Method for treating wastewater containing cyanogen and ammonia
A treatment method and wastewater technology, applied in the direction of oxidized water/sewage treatment, bromine oxygen compounds, etc., can solve the problems of cost increase, chlorine gas generation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
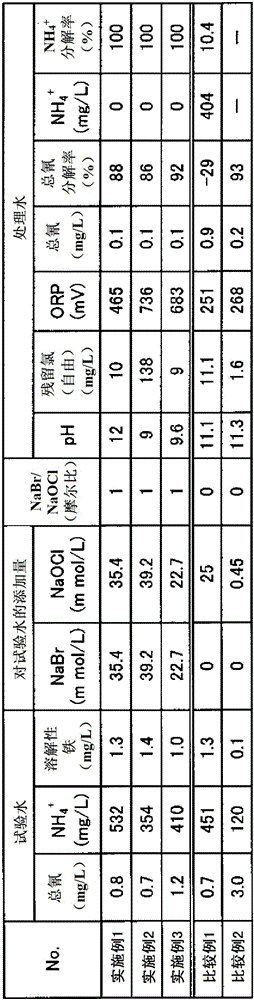
[0049] [Example 1 (treatment with liquid containing sodium hypobromite)]
[0050] As test water, steel mill wastewater of the following water quality was used.
[0051] pH: 8.3,
[0052] Total cyanide concentration: 0.8mg / L,
[0053] Ammonium ion concentration: 532mg / L,
[0054] TOC: 22mg / L,
[0055] Soluble iron: 1.3mg / L
[0056] ORP: 90mV
[0057] For a liquid containing sodium hypobromite as a chemical solution, use a sodium bromide solution with a concentration of 40wt% and a sodium hypochlorite solution with a concentration of 12wt% in NaBr:NaOCl=1:1 (molar ratio) to generate hypobromous acid Sodium hypobromite and sodium hypochlorite in water.
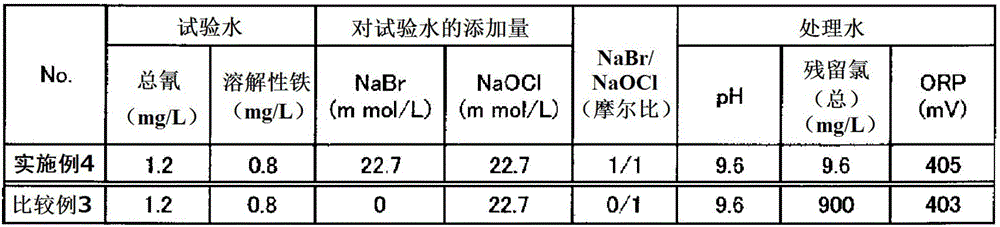
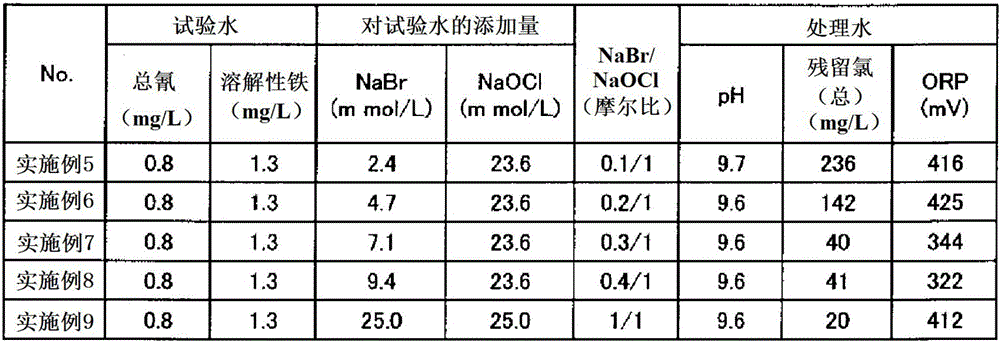
[0058] 1000 mL of test water was stored in a glass container, the temperature of the water was kept at 50° C., and the pH was adjusted to 12 with NaOH, then the chemical solution (sodium hypobromite and sodium hypochlorite aqueous solution) was added under the conditions in Table 1. The reaction time of the cyanide decompo...
Embodiment 2
[0061] As test water, steel mill wastewater of the following water quality was used.
[0062] pH: 8.15,
[0063] Total cyanide concentration: 0.7mg / L,
[0064] Ammonium ion concentration: 354mg / L,
[0065] TOC: 17mg / L,
[0066] Soluble iron: 1.4mg / L
[0067] ORP: 230mV
[0068] For the sodium hypobromite-containing liquid as the chemical solution, the same liquid as in Example 1 was used. And it processed similarly to Example 1 except having made pH into 9 with NaOH. Table 1 shows the amount of chemical reagents added, free residual chlorine concentration after the aforementioned reaction time, ORP, total cyanide concentration, total cyanide decomposition rate, ammonium ion concentration, and ammonium ion decomposition rate.
Embodiment 3
[0070] As test water, steel mill wastewater of the following water quality was used.
[0071] pH: 8.6,
[0072] Total cyanide concentration: 1.2mg / L,
[0073] Ammonium ion concentration: 410mg / L,
[0074] TOC: 18mg / L,
[0075] Soluble iron: 1.0mg / L
[0076] ORP: 264mV
[0077] Except having added NaOH so that pH might become 9.6, it processed similarly to Example 2, and tested water. The results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com