Method for producing formaldehyde-free artificial boards from hemp stalks
A manufacturing method and technology of wood-based panels, applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, flat products, and pretreatment of molding materials, etc., can solve problems affecting large-scale industrial applications, high manufacturing costs of wood-based panels, and heavy boards, and achieve improvement Pasting effect, improving adhesive effect, improving the effect of weak acidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
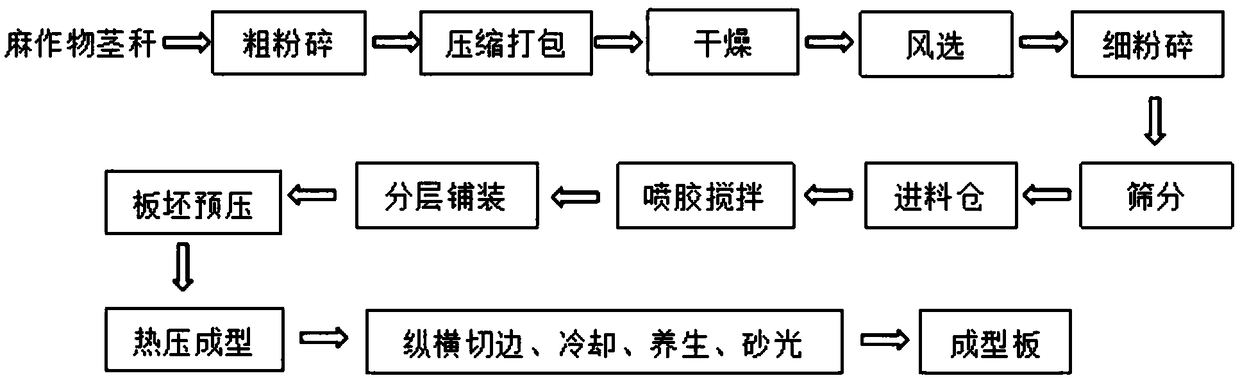
[0028] In the first step, the collected jute stalks are coarsely crushed, then compressed and packaged for storage. Coarsely crushed jute stalks are dried by a tumble dryer so that their moisture content is within the range of 9% to 17%. The dried jute stalks are then passed through wind selection and other equipment to remove impurities such as iron and stones, and then enter the fine grinder to be crushed to a fineness of 20-50 meshes. Sorting jute stalks according to fineness and removing dust. The jute stalks are sieved into 20-30 mesh fineness and 30-50 mesh fineness according to the fineness, and sent to the core layer silo and surface layer silo accordingly.
[0029] Step 2: Weigh the crushed jute stalks in different silos, measure their moisture content with a moisture tester, and send them to different mixers respectively, and use PLC to control the glue spraying device to spray glue, and control according to the corresponding weight Glue spraying amount, control th...
Embodiment 2
[0036]In step one, the collected kenaf stalks are coarsely crushed, then compressed and packaged for storage. Coarsely crushed kenaf stalks are dried by a tumble dryer so that the moisture content is within the range of 9% to 17%. The dried kenaf stalks are then passed through wind selection and other equipment to remove impurities such as iron and stones, and then enter the fine grinder to be crushed to a fineness of 20-50 meshes. Sorting kenaf stalks according to fineness and removing dust. The kenaf stalks are sieved into 20-30 mesh fineness and 30-50 mesh fineness according to the fineness, and sent to the core layer silo and surface layer silo accordingly.
[0037] Step 2: Weigh the crushed kenaf stalks in different silos, measure their moisture content with a moisture tester, send them to different mixers respectively, and use PLC to control the glue spraying device to spray glue, according to the corresponding weight Control the amount of glue sprayed, and control the...
Embodiment 3
[0044] In the first step, the collected kenaf stalks and flax stalks are coarsely crushed, and then compressed and packaged for storage. The coarsely crushed mixed hemp stalks are dried by a tumble dryer so that the moisture content is within the range of 9% to 17%. The dried mixed hemp stalks are then passed through wind selection and other equipment to remove impurities such as iron and stones, and then enter the fine grinder to be crushed to a fineness of 20-50 mesh. Sorting the mixed hemp stalks according to the fineness and removing the dust. The mixed hemp stalks are sieved into 20-30 mesh fineness and 30-50 mesh fineness according to the fineness, and sent to the core layer silo and surface layer silo accordingly.
[0045] Step 2: Weigh the crushed and mixed hemp stalks in different silos, measure their moisture content through a moisture tester, and send them to different mixers respectively, and use PLC to control the glue spraying device to spray glue, according to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com