Patents
Literature
73 results about "Osteoblastic cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Science definitions for osteoblastic. osteoblast. A specialized bone cell that produces and deposits the matrix that is needed for the development of new bone and consists primarily of collagen fibers.
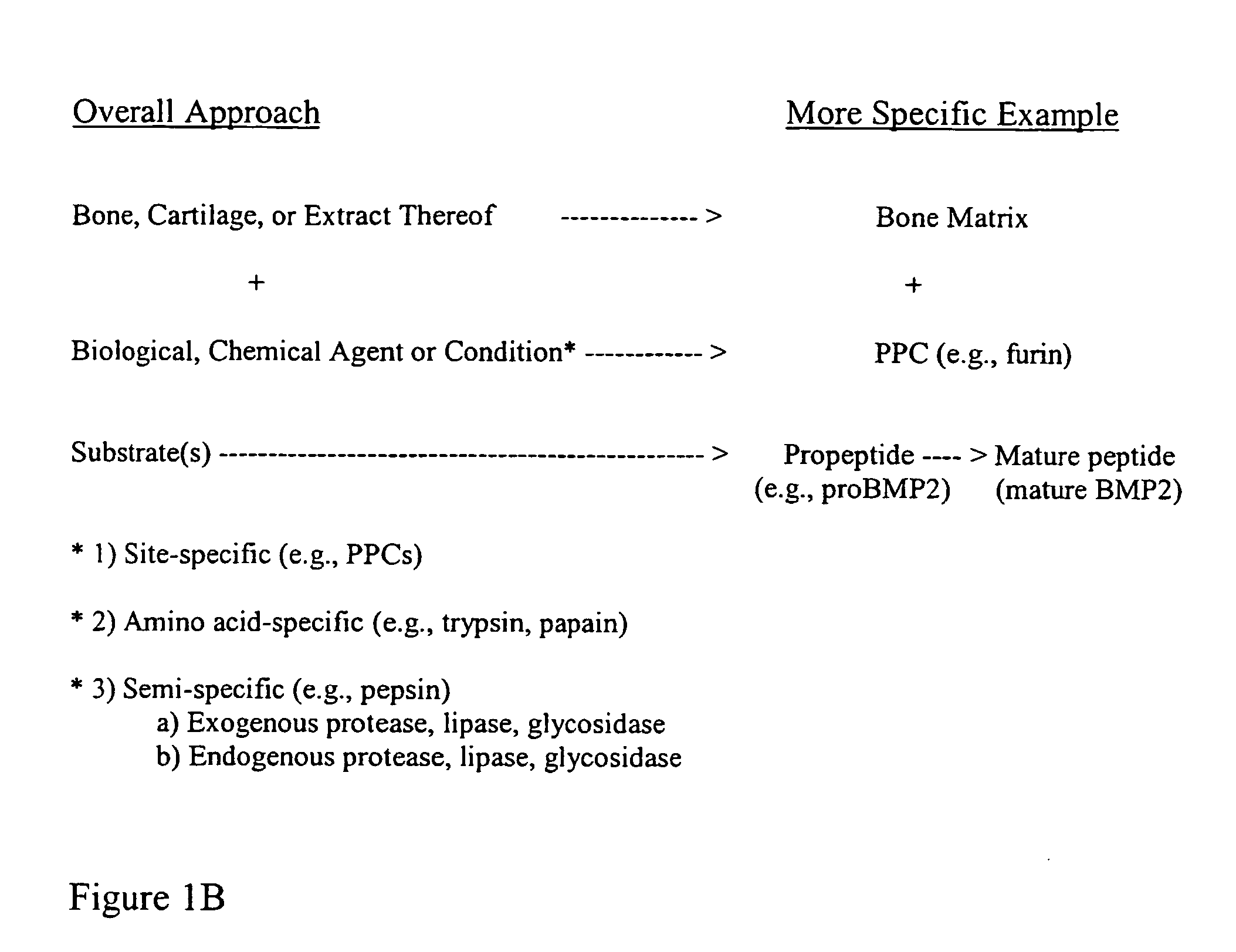
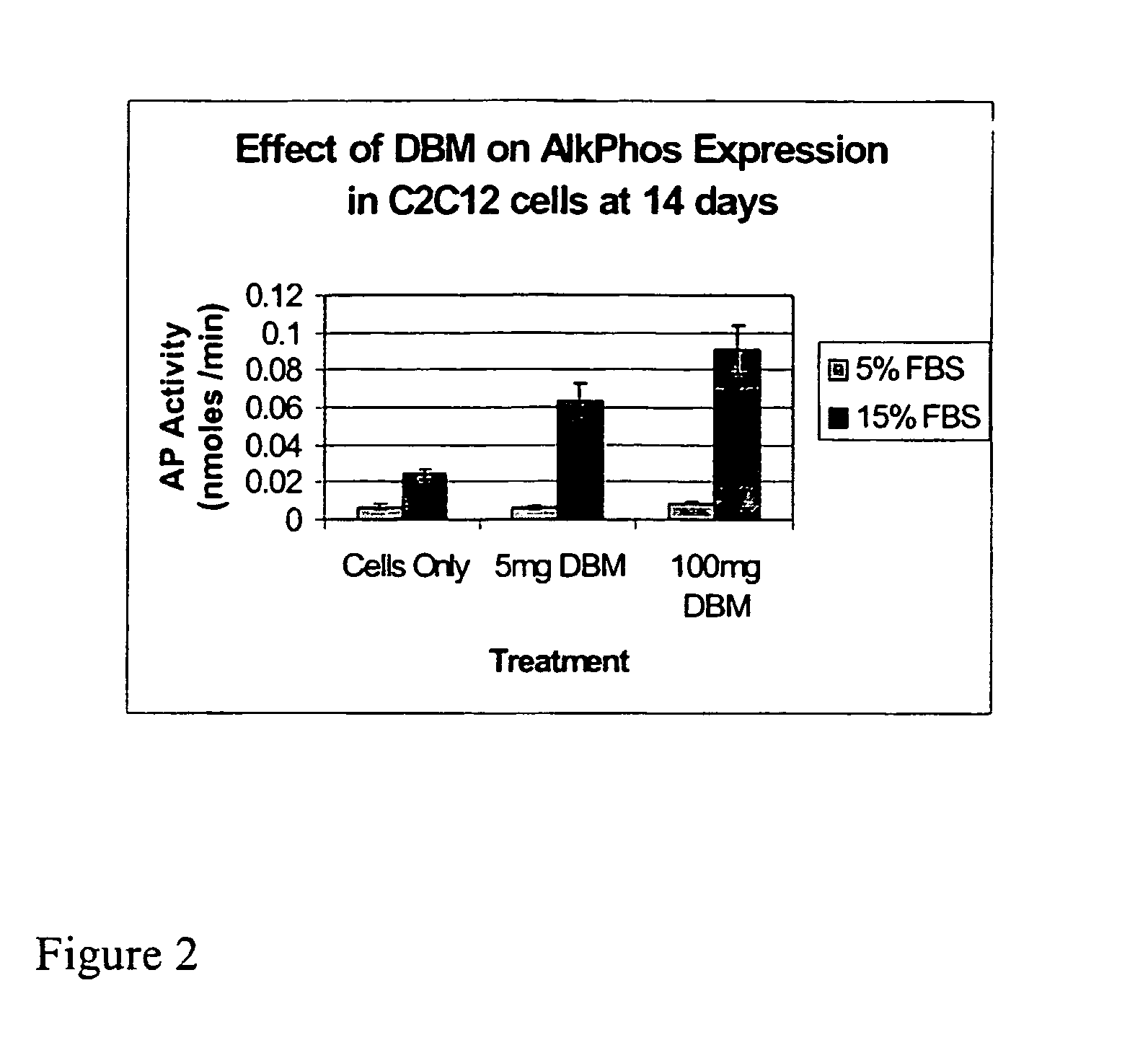
Bone matrix compositions and methods
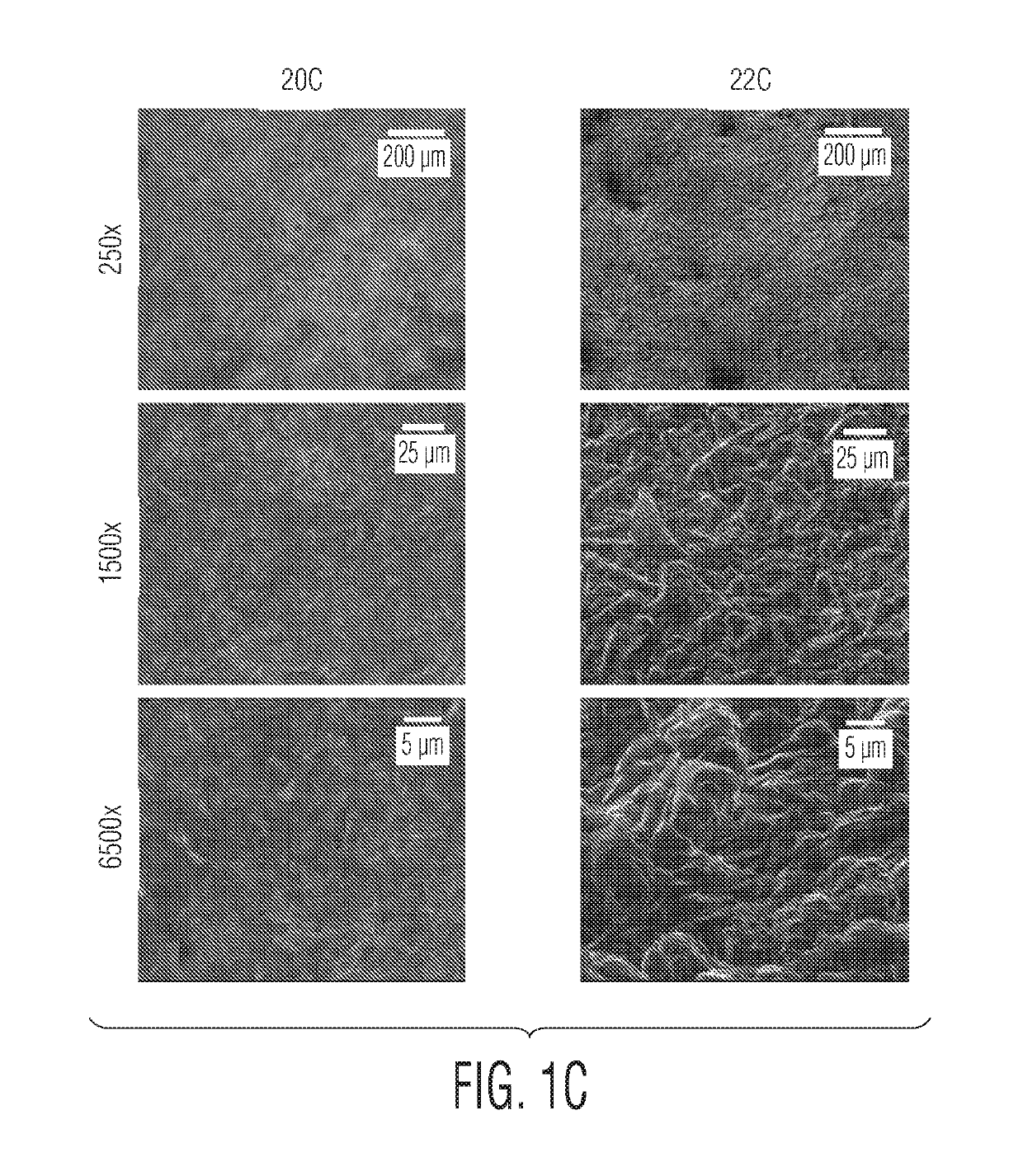
ActiveUS20070154563A1Good osteoinductivityHigh activityHydrolysed protein ingredientsBone implantOsteoblastLine of therapy
The present invention provides methods of improving the osteogenic and / or chondrogenic activity of a bone matrix, e.g., a dermineralized bone matrix (DBM), by exposing the bone matrix to one or more treatments or conditions. In preferred embodiments the bone matrix is derived from human bone. The treatment or condition may alter the structure of the bone matrix and / or cleave one or more specific proteins. Cleavage may generate peptides or protein fragments that have osteoinductive, osteogenic, or chondrogenic activity. Preferred treatments include collagenase and various other proteases. The invention further provides improved bone and cartilage matrix compositions that have been prepared according to the inventive methods and methods of treatment using the compositions. The invention further provides methods of preparing, testing, and using the improved bone matrix compositions. Ona assay comprises exposing relatively undifferentiated mesenchymal cells to a bone matrix composition and measuring expression of a marker characteristic of osteoblast or chondrocyte lineage(s). Increased expression of the marker relative to the level of the marker in cells that have been exposed to a control matrix (e.g., an inactivated or untreated matrix) indicates that the treatment or condition increased the osteogenic and / or chondrogenic activity of the bone matrix. Suitable cells include C2C12 cells. A suitable marker is alkaline phosphatase. The inventive methods increase the osteogenic and / or chondrogenic activity of human DBM when tested using this assay system.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Method of forming micro-tubular polymeric materials
The present invention discloses the design and fabrication of highly porous (up to 97%) scaffolds from biodegradable polymers with a novel phase-separation technique to generate controllable parallel array of micro-tubular architecture. The porosity, diameter of the micro-tubes, the tubular morphology and their orientation may be controlled by the polymer concentration, solvent system and temperature gradient. The mechanical properties of these scaffolds are anisotropic. Osteoblastic cells are seeded in these 3-D scaffolds and cultured in vitro. The cell distribution and the neo-tissue organization are guided by the micro-tubular architecture. The method has general applicability to a variety of polymers, therefore the degradation rate, cell-matrix interactions may be controlled by the chemical composition of the polymers and the incorporation of bioactive moieties. These micro-tubular scaffolds may be used to regenerate a variety of tissues with anisotropic architecture and properties.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Three-dimensional porous tissue engineering stand material and preparation thereof
A 3D porous scaffold material for tissue engineering to induce the generation of bone tissue is prepared from chitosan, gelatin, GPSM and calcium nitrate through sol-gel process, chemical treating and freeze drying. Its advantages are high bioactivity and degradability, proper porosity and pore diameter, and controllable properties.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for fostering bone formation and preservation
ActiveUS20050256047A1Rapid bone formationShorten the lengthPeptide/protein ingredientsChiropractic devicesSufficient timeBlood concentration
A method of inducing bone formation in a subject in need of such inducement comprises the steps of mechanically inducing an increase in osteoblast activity in the subject and elevating blood concentration of at least one bone anabolic agent in the subject. The method steps may be performed in any order, but in sufficient time proximity that the elevated concentration of the anabolic agent and the mechanically induced increase in osteoblast activity overlaps. The method may additionally comprise providing the subject with an elevated blood concentration of at least one antiresorptive agent, wherein the elevated concentration is sufficient to prevent resorption of new bone growth produced due to the osteoblast activity. Use of the method permits targeting of specific bones of the subject for bone production and preservation, faster bone production and earlier discontinuation of bone anabolic pharmaceuticals. Kits adapted for performing the method are provided.
Owner:UNIGENE LABORATORIES +1
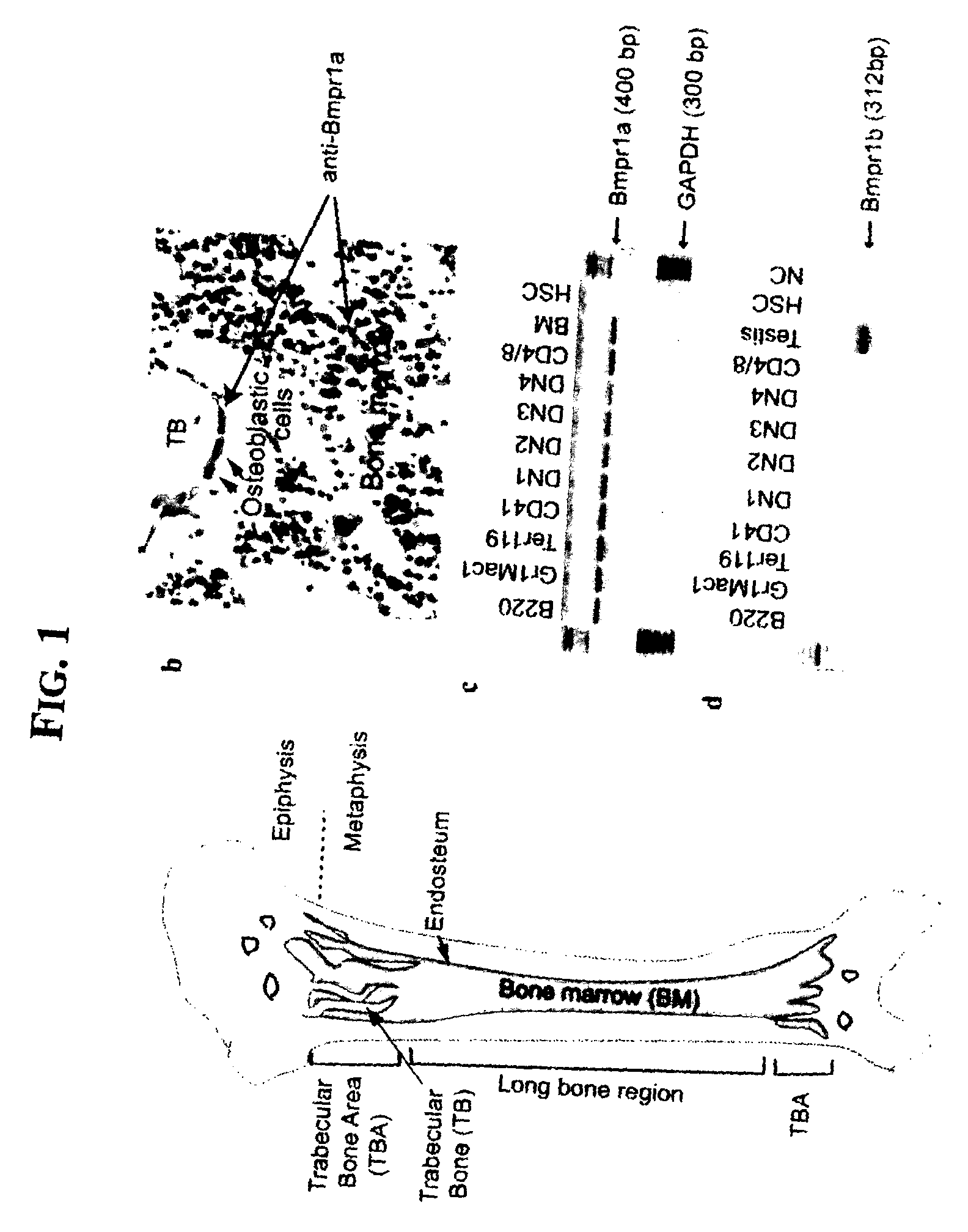
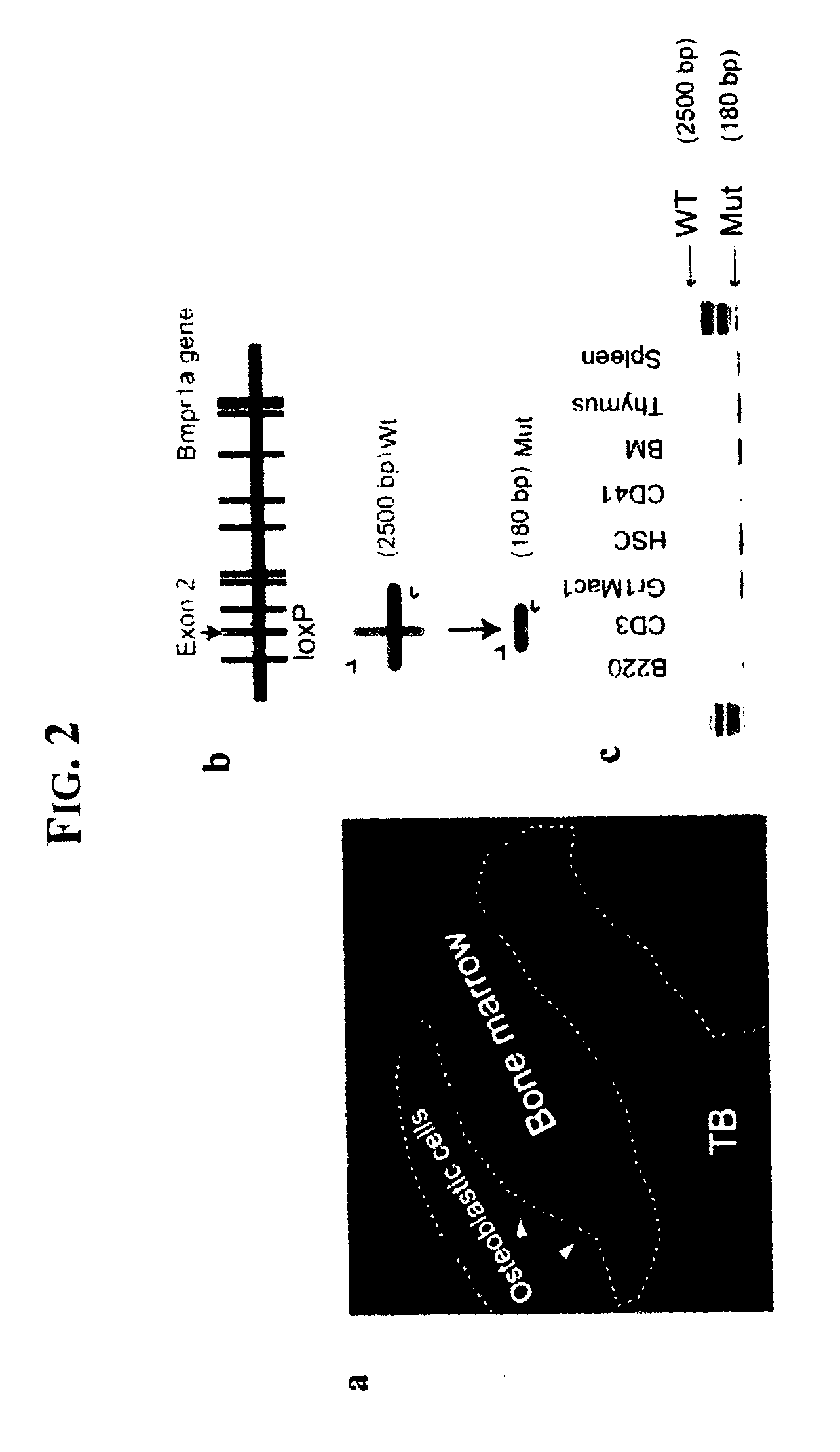
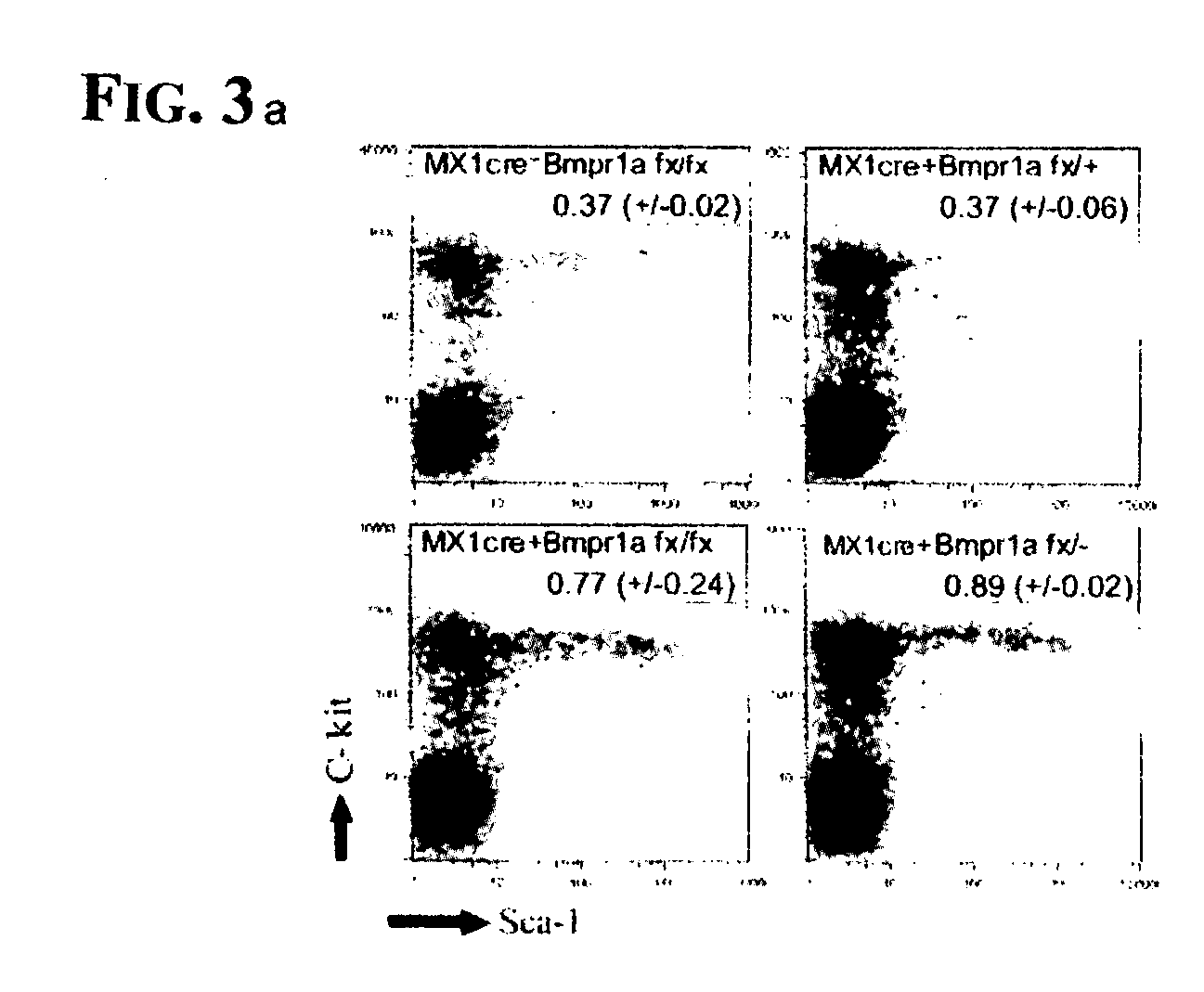
Hematopoietic stem cell niche cells
The present invention relates to an isolated population of osteoblastic cells, which are characterized by cell surface markers N-cad<+> and CD45<->, with such osteoblastic cells used in vitro to promote and support growth of HSCs. Additionally, the present invention relates to vectors, which include a Bmpr1a nucleic acid sequence, recombination sites, and a plasmid, wherein the vectors can be used to promote an increase in the HSC population in vivo.
Owner:STOWERS INST FOR MEDICAL RES
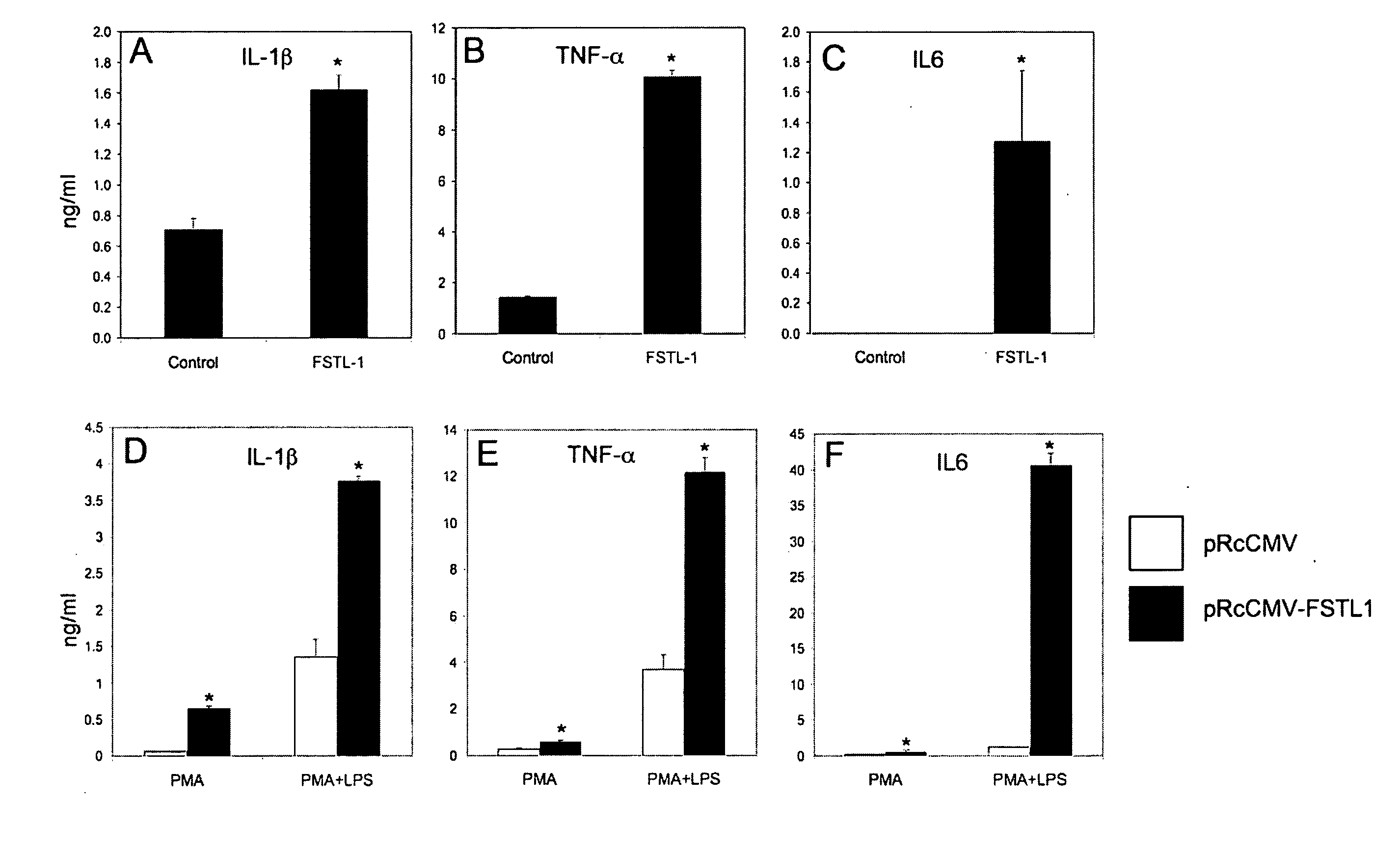
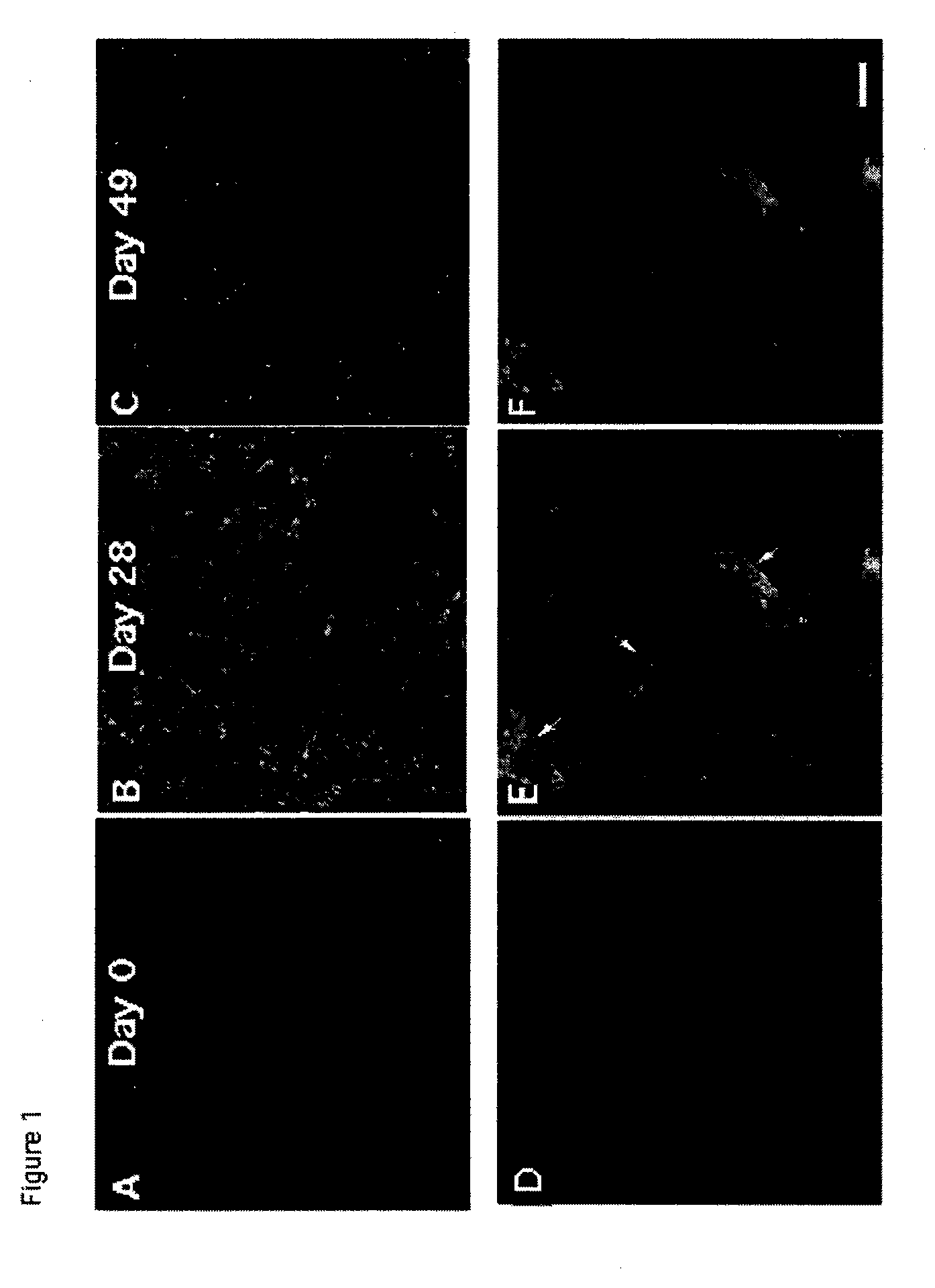
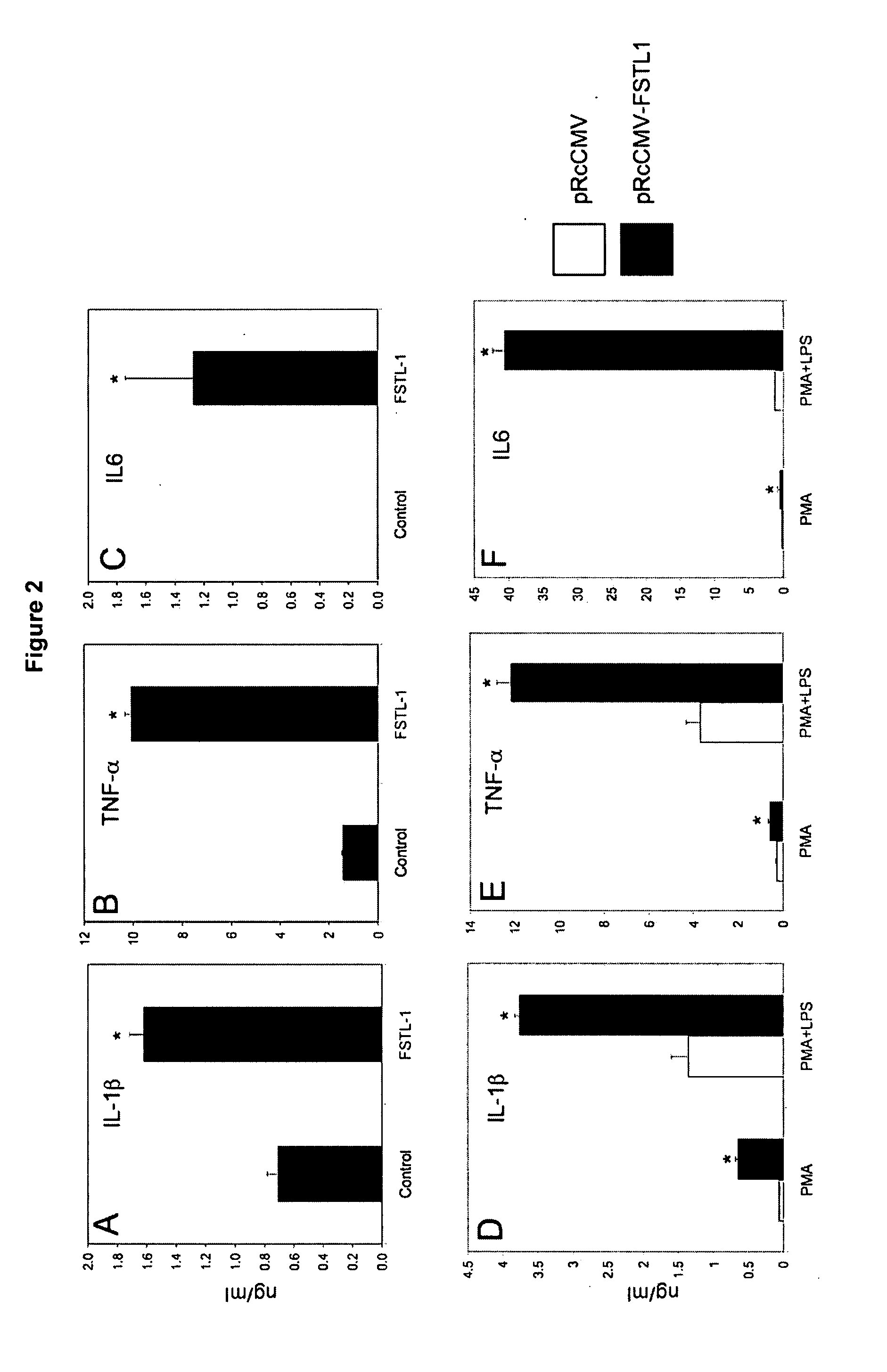
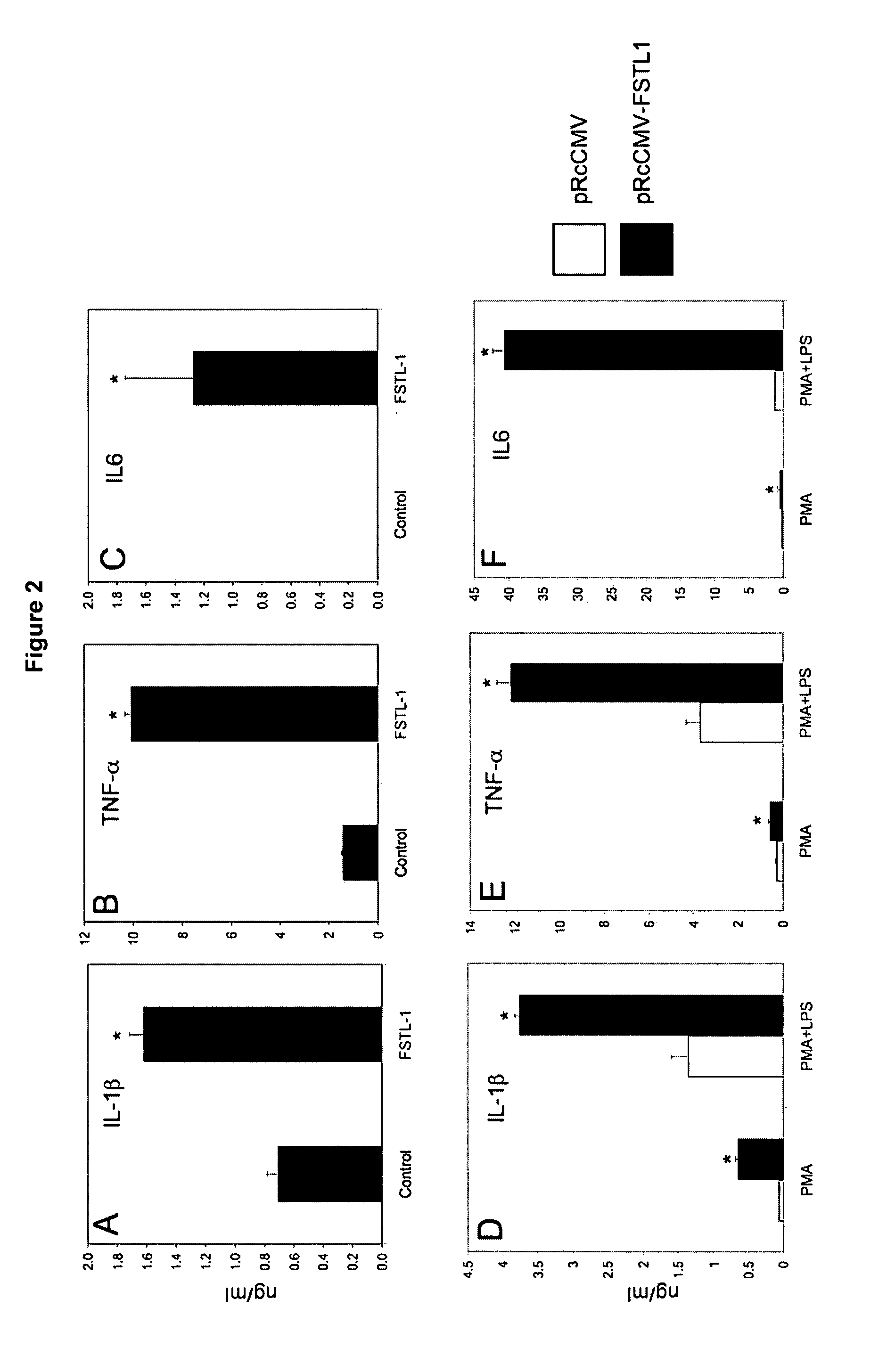
Immunomodulation of inflammatory conditions utilizing follistatin-like protein-1 and agents that bind thereto
ActiveUS20070253962A1High expressionDecrease in proinflammatory effectNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAutoimmune conditionAntibody fragments
Follistatin-like protein (FSTL-1) is a secreted glycoprotein of unknown function, first isolated from mouse osteoblastic cells as a transforming growth factor-β1-inducible gene. The inventors have discovered that FSTL-1 is a proinflammatory mediator. As such, the invention provides for composition and methods of using agents that bind to FSTL-1 to modulate various types of inflammation (e.g., autoimmune diseases). Inhibitors and antagonists of FSTL-1, particularly antibodies or antibody fragments, may be used to treat conditions related to inflammation, such as arthritis. In addition, the inventors have discovered that FSTL-1 has a role in the Th17 pathway. Accordingly, the invention provides for compositions and methods of using agents which bind to FSTL-1 to modulate the generation of Th17 cells. Such agents are useful for delaying development of and treating diseases associated with undesired production of Th17 cells, such as autoimmune diseases. Furthermore, since FSTL-1 is a proinflammatory mediator with a role in cancer, the invention provides for compositions and methods of using a pharmaceutical composition of FSTL-1 to delay development of or treat cancer.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
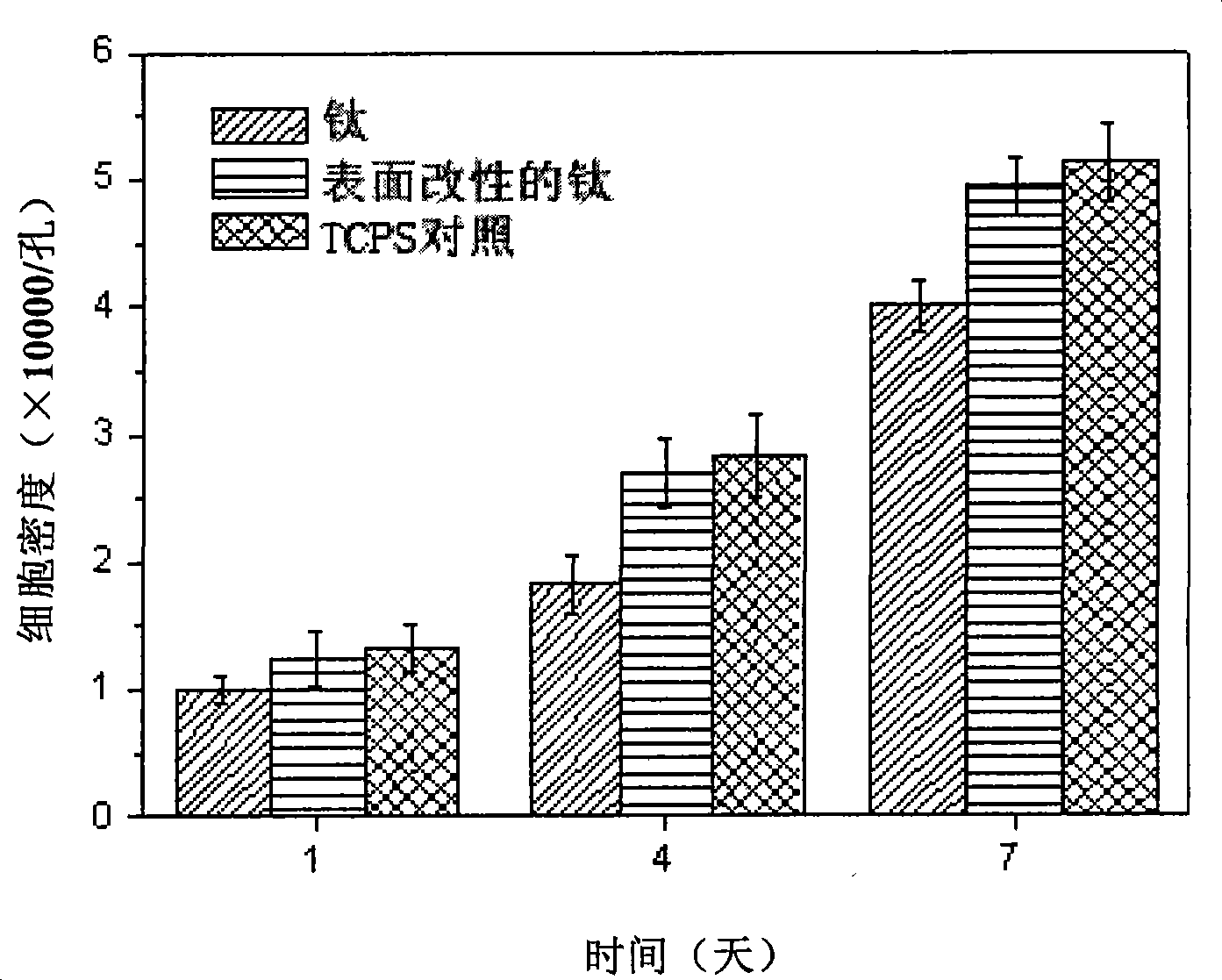
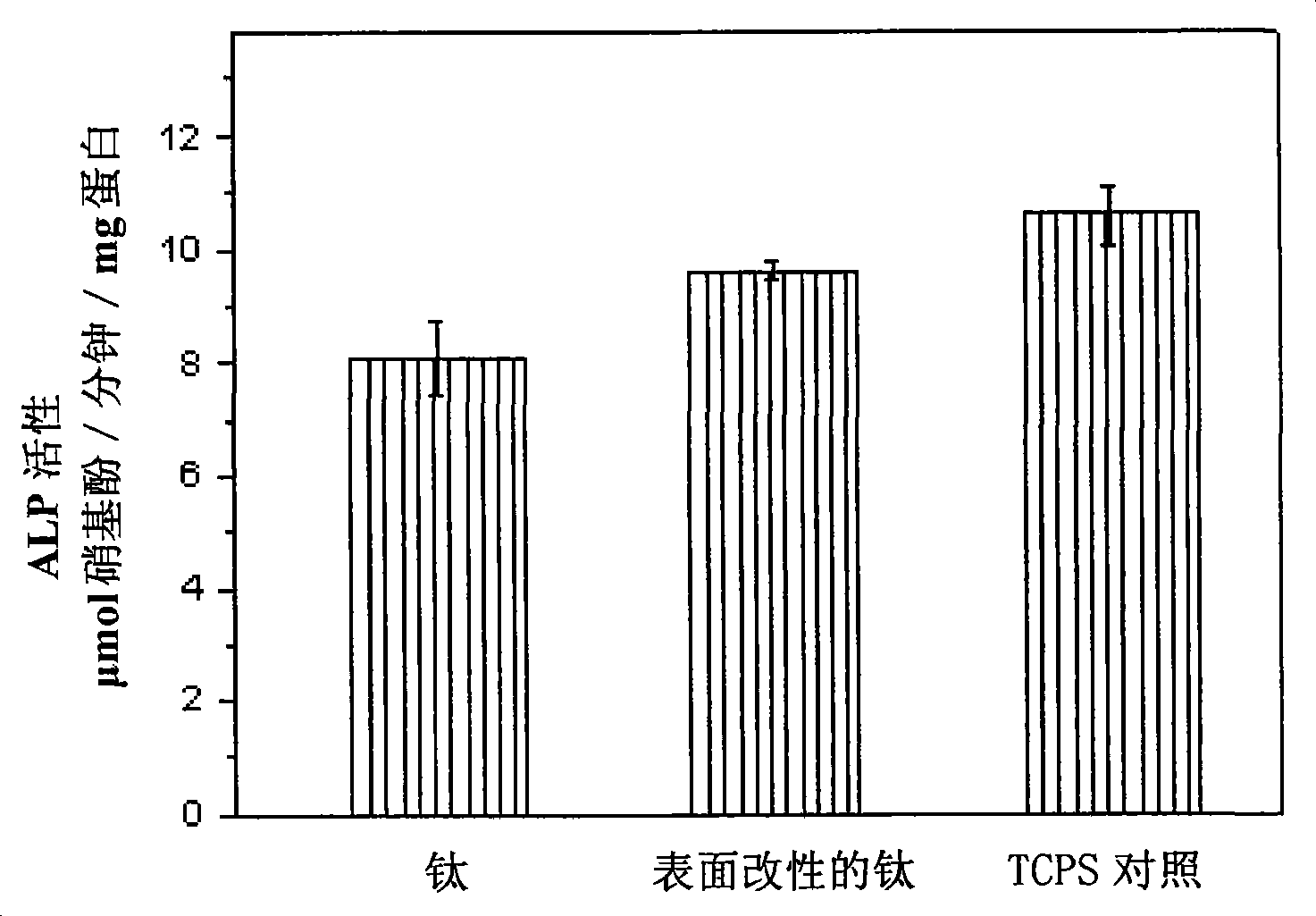
Titanium or titanium alloy material with modified surface as well as preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101411893AGood osteoblast compatibilityPromote proliferation and differentiationCoatingsProsthesisImplant materialBone cell
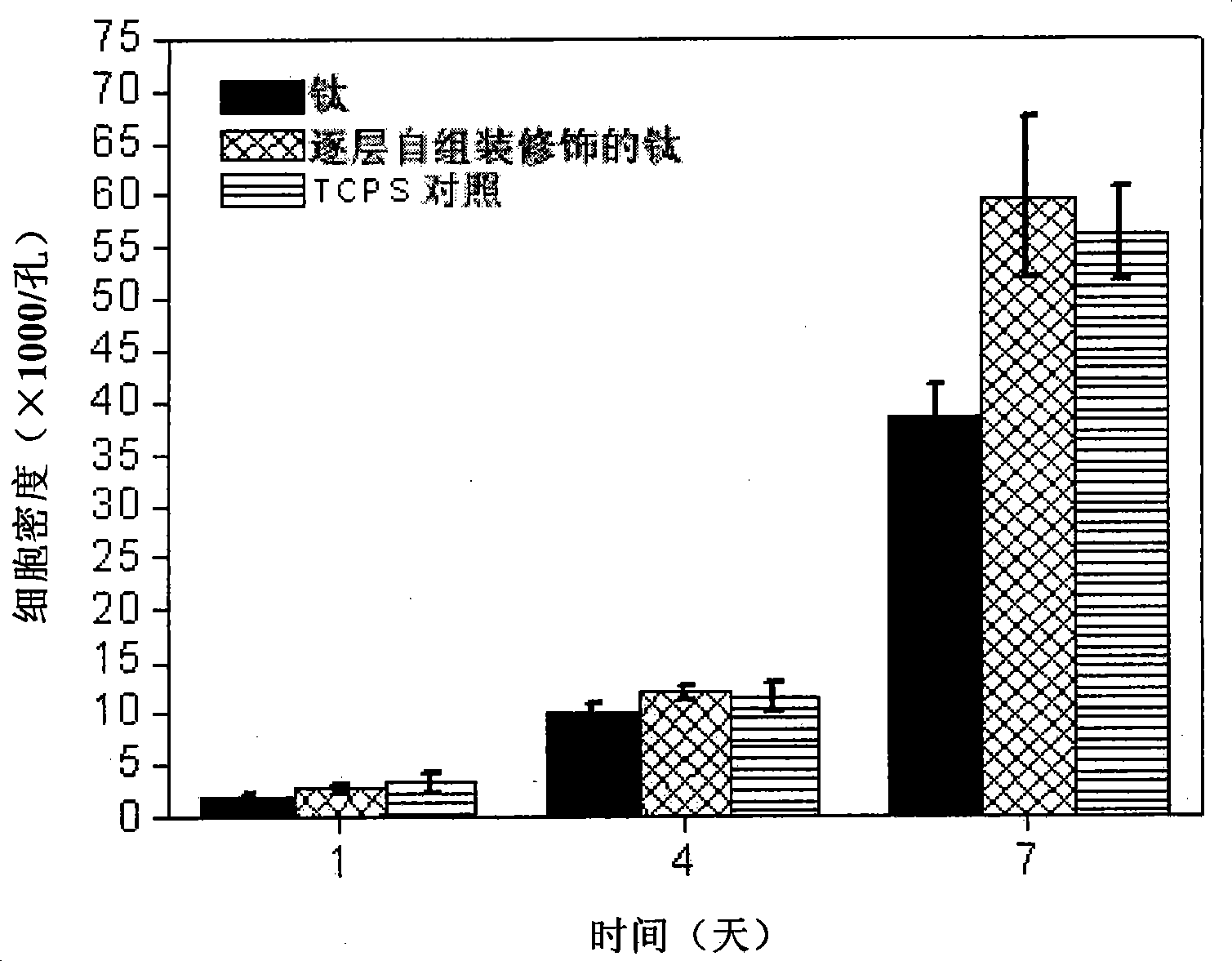
The invention discloses a surface modified titanium or titanium alloy material. The surface of the material is provided with at least five layers of bioactive coats consisting of double-layer chitosan-silk fibroin. The material has favorable osteoplast compatibility, can promote multiplication and division of osteoplast, shows potential for further developing a novel medical hard tissue implant material, and has favorable clinical application prospect. The surface modified titanium or titanium alloy material can be prepared by a self-assembly method layer by layer; alternate layers of polycation electrolyte chitosan and polyanion electrolyte gelatin are laminated and assembled on the surface of the titanium or titanium alloy material through electrostatic adsorption action; and the preparation method is simple, can control coating thickness, is not affected by size and shape of the material, is suitable for the materials with complex appearance, has moderate preparation conditions, needs no special equipment, and has low production cost, strong practicability, and better popularization and application values.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Biological compound material based on fish skin collagen and preparation method of biological compound material
InactiveCN103690996AThe promotion effect is obviousImprove the nutritional environmentProsthesisEngineeringBiology
The invention discloses a biological compound material based on fish skin collagen and a preparation method of the biological compound material. The biological compound material consists of collagen, calcium nitrate and diammonium hydrogen phosphate by a certain ratio. The preparation method comprises the following steps: A, extracting the fish skin collagen; B, in-situ compounding the collagen and hydroxyapatite; C crosslinking the biological compound collagen material. The obtained biological compound collagen material has the advantages of good biological compatibility, reasonable formula, convenient operation and reduction in environment pollution. The method is easy to realize and simple to operate, a safe collagen extracting method is adopted, the compound material is synthesized through the proper proportioning of the collagen, the calcium nitrate and the diammonium hydrogen phosphate, and the biological compound collagen material has certain mechanical performance and excellent biological compatibility. A proper growth environment can be provided for the growth of bone cells, and the biological compound collagen material is a potential substitute for clinic bone materials.
Owner:YANGTZE RIVER FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for preparing two-stage micron-submicron microstructure on surface of titanium alloy dental implant
InactiveCN102525675AGood biocompatibilityImprove early osseointegration rateDental implantsEtchingOsteoblastic cell
The invention discloses a method for preparing a two-stage micron-submicron microstructure on the surface of a titanium alloy dental implant. The titanium alloy implant is activated, and is processed through surface modification such as direct current electrolytic etching and alternating current etching, so that a two-stage micron-submicron microstructure shape can be formed on the surface of the implant. The two-stage micron-submicron microstructure shape is prepared on the surface of the titanium alloy dental implant, so that the method achieves the property of guiding the adhesion of osteoblasts, can simulate natural histomorphology in vivo, can guide the bone matrix formation on the surface rapidly, and can promote the formation of good synosteosis. Therefore, the titanium alloy dental implant can promote the formation of new bones, can short the healing time, and can achieve the ideal effect that the titanium alloy dental implant can take on the recovery function as soon as being implanted further.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Preparation method and applications of 3D printing composite magnetic metal scaffold
InactiveCN107715182ALarge apertureHigh porosityAdditive manufacturing apparatusPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMagnetite NanoparticlesBiocompatibility Testing
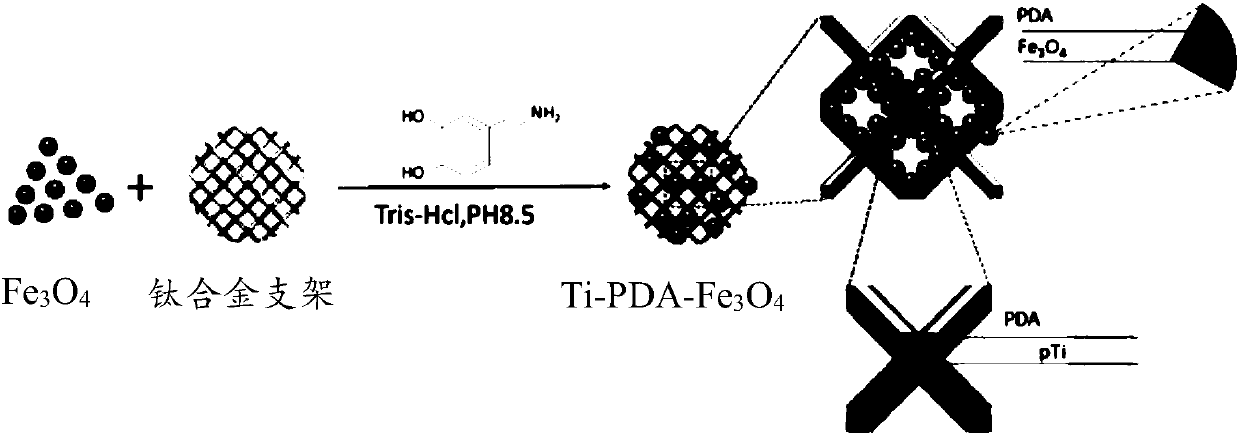
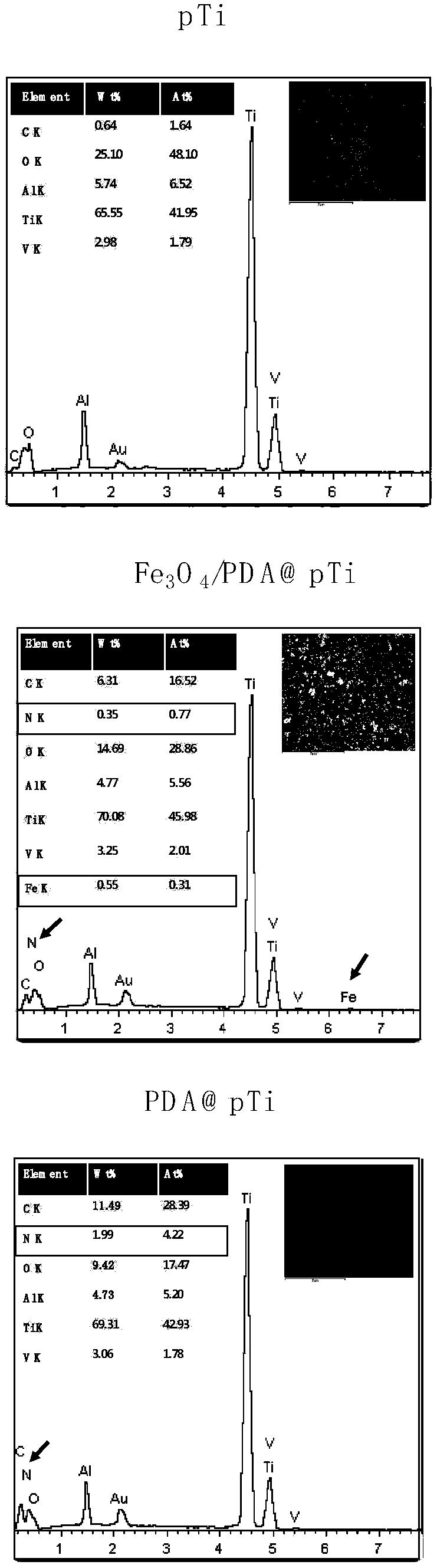
The present invention discloses a 3D printing composite magnetic metal scaffold preparation method, which comprises: establishing a three-dimensional model with a porous structure, printing a three-dimensionally-penetrating porous metal scaffold by using a 3D printing technology, and modifying the porous metal scaffold with poly dopamine and Fe3O4@PDA composite magnetic nanoparticles through a one-step method so as to obtain the 3D printing composite magnetic metal scaffold. According to the present invention, the 3D printing composite magnetic metal scaffold can meet the requirement of the bone repair material on the mechanical strength, and further has advantages of advantages of good biocompatibility, good hydrophilicity and reduced cytotoxicity, wherein the coated material has weak magnetism, such that the osteoblast differentiation can be easily achieved, and the osteogenesis is easily achieved; and the preparation method has advantages of simple and easy operation, rapidness, high efficiency and easy production.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Dental Material And Composite Dental Material Formed By Using Hydroxy Apatite
InactiveUS20090004627A1Avoid contactImprove bone formationDental implantsImpression capsBioabsorbable membraneOsteoblast
It is intended to provide a dental material formed by using a hydroxy apatite, which is suitable for performing the guided bone regeneration (GBR) method in the implant therapy of dentistry. Also, it is intended to provide a composite dental material which is a bioabsorbable film provided integrally with hydroxy apatite, which is capable of rapidly attracting the osteoblast and blocking the fibroblast. The dental material is a membrane to be used for a guided bone regeneration method of guiding a bone formation by preventing invasion by anaplastic fibroblast by covering a bone developing site with a blocking membrane and filling the bone developing site with osteoblast, wherein a membrane main body of the blocking membrane is formed by using hydroxy apatite having osteoconductive capability of rapidly attracting osteoblast for the purpose of disposing the hydroxy apatite at a bone developing site side of the membrane main body. The composite dental material is a membrane to be used for a guided bone regeneration method of guiding a bone formation by preventing invasion by anaplastic fibroblast by covering a bone developing site with a blocking membrane and filling the bone developing site with osteoblast, wherein a membrane main body of the blocking membrane is formed by using a bioabsorbable membrane, and the bioabsorbable membrane is integrally provided with hydroxy apatite having osteoconductive capability of rapidly attracting osteoblast and a structure of being disposed at a bone developing site side of the membrane main body.
Owner:ISHIMOTO MITSUNORI +1
Self-assembly modified titanium or titanium alloy material from layer to layer as well as preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101411894AThickness is easy to controlPromote proliferationCoatingsProsthesisMetallurgyLayer by layer self assembly
The invention discloses a titanium or titanium alloy material for self-assembly decoration layer by layer. The surface of the material is self-assembled with at least five layers of bioactive coats consisting of double-layer chitosan-gelatin. The material has favorable osteoplast compatibility, can promote multiplication and skeleton remolding of osteoplast, shows potential for further developing a novel medical hard tissue implant material, and has favorable clinical application prospect. The titanium or titanium alloy material for surface decoration is prepared by a self-assembly method layer by layer; alternate layers of polycation electrolyte chitosan and polyanion electrolyte gelatin are laminated and assembled on the surface of the titanium or titanium alloy material through electrostatic adsorption action; and the preparation method is simple, can control coating thickness, is not affected by size and shape of the material, is suitable for the materials with complex appearance, has moderate preparation conditions, needs no special equipment, and has low production cost, strong practicability, and better popularization and application values.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Magnesium alloy surface modification method
InactiveCN104746073AMeet the needs of implant materialsImprove adhesionAnodisationSuperimposed coating processPlasma electrolytic oxidationMicro arc oxidation
The invention discloses a magnesium alloy surface modification method which comprises the following steps: pretreating the magnesium alloy surface, performing micro-arc oxidation, and forming a micro-arc oxidation coating; depositing poly-dopamine on the micro-arc oxidation coating, immersing the magnesium alloy on which poly-dopamine is deposited in a hydroxyapatite solution, thereby obtaining a surface modified magnesium alloy. The micro-arc oxidation can provide a corrosion prevention effect for the magnesium alloy, the hydroxyapatite belongs to bioactive degradable ceramics and is deposited on the surface of the micro-arc oxidation magnesium alloy, the biological activity can be effectively improved, and adhesion and growth of osteoblasts on the material surface are promoted, so that the requirement on the magnesium alloy serving as an in-vivo implant material is met. Compared with the conventional electrodeposition method for preparing a hydroxyapatite coating, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that instruments and equipment are not needed, the cost is low, and the application range is widened.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Preparation method for forming calcium-containing nanosheet film layer on surface of sandblasted and acid-etched titanium
InactiveCN105696054APromote osseointegrationGood compatibilitySurface reaction electrolytic coatingPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAcid etchingOsseointegration
A preparation method for forming a calcium-containing nanosheet film layer on the surface of sandblasted and acid-etched titanium includes the following steps that (A) pure titanium is polished, sandblasted, subjected to ultrasonic cleaning and dried; (B) the pure titanium is acid-etched with hydrofluoric acid / nitric acid mixed liquid, subjected to ultrasonic cleaning with double distilled water and dried, and then acid-etched with concentrated hydrochloric acid / concentrated sulfuric acid mixed acid, subjected to ultrasonic cleaning with double distilled water and dried, so that a micron structure is formed on the surface of the titanium; and (C) the sandblasted and acid-etched pure titanium is subjected to a calcium hydroxide and hydrogen peroxide hydrothermal solution reaction for 0.5-24 hours under a water bath at the temperature of 70-90 DEG C, the calcium-containing nanosheet film layer is formed, and the titanium is processed for 1-3 hours at the temperature of 300-500 DEG C. By means of the surface nanosheet film layer and the calcium element contained in the prepared sample, the compatibility and combining capacity of the prepared sample with bones can be enhanced, adhesion, proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts on the surface of the titanium are facilitated, and thus the osseointegration capacity of the titanium is improved. Meanwhile, the method is simple in process, processing is easy, and the preparation cost is low.
Owner:AFFILIATED STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL OF NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Multi-component bone tissue engineering scaffold material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a multi-component bone tissue engineering scaffold and a preparation method thereof. The multi-component bone tissue engineering scaffold is prepared from chitosan, gelatin, pectin and nano hydroxyapatite by weight percent. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: selecting the chitosan and the pectin to prepare a hydroxyapatite / chitosan-pectin compound by virtue of a codeposition technology, wherein the particle diameter of the hydroxyapatite is 10-100nm; and dispersing nHCP into a chitosan-gelatin solution, crosslinking with glutaric dialdehyde and then freeze-drying to obtain the multi-component bone tissue engineering scaffold. In the scaffold prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention, nHCP can be uniformly dispersed in the scaffold and is difficult to agglomerate; the pore diameter of the scaffold is 100-300 mu m, and the porosity of the scaffold is greater than 80%; and the scaffold disclosed by the invention can be used for promoting the adhersion and growth of skeletogenous cells, has good biocompatibility and is expected to be used as a novel bone tissue engineering biological material.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing antibacterial titanium material having good biocompatibility and containing silver on surface
InactiveCN108434524AEasy to operateImprove controllabilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCoatingsCationic polyelectrolytesBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a method for preparing an antibacterial titanium material having a good biocompatibility and containing silver on the surface. The method comprises the following steps: constructing uniform titanium dioxide nanotubes on the surface of a titanium material by an anodization technology, used as a silver nanoparticle store; and oxidizing sodium alginate by sodium periodate to obtain dialdehyde sodium alginate denoted as ADA and used as an anionic polyelectrolyte, and performing layer-by-layer self-assembling on the anionic polyelectrolyte and cationic polyelectrolyte CHI toform a polyelectrolyte multilayer film. The driving force for forming the multilayer film is derived from the electrostatic interaction between the ADA and the CHI and the covalent interaction between the aldehyde group on the ADA and the amino group on the CHI, so the constructed stable multilayer film can effectively control the release of silver ions, reduce the toxicity of the silver ions toosteoblasts and achieve good biocompatibility, and also can achieve excellent antibacterial properties in order to make a titanium-based implant have good antibacterial and osteogenic properties.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
M-CSF-Specific Monoclonal Antibody and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20100092464A1Prevent and reduce bone lossReduce and preventSkeletal disorderAntibody ingredientsDiseaseOsteoblast
M-CSF-specific RX1-based or RX-I derived antibodies are provided, along with pharmaceutical compositions containing such antibody, kits containing a pharmaceutical composition, and methods of preventing and treating bone loss in or remodeling in a subject afflicted with an osteoblastic or osteolytic disease.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Compound protein tabletted candy and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104382033AIncrease the number ofPromote generationPeptide/protein ingredientsConfectioneryIncreased Bone DensityPhosphopeptide
The invention discloses a compound protein tabletted candy and a preparation method thereof. The compound protein tabletted candy is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 3-5% of foremilk basic protein, 15-20% of collagen, 5-10% of casein phosphopeptides, 20-30% of halimasch, 5-10% of radix puerariae extractives, 3-5% of calcium carbonate, 1-3% of xylooligosaccharide, 1-2% of erythritol, 30-60% of sorbitol and 5-10% of microcrystalline celluloses. The preparation method comprises the following main steps of (1) mixing; (2) pelletizing; (3) drying; (4) finishing pellets; and (5) tabletting. The compound protein tabletted candy disclosed by the invention has the effects of increasing the bone density and the osteoblast amount and promoting the generation of bones and teeth and can be used for activating the motive powers of bones, promoting the extension of the bones, promoting the calcinosis of the bones, enhancing the toughness of the bones, inhibiting the growth of osteoclasts and maintaining the balance of bone components.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG JOHNSUN BIOLOGICAL ENG CO LTD
Gene expression associated with osteobla st differentiation
The present invention identifies genes whose expression pattern is altered when pre-osteoblastic cells undergo differentiation into mature osteoblasts. The genes identified may be used as markers for the differentiation process. The present invention also provides methods to screen agents that are capable of modulating the differentiation process. The present invention also provides methods of identifying therapeutic agents that stimulate bone formation by analyzing the expression of one or more of the genes identified.
Owner:SUSA SPRING MIRA +1
Preparation method of wood-based bionic bone scaffold material
ActiveCN111068121AGood biocompatibilityImprove water retentionSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismWood fibreFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a preparation method of a wood-based bionic bone scaffold material, and belongs to the field of bionic bone scaffolds. The method comprises the following steps: soaking wood fibers in an alkali solution, and performing mechanical grinding to obtain fiber pulp; mixing the fiber pulp with a polysaccharide polymer solution, and performing uniform stirring to obtain a mixed solution; adding hydroxyapatite into the mixed solution, and performing magnetic stirring in a water bath to obtain a scaffold material precursor mixed solution; freezing the scaffold material precursormixed solution, and performing freeze-drying to obtain an aerogel scaffold; performing cross-linking treatment on the aerogel scaffold with a glutaraldehyde solution, and performing rinsing with ethanol and deionized water; and freezing the rinsed scaffold material, and then performing freeze-drying to obtain the wood-based bionic bone scaffold material. According to the invention, the wood-basedbionic bone scaffold material with a three-dimensional porous structure is prepared by a circulating freeze drying technology. The scaffold material has no cytotoxicity and has high compressive strength; and mouse osteoblasts can adhere and grow on the scaffold material, so that requirements of a bone scaffold material are met.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Implant surfaces that enhance osteoinduction
ActiveUS20190192303A1Enhance osteoinductionPromote osteogenesisBone implantSkeletal disorderOsteoblastScale structure
Bone-contacting surfaces and free surfaces of orthopedic implants. The implants are additively manufactured, followed by mechanical, chemical, or mechanical and chemical erosion. At least some of the surfaces of the implants include an osteoinducting roughness that has micro-scale structures and nano-scale structures that facilitate and enhance osteoinduction and osteogenesis, as well as enhanced alkaline phosphatase, osterix, and osteocalcin expression levels along the pathway of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation to osteoblasts.
Owner:TITAN SPINE
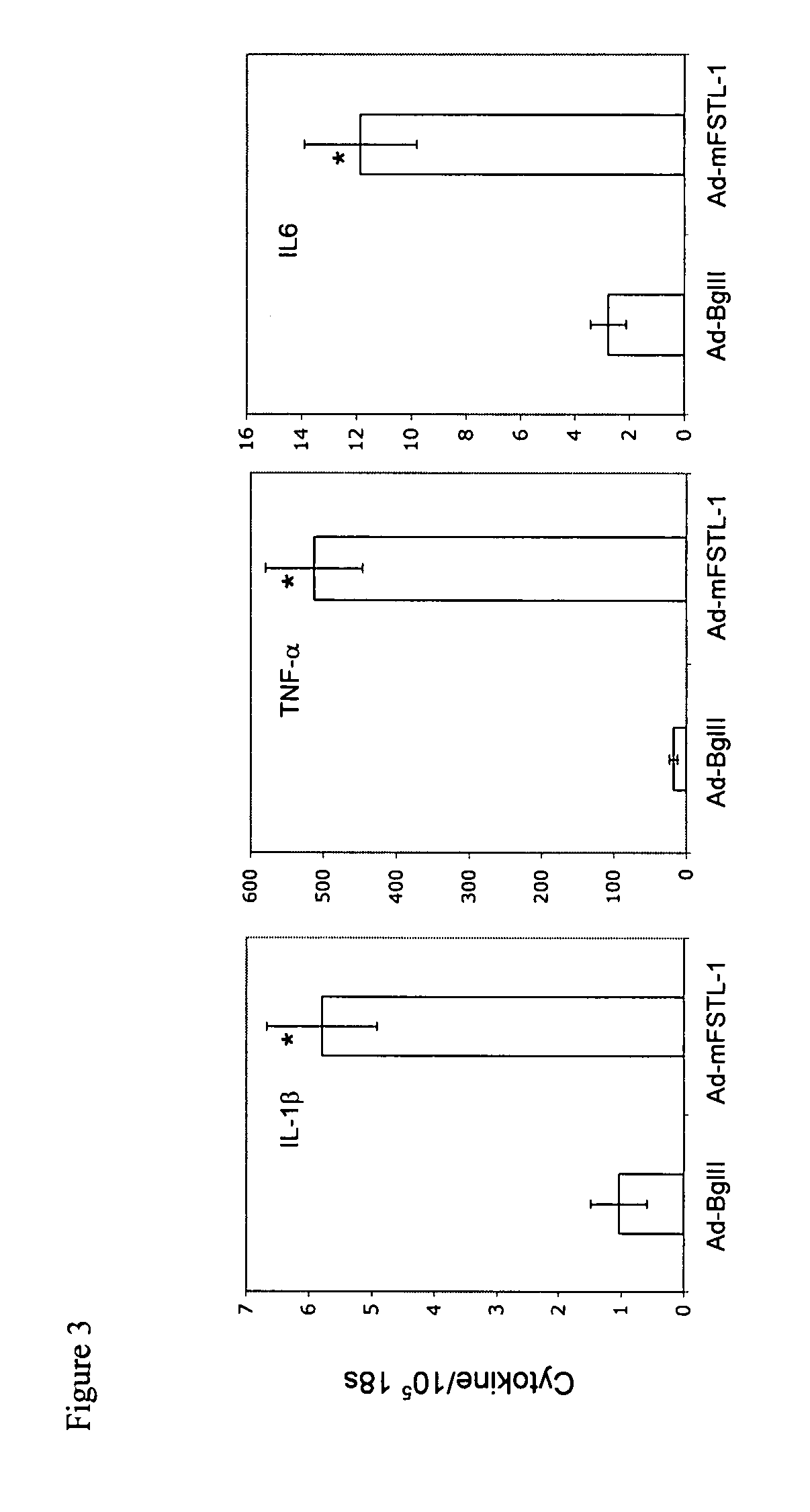
Immunomodulation of inflammatory conditions utilizing Follistatin-like protein-1 and agents that bind thereto
ActiveUS7972599B2Reduce inductionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAntibody fragments
Follistatin-like protein (FSTL-1) is a secreted glycoprotein of unknown function, first isolated from mouse osteoblastic cells as a transforming growth factor-β1-inducible gene. The inventors have discovered that FSTL-1 is a proinflammatory mediator. As such, the invention provides for composition and methods of using agents that bind to FSTL-1 to modulate various types of inflammation (e.g., autoimmune diseases). Inhibitors and antagonists of FSTL-1, particularly antibodies or antibody fragments, may be used to treat conditions related to inflammation, such as arthritis. In addition, the inventors have discovered that FSTL-1 has a role in the Th17 pathway. Accordingly, the invention provides for compositions and methods of using agents which bind to FSTL-1 to modulate the generation of Th17 cells. Such agents are useful for delaying development of and treating diseases associated with undesired production of Th17 cells, such as autoimmune diseases. Furthermore, since FSTL-1 is a proinflammatory mediator with a role in cancer, the invention provides for compositions and methods of using a pharmaceutical composition of FSTL-1 to delay development of or treat cancer.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
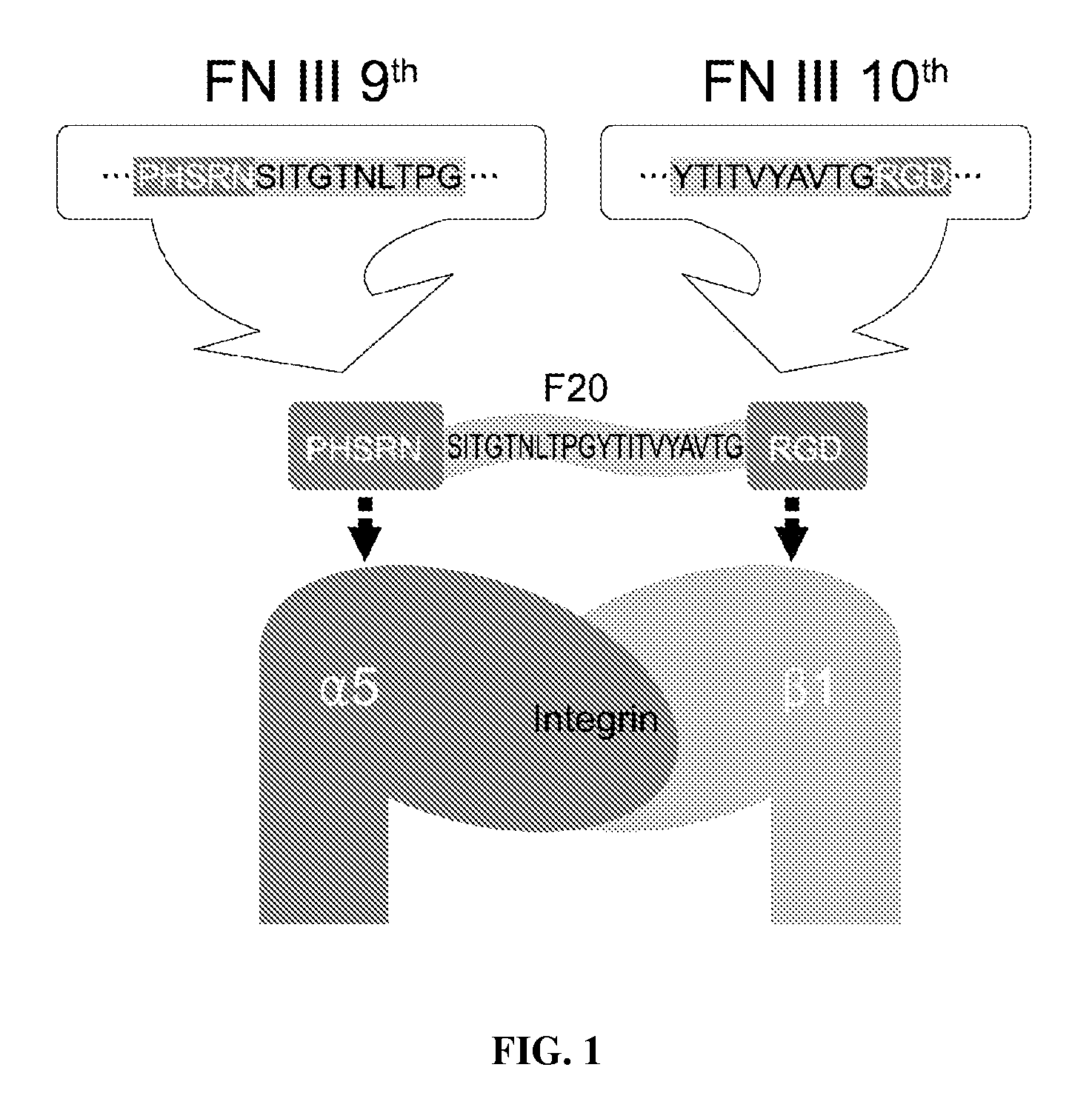
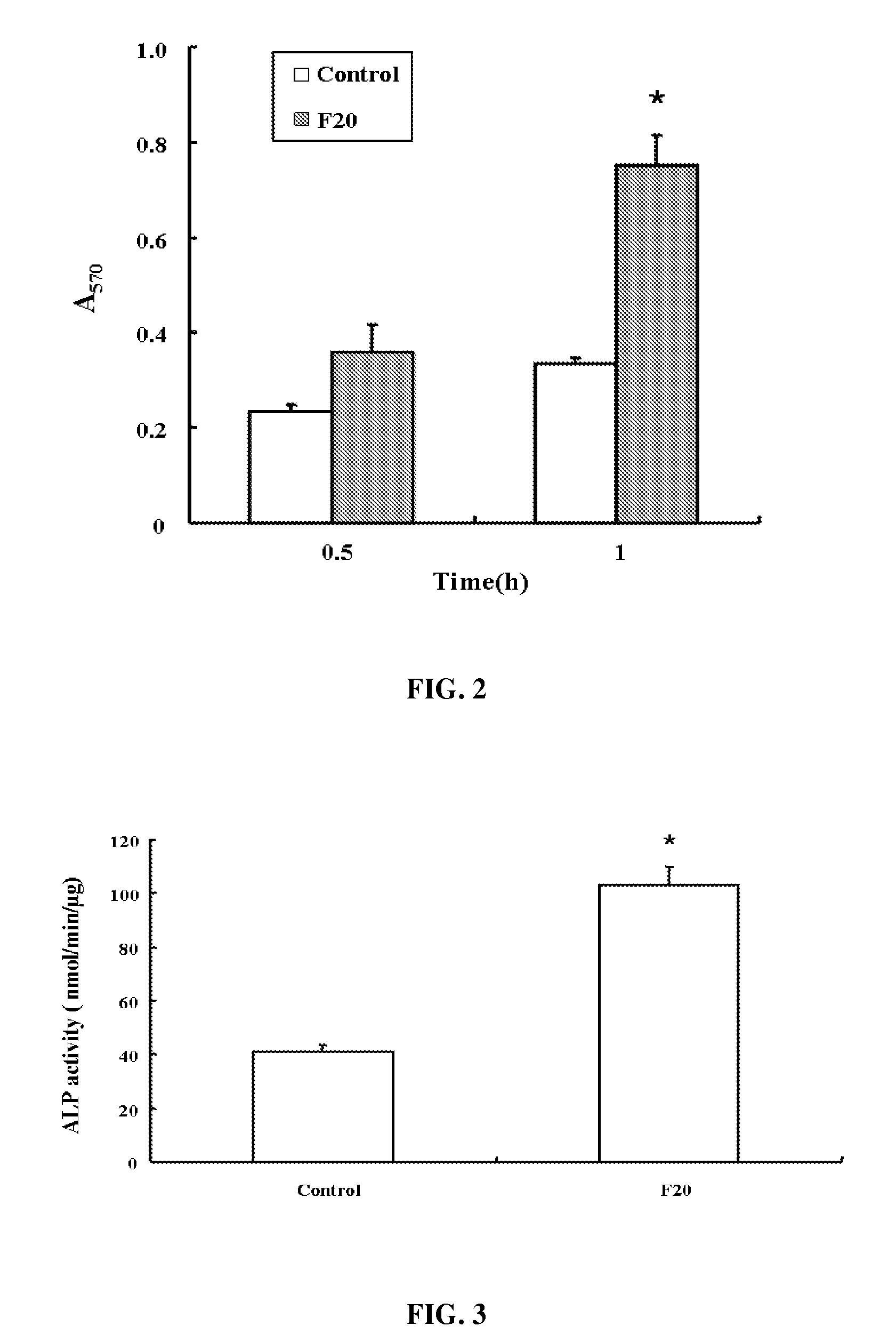
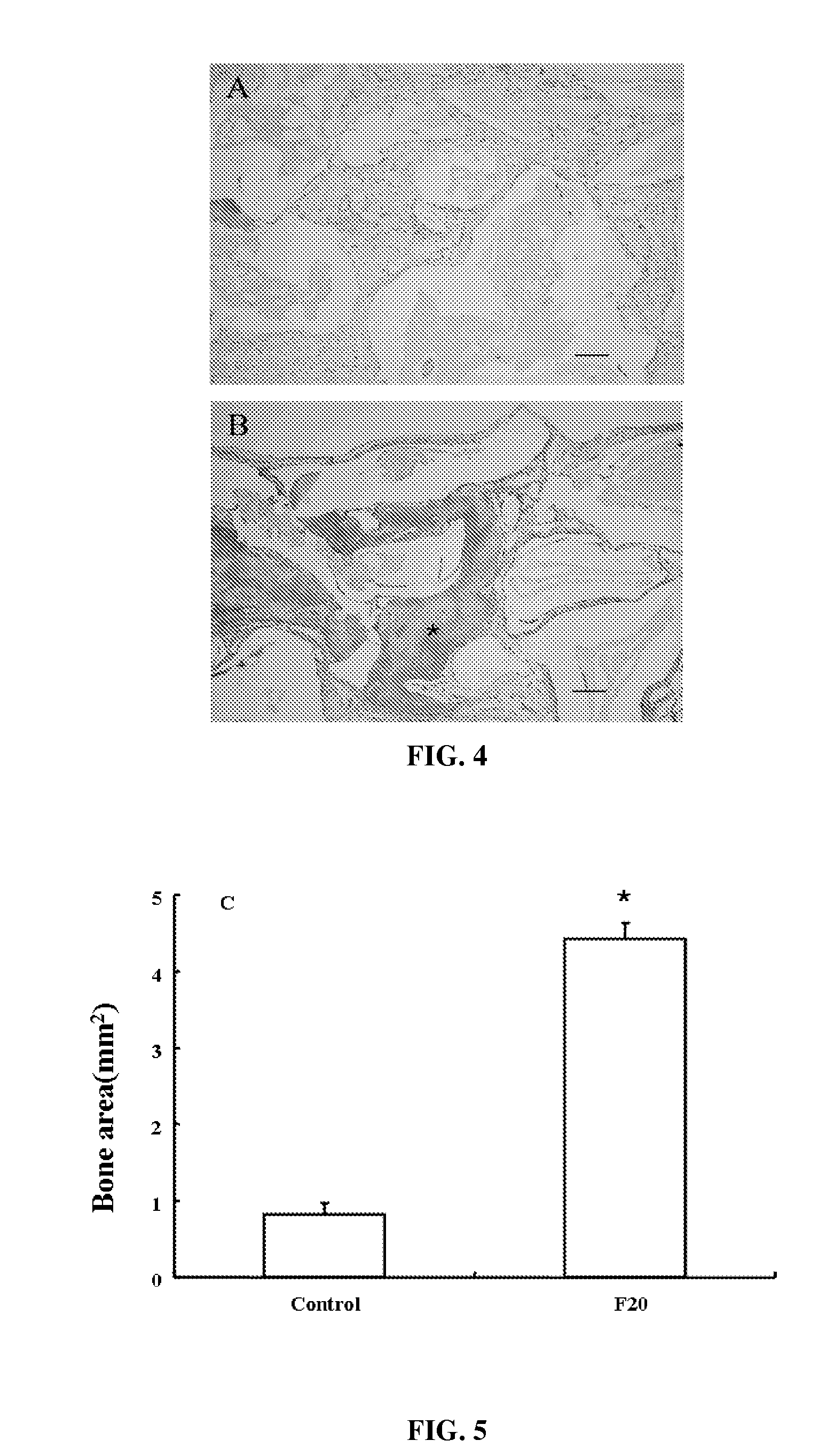
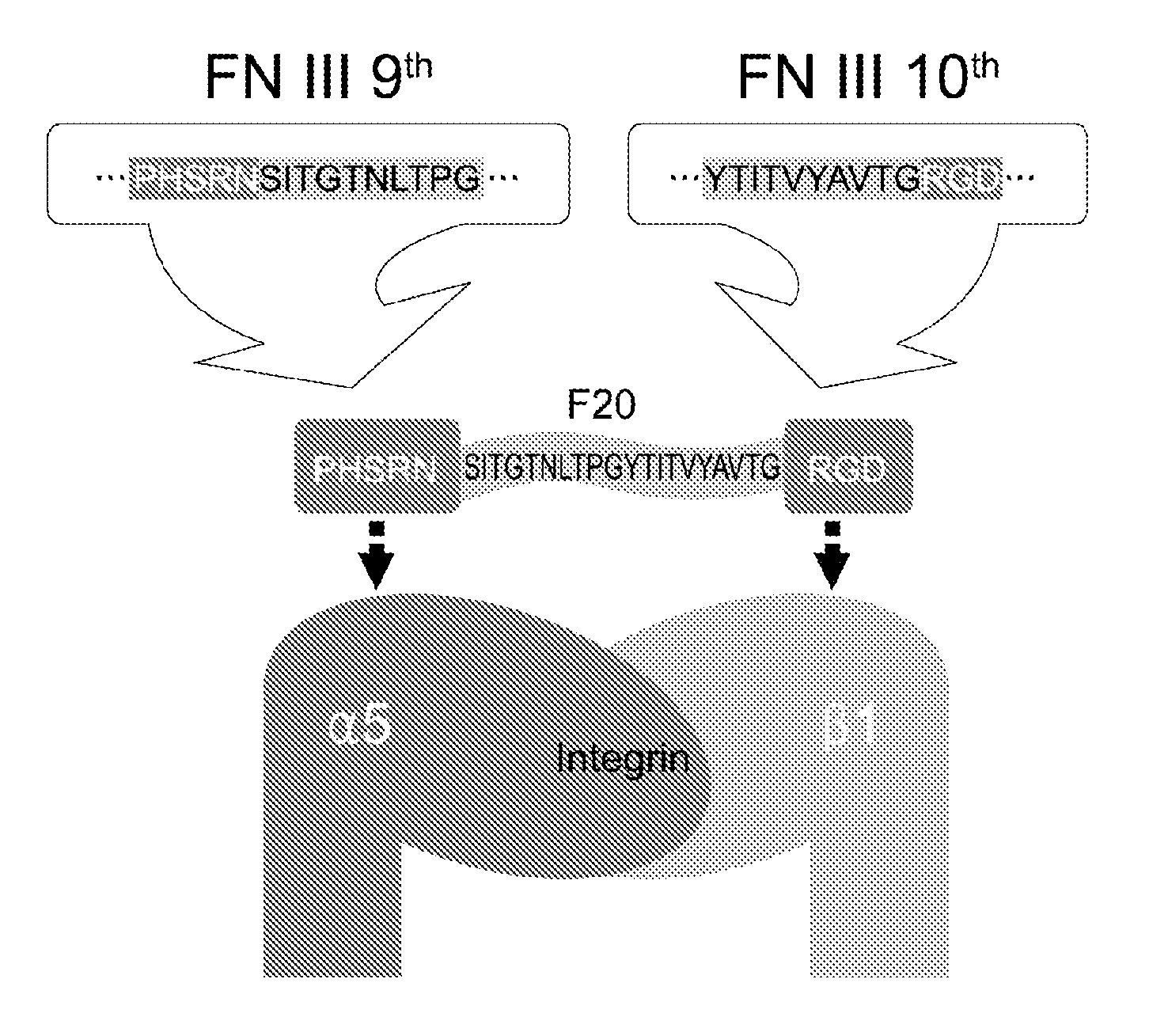
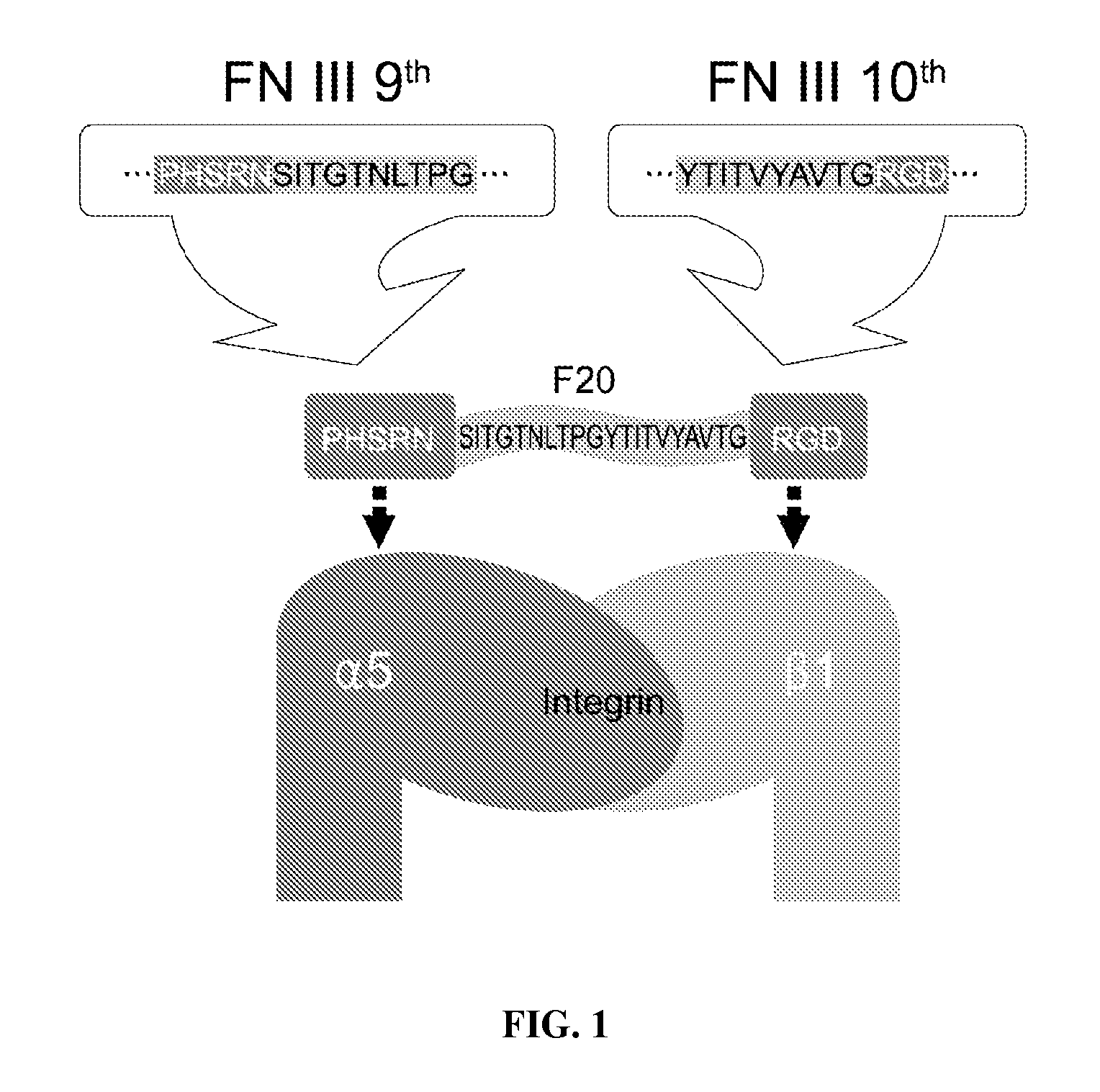
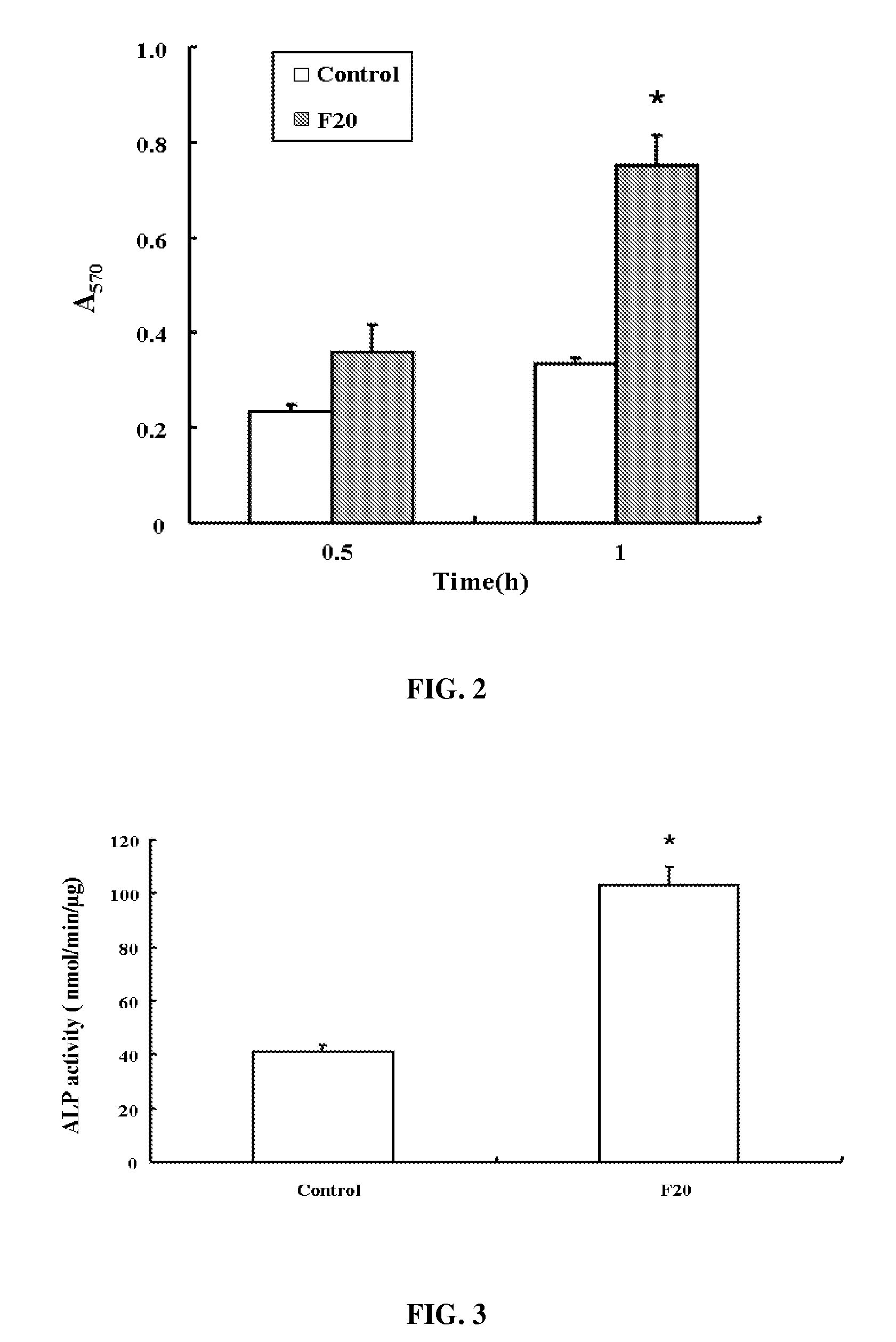
Composition of bone formation with PHSRN-RGD containing oligopeptide
InactiveUS7897722B2Connective tissue peptidesIn-vivo radioactive preparationsOsteoblast adhesionBone tissue
A PHSRN-RGD-containing oligopeptide and a composition for promoting bone formation, which contains such oligopeptide as an effective ingredient. The oligopeptide promotes osteoblastic cell adhesion and differentiation and enhances bone regenerative ability, so that the inventive oligopeptide can be effectively used in regenerative treatment of bone tissue and periodontal tissue.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Composition of bone formation with phsrn-rgd containing oligopeptide
InactiveUS20090010988A1Connective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsOsteoblast adhesionBone tissue
A PHSRN-RGD-containing oligopeptide and a composition for promoting bone formation, which contains such oligopeptide as an effective ingredient. The oligopeptide promotes osteoblastic cell adhesion and differentiation and enhances bone regenerative ability, so that the inventive oligopeptide can be effectively used in regenerative treatment of bone tissue and periodontal tissue.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
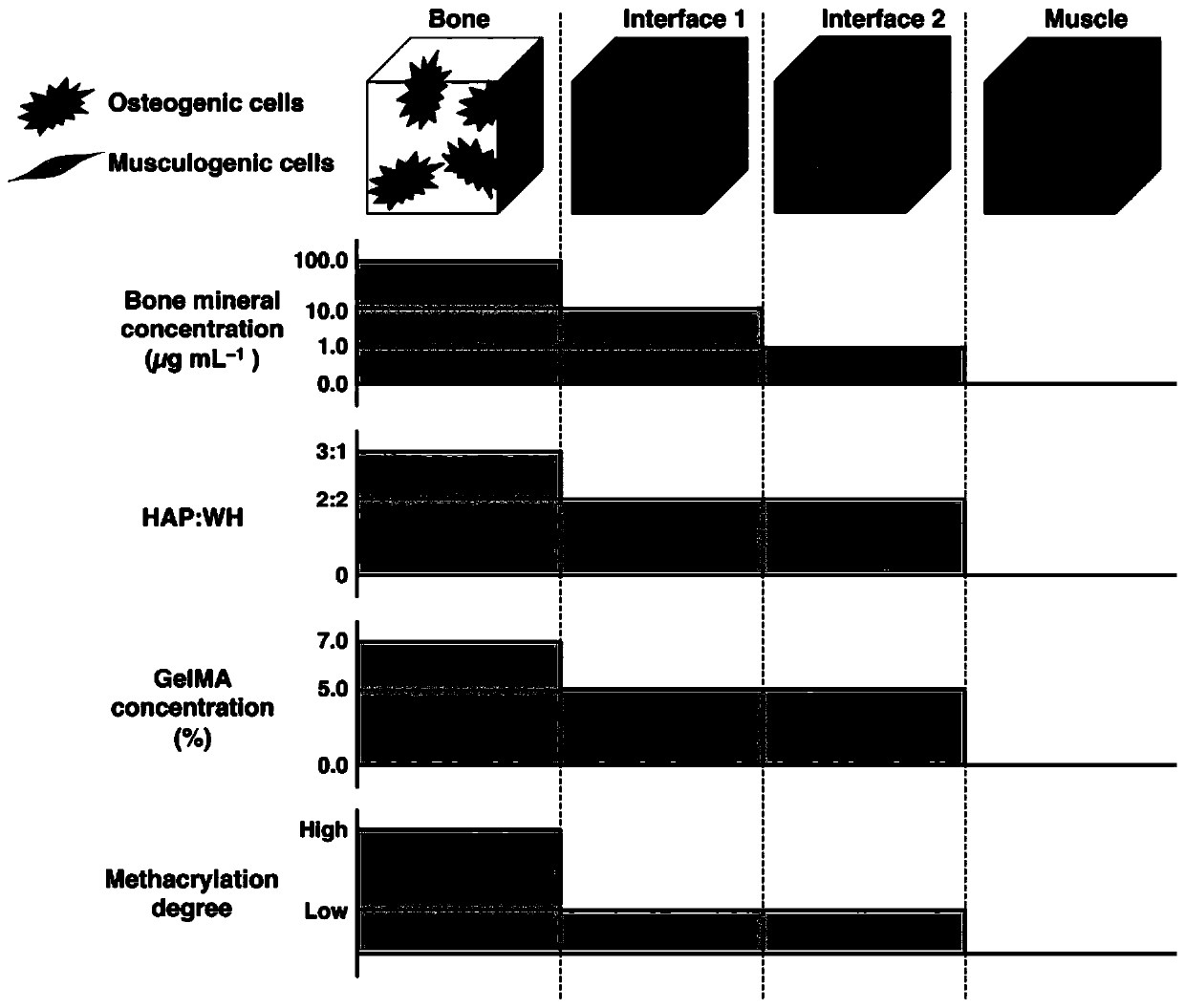
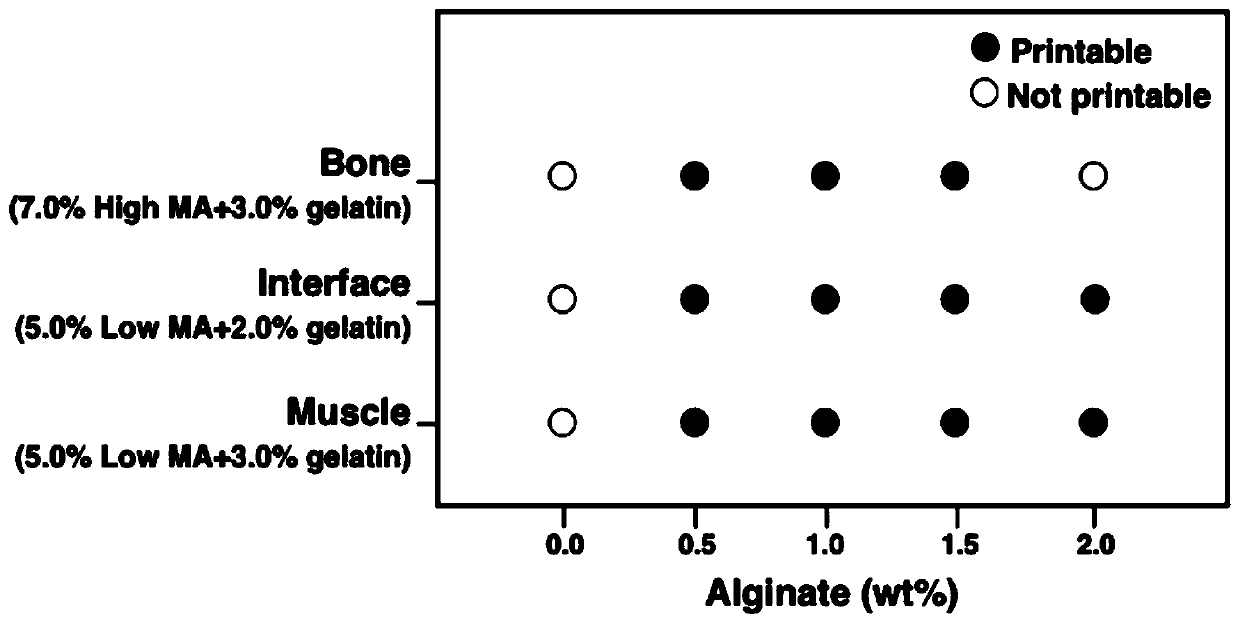
Method for preparing bionic skeletal muscle composite tissue through multi-channel extrusion 3D biological printing
ActiveCN110743040AReduce fibrosisEasy to customizeAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationMyogenic cellComputer printing
The invention discloses a method for preparing a bionic skeletal muscle composite tissue through multi-channel extrusion 3D biological printing. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing bone scaffold bionic bio-ink, periosteum bionic bio-ink, sarcolemma bionic bio-ink and muscle bionic bio-ink; respectively mixing MSCs and C2C12 with the corresponding bionic bio-inks; and printing and forming a bionic bone, bionic periosteum, bionic sarcolemma and bionic muscle four-layer composite tissue engineering scaffold by using a multi-channel extrusion 3D biological printer. Themethod for preparing the bionic skeletal muscle composite tissue through multi-channel extrusion 3D biological printing can minimize fibrosis during traumatic skeletal muscle injury recovery; the bionic skeletal muscle composite tissue prepared through multi-channel extrusion 3D biological printing can replace structures and functions of bones and skeletal muscles at the same time, and supports proliferation and differentiation of myoblasts and osteoblasts; and an implant is easy to customize by utilizing a 3D biological printing technology, so that the implant is suitable for any defect shape.
Owner:福建省安悦莱生物科技有限公司
Health care product capable of improving bones and joints and preparation method of health care product
InactiveCN105079028AAvoid failureFreedom of movementOrganic active ingredientsSkeletal disorderChitosamineBone density
The invention relates to the technical field of a health care product, and in particular provides a health care product capable of improving bones and joints and a preparation method of the health care product, wherein the health care product is mainly prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: as for active ingredients: 10-40 parts of calcium carbonate, 15-40 parts of chitosamine hydrochloride and 10-30 parts of chondroitin sulfate, and as for accessories: 0.1-1 part of glucose essence and 1-5 parts of a thin-film coating agent. The preparation method of the health care product capable of improving bones and joints comprises five steps, namely preparing powder, mixing, granulating, mixing materials and tabletting, and coating. The health care product provided by the invention is high in calcium content, good in effect and good in absorption, and the health care product, by supplementing calcium and promoting osteoblastic cell proliferation, has a function of enhancing bone density so as to take better effects on preventing and improving osteoporosis and improving life level of middle aged and elderly people; and the health care product is low in cost and is applicable to extensive popularization and application. The preparation method of the health care product provided by the invention is simple and efficient, high in active ingredient utilization rate and suitable for industrial popularization.
Owner:北京世纪合辉医药科技股份有限公司
Electrochemical method for preparing hydroxyapatite dendritic micro nano composite coating on surface of metallic titanium
InactiveCN102899698AImprove biological activitySuitable for biodegradabilityElectrolytic inorganic material coatingMicro nanoElectrolytic agent
The invention discloses an electrochemical method for preparing a hydroxyapatite dendritic micro nano composite coating on the surface of metallic titanium, comprising the following steps: preparing two electrolytes containing Ca-P with a high concentration and a low concentration, wherein Ca-P is the component element of hydroxyapatite; adding the electrolytes in a container equipped with a constant temperature heating system; by taking Pt as anode and metallic Ti as cathode, immersing the two electrodes in the electrolytes; after depositing in the Ca-P electrolyte with the low concentration, continue to deposite in the Ca-P electrolyte with the high concentration to form the hydroxyapatite dendritic micro nano composite coating on the surface of the metallic titanium matrix; taking out the matrix and cleaning the matrix to remove the electrolytes adhered on the surface, and drying in a drying box. According to the invention, the prepared coating disclosed has surface geometric externality with double dimensions from nanometer to micrometer, benefits the adhesion of osteoblast and subsequent growth by differentiation, simultaneously changes the dissolving characteristic of the coating, has good wettability, and has great application values.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
HA (Hydroxyapatite) coating with high degree of crystallinity and nano-structure and preparation method of HA coating
InactiveCN105641741AHigh purityHigh crystallinityMolten spray coatingProsthesisOsseointegrationNano structuring
The invention relates to an HA (Hydroxyapatite) coating with high degree of crystallinity and a nano-structure and a preparation method of the HA coating. The HA coating comprises 95% or above of hydroxyapatite, the degree of crystallinity is 85% or above, and the surface structure of the HA coating comprises the nano-structure. The HA coating has high purity and high degree of crystallinity, so that the problems that the phase decomposition and low degree of crystallinity of the traditional coating cause the coating degradation, and further, the coating falls off, an implant becomes loose, and the like, are solved; meanwhile, the coating has the nano-structure, and can promote the adhesion and proliferation of osteoblasts and the osteogenic differentiation, so that the osseointegration performance of the implant of the HA coating is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
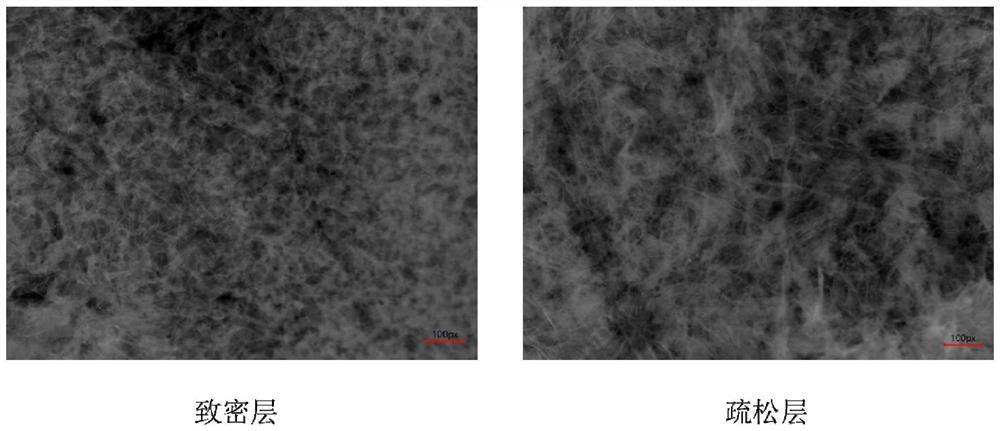
Fish skin-derived medical collagen membrane with compact outer layer and loose inner layer and preparation method of medical collagen membrane
PendingCN113372436AEasy to integratePromote proliferationConnective tissue peptidesSurgeryHydrolysatePepsin
The invention provides a medical collagen membrane with a compact outer layer and a loose inner layer in structure. Fish skin pepsin-solubilized collagen is dissolved in an acid solution to prepare collagen solutions with different concentrations, then laying is performed according to the concentrations from high to low, and pressing is performed to prepare a collagen membrane, wherein the fish skin pepsin-solubilized collagen is prepared by treating fish skin with alkali liquor, and then carrying out enzymolysis with pepsin under a weak acid condition; an enzymatic hydrolysate is centrifuged, a supernate is collected, and the supernate is salted out; precipitates are collected, the precipitates are redissolved with a weak acid solution, and then dialysis treatment is performed; and a dialysate is freeze-dried to prepare the fish skin pepsin-solubilized collagen. The collagen membrane prepared in the invention has three layers of different structures, the aperture of the inner layer is relatively large to promote the growth of osteoblasts, the small aperture of the outer layer can prevent soft tissue cells from entering and allow stem cells and nutrient substances to pass through, and a certain transition layer exists between the inner layer structure and the outer layer structure to facilitate tissue integration.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for raising biocompatibility of polyester fiber artificial ligament by graphene modification
The invention discloses a method for raising biocompatibility of polyester fiber artificial ligament by graphene modification. According to the method, a large area of single-layer graphene which grows by a CVD method is transferred to polyester fiber-woven artificial ligament by a matrix corrosion method so as to raise biocompatibility of the artificial ligament. A graphene coating is applied on the polyester fiber micropore-woven artificial ligament, thus greatly raising biocompatibility of the artificial ligament material, especially cytocompatibility. Adhesion of cells to the surface of the material and propagation of cells are promoted; BMSC is induced to differentiate into osteoblastic cells; and bone tunnel healing during implantation of the artificial ligament into body is accelerated. In addition, the graphene coating hasn't caused adverse effect on porosity, strength and creep resistance of the material. The method provided by the invention is simple to operate and has good repeatability.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com