An optical component and its manufacturing method
An optical component and manufacturing method technology, applied in the field of optical communication, can solve problems such as failure, unfavorable clamp clamping, small lens size, etc., and achieve the effect of precise coupling or collimation and avoiding lens position deviation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
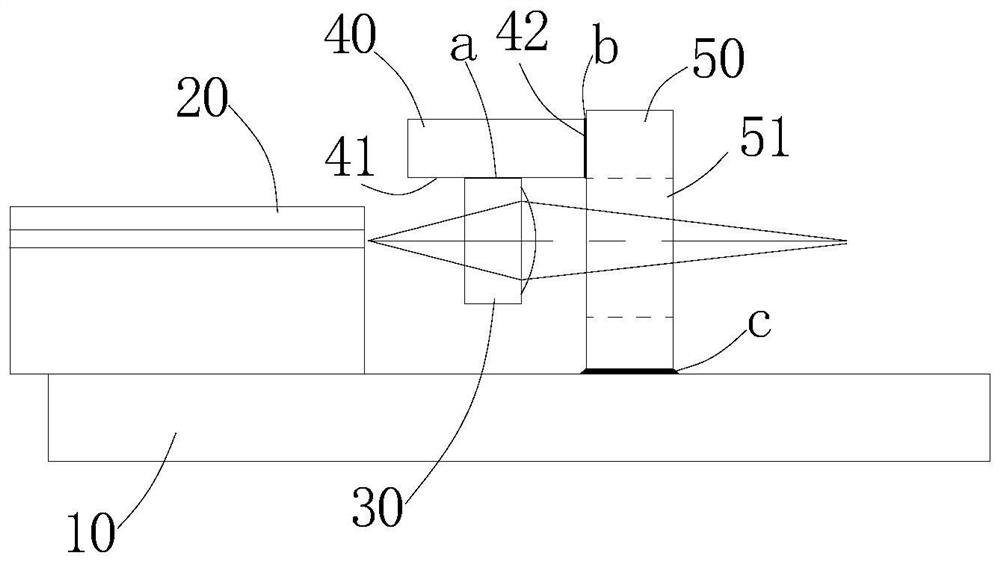
[0059] Specifically, such as figure 2 In the illustrated embodiment 1, the optical component in this embodiment includes a light emitting end. The light emitting end includes a semiconductor laser as a light-extracting element 20 , a lens element 30 and an optical waveguide 60 . Wherein, the semiconductor laser is fixed on the substrate 10 through a small substrate 11, and the lens element 30 is installed on the substrate 10 through the above-mentioned auxiliary member 40 and the support member 50. Here, the lens element 30 is a coupling lens, which can be a large power ball lens or an aspheric lens. lens etc. The optical signal emitted by the semiconductor laser is coupled into the optical waveguide 60 through the lens element 30 . The above-mentioned optical waveguide 60 may also be an optical integrated chip, optical fiber or other media for transmitting optical signals. Here, the substrate 10 may be a plane of the package housing, or may be a heat sink or other flat pl...
Embodiment 2
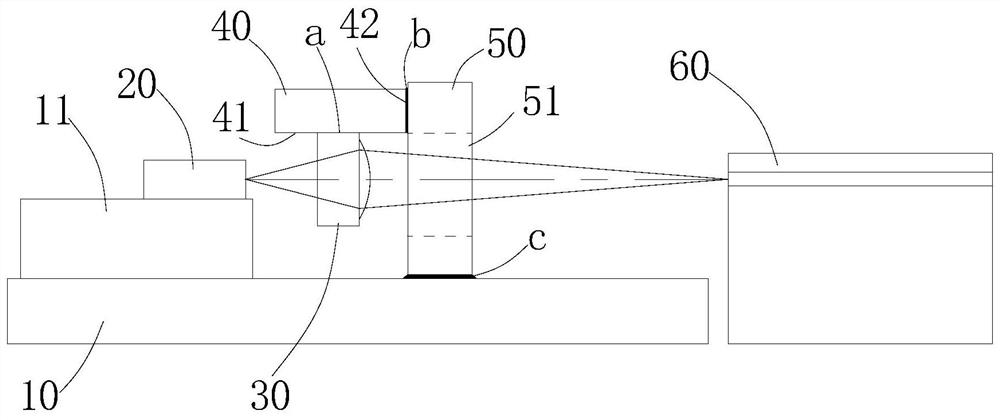
[0079] Such as image 3 In the illustrated embodiment 2, the optical assembly in this embodiment also includes a light emitting end. The difference from embodiment 1 is that in this embodiment, the connection surface 41 of the auxiliary part 40 is facing away from the substrate 10, and the lens element 30 is located on the auxiliary part 40 Above; the bonded position of the support member 50 and the auxiliary member 40 is below the light-transmitting surface or the light-through hole 51 , and other structures are consistent with Embodiment 1. When assembling, it is necessary to use a clamp to clamp the auxiliary part 40 from both sides of the auxiliary part 40 under the lens element 30. Also, the auxiliary part 40 is still not bonded to the substrate by bonding the bonding surface 42 of the auxiliary part 40 to the side of the support part 50. 10 contacts, avoiding the problem that the lens position may deviate due to temperature changes or moisture absorption due to too thick...
Embodiment 3
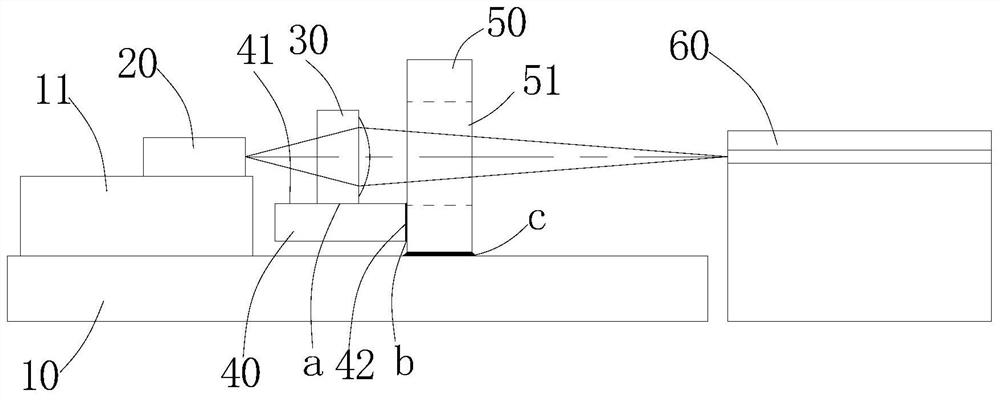
[0081] Such as Figure 4 The illustrated embodiment 3 is different from the embodiment 1 in that in this embodiment, the connection surface 41 of the auxiliary component 40 is perpendicular to the substrate 10 , and the lens element 30 is located on the side of the auxiliary component 40 . The bonding of the auxiliary part 40 and the support part 50 can be as Figure 5 and 6 Two bonding methods are shown.
[0082] Such as Figure 5 According to the bonding method, the bonding surface 42 of the auxiliary part 40 is still perpendicular to its connecting surface 41, and the side where the supporting part 50 and the auxiliary part 40 are bonded is on the same plane as the side where the light-transmitting surface or the light-passing hole 51 is located, and is located in the through-hole. The light surface or the side of the light hole 51 . The figure only shows that the bonding position of the auxiliary part 40 and the supporting part 50 is on one side of the light-transmitti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com