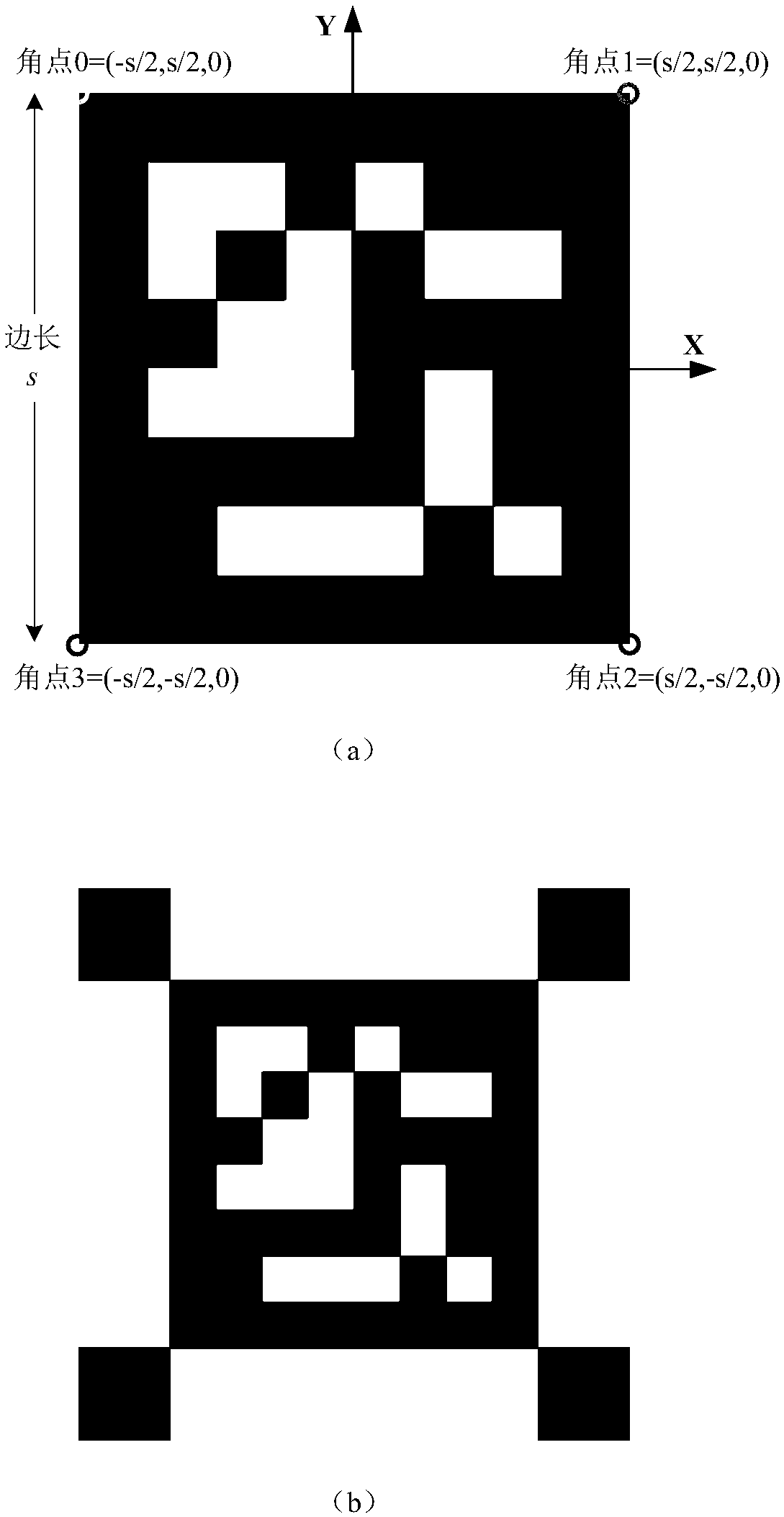Mobile robot visual positioning and navigating method based on ArUco code
A mobile robot and visual positioning technology, applied in surveying and mapping and navigation, navigation, navigation calculation tools, etc., can solve problems such as inability to complete curved driving, high environmental requirements, and inflexibility, etc., to overcome the strong dependence on auxiliary physical conditions and reduce Environmental requirements, convenient and flexible layout
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0048] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment the present invention is described in further detail:
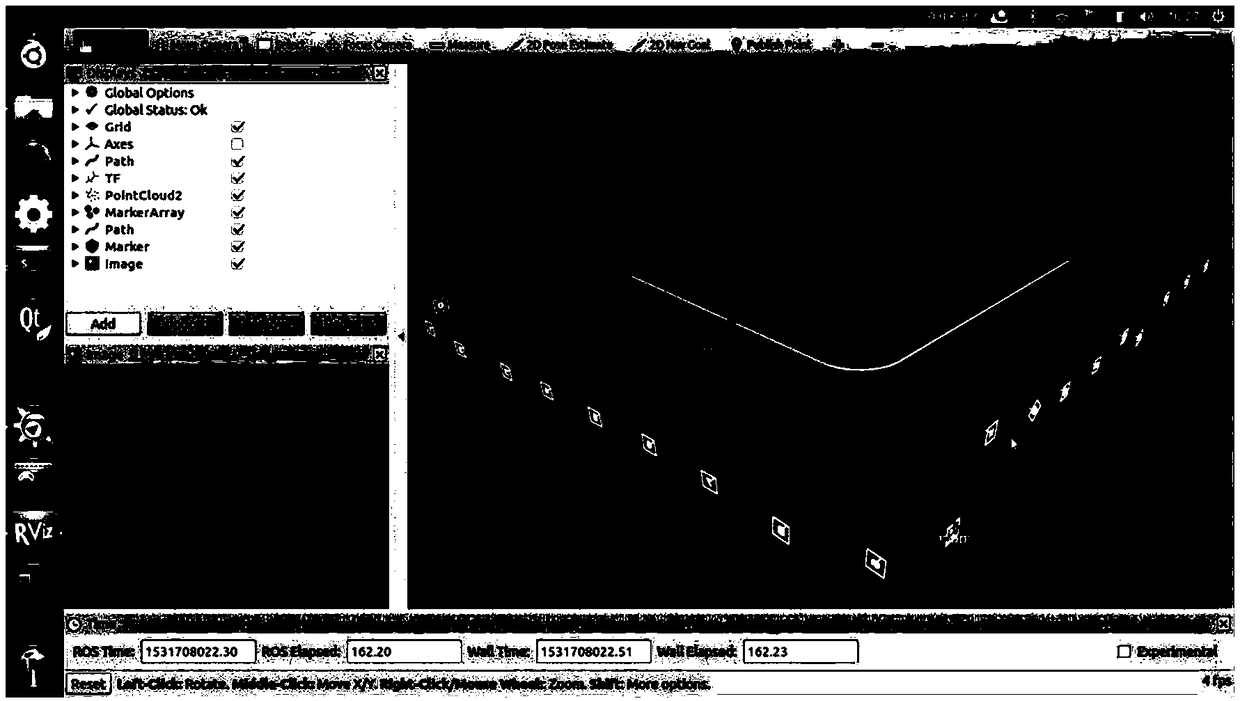
[0049] Such as figure 1 Shown is the functional schematic diagram of the present invention using ArUco codes to realize robot vision positioning and navigation. In this embodiment, by creating the distribution map of ArUco codes in the environment and the navigation path of the robot in advance, using a monocular camera to observe the randomly distributed ArUco codes in the room, the three-dimensional coordinates and posture of the robot in the world coordinate system are obtained in real time, and according to the current position of the robot The direction vector between the coordinate point of the navigation path and the navigation path determines the yaw angle α of the robot during its travel. The robot can adjust its own movement direction in real time according to the yaw angle α, so as to reach the target position along the preset naviga...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com