Dual-layer micro-dust low-noise ceramic brake material and preparation method thereof
A technology of brake pads and ceramics, which is applied to the analysis of materials, brake discs, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of high noise and dust, and achieve the effects of good wear resistance, increased contact area and less dust
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
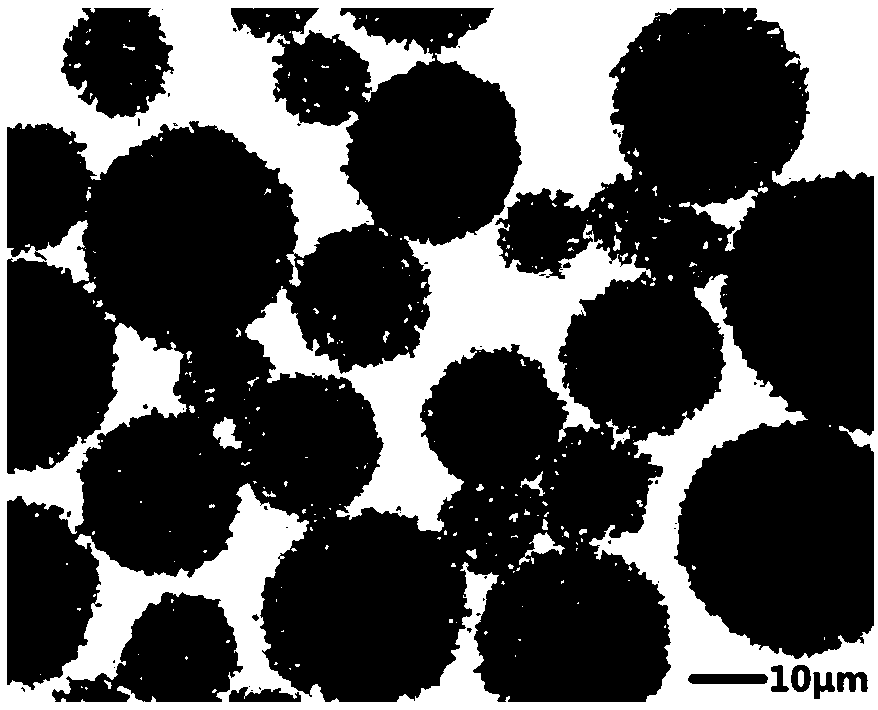
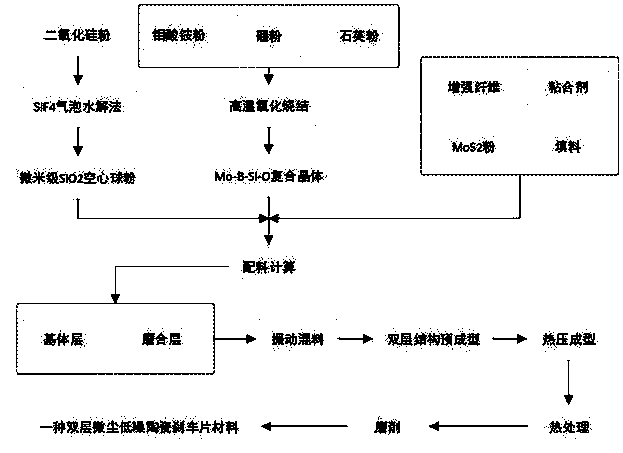
[0038] A double-layer fine-dust low-noise ceramic brake pad material, with ceramic fibers, aramid fibers, and carbon fibers as reinforcing fibers, cashew nut oil modified phenolic resin and nitrile rubber powder as binders, and MoS 2 powder and micron SiO 2 Hollow spherical powder is used as a friction coefficient regulator, Mo-B-Si-O composite crystal is used as a friction noise reducer, supplemented by fillers such as vermiculite, mica, barite and alumina, and a double-layer friction structure is adopted. Wherein, the matrix layer and the running-in layer in the double-layer friction structure are composed of the following components by weight percentage:
[0039] Substrate layer: ceramic fiber 15%, aramid fiber 18%, carbon fiber 8%, cashew oil modified phenolic resin 12%, nitrile rubber powder 4%, MoS 2 Powder 8%, Micron SiO 2 Hollow sphere powder 5%, Mo-B-Si-O composite crystal 8%, vermiculite 5%, mica 4%, barite 10%, alumina 3%;
[0040] Running-in layer: ceramic fiber...
Embodiment 2
[0051] A double-layer fine-dust low-noise ceramic brake pad material, with ceramic fibers, aramid fibers, and carbon fibers as reinforcing fibers, cashew nut oil modified phenolic resin and nitrile rubber powder as binders, and MoS 2 powder and micron SiO 2 Hollow spherical powder is used as a friction coefficient regulator, Mo-B-Si-O composite crystal is used as a friction noise reducer, supplemented by fillers such as vermiculite, mica, barite and alumina, and a double-layer friction structure is adopted. Wherein, the matrix layer and the running-in layer in the double-layer friction structure are composed of the following components by weight percentage:
[0052] Substrate layer: ceramic fiber 17%, aramid fiber 14%, carbon fiber 10%, cashew oil modified phenolic resin 12%, nitrile rubber powder 4%, MoS 2 Powder 5%, Micron SiO 2 Hollow sphere powder 7%, Mo-B-Si-O composite crystal 9%, vermiculite 5%, mica 4%, barite 10%, alumina 3%;
[0053] Running-in layer: ceramic fibe...
Embodiment 3
[0064] A double-layer fine-dust low-noise ceramic brake pad material, with ceramic fibers, aramid fibers, and carbon fibers as reinforcing fibers, cashew nut oil modified phenolic resin and nitrile rubber powder as binders, and MoS 2 powder and micron SiO 2 Hollow spherical powder is used as a friction coefficient regulator, Mo-B-Si-O composite crystal is used as a friction noise reducer, supplemented by fillers such as vermiculite, mica, barite and alumina, and a double-layer friction structure is adopted. Wherein, the matrix layer and the running-in layer in the double-layer friction structure are composed of the following components by weight percentage:
[0065] Substrate layer: ceramic fiber 16%, aramid fiber 13%, carbon fiber 10%, cashew oil modified phenolic resin 13%, nitrile rubber powder 4%, MoS 2 Powder 6%, Micron SiO 2 Hollow sphere powder 6%, Mo-B-Si-O composite crystal 8%, vermiculite 5%, mica 4%, barite 12%, alumina 3%;
[0066] Running-in layer: ceramic fibe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wall thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com