MiRNA apla-mir-25-42 related to follicular development of laying ducks and detection primers, inhibitors and application thereof
A follicle development and inhibitor technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problem of lack of miRNA markers, and achieve the effects of inhibiting expression, improving genetically assisted breeding, and improving the fecundity of laying ducks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Example 1 Obtaining PCR of laying duck miRNA apla-mir-25-42 and its fluorescence quantitative detection kit and method
[0057] 1. Obtained from laying duck apla-mir-25-42
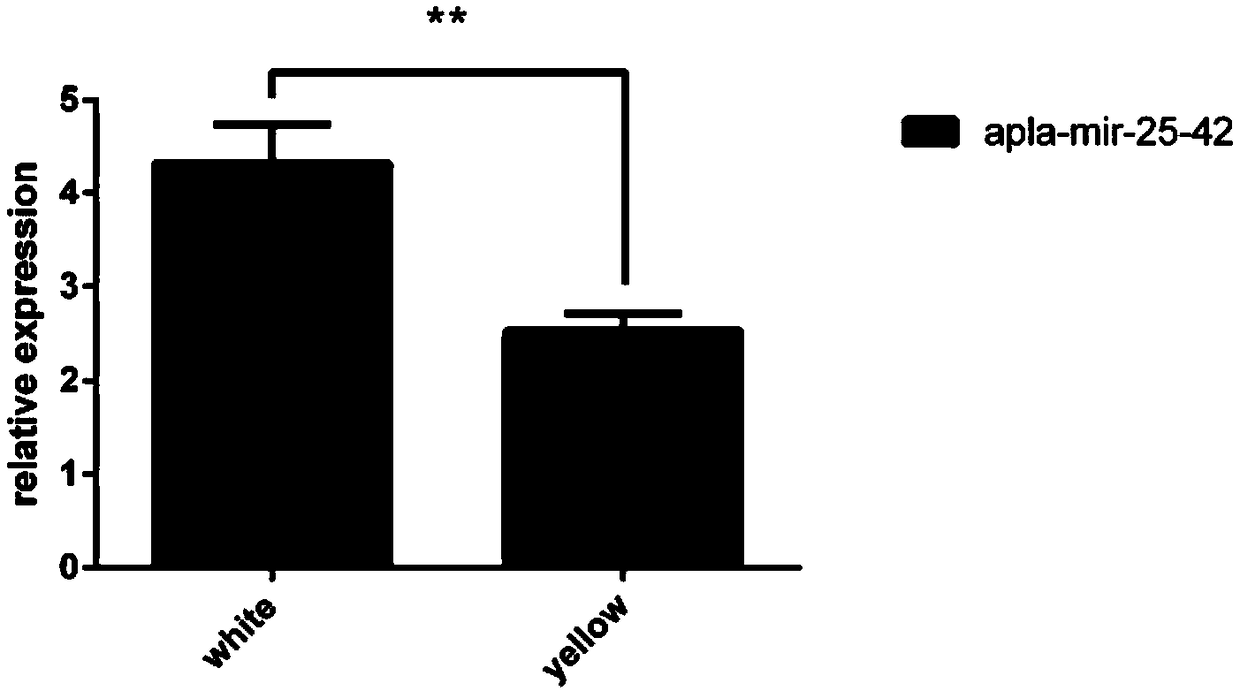
[0058] The nucleotide sequence corresponding to the laying duck apla-mir-25-42 described in this example is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The laying duck apla-mir-25-42 of the present invention is the laying duck completed by the applicant based on the previous stage The whole transcriptome sequencing results of follicle tissue, a new miRNA molecule obtained through a large number of bioinformatics analysis and screening of the sequencing results of two groups of follicle tissue samples at different developmental stages. The applicant named it the laying duck apla-mir-25-42.
[0059] 2. Fluorescent quantitative PCR detection primer pair and its detection kit and method for laying duck miRNA apla-mir-25-42
[0060] In this example, a pair of fluorescent quantitative PCR detection primers was designed to i...
Embodiment 2
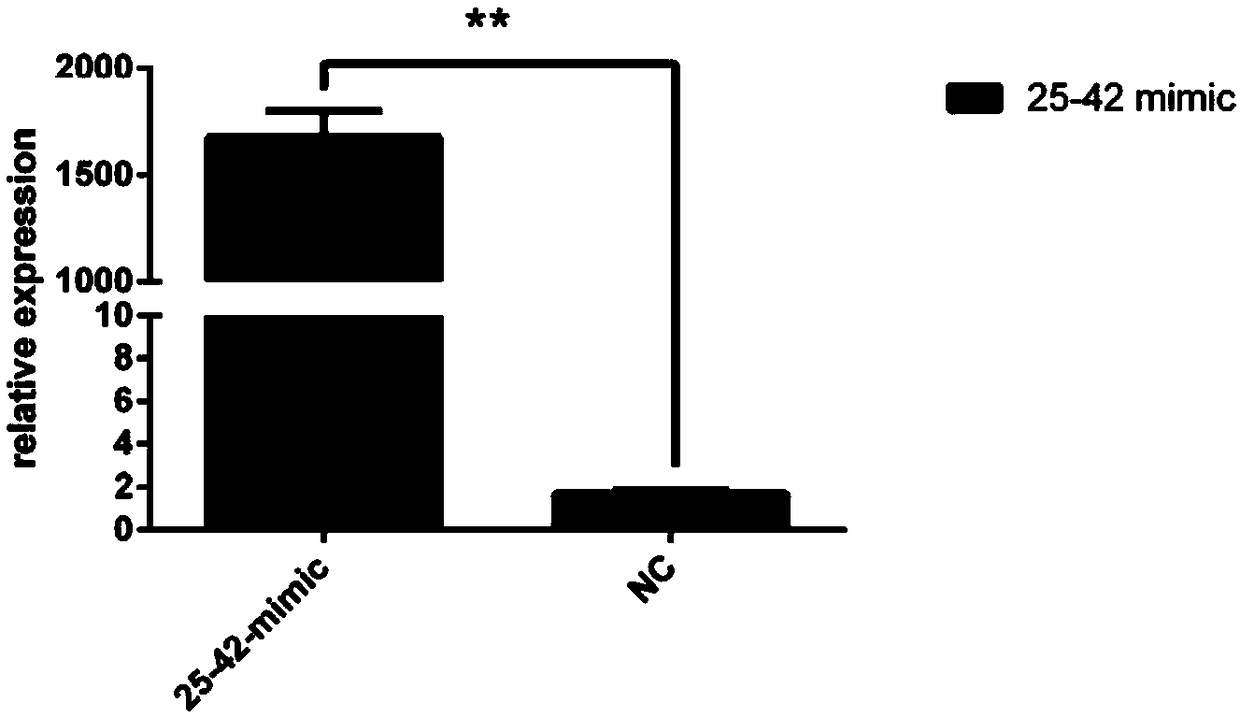
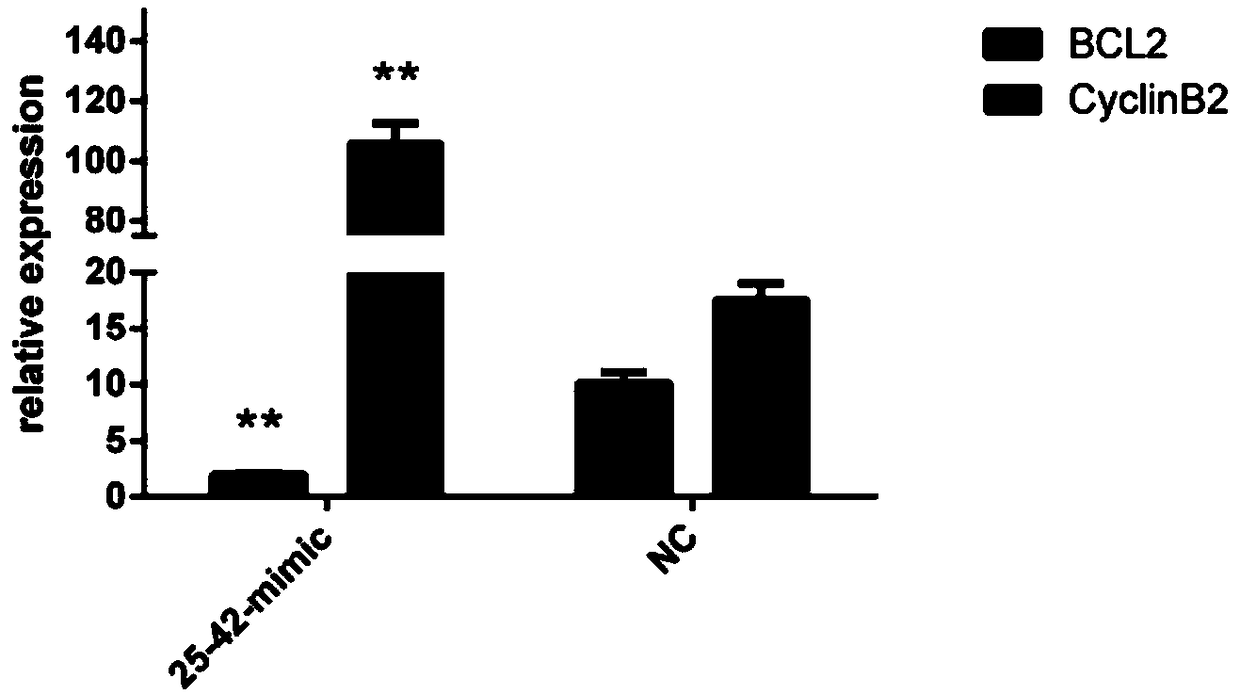
[0100] Example 2 Application of apla-mir-25-42 as a molecular marker in detecting the proliferation and differentiation of egg follicle granulosa cells in laying ducks
[0101] 1. Isolation of egg follicle granulosa cells in laying ducks
[0102] The following steps are used for the isolation of laying duck follicular granulosa cells:
[0103] 1. Select laying ducks at the peak egg production period, and kill them by bleeding from the jugular vein; take out the entire ovarian tissue and place it in a sterile petri dish filled with pre-cooled PBS;
[0104] 2. Rinse blood stains with PBS buffer solution with double antibody, rinse 3 times;
[0105]3. Transfer the rinsed follicles to a plate filled with pre-cooled PBS buffer, and peel off the follicle adventitia, connective tissue and vascular network;
[0106] 4. Use a scalpel to make a 1-2cm long incision on the surface of the follicle (the action should be fast), release the yolk, rinse the remaining yolk liquid with PBS buf...
Embodiment 3
[0134] Example 3 Design and construction of apla-mir-25-42 target gene TGFB2 dual luciferase reporter gene detection system in laying ducks
[0135] First, for the selected miRNA apla-mir-25-42, association analysis was performed in the whole transcriptome sequencing results, and the target gene TGFB2 interacting with apla-mir-25-42 was screened out from the mRNA sequencing results. miRBase analysis showed that the binding site between apla-mir-25-42 and TGFB2 was ATCCCCA.
[0136] Subsequently, the 3'-UTR sequence of TGFB2 (that is, the inhibitor of apla-mir-25-42) was obtained from NCBI, and the ATCCCCA in the inhibitor of apla-mir-25-42 was mutated into CAGGCGC by mutation method, respectively The above two gene fragments were cloned into the pmirGLO vector to obtain the corresponding vector (pmirGLO-TGFB2-wt) containing the inhibitor sequence of apla-mir-25-42 and the vector containing the inhibitor mutation sequence of apla-mir-25-42 Vector (pmirGLO-TGFB2-mut). Vector c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com