A porous waste plastic sheet toughened cement-based composite material
A composite material and plastic sheet technology, which is applied in the field of civil engineering and construction materials, can solve the problems of obvious difference in recycling rate and poor toughness, and achieve important technical and engineering values, large ultimate tensile strain, high impact strength and resistance The effect of bending strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
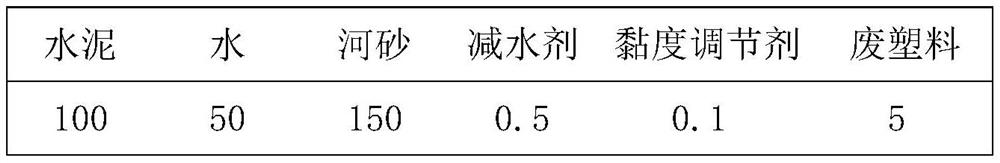
[0033] Embodiment 1: The material component ratio (mass part ratio) of this embodiment is shown in Table 1.
[0034] Table 1 present embodiment material component ratio (mass ratio):
[0035]
[0036] The cement used above is ordinary Portland cement of strength grade 42.5, the particle size of the river sand is 0.3-0.8 mm, the fineness coefficient is 1.65, and the viscosity of the viscosity modifier is 12000 mPa.s.
[0037] The preparation steps are as follows:
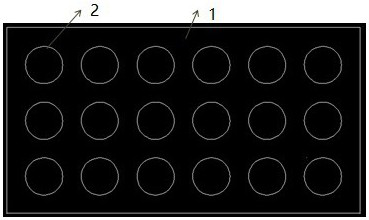
[0038] 1) Preparation of waste plastic sheets with holes. Cut the waste plastic sheet to the size of the mold cavity, remove the oil stains on the surface of the waste plastic, and prepare circular through holes with a diameter of 8 mm on the surface of the waste plastic sheet. The distribution of the through holes is shown in figure 1 ;
[0039] A perforated corrugated plastic sheet is prepared. Put 5 plastic sheets with holes on the mold of the hot press, set the temperature of the upper and lower mold plate...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2: The material component ratio (mass part ratio) of this embodiment is shown in Table 2.
[0047]Table 2 present embodiment material component ratio (mass ratio):
[0048]
[0049] The cement used above is ordinary Portland cement of strength grade 42.5, the particle size of the river sand is 0.3-0.8 mm, the fineness coefficient is 1.65, and the viscosity of the viscosity modifier is 12000 mPa.s.
[0050] The preparation steps are as follows:
[0051] 1) Preparation of waste plastic sheets with holes. Cut the waste plastic sheet to the size of the mold cavity, remove the oil stains on the surface of the waste plastic, and prepare square through holes with a side length of 10mm on the surface of the waste plastic sheet. The distribution of the through holes is shown in figure 1 ;
[0052] A perforated corrugated plastic sheet is prepared. Put 6 perforated plastic sheets on the mold of the hot press, set the temperature of the upper and lower mold plate...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3: The material component ratio (mass part ratio) of this embodiment is shown in Table 3.
[0060] Table 3 present embodiment material component ratio (mass ratio):
[0061]
[0062] The cement used above is ordinary Portland cement of strength grade 42.5, the particle size of the river sand is 0.3-0.8 mm, the fineness coefficient is 1.65, and the viscosity of the viscosity modifier is 12000 mPa.s.
[0063] The preparation steps are as follows:
[0064] 1) Preparation of waste plastic sheets with holes. Cut the waste plastic sheet to the size of the mold cavity, remove the oil stains on the surface of the waste plastic, and prepare diamond-shaped through holes with a side length of 10mm on the surface of the waste plastic sheet. The distribution of the through holes is shown in figure 1 ;
[0065] A perforated corrugated plastic sheet is prepared. Put 5 plastic sheets with holes on the mold of the hot press, set the temperature of the upper and lower m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com