantsImpression capsOsteoblast adhesionApatite
Nanotubular structured titanium (Ti) substrates have been coated with nanoparticulate hydroxyapatite (nano-HA). The nano-HA surface is highly adherent to the nanotubular Ti surface and is free of microparticles. The nano-HA coated nanotubular Ti surface promotes osteoblast cell adhesion and is particularly suitable for orthopedic and dental implants where deposition of osteoblasts and other proteins is important in bone formation.
Owner:METASCAPE
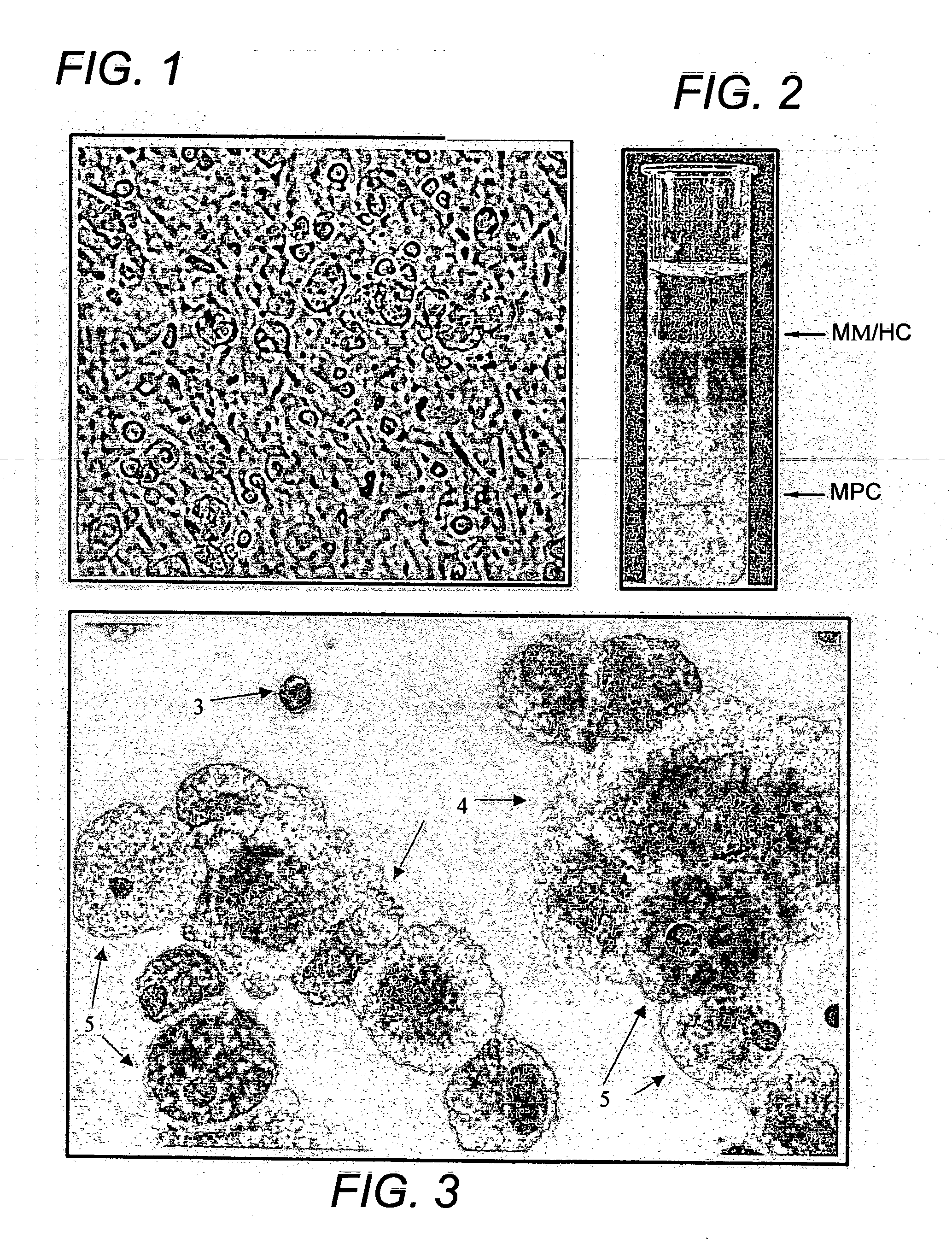
Tissue-like organization of cells and macroscopic tissue-like constructs, generated by macromass culture of cells, and the method of macromass culture
InactiveUS20040082063A1Sectioned easilySmall sizeEpidermal cells/skin cellsMammal material medical ingredientsHigh cellFiber
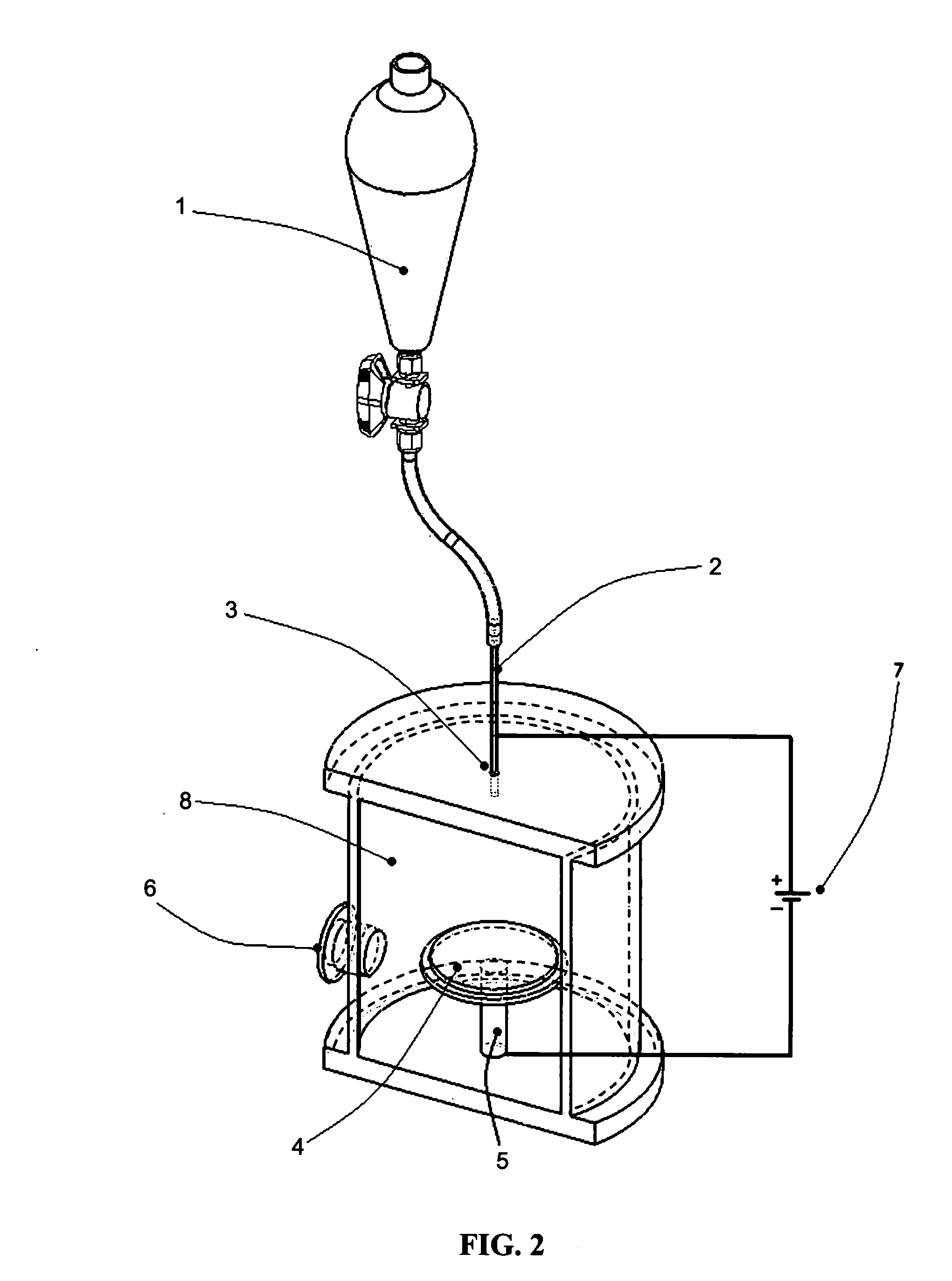
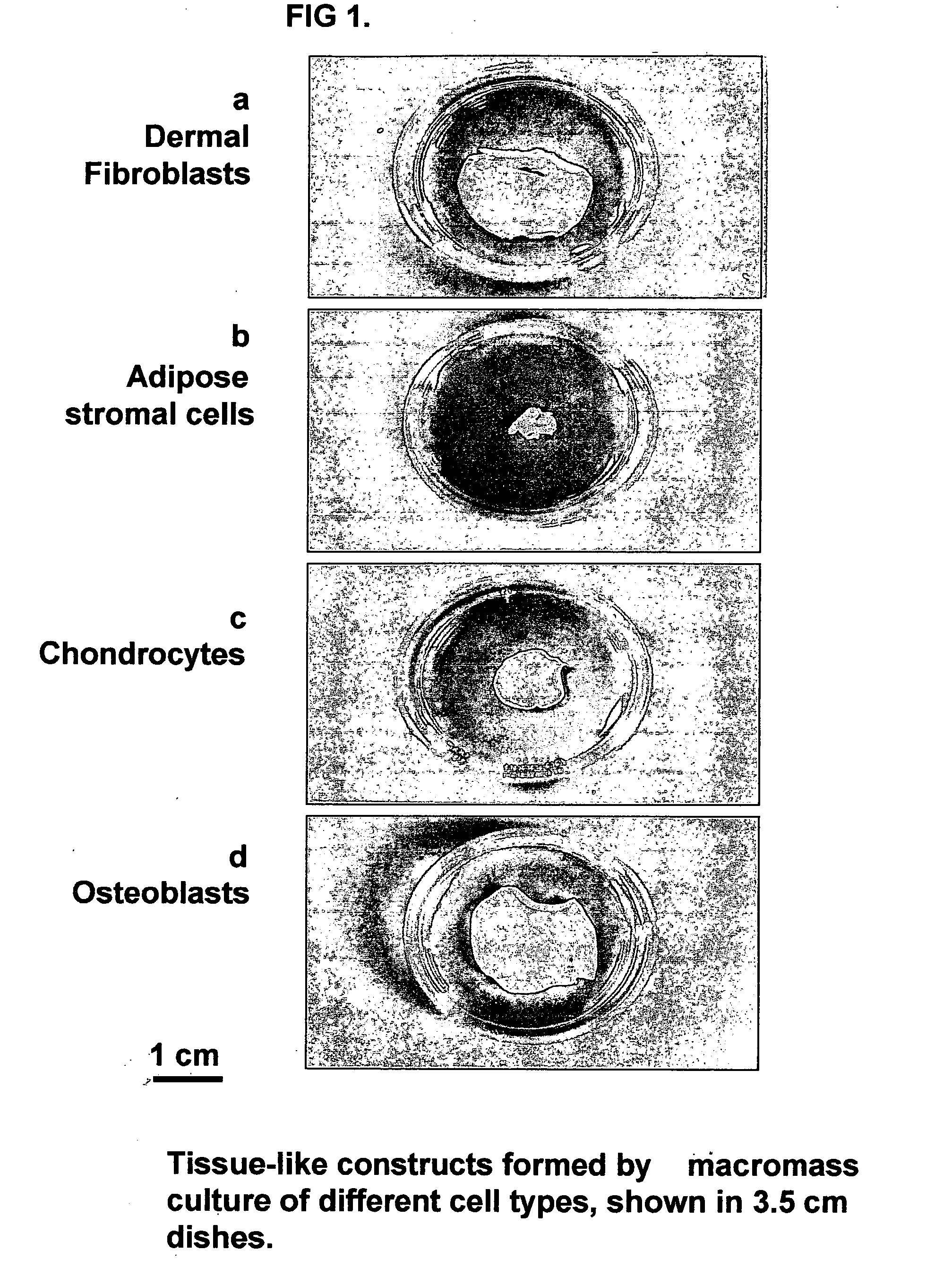
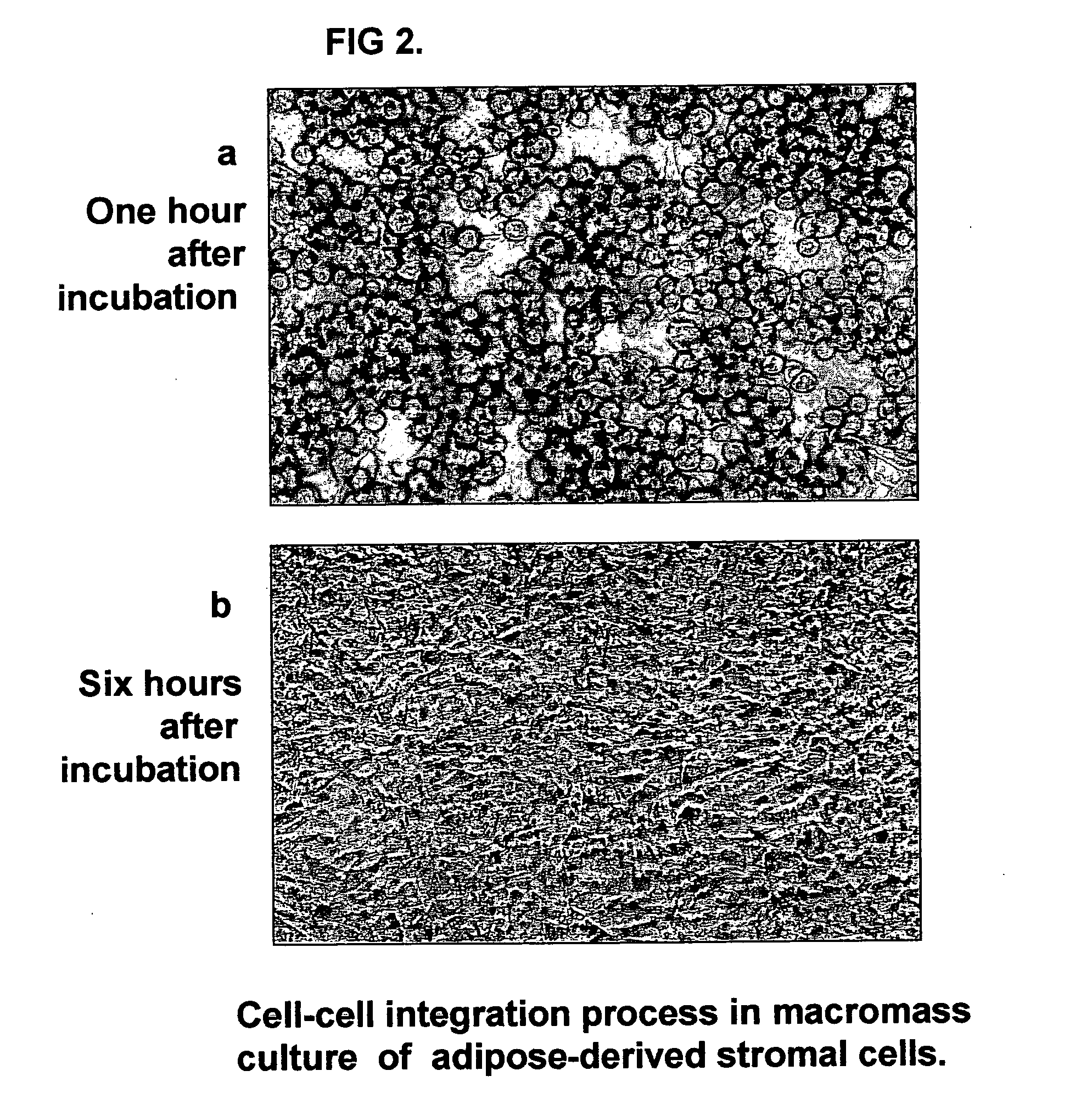
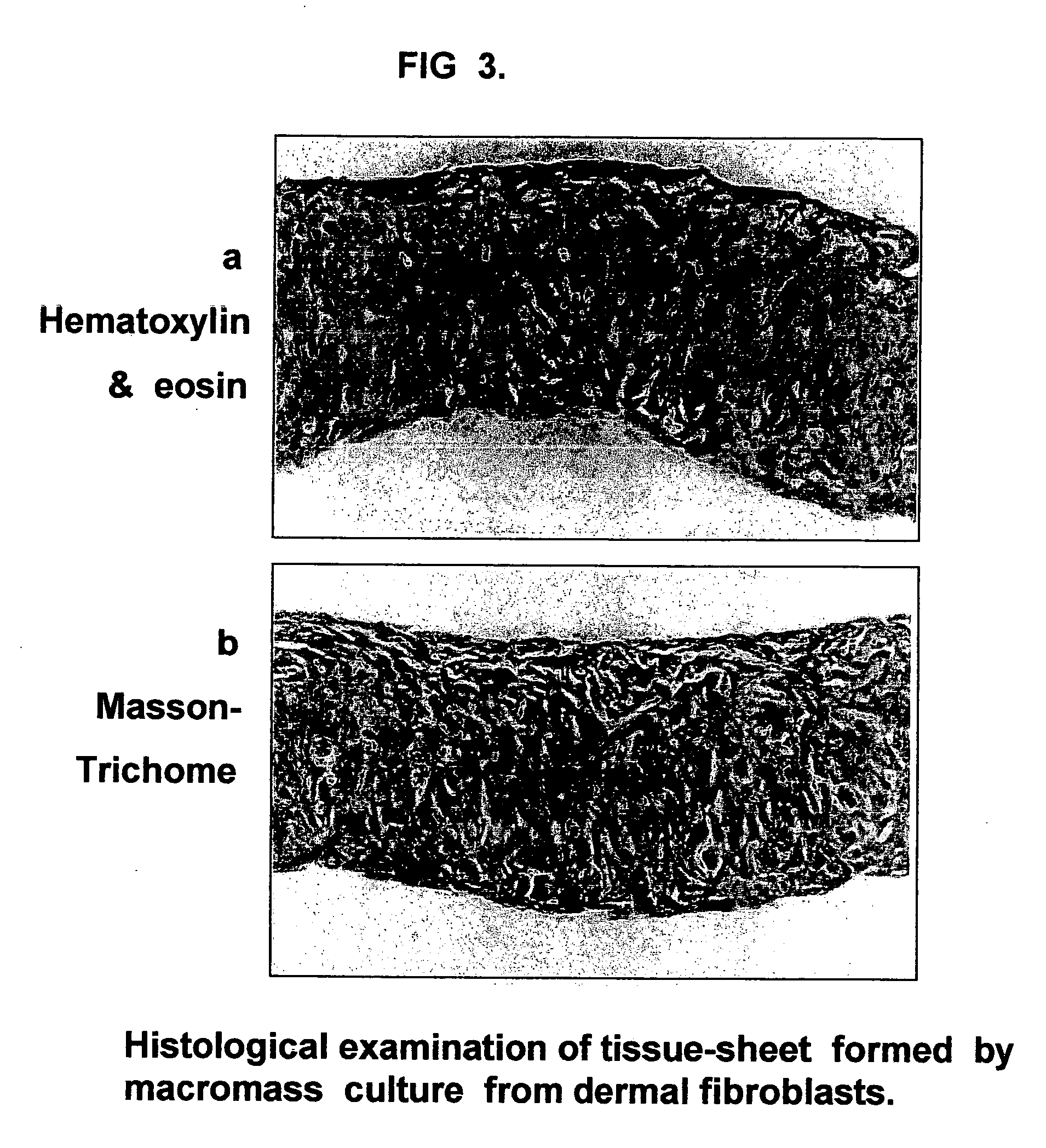
Three-dimensional tissue-like organization of cells by high cell-seeding-density culture termed as macromass culture is described. By macromass culture, cells can be made to organize themselves into a tissue-like form without the aid of a scaffold and three-dimensional macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be made wholly from cells. Tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be generated from fibroblastic cells of mesenchymal origin (at least), which can be either differentiated cells or multipotent adult stem cells. In this work, tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs have been generated from dermal fibroblasts, adipose stromal cells-derived osteogenic cells, chondrocytes, and from osteoblasts. The factor causing macroscopic tissue formation is large scale culture at high cell seeding density per unit area or three-dimensional space, that is, macromass culture done on a large scale. No scaffold or extraneous matrix is used for tissue generation, the tissues are of completely cellular origin. No other agents (except high cell-seeding-density) that aid in tissue formation such as tissue-inducing chemicals, tissue-inducing growth factors, substratum with special properties, rotational culture, etc, are employed for tissue formation. These tissue-like masses have the potential for use as tissue replacements in the human body. Tissue-like organization by high cell-seeding-density macromass culture can also be generated at the microscopic level.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Human mesenchymal progenitor cell
InactiveUS20050059147A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsProgenitorBone marrow transplantations
The present invention provides isolated pluri-differentiated human mesenchymal progenitor cells (MPCs), which simultaneously express a plurality of genes that are markers for multiple cell lineages, wherein the multiple cell lineages comprise at least four different mesenchymal cell lineages (e.g., adipocyte, osteoblast, fibroblast, and muscle cell) and wherein each of the markers is specific for a single cell lineage. The present invention also method for isolating and purifying human mesenchymal progenitor cells from Dexter-type cultures for characterization of and uses, particularly therapeutic uses for such cells. Specifically, isolated MPCs can be used for diagnostic purposes, to enhance the engraftment of hematopoietic progenitor cells, enhance bone marrow transplantation, or aid in the treatment or prevention of graft versus host disease.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
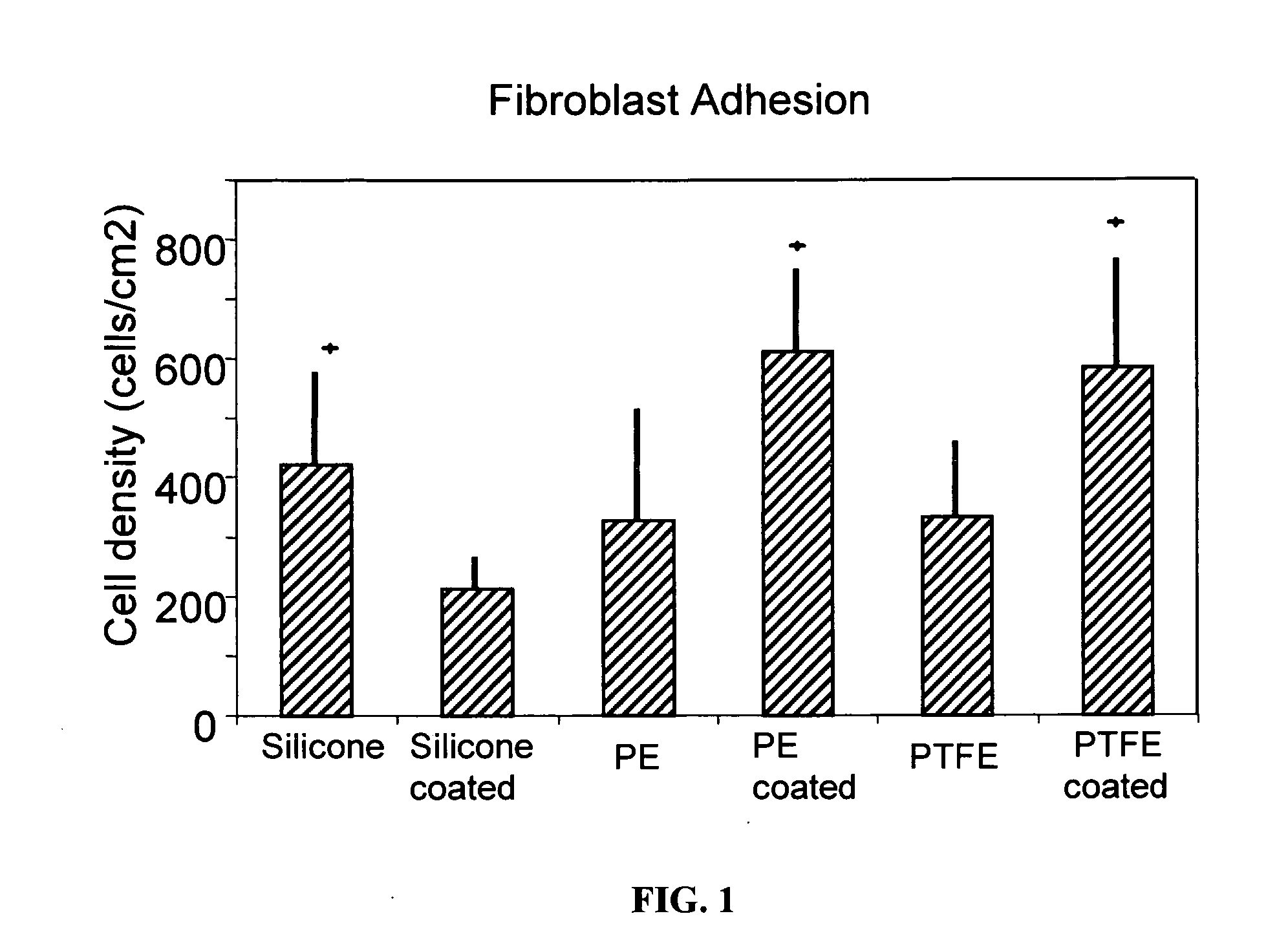
Inhibitory cell adhesion surfaces
InactiveUS20080275546A1Efficient changeHigh surface energyStentsMammary implantsCell adhesionIn vivo
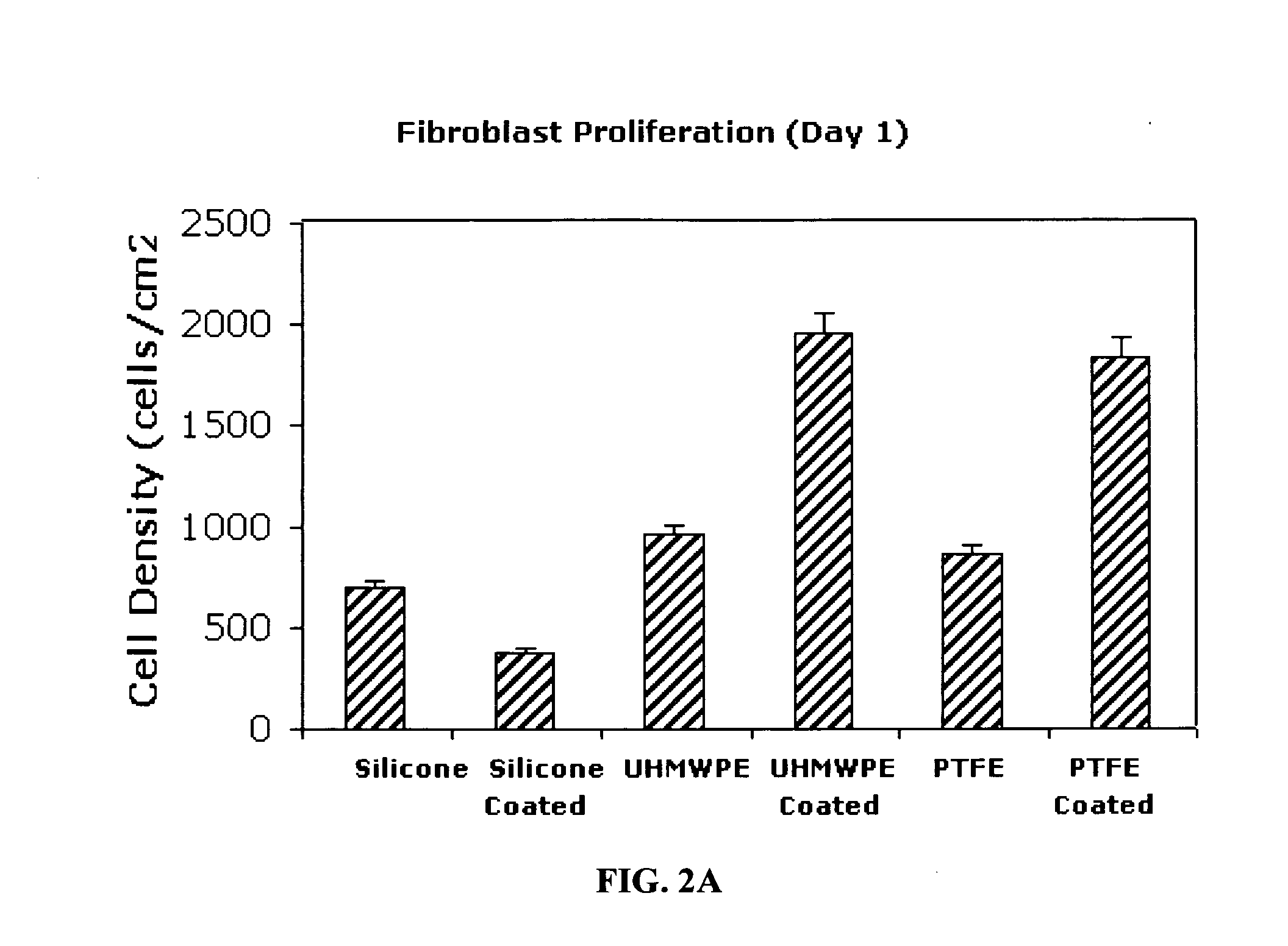
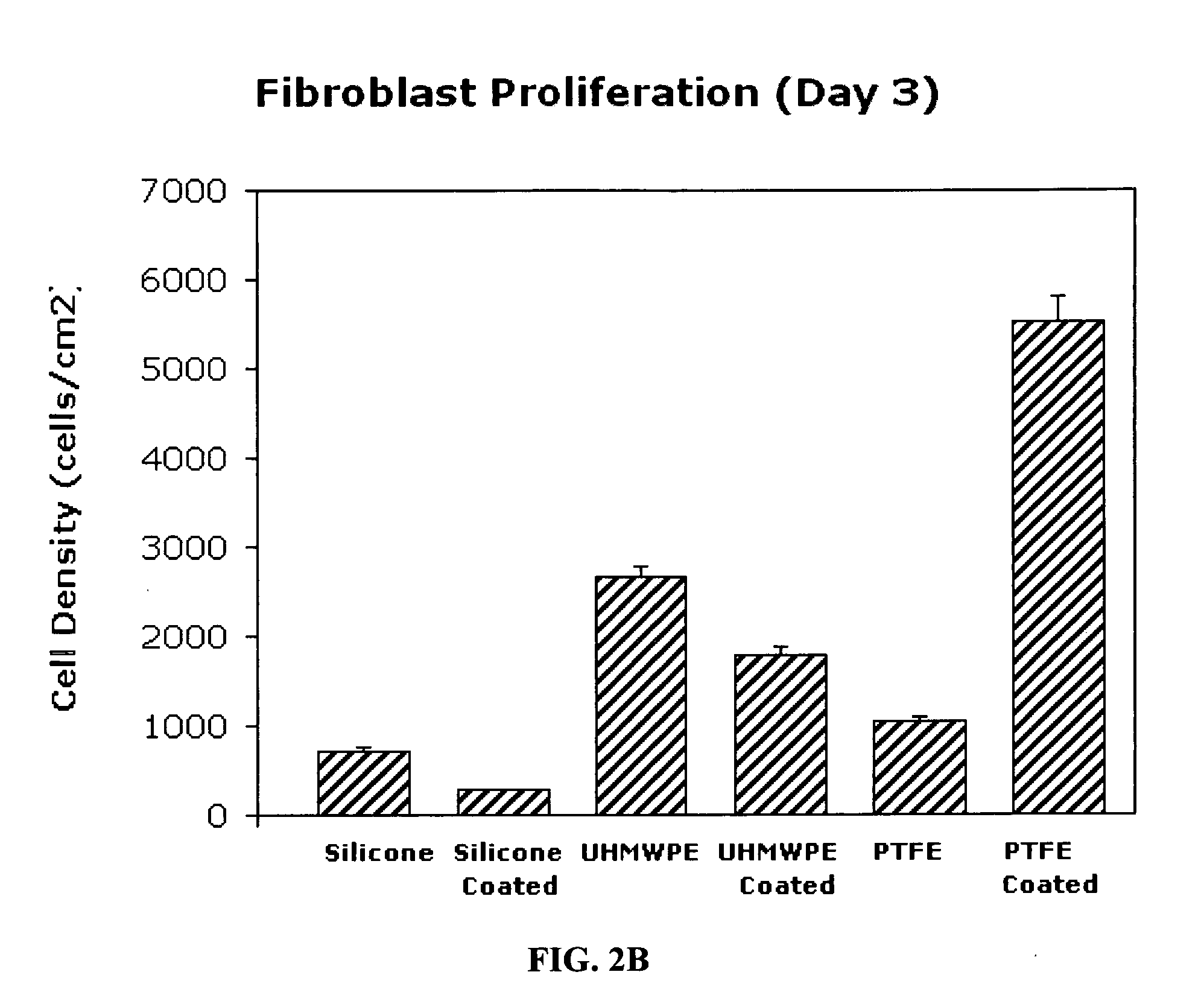
Textured nanostructured surfaces are described which are highly resistant to cell adhesion. Such surfaces on medical implants inhibit fibroblast adhesion particularly on titanium treated silicone. The surfaces can also be engineered so that other cell types, such as endothelial and osteoblast cells, show little if any tendency to attach to the surface in vivo.
Owner:NANOSURFACE TECH
Method for osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stem cells (BMSC) and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090081169A1Reduce chanceLess of contaminationBiocideAntipyreticBone Marrow Stem CellOsteocyte
Methods for obtaining osteoprogenitors, osteoblasts or osteoblast phenotype cells, as well as cell populations including such cells, from human bone marrow stem cells in vitro or ex vivo are disclosed. Bone marrow stem cells are contacted with human serum or plasma and a growth factor or a biologically active variant or derivative thereof. In addition, osteoprogenitor, osteoblast or osteoblast phenotype cell types and cell populations are provided. The cell populations may include additional cell types, such as endothelial cells or progenitors. The osteoprogenitors, osteoblasts or osteoblast phenotype cells may be used in therapy, particularly bone therapy.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
Composite membrane for guiding bone tissue regeneration and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103083735AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove biological activitySurgeryCoatingsBone tissueGlycolic acid
The invention discloses a composite membrane for guiding bone tissue regeneration and a preparation method thereof. The composite membrane comprises a basal layer, an intermediate modified layer and a functional surface layer, wherein the basal layer is a poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) membrane, the intermediate modified layer is formed by polymerizing dopamine to form polydopamine and adsorbing the polydopamine to the surface of the PLGA membrane, and the functional surface layer is formed by reaction of I-type collagen or a collagen / chitosan mixture and active groups in the polydopamine. The preparation method for the composite membrane comprises a series of steps of membrane preparation, rinsing, airing and the like. The artificially synthesized macromolecular polymer is used as a basal material, the surface of the membrane obtained after the basal material is grafted with a natural polymer to undergo surface function activation and functional modification has a nano structure and active groups which are not owned by the original synthesized polymer, the affinity of osteoblasts is improved, and adhesion and proliferation of cells are promoted; and by using the synthesized macromolecular polymer as the base, high mechanical strength and controllable degradability are provided, and the grafted natural polymer is combined with the base firmly by pre-modification of the surface of the synthesized macromolecular polymer.
Owner:AFFILIATED STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL OF NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Culture method for inducing adipose tissue-derived stromal cells to differentiate to chondrocyte
InactiveCN106350483AShort induction timeHigh differentiation rateCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPrimary cellBrown adipose tissue
The invention relates to a culture method for inducing adipose tissue-derived stromal cells to differentiate to chondrocyte, and aims to solve the problem that the prior art is low in differentiation rate. The culture method comprises the following steps: 1) performing separation of primary cells of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells; 2) performing amplification and passage of the adipose tissue-derived stromal cells; and 3) performing differentiation culture on P5-generation adipose-derived stem cells to chondrocyte, namely, adding the adipose tissue-derived stromal cells into a condition culture medium, namely, an adipose tissue-derived stromal cell chondrocyte differentiation culture medium, after P5 generation of passage, performing chondrocyte differentiation culture, replacing the medium of the cells every 3 days, observing the morphological change of the cells, and after 16 days of induction, performing Alcian blue dyeing, and identifying the chondrocyte differentiation situation of the adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. The result of Alcian blue dyeing identification shows that the chondrocyte can be formed, and the Alcian blue dyeing is positive. The culture method has the characteristics of being simple and feasible, short in induction time as the induction culture medium is a serum-free culture system, good in test repeatability and high in osteoblast differentiation rate.
Owner:中卫华医(北京)生物科技有限公司 +1
Preparation method of multifunctional layered joint cartilage support
InactiveCN108355174ARealize regulationReduce rejectionAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationCartilage cellsOsteoblast
The invention provides a preparation method of a multifunctional layered joint cartilage support. The multifunctional layered joint cartilage support capable of simulating the biological property andthe mechanical property of natural cartilage is prepared by taking hydrogel as a support material, taking mesenchymal stem cells, cartilage cells and osteoblasts as inducing and developing objects andby adopting a 3D printing technology. The multifunctional layered joint cartilage support can accurately simulate the internal tissue form and the contour of each layer of the natural cartilage and can realize that different layers have different mechanical and biological characteristics. The prepared artificial cartilage support cells are derived from patients, the support serves as a degradablehydrogel material and the rejection reaction after implantation is greatly reduced. Various nutritional substances and growth factors are mixed in the hydrogel support, so that the sustained releaseeffect can be achieved and regulation and control of the growth and development of the artificial cartilage can be realized.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for cell implantation
An endoscopic method for treating cartilage or bone defects in an animal, said method comprising the steps of: I) identifying the position of the defect, ii) applying cells selected from the group consisting of chondrocytes, chondroblasts, osteocytes and osteoblasts and combinations thereof into the cartilage or bone defect. In particular, the invention relates to a method for arthroscopic or endoscopic implantation of homologous or autologous cells into a defect of an animal body, the method comprising a step of I) arthroscopic or endoscopic application of a fluid to a cavity or surface containing the defect, and the steps of ii) application of the cells to the defect substantially simultaneously with a support material, the application being performed at the defect covered by the fluid, iii) mixing of the cells and the supporting material, iv) solidification of the supporting material so that the defect is covered by a mixture of cells and support material without any significant amount of fluid, and v) optionally, removal of the fluid from the cavity or surface by drainage or suction.
Owner:INTERFACE BIOTECH
Kit for inducing differentiation from bone mesenchymal stem cells to osteoblasts, application of kit and method for inducing cell differentiation
InactiveCN102041245ADemonstrated differentiation abilityPromote repairSkeletal/connective tissue cellsVitamin CSodium glycerophosphate
The invention provides a kit and method for inducing differentiation from bone mesenchymal stem cells to osteoblasts. The kit comprises an osteoblast inducing culture solution and an osteoblast identification solution, wherein the inducing culture solution comprises a cell culture solution A, a cell culture solution B, a cell culture solution C, a cell culture solution D and a cell culture solution E; the osteoblast identification solution comprises a cell immobilizing solution, coloring agents and a detergent; the cell culture solution A is an alpha-minimum essential medium (MEM) liquid culture medium; the cell culture solution B is fetal bovine serum; the cell culture solution C is a dexamethasone solution; the cell culture solution D is a beta-sodium glycerophosphate solution; the cell culture solution E is a vitamin C solution; the cell immobilizing solution is 4% paraformaldehyde; the coloring agents include sodium thiosulfate, silver nitrate and neutral red; and the detergent is double distilled water.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Artificial tooth root with micro-nano hierarchical topologic surface structure and preparation method of artificial tooth root
InactiveCN102743789ABiological activity hasCapable of regulating cellsDental implantsImpression capsBone cellBiocompatibility Testing
Disclosed are an artificial tooth root with a micro-nano hierarchical topologic surface structure and a preparation method of the artificial tooth root. The artificial tooth root is prepared by compounding a porous titanium dioxide surface layer with a zinc oxide nanorod or nanocone sedimentarily growing on the surface pore wall of the porous titanium dioxide surface layer, wherein the porous titanium dioxide surface layer is prepared with pure titanium or titanium alloy matrix by a microarc oxidation method, namely, the porous titanium dioxide bioactivity surface layer with an adjustable pore size is obtained by adjusting microarc oxidation parameters on the titanium matrix surface of the artificial tooth root, and the zinc oxide nanorod / nanocone is sedimentarily prepared on the titanium dioxide bioactivity surface layer by further adjusting electro-deposition parameters, so that the artificial tooth root with the micro-nano hierarchical topologic surface structure is formed. By the aid of the titanium dioxide micron porous structure with a rich surface and the zinc oxide nano-topologic structure sedimentarily growing on the pore wall of the titanium dioxide micron porous structure, the artificial tooth root can enhance biological effects of adhesion, growth, multiplication and the like of surface osteoblasts, slowly release zinc, and greatly improve antibacterial activity, biological activity, biocompatibility and cell regulation capacity of the surface in the early stage of implantation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Tissue engineered bone-cartilage complex tissue graft and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a tissue engineered bone-cartilage composite tissue transplant and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the tissue engineering field. The method comprises the following steps: seed cells are implanted on a scaffold material and cultured in vitro to form the tissue engineered bone-cartilage composite tissue transplant; the seed cells are osteogenic stem cells; the scaffold material comprises an osteogenic part and a chondroblast part, and the osteogenic part is added with an osteoblast induction factor and modified by a type-I collagen in a preparation process; and the chondroblast part is added with a chondroblast induction factor and modified by a type-II collagen. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are successfully induced into osteocytes and chondrocytes, and bone tissues and cartilage tissues are formed after the obtained transplant is transplanted in vivo. Satisfactory effect is obtained from the tissue engineered bone-cartilage composite tissue which is constructed by the transplant.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Cell-specific molecule and method for importing DNA into osteoblast nuclei
ActiveUS20060242725A1Easy to transportOvercome obstaclesPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesCore binding factorPromoter
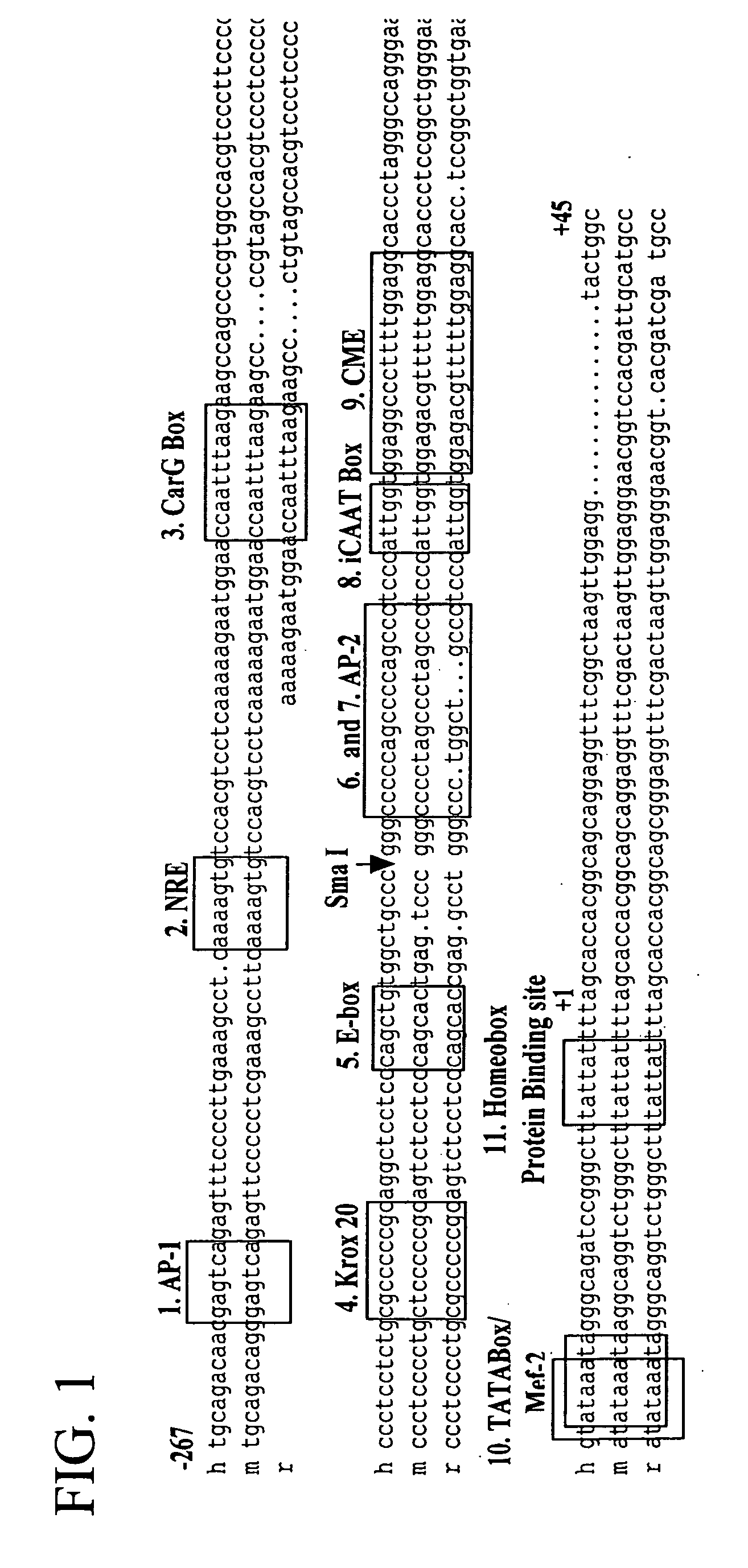
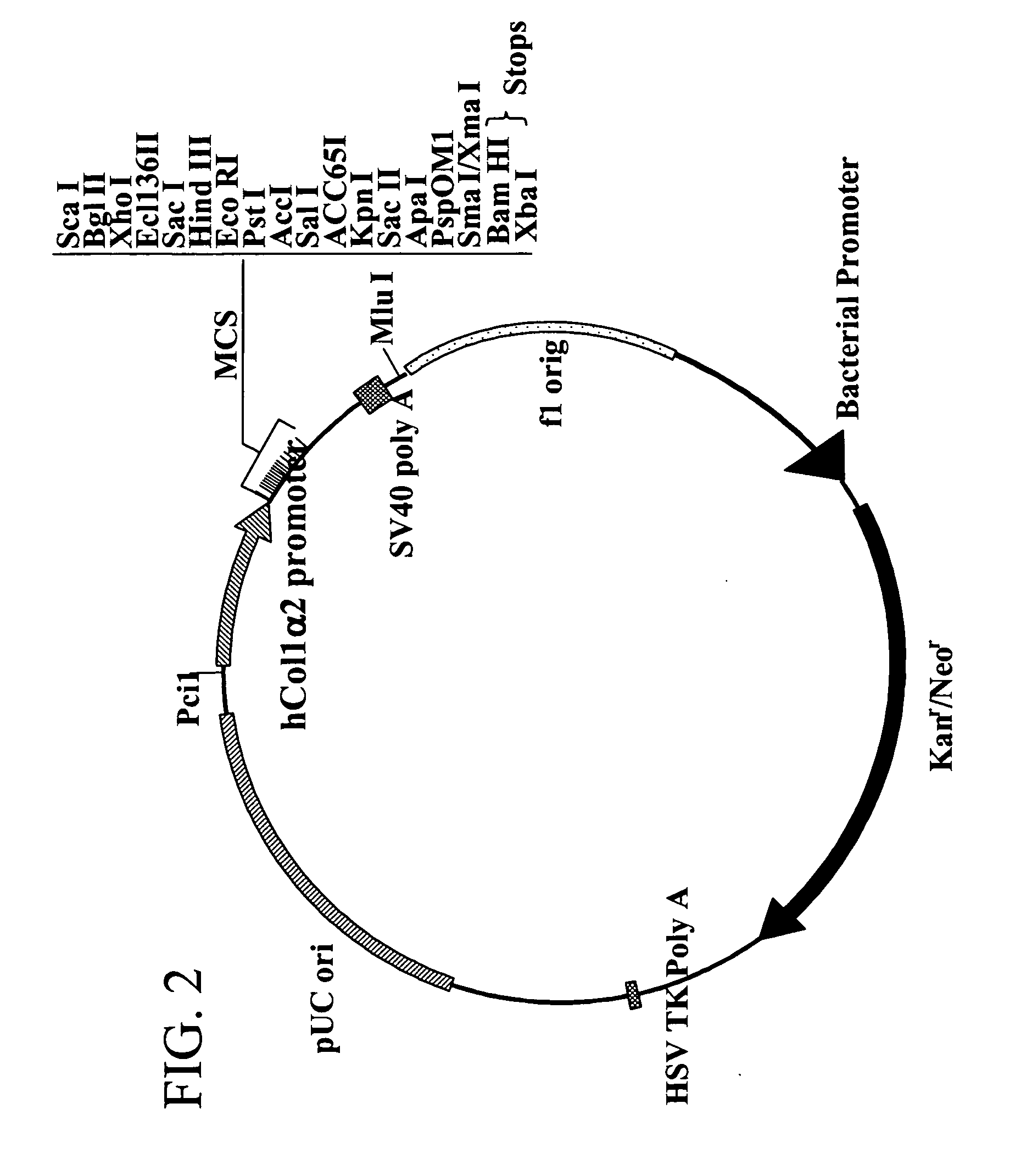
A plasmid, viral or linear DNA molecule containing a nucleic acid sequence derived from the promoter region of the hCol1α2 gene, which is selectively transported into the nuclei of cells in the osteoblast lineage. The sequence can be used independently as a nuclear entry sequence only, and / or as a nuclear entry sequence without regard to position, in a vector or linear DNA that directs gene expression and nuclear entry. The disclosure further includes a chimeric DNA sequence derived by the addition of osteoblast-specific enhancer sequences to the nuclear entry sequence / promoter sequence, to increase osteoblast-specific expression while retaining osteoblast-specific nuclear import. An enhancer sequence is derived from the promoter region of the human Core Binding Factor alpha 1 (Cbfa1 / Runx2) gene. The Cbfa1 / Runx2 promoter can be added to the sequence derived from, or alternatively, comprising the promoter region of the hCol1α2 gene. Also provided are methods of use of the novel sequences.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIVERSITY +3
Enhanced bonding layers on titanium materials
The present invention provides a dense-coverage, adherent phosphorous-based coating on the native oxide surface of a material. Disclosed phosphorous-based coatings include phosphate and organo-phosphonate coatings. The present invention also provides further derivatization of the phosphorous-based coatings to yield dense surface coverage of chemically reactive coatings and osteoblast adhesion-promoting and proliferation-promoting coatings on the native oxide surface of a titanium material.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Method for preparing medical titanium material with high anti-cancer and antibacterial properties
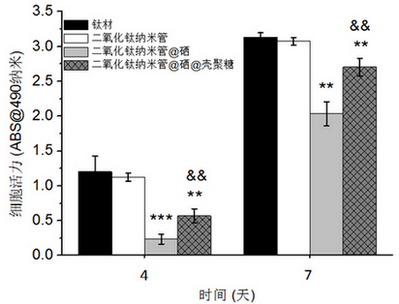
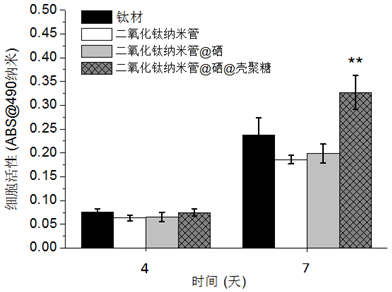
InactiveCN102560598AGood anticancer and antibacterial propertiesEasy to operateLiquid surface applicatorsElectrolytic inorganic material coatingOsteocyteAntibacterial property
The invention relates to a method for preparing a medical titanium material with high anti-cancer and antibacterial properties. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, generating highly regular and ordered titanium dioxide nanotube arrays on the surface of the titanium material by an anodic oxidation method; secondly, generating selenium nanoparticles in titanium dioxide nanotubes in situ by an electrochemical deposition method; and finally, modifying multi-layer chitosan on the surface of the titanium material by a spin-coating method to obtain the medical titanium material with high anti-cancer and antibacterial properties. The method is easy to operate and low in cost, special equipment is not needed, and tests prove that the obtained product can inhibit the growth of bone tumor cells for a long time and promote the growth of normal osteoblasts simultaneously and has high antibacterial property.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Aggregation-induced emission nanoparticle and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106085416AGood tracer effectHigh cell staining efficiencyFluorescence/phosphorescenceIn-vivo testing preparationsBone cellWater soluble
The invention discloses an aggregation-induced emission nanoparticle and preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving an aggregation-induced emission compound shown in a formula I and an amphiphilic polymer in a water-soluble organic solvent, then adding the mixture to water, and conducting ultrasonic reaction; removing organic solvents by volatilization to form nanoparticles loaded with the aggregation-induced emission compound; adding cell penetrating peptides in aqueous solution of the nanoparticle, reacting to form aggregation-induced emission nanoparticles capable of efficiently staining cells. The fluorescent particles can be used for tracing long-term differentiation of stem cells, especially the tracing of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the process of osteogenic differentiation. Compared with the commercial tracer reagent in the prior art, which can only trace 6 generations of cell proliferation, the nanoparticle has a better tracing effect, which can trace to more than 12 generations of cell proliferation. The aggregation-induced emission nanoparticle has the advantages of high cell staining efficiency, long-term tracing ability, high light stability and low cell toxicity.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Medical kit and using method thereof
InactiveUS20100034783A1Easy to useReduce decreaseBiocidePower operated devicesBlood collectionOsteoblast
An aseptic / sterile medical kits are comprising a cartilage regeneration kit, a bone regeneration kit or an umbilical cord blood storage kit in a configuration that each process performs according to functionally-specialized kit sets for each step, via division of overall processes into corresponding steps for isolation, culture, collection and storage of cells, and implantation of desired cells into target sites of the body. The cartilage is regenerated by cartilage tissue collection; chondrocyte isolation; chondrocyte medium change and subculture; preparation of chondrocyte therapy product; media for isolation / culture / preparation / cryopreservation of cells; and media for isolation / culture / cryopreservation of cells, using the cartilage regeneration kit. The bone is regenerated by bone marrow collection; osteoblast isolation; osteoblast medium change and subculture; and preparation of osteoblast therapy product, using the bone regeneration kit. Additionally, the umbilical cord blood is stored by umbilical cord blood collection; hematopoietic stem cell isolation; and cryopreservation of hematopoietic stem cells, using the umbilical cord blood storage kit.
Owner:SEWON CELLONTECH CO LTD
Porous active artificial bone and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a porous active artificial bone. In the porous active artificial bone, a calcium phosphate-based biological ceramic material is used as a matrix, and the porous active artificial bone comprises small pores, dense parts and directional pore channels and chelates with diphosphonate. A preparation method of the porous active artificial bone comprises the steps of preparing calcium phosphate precursor powder, compression molding a ceramic blank by using a pore-foaming agent, polyester fiber and the precursor powder, high temperature sintering into a calcium phosphate-based ceramic sintered body and forming the dense parts, the small pores distributed alternately; and immersing calcium phosphate-based ceramic sintered body in a diphosphonate solution to chelate with the diphosphonate so as to obtain the drug-loaded porous active artificial bone. The artificial bone provided by the invention has longitudinal directional pores and a porous structure suitable for osteoblast migration, propagation and growth metabolism, can slowly release small molecular drugs capable of promoting the growth of the osteoblast and inhibiting osteoclast, and is particularly suitable for the fields of treating bone defects of osteoporosis patients, dental restoration, and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN LANDO BIOMATERIALS
Medical implant material surface modifying method
InactiveCN103143056AImprove bindingPromotes a tight fitAbrasion apparatusProsthesisTitanium alloyMaterials science
The invention discloses a medical implant material surface modifying method which comprises the following steps of: putting a titanium alloy implantation body into a mixture liquid, washing for 15-30 minutes in an ultrasonic mode, and drying; putting into the mixture liquid and treating for 30-45 seconds at 50-60 DEG C, and drying; carrying out sand spraying treatment to form a high-low rough surface on the surface, subsequently putting ethanol to carry out ultrasonic washing, and drying; treating a sample by using a strong current pulse electronic beam system so as to generate micron and submicron grade pores on the surface on the basis of the original recesses; putting into the mixture liquid and treating for 2-4 minutes at 110-130 DEG C, wherein pores less than 0.5 micrometer are generated on the inner walls and the pore ridges of the original pores; taking out the sample, putting into deionized water to be subjected to ultrasonic washing, and drying. By preparing the surface with micron and nano multi-grade micropore composite structures in such mode, the ambient tissue reaction activity can be irritated, and osteoblast cells are good in adhesion and extension.
Owner:大连理工(营口)新材料工程中心有限公司
Compositions and methods for re-programming cells without genetic modification for repairing cartilage damage
InactiveUS20140289882A1Increased collagen typeType of reductionPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderDiseaseReprogramming
The present inventions are directed to compositions and methods regarding the reprogramming of other cells (such as embryonic stem cells (ESCs), induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), MSCs, fibroblasts, hematopoietic stem cells, endothelian stem cells, adipocytes, chondrocytes, osteoblasts, osteoclasts and endothelial cells) into chondrogenic cells without introducing exogenous genes to the samples. In particular, the present inventions are directed to transducible materials that are capable of transducing into the biological samples but are not genes or causing genetic modifications. The present inventions also are directed to methods of reprogramming the path of biological samples or treating diseases using the tranducible compositions thereof.
Owner:VIVOSCRIPT
3D (three-dimensional) uniform porous scaffold material and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN103992499ASuitable for adhesionHigh mechanical strengthProsthesisMicro structureCell adhesion
The invention relates to a 3D (three-dimensional) uniform porous scaffold material and a preparing method of the 3D uniform porous scaffold material. The existing artificial bone scaffold material has the defects that the porosity is low, and the cell migration and the new tissue formation are limited; the micropore diameter distribution is nonuniform, and the condition is unfavorable for the distribution of osteoblast cells and the like on the surface of the material; and the pore diameter is greater, and the condition is unfavorable for the cell adhesion and cell proliferation. According to the preparing method, collagen is dissolved in a sodium carbonate solution; nanometer hydroxyapatite is added; the mixture is subpackaged into a mold; the mold is subjected to freezing and vacuum drying; a cross-linking reaction is carried out on the frozen and dried sample in an alkaline cross-linking environment; a cross-linking reaction is carried out on the cross-linked sample in an acid environment; the obtained sample is washed; and the washed sample is subjected to vacuum freeze drying, sterilization and packaging. The 3D uniform porous scaffold material and the preparing method have the advantages that the collagen and the nano-hydroxyapatite are used as raw materials, and carbon dioxide produced by reaction between sodium carbonate and alkali and ice crystal sublimation carried out in the vacuum freeze drying process are utilized, so that a micropore structure is obtained with uniform pore diameter distribution and with a pore diameter and porosity suitable for cell adhesion, proliferation and migration, and a uniform porous scaffold obtained through preparation has certain pressure resistance intensity and has a good microstructure and good biocompatibility.
Owner:SHAANXI GIANT BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
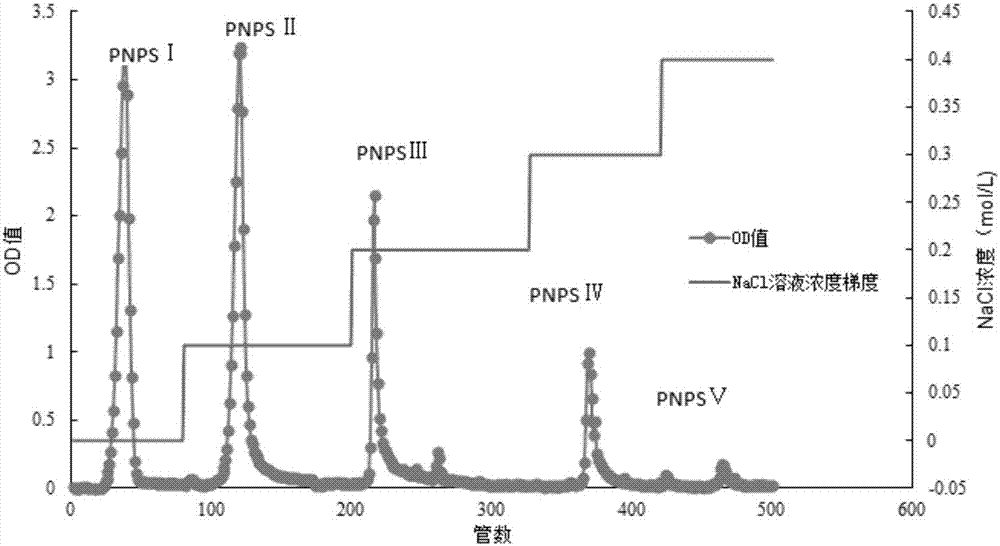
Method for extracting and purifying neutral pseudo-ginseng polysaccharide, research and application for pharmacological activity for promoting cell proliferation
ActiveCN107286265APromotes significant proliferationStrong value-added effectOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsOsteoblastPeriodontal ligament stem cells
The invention relates to a method for extracting and purifying neutral pseudo-ginseng polysaccharide, a research and an application for pharmacological activity for promoting cell proliferation. The pseudo-ginseng waste residue of the notoginsenoside extracted in the production process is taken as a raw material, a water extract and alcohol precipitation method is adopted for acquiring crude pseudo-ginseng polysaccharide and the DEAE Sepharose Fast Flow anion exchange chromatography is adopted for purifying the crude pseudo-ginseng polysaccharide so as to acquire five components: neutral pseudo-ginseng polysaccharide PNPS I and acidic pseudo-ginseng polysaccharide PNPS II, PNPS III, PNPS IV and PNPS V five samples. The research on the influence of the pseudo-ginseng polysaccharide on human periodontal ligament stem cell, mice osteoblast and human skin epidermis cell in vitro proliferation proves that the neutral pseudo-ginseng polysaccharide PNPS I is effective in boosting the periodontal ligament stem cell, mice osteoblast and human skin epidermis cell in vitro proliferation and the neutral pseudo-ginseng polysaccharide PNPS I can be used as an important drug intermediate for developing a new drug and a natural raw material for a functional healthcare food and also can be used as an active raw material of the household chemicals.
Owner:云南多糖生物科技有限公司
Application of autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in preparation of medicines for treating joint diseases
InactiveCN103550256AGood differentiation potentialInhibit inflammationAntipyreticAnalgesicsArticular cavityJoint disease
The invention relates to an application of autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in preparation of medicines for treating joint diseases. The application is characterized in that adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (Ad-MSCs) separated and extracted from autologous adipose tissues of the patient are injected to the diseased articular cavity in a large dose once. The adopted mesenchymal stem cells have immunophenotyping and representing biological marks of Ad-MSC through flow cytometry authentication, and can be directionally induced and differentiated to osteoblast and chondrocyte. Primary cells are directly injected to the articular cavity of the diseased joint to treat various joint diseases. With the adoption of the autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells as the primary cells, the cells have better differentiative potential and the ability of inhibiting inflammation and immunoregulation ability. The adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplant provides a novel effective means for treating osteoarticular diseases. The method is simple and feasible, and the quantity of cells collected is great and the trauma is small. The autologous mesenchymal stem cells of the patient are applied without invading related ethics, so that the risk of immunological rejection, infectious diseases and the like is avoided.
Owner:南京优而生物科技发展有限公司
Ferroferric oxide superparamagnetic nanoparticle stimulating stem cell for exosome osteogenesis
ActiveCN109745341AFacilitate depositionStimulate osteogenic activitySkeletal disorderSkeletal/connective tissue cellsOsteoblastOrthopedic disorders
The invention discloses an exosome preparation derived from a stem cell. The exosome preparation is an exosome secreted by a Fe3O4 superparamagnetic nanoparticle stimulating the stem cell. The invention further provides the application of the exosome preparation in preparing a pharmaceutic preparation for promoting mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation and the application of the exosomepreparation in preparing a biological agent for treating orthopedic disorders or bone repair materials. In consideration of the complicated pathophysiologic process of osteonecrosis and bone defects,the exosome preparation prepared by the exosome secreted by the Fe3O4 superparamagnetic nanoparticle stimulating the stem cell is adopted, intramuscular administration can be adopted at local bone defect parts, or local filling is performed after the exosome preparation is mixed with absorbable gel, the exosome preparation directly reaches the focus, the osteogenic activity of the mesenchymal stem cell is motivated, the deposition of osteoblasts is promoted, and the repair of the osteonecrosis or bone defects is promoted.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
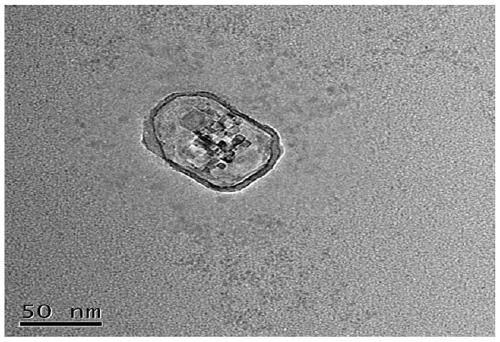
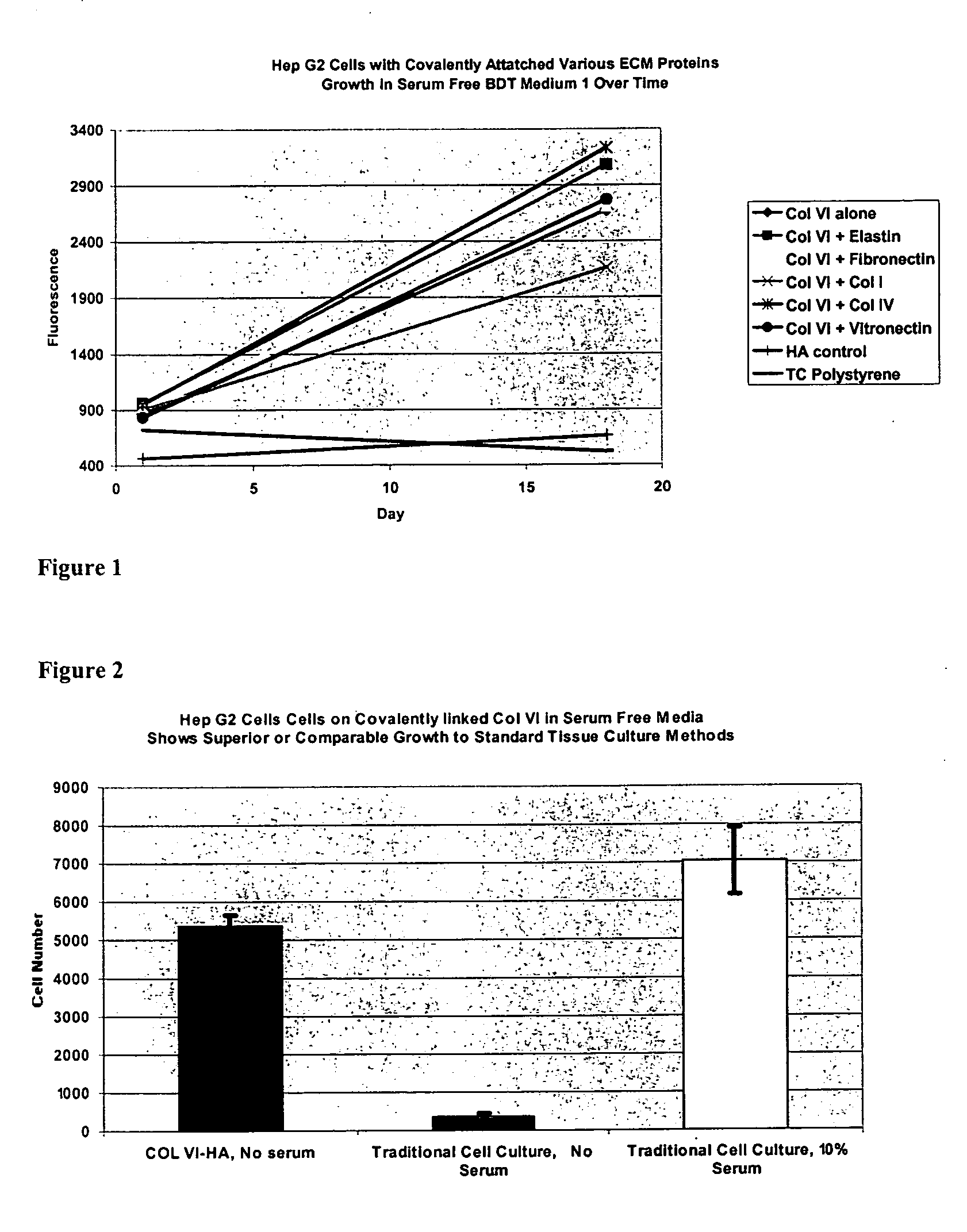
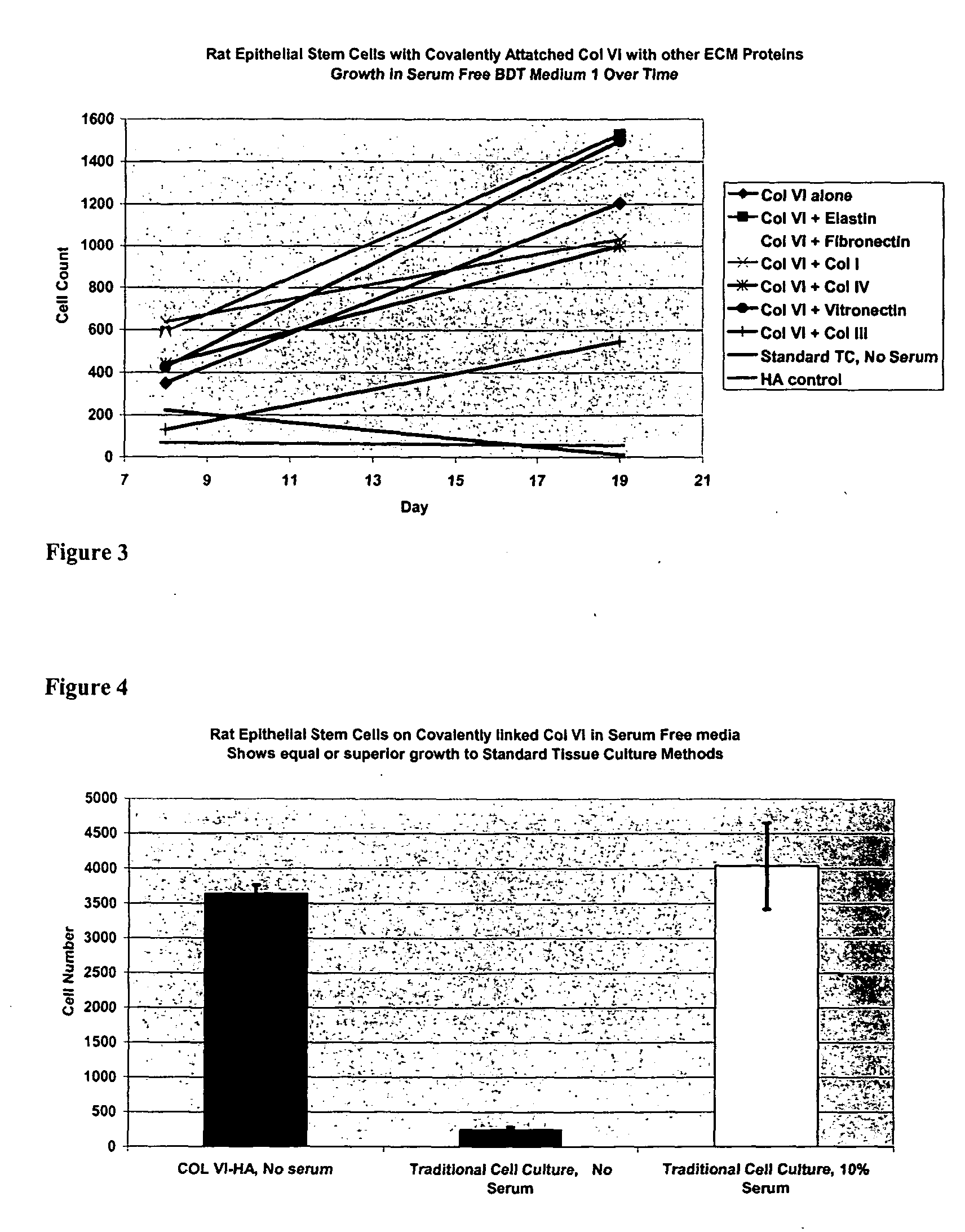
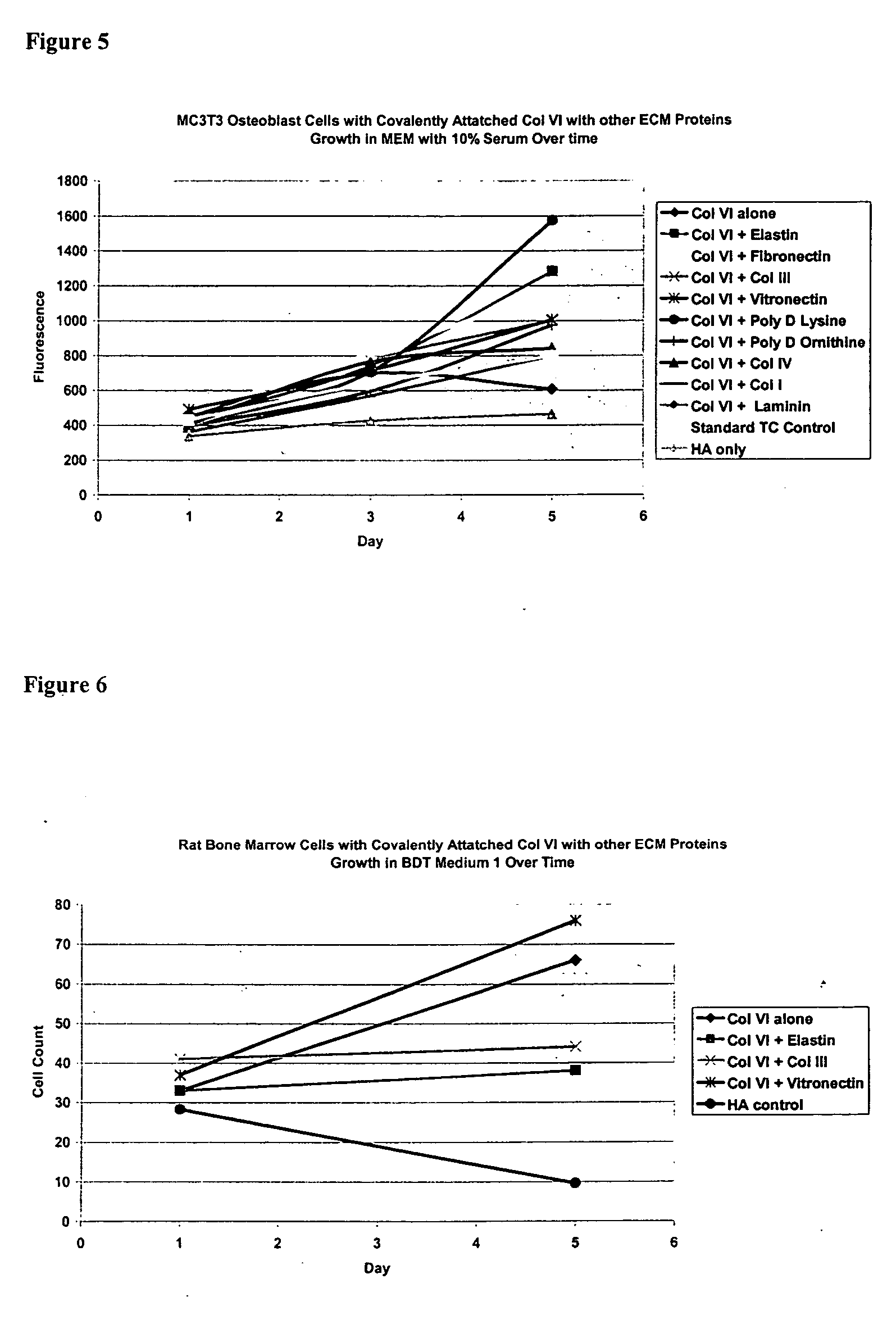
Covalently attached collagen VI for cell attachment and proliferation
InactiveUS20050058687A1Promote proliferationEasy SurvivalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCollagen VIPolymer
Surfaces useful for cell culture comprise a support to which is bound a CAR material, and, bound to the CAR material, collagen VI or a biologically active fragment or variant thereof and, optionally, one or more other ECM proteins (or fragments or variants thereof) such as elastin, fibronectin, vitronectin, tenascin, laminin, entactin, aggrecan, decorin, collagen I, collagen III, and collagen IV. Also, optionally present on the surface is one or more polycationic polymers, such as poly-D-lysine or poly-D-ornithine. This surface is used in cell culture to promote cell attachment, survival, and / or proliferation of a number of different cell types such as (a) liver cells (e.g., HepG2 tumor cells, and a newly discovered line of rat liver epithelial stem cells) (b) osteoblasts, such as the murine cell line MC3T3 cell line and (c) primary bone marrow cells. Kits comprising the surfaces and additional reagents are also disclosed.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Compositions and methods for inducing osteogenesis
The present invention provides compositions and methods for differentiating and transdifferentiating mammalian cells into cells of an osteoblast lineage, using compounds of the following formula:wherein R4 is a functional group including, for example, C1-4alkyl, C3-8cycloalkyl, hydroxyl-C1-4alkyl, aryl-C0-3alkyl, substituted with 0-2 R4a groups, and heterocyclo-C0-2alkyl, optionally substituted with C1-4alkyl; R5 is hydrogen and R6 is a functional group including, for example, halogen, C1-4alkyl, —C(O)—C1-4alkyl, —SO2—N(R2b R2b), halo—C1-4alkyl, —O-aryl and —N(R7 R8), or when R5 and R6 are on adjacent ring atoms they are optionally taken together to form —O—(CH2)1-2—O—; and all pharmaceutically acceptable salts and hydrates thereof.
Owner:IRM +1
Bone repair material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111888521AAvoid the risk of further fracturesPromote ingrowthAntibacterial agentsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBiocompatibilityCell growth
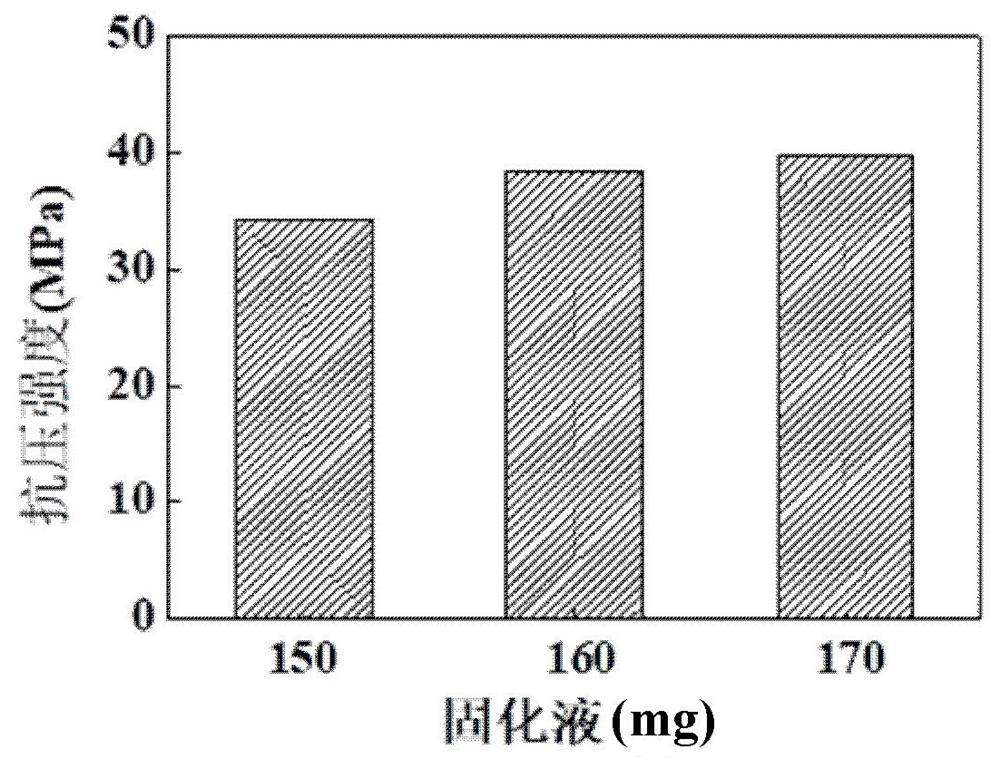
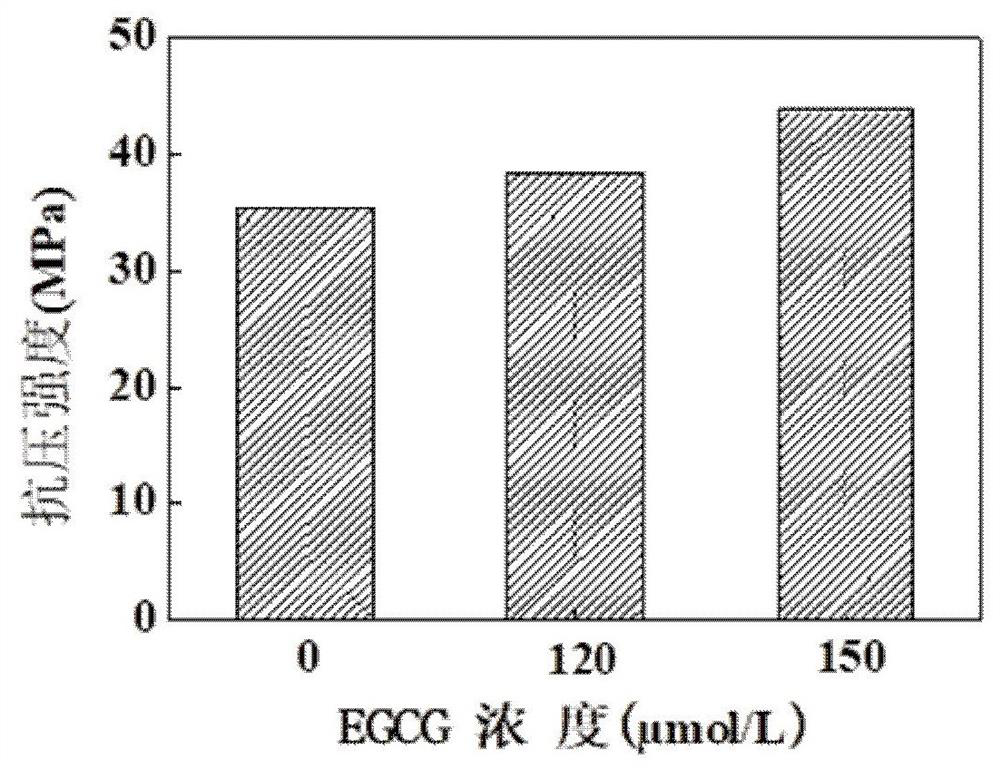
The invention discloses a bone repair material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The bone repair material comprises the following components: magnesium oxide, monocalcium phosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate and calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite. The molar ratio of the magnesium oxide to the monocalcium phosphate to a sodium dihydrogen phosphate bone cement powder is 6:1:4,5:1:3 or 3:1:1, and the calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite accounts for 20% of the total mass. A curing liquid of the bone cement is an EGCG aqueous solution, and the concentration is 120 [mu]mol / L. Aloaded drug is deferoxamine. The preparation method of the bone repair material is simple and feasible; and the setting time is suitable, the bone cement has good biocompatibility, osteogenesis and degradability, and can promote adhesion, proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts, stimulate cell growth and stimulate differentiation of the osteoblasts into the osteoblasts, and the bone repair material can be directly injected into a bone defect part.
Owner:上海禾麦医学科技有限公司
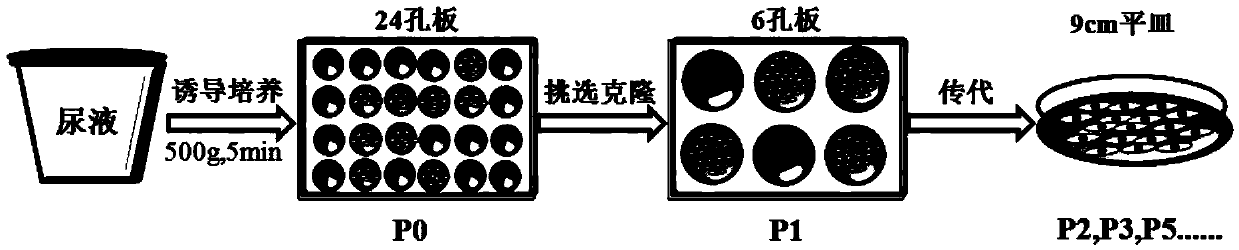
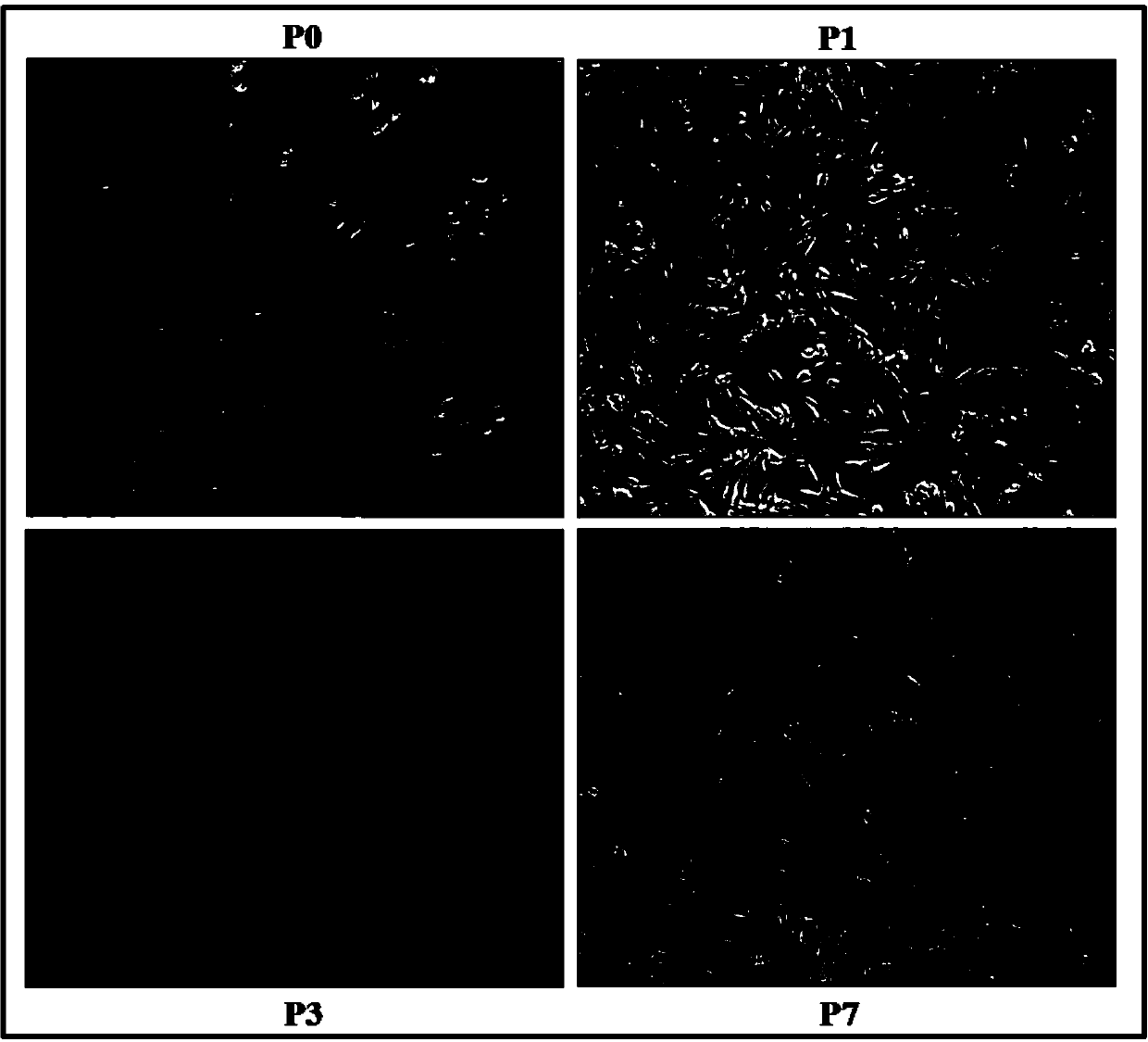
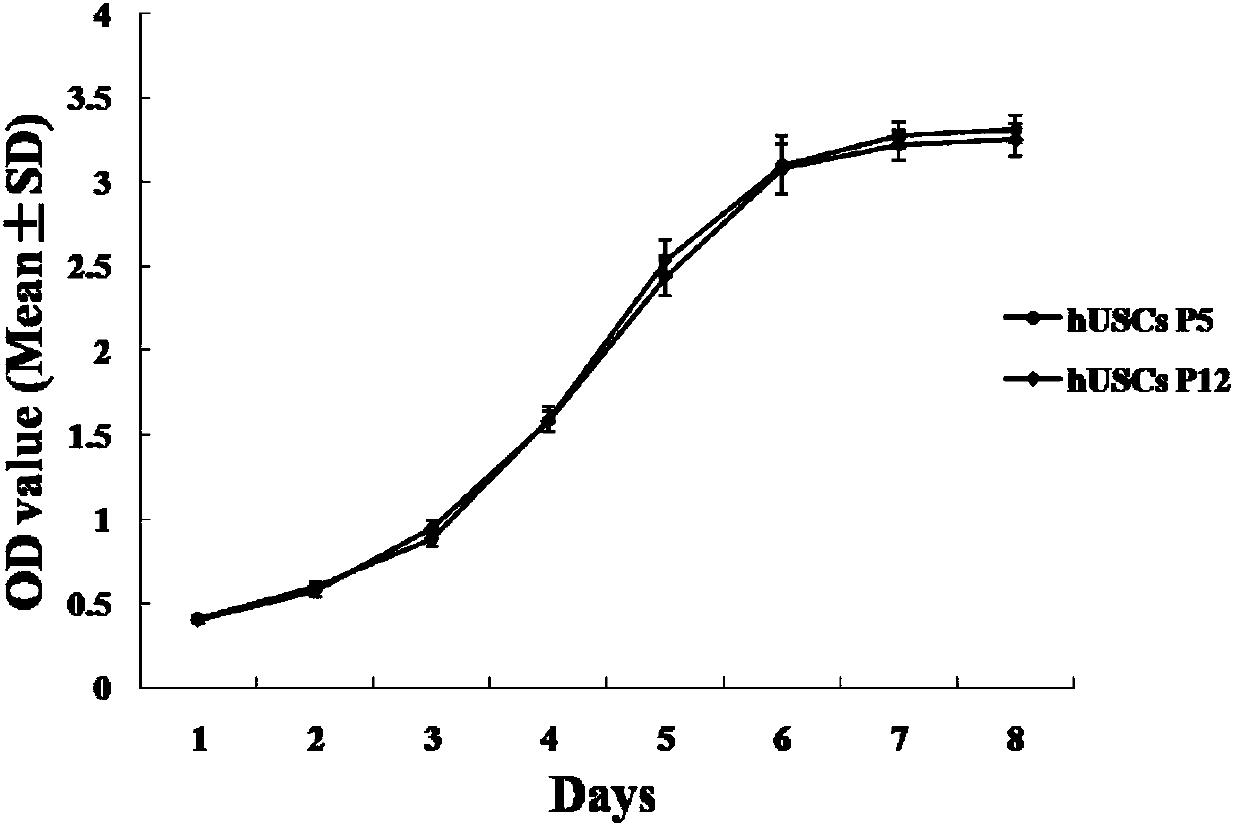
Method for culture of urine-derived pluripotent stem cells by virtue of in vitro small molecule induction
ActiveCN104212762APromote new lifeEnhanced Blood Flow RestorationNervous disorderMetabolism disorderDiseaseBlood flow
The invention discloses a method for culture of urine-derived pluripotent stem cells by virtue of in vitro small molecule induction. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining urine-derived cells from a human urine sample; carrying out in vitro small molecule induction and culturing on the obtained primary cells to obtain P1 generation hUSCs clones growing with adherence; picking up the hUSCs clones in good growing state to inoculate; and continuously carrying out continuous cell culture to obtain hUSCs with the cells which are elongated and good in state. The hUSCs prepared by the method disclosed by the invention, by virtue of induction, can be directionally differentiated to osteoblasts, adipose cells, skeletal muscle cells, nerve cells, fibroblasts or smooth muscle cells. The hUSCs are transplanted into a diabetic lower extremity ischemia model, and research results show that the hUSCs can remarkably enhance blood flow recovery and angiogenesis in an ischemia part. The hUSCs prepared by the method can be applied to treating and repairing diseased tissues and organs of diabetes and diabetic complications, cardiovascular, cerebrovascular and renovascular diseases, Alzheimer's disease, osteoporosis, arthritis and the like as well as early-warning tumors of the urinary system and screening cell drugs.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
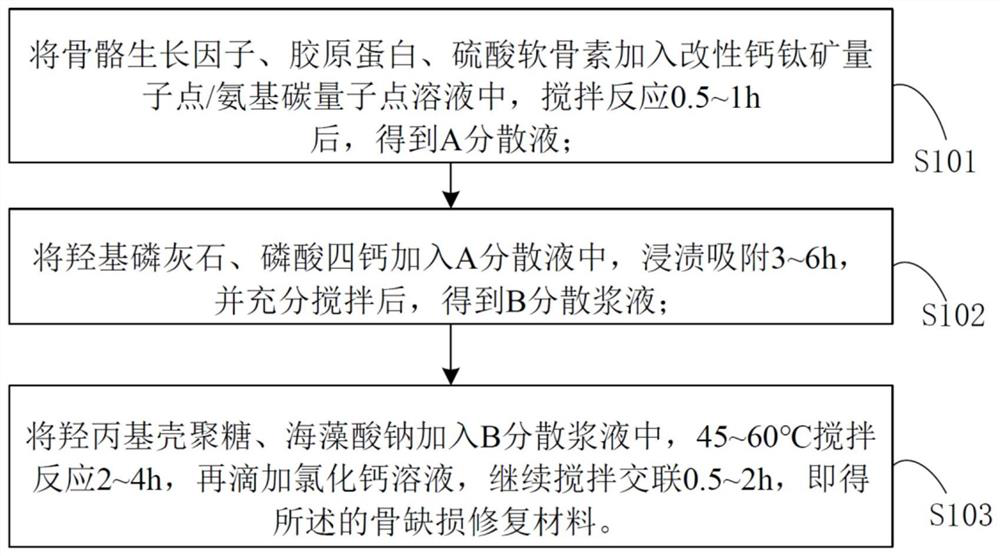
Bone defect repair material based on modified perovskite quantum dots/amino carbon quantum dots and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112618788AStimulate proliferation and regenerationHigh fluorescence quantum efficiencyTissue regenerationProsthesisPhosphoric acidAcyl group
The invention discloses a bone defect repair material based on modified perovskite quantum dots and a preparation method of the bone defect repair material. The bone defect repair material comprises the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 20-30% of hydroxyapatite, 10-20% of octacalcium phosphate, 0.5-2% of bone morphogenetic protein, 1-5% of collagen, 0.5-2% of chondroitin sulfate, 3-5% of carboxymethyl chitosan and the balance of a modified perovskite quantum dot solution. The modified perovskite quantum dot / amino carbon quantum dot solution is prepared from the following reaction raw materials in parts by mass: 0.5 to 1.5 parts of perovskite quantum dots, 8 to 16 parts of dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl ethanolamine, 3 to 7 parts of acidic amino acid, 1 to 3 parts of reduced glutathione, 0.5 to 1 part of EDC.HCl, 20 to 30 parts of chloroform and 100 parts of deionized water. Perovskite quantum dots and amino carbon quantum dots are introduced into the bone defect repair material for the first time, stem cell transfection is mediated by quantum dot and stem cell behavior changes are monitored by utilizing a fluorescence microscopy imaging technology; meanwhile, the stem cells are induced to differentiate towards osteoblasts and chondroblasts, and proliferation and regeneration of the osteoblasts are stimulated.
Owner:蚌埠泰鑫材料技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com