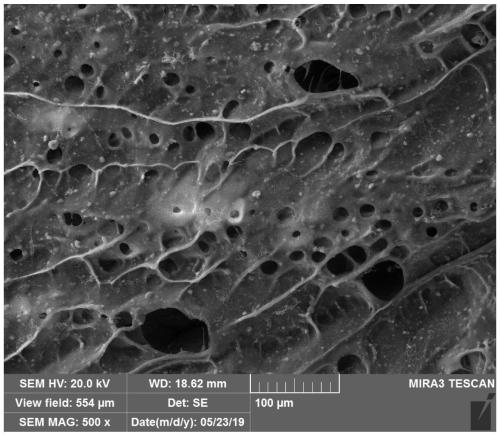
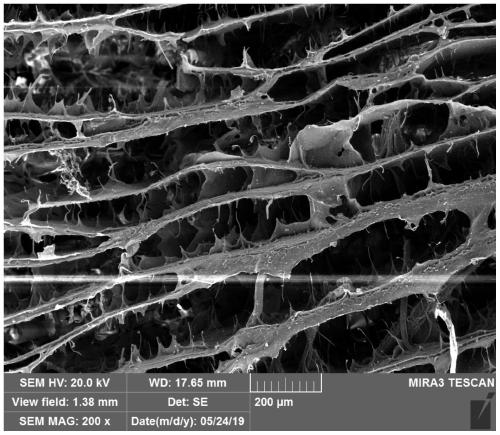
Preparation method of wood-based bionic bone scaffold material
A scaffold material and bionic bone-based technology, applied in the field of bionic bone scaffolds, to achieve the effect of high three-dimensional porous structure, no cytotoxicity, and good bone cell compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] (1) Soak the wood fiber in the alkali solution prepared with 0.01mol / L sodium hydroxide solution and 0.01mol / L sodium sulfite solution according to the mass ratio of 1:1, and then perform mechanical grinding at a speed of 2800r / min Treat for 2 hours to prepare fiber pulp with a mass fraction of 10%;
[0050](2) In a water bath at 40°C, chitosan is dissolved in pure water to prepare a chitosan polymer solution with a mass fraction of 10%, and the fiber pulp with a mass fraction of 10% obtained in step 1 and 10% mass fraction The chitosan polymer solution was mixed at a mass ratio of 1:1, stirred evenly, and kept magnetically stirred in a water bath at 40°C for 0.5h to obtain a mixed solution;
[0051] (3) Add hydroxyapatite to the mixed solution obtained in step 2, and carry out magnetic stirring at 40°C in a water bath for 0.5h to obtain a scaffold material precursor mixed solution, wherein the amount of hydroxyapatite added is the same as that of chitosan and wood The...
Embodiment 2
[0056] (1) Soak the wood fiber in the alkali solution prepared with 0.01mol / L sodium hydroxide solution and 0.01mol / L sodium sulfite solution according to the mass ratio of 1:2, and then perform mechanical grinding at a speed of 2800r / min Treat for 2 hours to prepare fiber pulp with a mass fraction of 10%;
[0057] (2) In a water bath at 50°C, chitosan is dissolved in pure water to prepare a mass fraction of 10% chitosan macromolecule solution, and the fiber pulp with a mass fraction of 10% obtained in step 1 and 10% of the mass fraction The chitosan polymer solution was mixed and stirred evenly at a mass ratio of 1:2, and kept magnetically stirred in a water bath at 50°C for 0.5h to obtain a mixed solution;
[0058] (3) Add hydroxyapatite to the mixed solution obtained in step 2, and carry out magnetic stirring at 40°C in a water bath for 0.5h to obtain a scaffold material precursor mixed solution, wherein the amount of hydroxyapatite added is the same as that of chitosan and...
Embodiment 3
[0063] (1) Soak the wood fiber in the alkali solution prepared according to the mass ratio of 2:1 0.01mol / L sodium hydroxide solution and 0.01mol / L sodium sulfite solution, and then perform mechanical grinding at a speed of 2800r / min Treat for 2 hours to prepare fiber pulp with a mass fraction of 20%;
[0064] (2) In a water bath at 60°C, chitosan is dissolved in pure water to prepare a chitosan polymer solution with a mass fraction of 20%, and the fiber pulp with a mass fraction of 20% obtained in step 1 and 20% of the mass fraction The chitosan polymer solution was mixed and stirred evenly at a mass ratio of 1:1, and kept magnetically stirred in a water bath at 60°C for 0.5h to obtain a mixed solution;
[0065] (3) Add hydroxyapatite to the mixed solution obtained in step 2, and stir magnetically at 60° C. in a water bath for 0.5 h to obtain a scaffold material precursor mixed solution, wherein the amount of hydroxyapatite added is the same as that of chitosan and wood fiber...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com