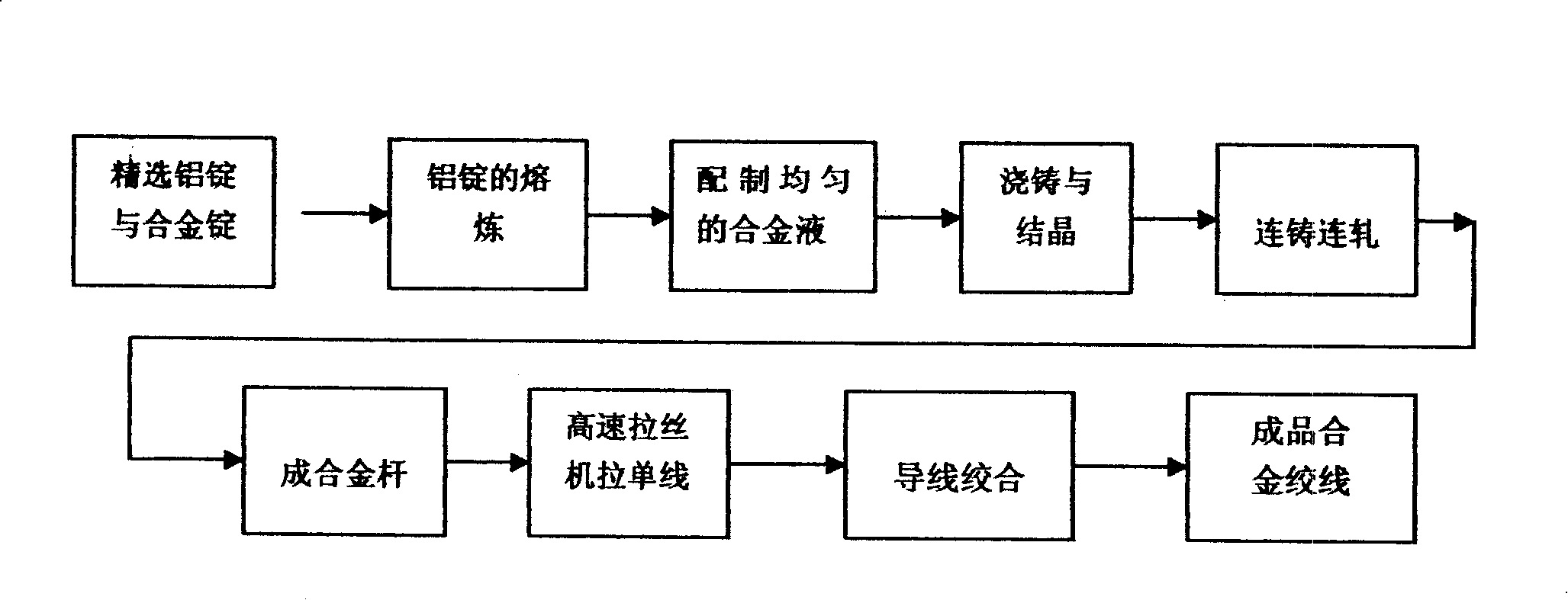
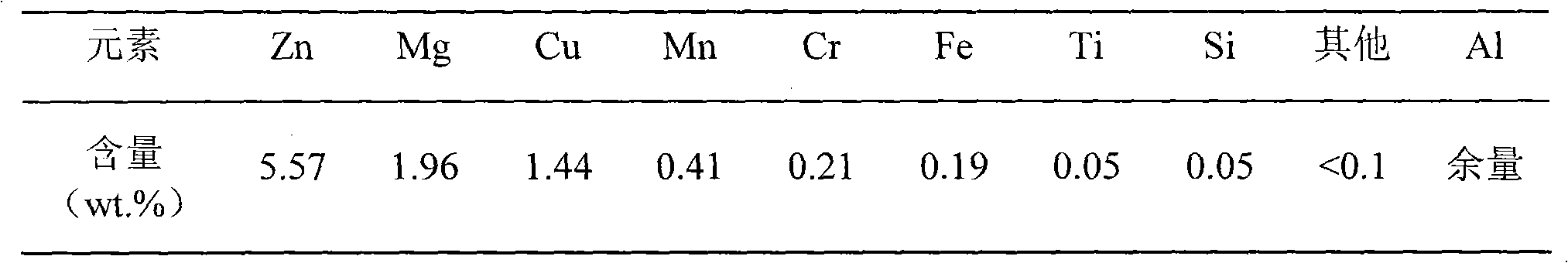
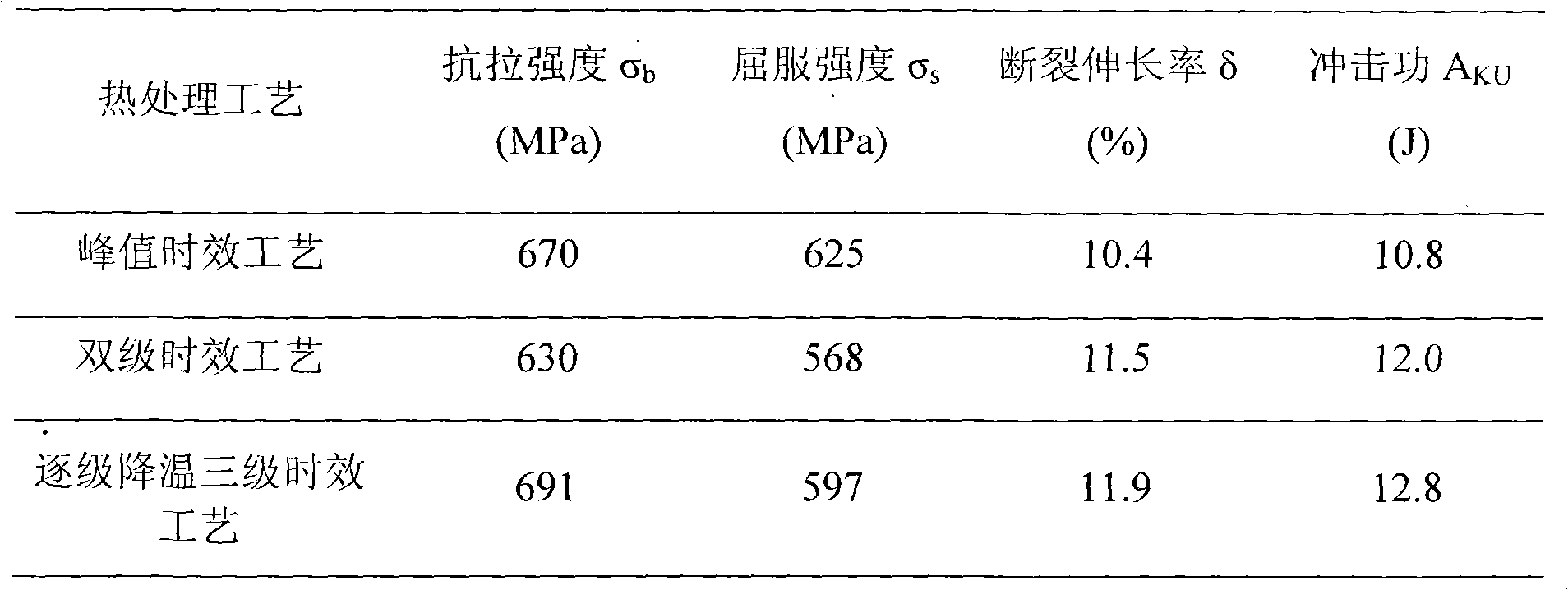
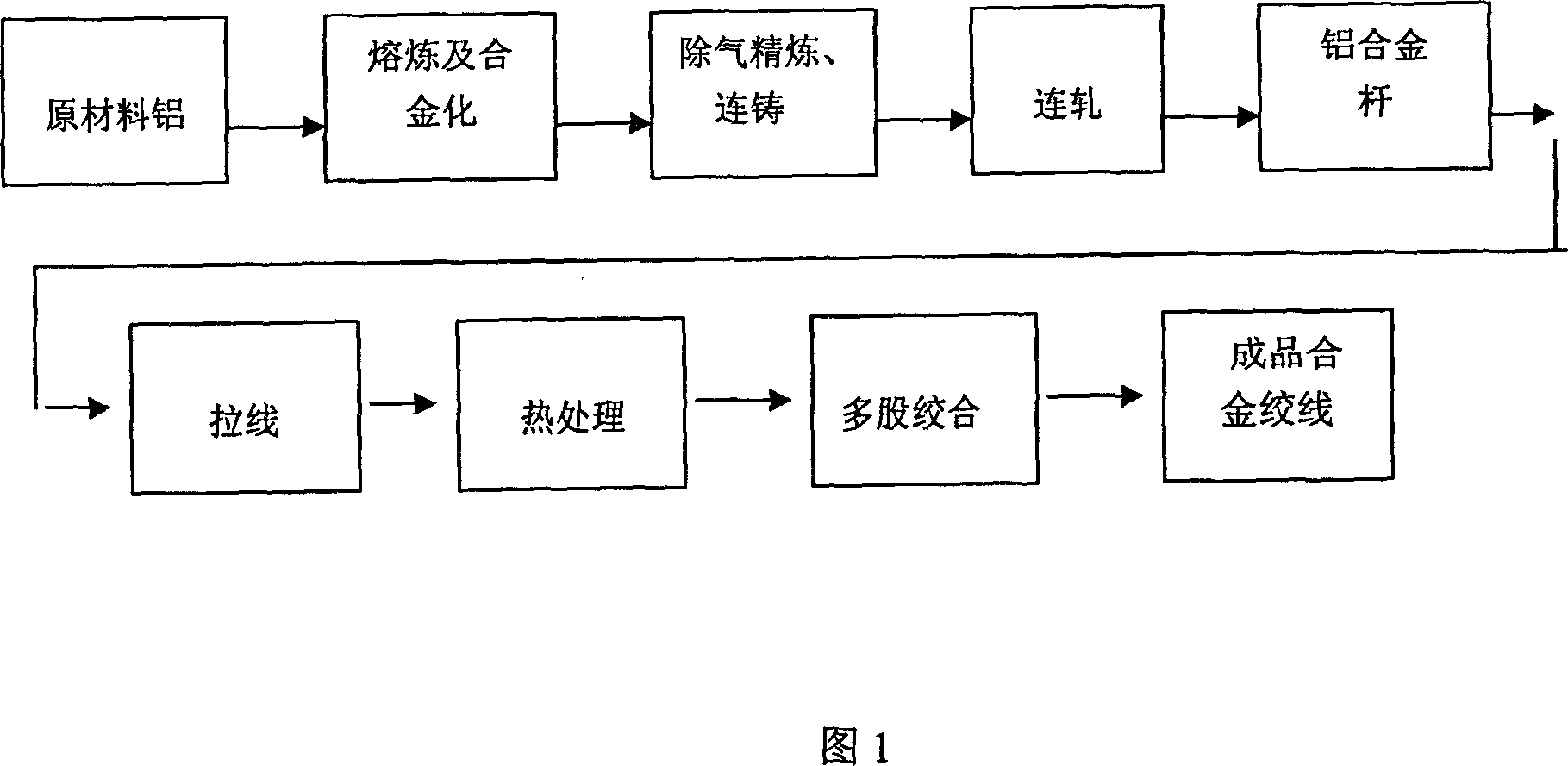
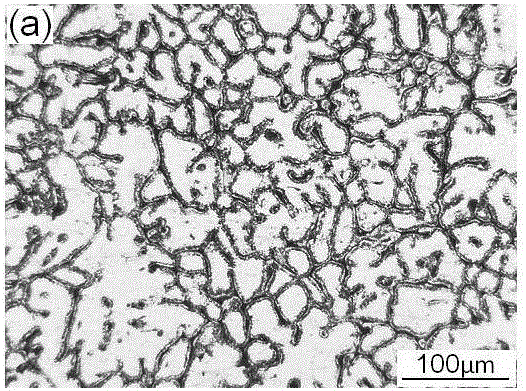
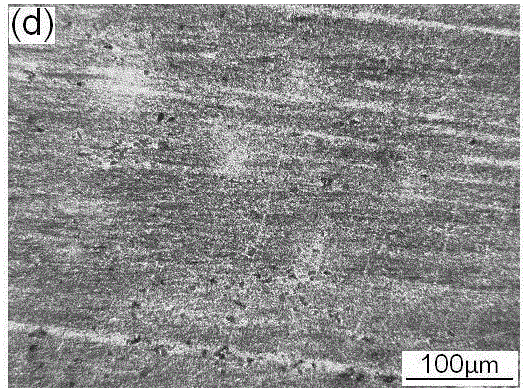
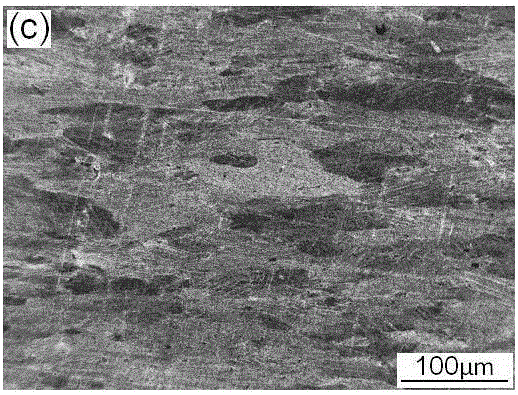
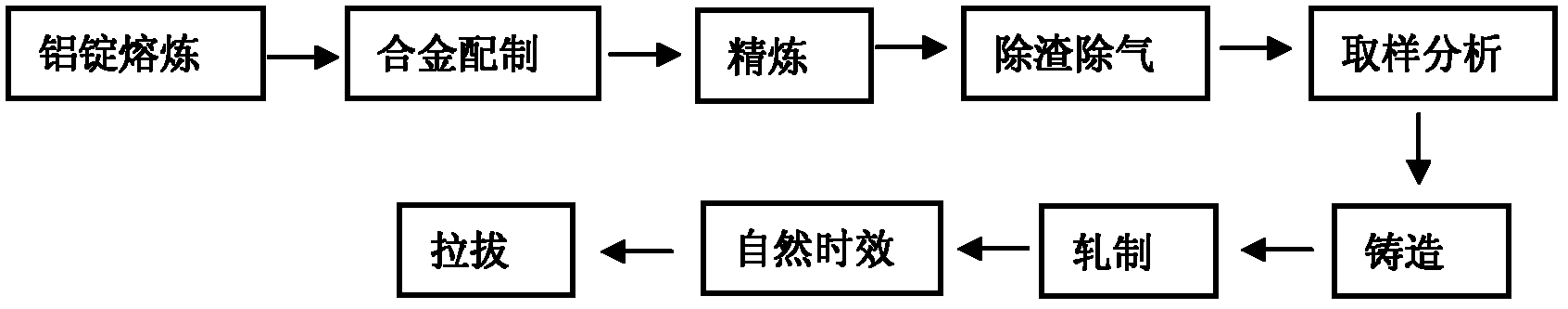
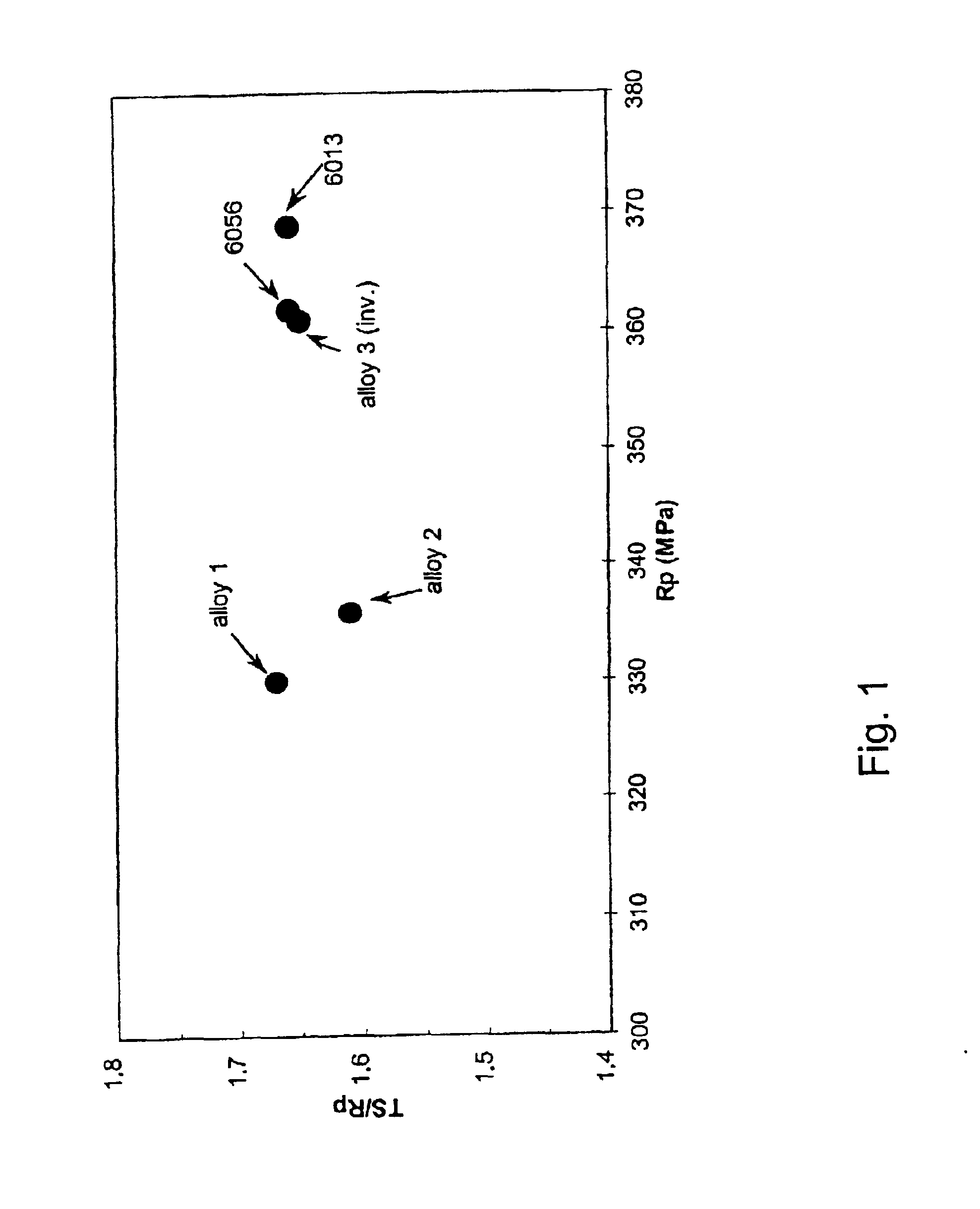
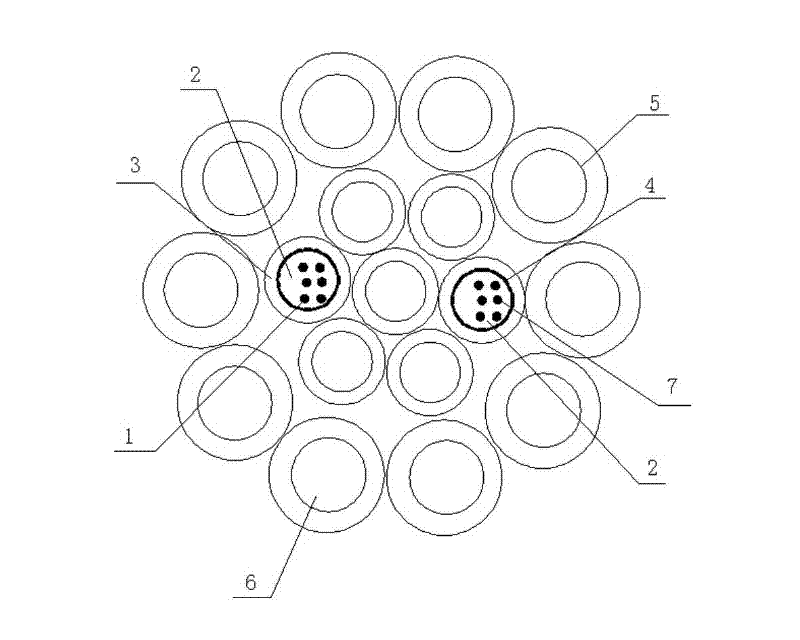
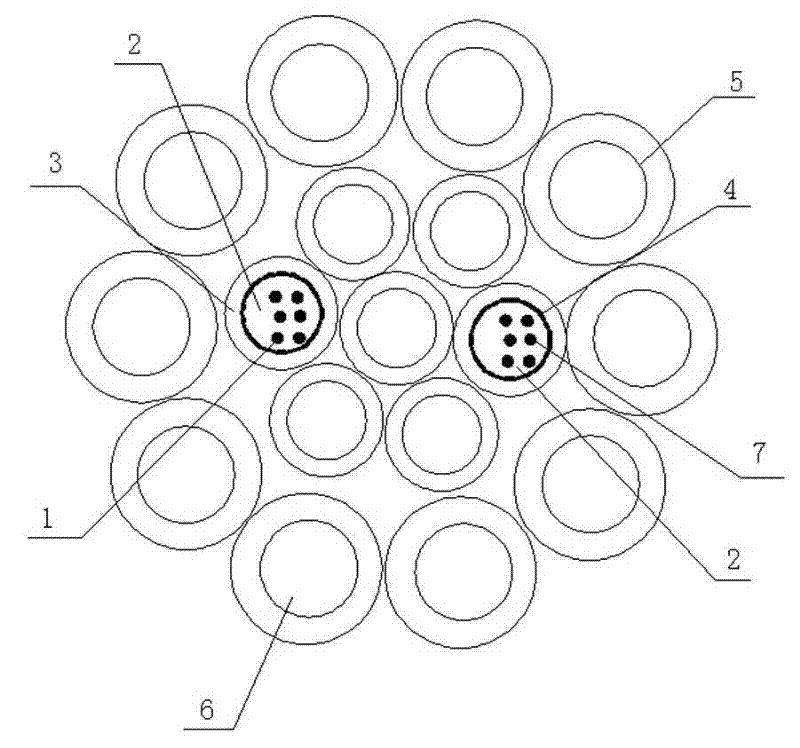
Patents
Literature
220 results about "High strength aluminium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
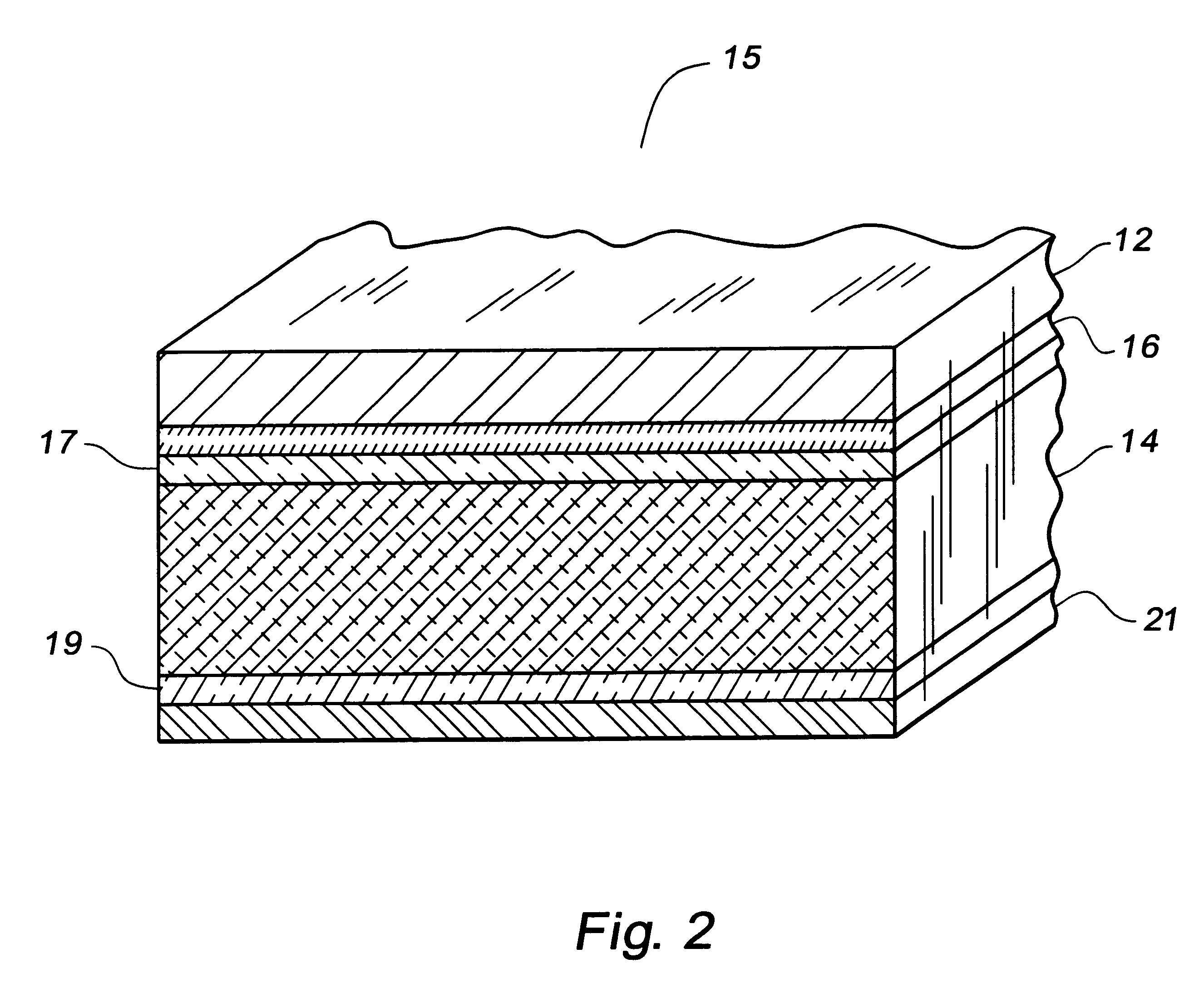
High strength aluminium alloy brazing sheet, brazed assembly and method for producing same
ActiveUS20050079376A1Good brazing propertyGood formability characteristicFurnace typesWelding/cutting media/materialsSiluminManganese
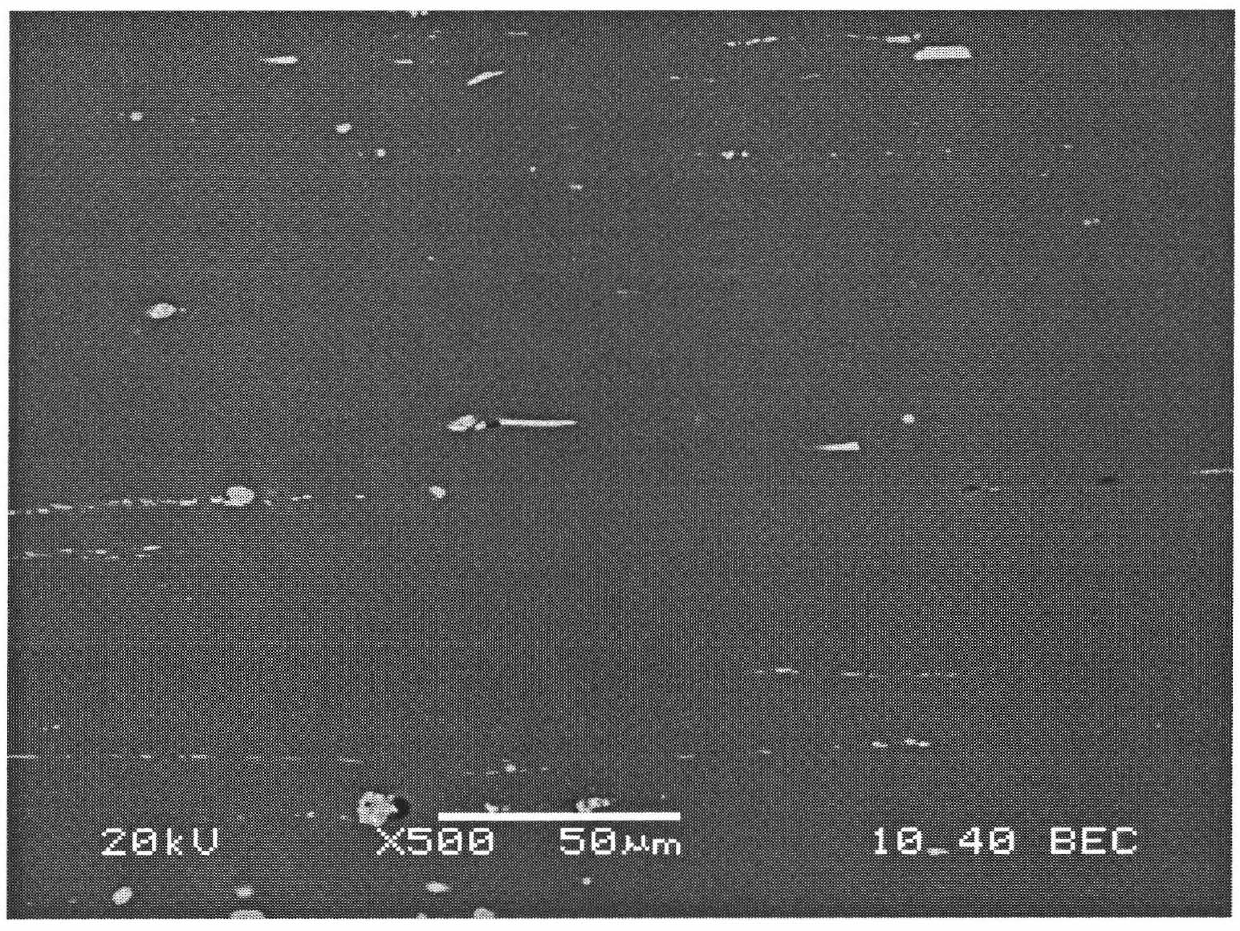
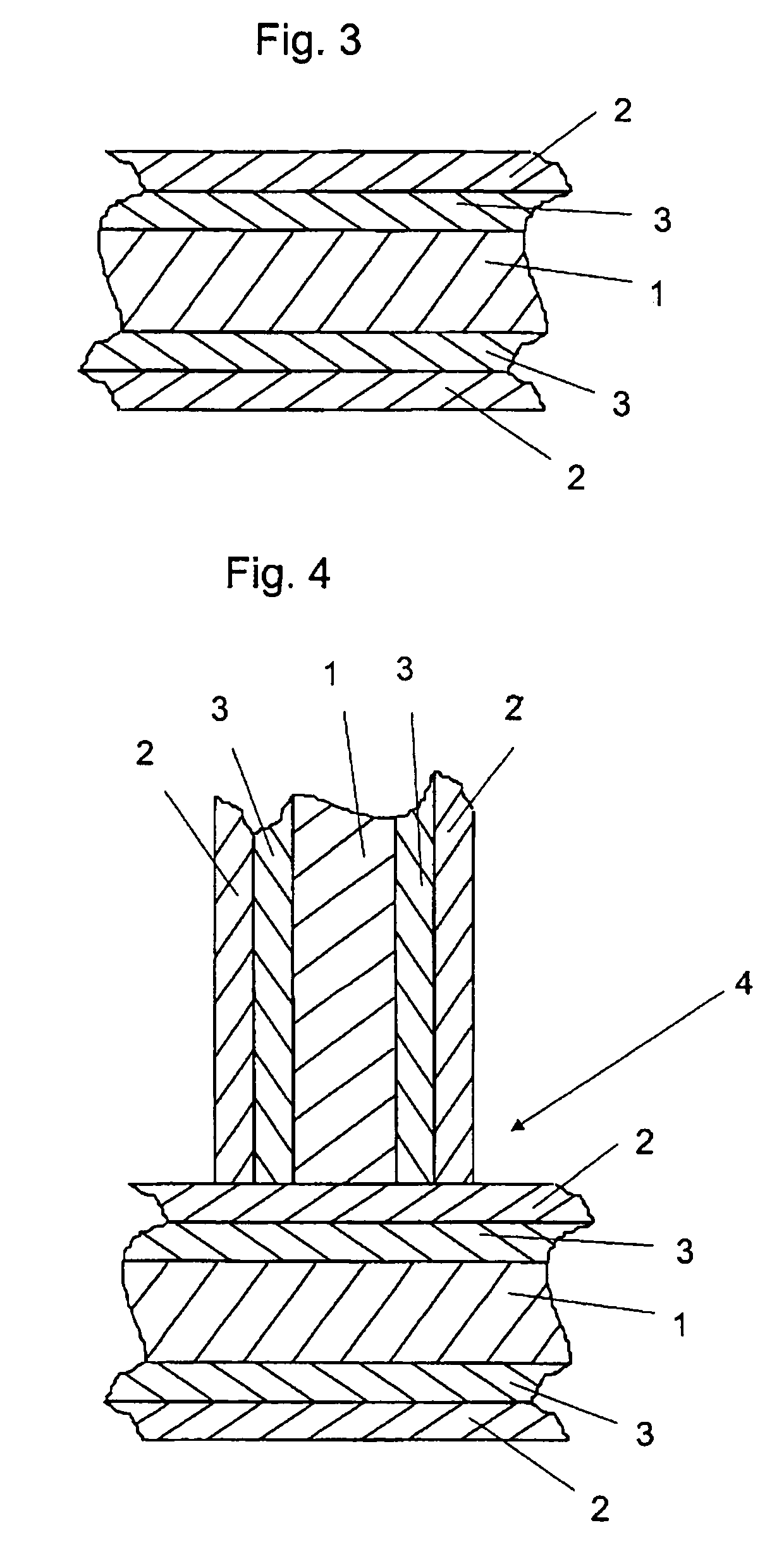
The present invention a high strength aluminium alloy brazing sheet, comprising an Al—Zn core layer and at least one clad layer, the core layer including the following composition (in weight percent): Zn1.2 to 5.5Mg0.8 to 3.0Mn0.1 to 1.0Cu<0.2Si <0.35Fe<0.5optionally one or more of: Zr<0.3Cr<0.3V<0.3Ti<0.2Hf<0.3Sc<0.5,the balance aluminium and incidental elements and impurities. The clad layer includes an Al—Si based filler alloy and is applied on at least one side of the core layer. The invention relates furthermore to a brazed assembly including such brazing sheet, to the use of such brazing sheet and to method for producing an aluminium alloy brazing sheet.
Owner:ALERIS ALUMINUM KOBLENZ GMBH
High-strength metal aluminide-containing matrix composites and methods of manufacture the same
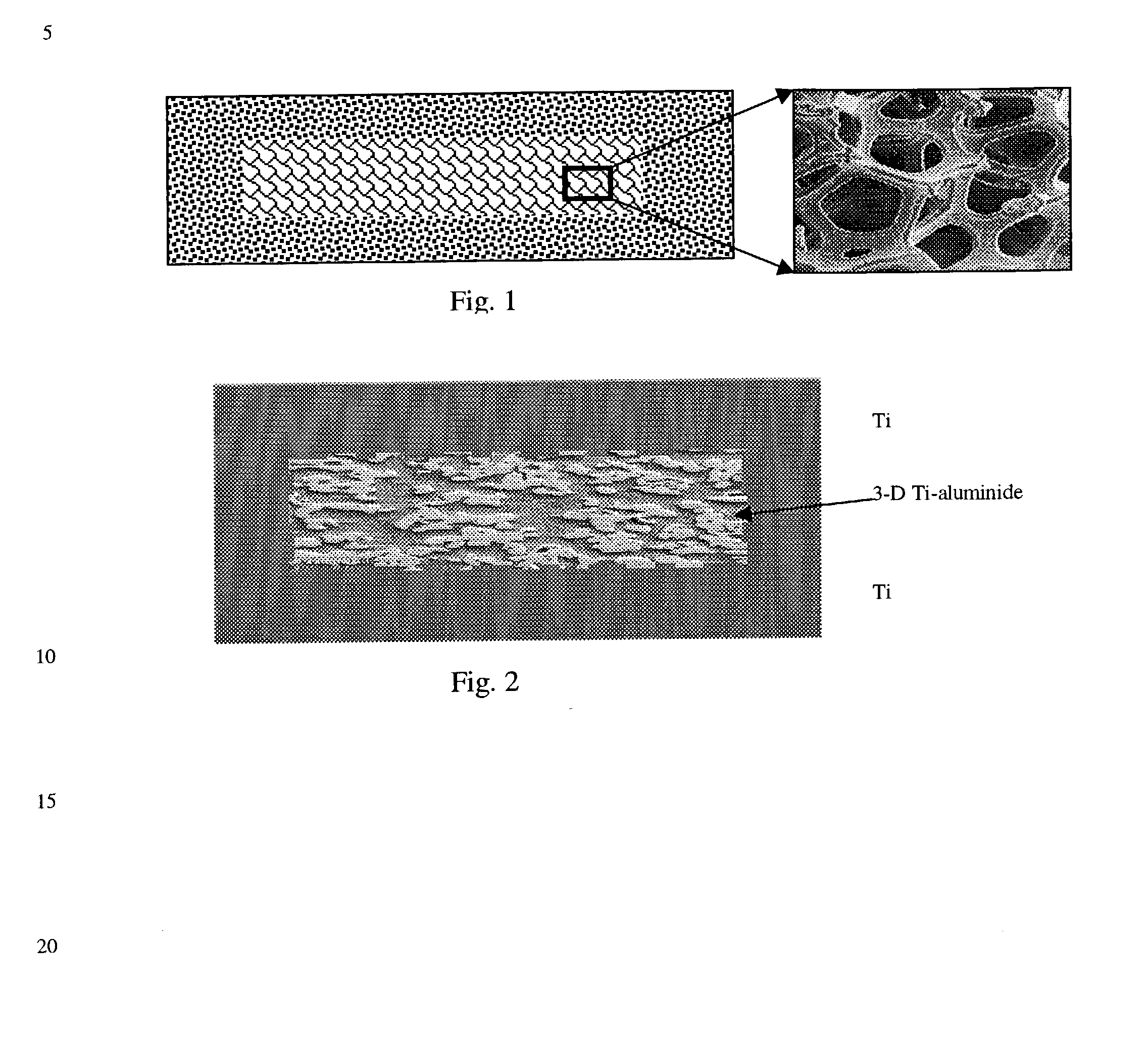
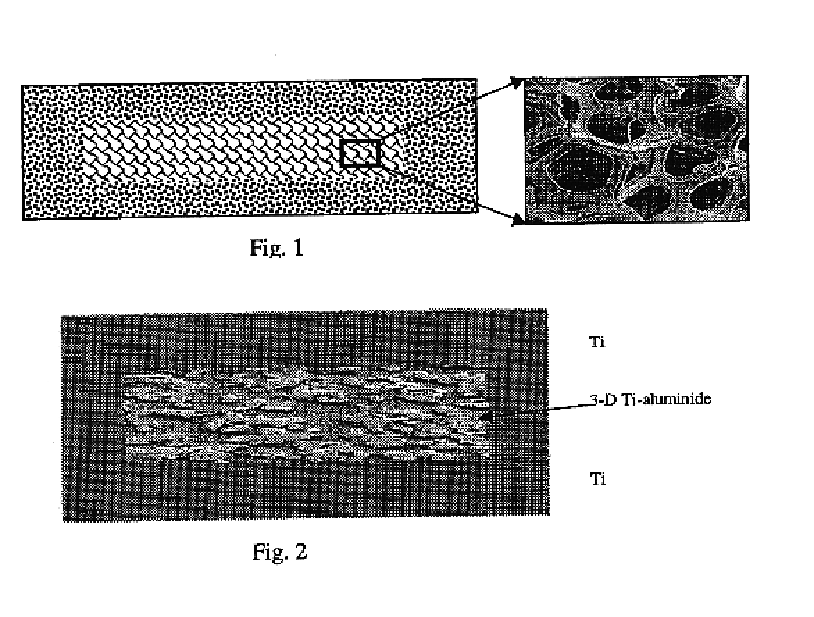
(a) The metal matrix composite is suitable for the manufacture of flat or shaped titanium aluminide, zirconium aluminide, or niobium aluminide articles and layered metal composites having improved mechanical properties such as lightweight plates and sheets for aircraft and automotive applications, thin cross-section vanes and airfoils, heat-sinking lightweight electronic substrates, bulletproof structures for vests, partition walls and doors, as well as sporting goods such as helmets, golf clubs, sole plates, crown plates, etc. The composite material consists of a metal (e.g., Ti, Zr, or Nb-based alloy) matrix at least partially intercalated with a three-dimensional skeletal metal aluminide structure, whereby ductility of the matrix metal is higher than that of the metal aluminide skeleton. The method for manufacturing includes the following steps: (a) providing an aluminum skeleton structure having open porosity of 50-95 vol. %, (b) filling said skeleton structure with the powder of a reactive matrix metal, (c) compacting the aluminum skeleton / matrix powder composite preform by cold rolling, cold die pressing, cold isostatic pressing, and / or hot rolling, (d) consolidating the initial or compacted composite preform by sintering, hot pressing, hot rolling, hot isostatic pressing, and / or hot extrusion to provide, at least partially, a reaction between aluminum skeleton and matrix metal powder, and (e) diffusion annealing followed by any type of heat treatment needed to provide predetermined mechanical and surface properties of the resulting metal matrix composite. The combination of ductile matrix and metal aluminide skeletal structure results in significant improvement of mechanical properties of the composite material, especially hot strength. This high-strength aluminide-based material can also be used as a core component in multilayer metal matrix composites.
Owner:ADVANCE MATERIAL PRODS ADMA PRODS
Aluminum laminate
InactiveUS6235409B1Light weightHigh strengthHot-dipping/immersion processesAdhesive processesAlloy substrateAlclad
A bright finish aluminum alloy on high strength aluminum or aluminum alloy lamination is disclosed including a bright finish top sheet, a high strength aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate, and an adhesive bonding the bright finish metal top sheet to the high strength aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate to provide a bright finish aluminum on high strength aluminum or aluminum alloy lamination product having brighter finish than a sheet product of said high strength aluminum or aluminum alloy and higher strength than a sheet product of said bright finish aluminum of the same thickness as said lamination product, wherein said lamination product withstands galvanic corrosion. In one aspect, the bright finish metal top sheet is 5657 aluminum foil. In one aspect, the high strength aluminum alloy is 5182 alloy sheet.
Owner:ARCONIC INC
High strength aluminium alloy brazing sheet
InactiveUS20050064226A1Good brazing propertyGood formability characteristicFurnace typesHigh frequency current welding apparatusSiluminHigh intensity
Disclosed is a high strength aluminium alloy brazing sheet, including an Al—Cu core layer and at least one clad layer, the core layer having the following composition (in weight percent): Cu: 1.2-4.0, Mn: 0.06-1.5, Mg: 0.06-1.5, Si: up to 0.5, Zn: <0.4, Zr: ≦0.25, Fe: ≦0.5, Ti: ≦0.25, Cr: ≦0.25; V≦0.25; the balance substantially aluminium and impurities, the clad layer including an Al—Si based filler alloy and being applied on at least one side of the core layer. Also disclosed is a brazed assembly including the brazing sheet and the use of the brazing sheet for a brazing application such as a heat exchanger.
Owner:ALERIS ALUMINUM KOBLENZ GMBH
Method for preparing ligh high strength aluminium oxide hollow ball ceramic
InactiveCN1554616AWith shrinkageWith thermal shock resistanceCeramicwarePhosphoric acidShock resistance
The light high-strength alumina ceramic ball has phosphoric acid solution as binding agent, alpha-alumina powder as basic material and hollow alumina ball as aggregate. Compared with dense refractory material, it has low density, high heat shock resistance, good heat insulating performance, low heat capacity and other features; and compared with common heat insulating material, it has high compression strength, high loaded softening temperature, low re-burning linear shrinkage and other features. It may be used as heat insulating material directly and may be also used in direct contact with flame, such as being used as lining material in high temperature furnace and kiln. In addition, its strength may be further raised in secondary sintering.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
High-strength aluminium alloy plate and production method thereof
ActiveCN101649406AHigh strengthAccelerated corrosionQuenching agentsMetal rolling arrangementsHigh intensityQuenching
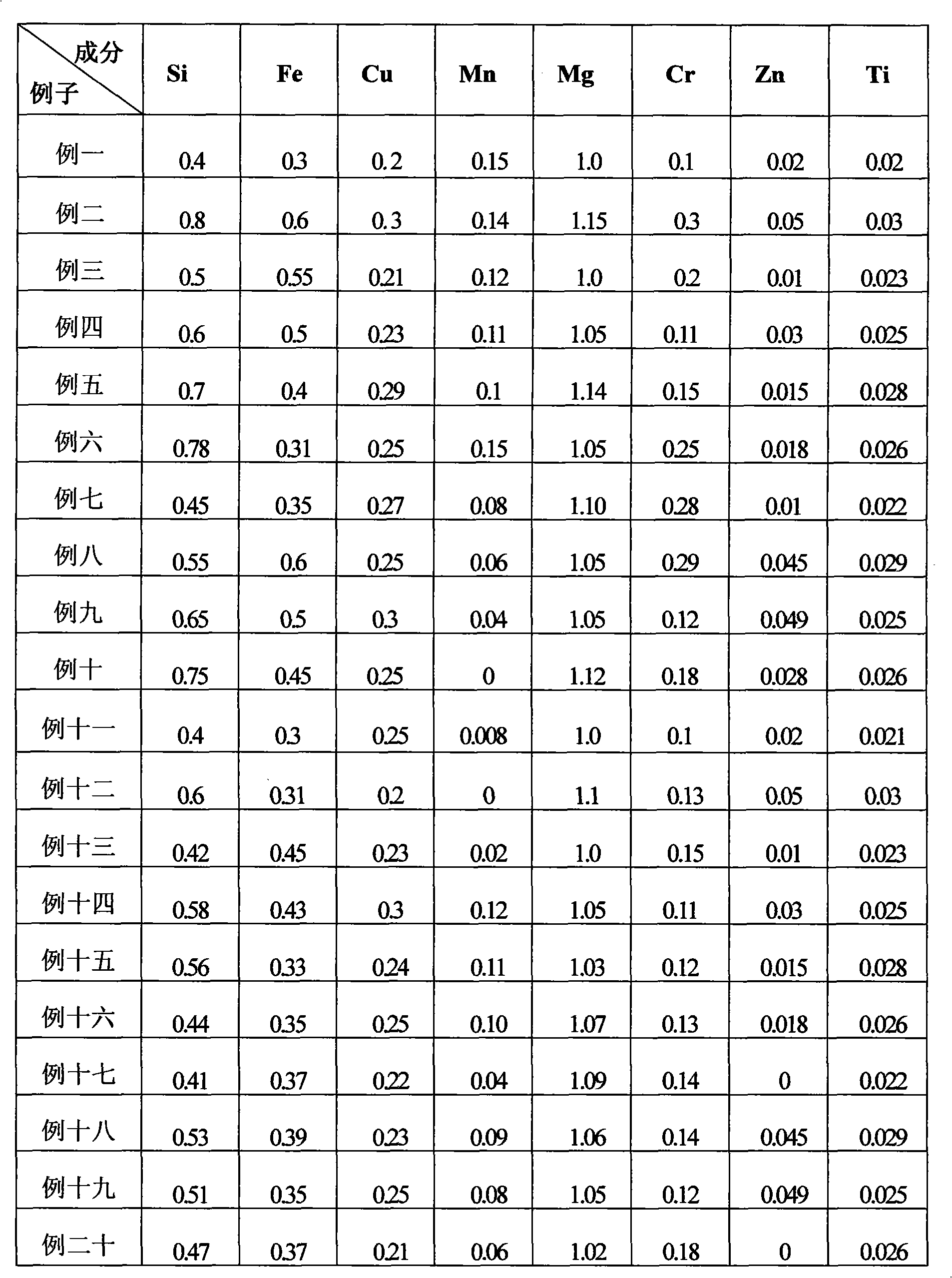
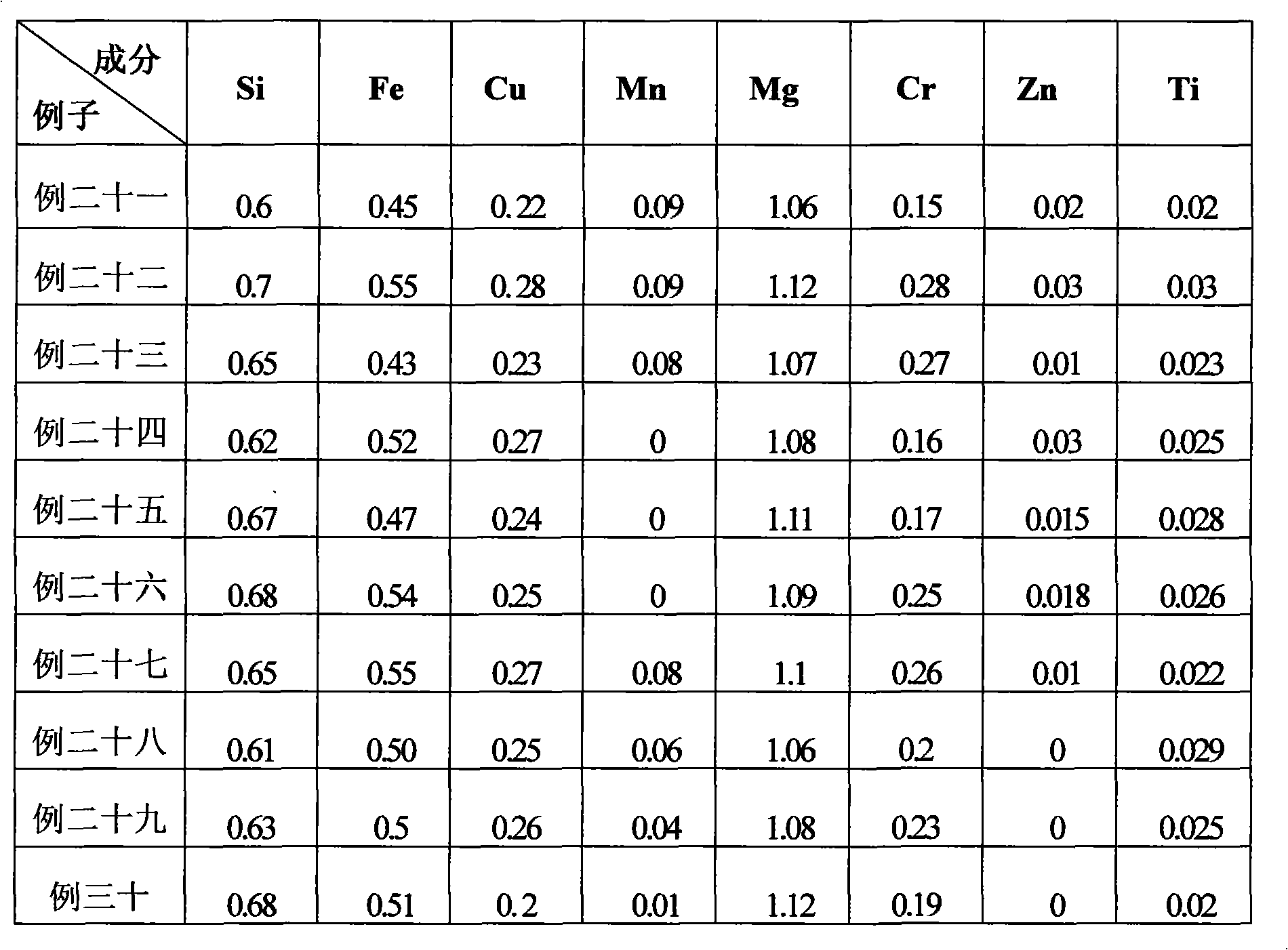
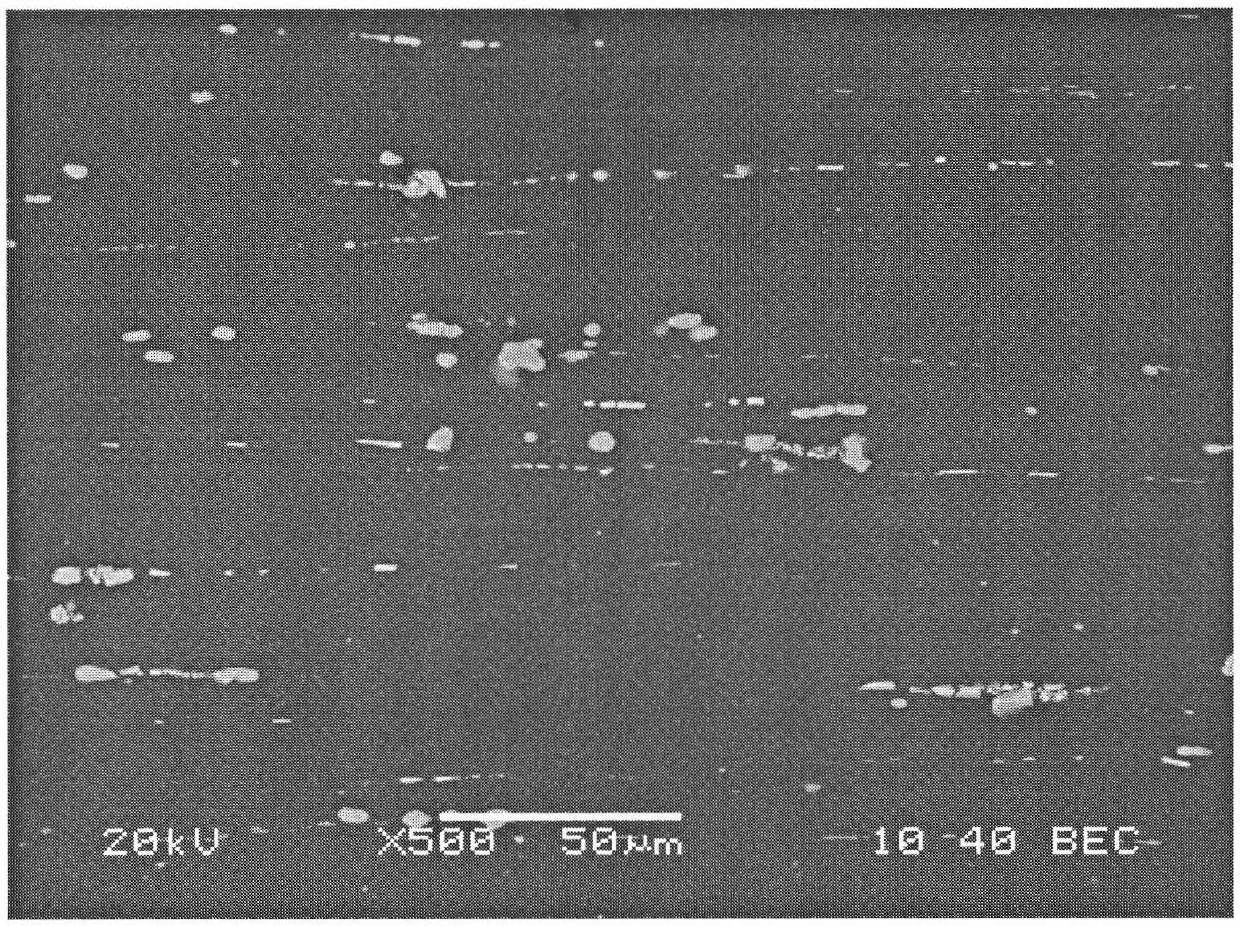
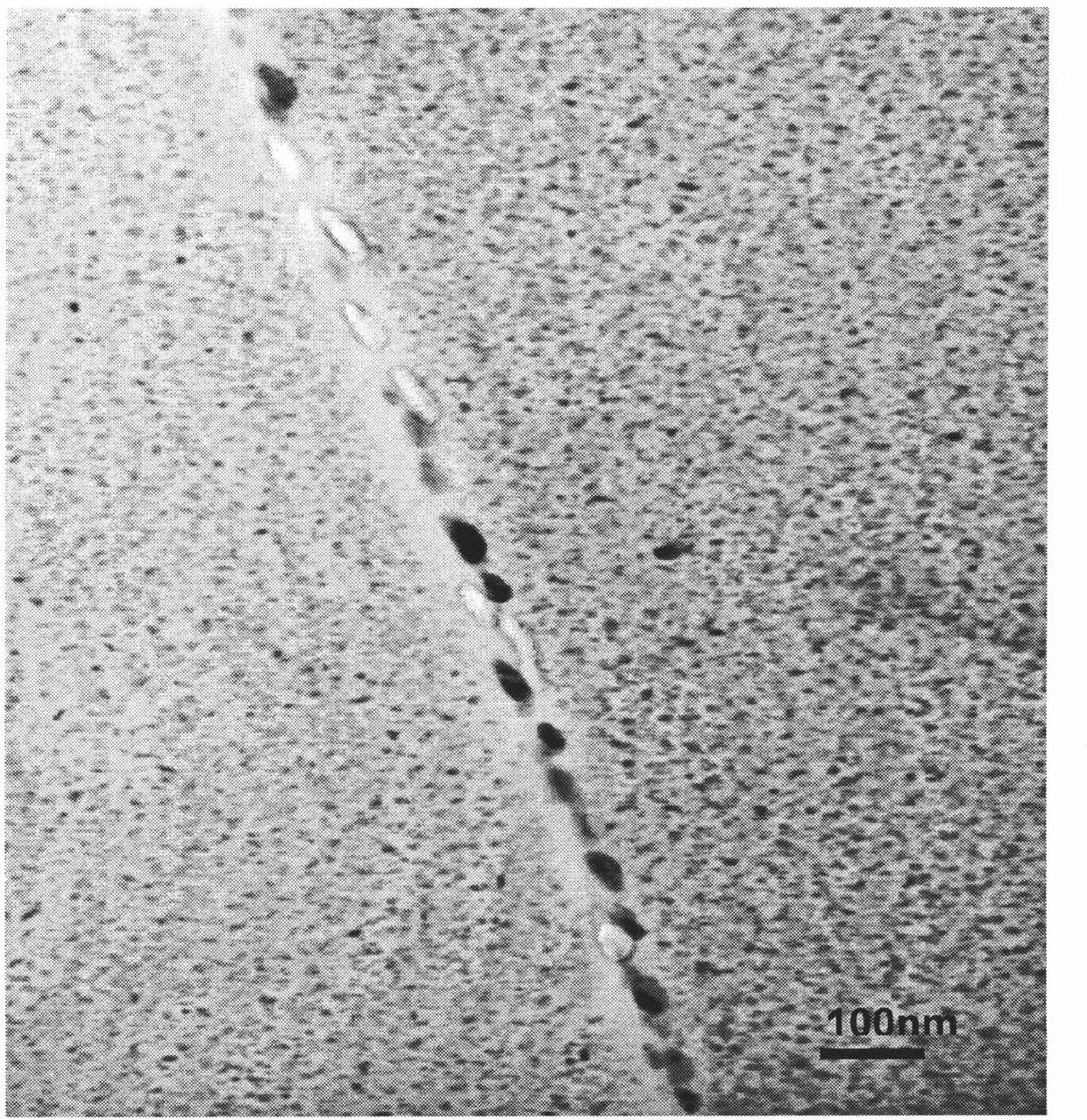
The invention relates to a high-strength aluminium alloy plate and a production method thereof. The high-strength aluminium alloy plate is made from the components in parts by weight: 0.4-0.8 part ofSi, 0.3-0.6 part of Fe, 0.2-0.3 part of Cu, not more than 0.15 part of Mn, 1.0-1.15 parts of Mg, 0.1-0.3 part of Cr, not more than 0.05 part of Zn, 0.02-0.03 part of Ti, not more than 0.01 part of other impurities and the balance of Al, wherein the total amount is 100 parts. The production method comprises following steps: smelting, refining, stewing, casting, face milling, hot rough rolling, hotprecision rolling, cold rolling and online continuous quenching, wherein furnace temperature is 590-610 DEG C, and the quenching speed is 0.7-2.0m / min; and then carrying out secondary cold rolling till a aluminium alloy platen is rolled to be 0.8-10mm; and finally obtaining a finished product through finishing and artificial ageing treatment. The plate has the advantages of high strength, corrosion resistance, good welding performance and the like; the adopted hot rolling method is a continuous quenching process, thereby realizing the rapidity and the continuity of uncoiling quenching and shortening the production cycle, therefore being beneficial to energy saving and consumption reducing and popularization and application.
Owner:河南明晟新材料科技有限公司
High strength aluminium alloy brazing sheet, brazed assembly and method for producing same
ActiveUS7226669B2Good brazing property and formability characteristicHigh strengthFurnace typesWelding/cutting media/materialsHigh intensityDouble bottom
The present invention a high strength aluminium alloy brazing sheet, comprising an Al-Zn core layer and at least one clad layer, the core layer including the following composition (in weight percent): <tables id="TABLE-US-00001" num="00001"> <tgroup align="left" colsep="0" rowsep="0" cols="3"> <colspec colname="offset" colwidth="56pt" align="left" / > <colspec colname="1" colwidth="14pt" align="left" / > <colspec colname="2" colwidth="147pt" align="center" / > <ROW> <ENTRY / > <entry namest="offset" nameend="2" align="center" rowsep="1" / > < / ROW> <ROW> <ENTRY / > <ENTRY>Zn< / ENTRY> <ENTRY>1.2 to 5.5< / ENTRY> < / ROW> <ROW> <ENTRY / > <ENTRY>Mg< / ENTRY> <ENTRY>0.8 to 3.0< / ENTRY> < / ROW> <ROW> <ENTRY / > <ENTRY>Mn< / ENTRY> <ENTRY>0.1 to 1.0< / ENTRY> < / ROW> <ROW> <ENTRY / > <ENTRY>Cu< / ENTRY> <ENTRY><0.2< / ENTRY> < / ROW> <ROW> <ENTRY / > <ENTRY>Si< / ENTRY> <ENTRY> <0.35< / ENTRY> < / ROW> <ROW> <ENTRY / > <ENTRY>Fe< / ENTRY> <ENTRY><0.5< / ENTRY> < / ROW> <ROW> <ENTRY / > <entry namest="offset" nameend="2" align="center" rowsep="1" / > < / ROW> < / TGROUP> < / TABLES> optionally one or more of: <tables id="TABLE-US-00002" num="00002"> <tgroup align="left" colsep="0" rowsep="0" cols="3"> <colspec colname="offset" colwidth="56pt" align="left" / > <colspec colname="1" colwidth="14pt" align="left" / > <colspec colname="2" colwidth="147pt" align="char" / > <ROW> <ENTRY / > <entry namest="offset" nameend="2" align="center" rowsep="1" / > < / ROW> <ROW> <ENTRY / > <ENTRY>Zr< / ENTRY> <ENTRY><0.3< / ENTRY> < / ROW> <ROW> <ENTRY / > <ENTRY>Cr< / ENTRY> <ENTRY><0.3< / ENTRY> < / ROW> <ROW> <ENTRY / > <ENTRY>V< / ENTRY> <ENTRY><0.3< / ENTRY> < / ROW> <ROW> <ENTRY / > <ENTRY>Ti< / ENTRY> <ENTRY><0.2< / ENTRY> < / ROW> <ROW> <ENTRY / > <ENTRY>Hf< / ENTRY> <ENTRY><0.3< / ENTRY> < / ROW> <ROW> <ENTRY / > <ENTRY>Sc< / ENTRY> <ENTRY><0.5,< / ENTRY> < / ROW> <ROW> <ENTRY / > <entry namest="offset" nameend="2" align="center" rowsep="1" / > < / ROW> < / TGROUP> < / TABLES> the balance aluminium and incidental elements and impurities. The clad layer includes an Al-Si based filler alloy and is applied on at least one side of the core layer. The invention relates furthermore to a brazed assembly including such brazing sheet, to the use of such brazing sheet and to method for producing an aluminium alloy brazing sheet.
Owner:ALERIS ALUMINUM KOBLENZ GMBH
High-strength metal aluminide-containing matrix composites and methods of manufacture the same
InactiveUS6852273B2Improve mechanical propertiesLayered productsSolid state diffusion coatingMetallic aluminumNiobium
(a) The metal matrix composite is suitable for the manufacture of flat or shaped titanium aluminide, zirconium aluminide, or niobium aluminide articles and layered metal composites having improved mechanical properties such as lightweight plates and sheets for aircraft and automotive applications, thin cross-section vanes and airfoils, heat-sinking lightweight electronic substrates, bulletproof structures for vests, partition walls and doors, as well as sporting goods such as helmets, golf clubs, sole plates, crown plates, etc. The composite material consists of a metal (e.g., Ti, Zr, or Nb-based alloy) matrix at least partially intercalated with a three-dimensional skeletal metal aluminide structure, whereby ductility of the matrix metal is higher than that of the metal aluminide skeleton. The method for manufacturing includes the following steps: (a) providing an aluminum skeleton structure having open porosity of 50-95 vol. %, (b) filling said skeleton structure with the powder of a reactive matrix metal, (c) compacting the aluminum skeleton / matrix powder composite preform by cold rolling, cold die pressing, cold isostatic pressing, and / or hot rolling, (d) consolidating the initial or compacted composite preform by sintering, hot pressing, hot rolling, hot isostatic pressing, and / or hot extrusion to provide, at least partially, a reaction between aluminum skeleton and matrix metal powder, and (e) diffusion annealing followed by any type of heat treatment needed to provide predetermined mechanical and surface properties of the resulting metal matrix composite. The combination of ductile matrix and metal aluminide skeletal structure results in significant improvement of mechanical properties of the composite material, especially hot strength. This high-strength aluminide-based material can also be used as a core component in multilayer metal matrix composites.
Owner:ADVANCE MATERIAL PRODS ADMA PRODS
High strength aluminium alloy wire and rod and their prepn process
ActiveCN1888107AQuality improvementChange the status quo of long-term dependence on importsMetal rolling arrangementsTitaniumHigh intensity
The present invention discloses one kind of high strength aluminum alloy wire and rod and their preparation process. The high strength aluminum alloy contains Fe 0.15-0.25 wt%, Mg 0.65-0.75 wt%, Si 0.56-0.66 wt%, Cu not more than 0.10 wt%, Zn not more than 0.10 wt%, Mn not more than 0.03 wt%, Cr not more than 0.03 wt%, B not more than 0.06 wt%, Ti 0.006-0.009 wt%, impurity not more than 0.10 wt% and Al for the rest.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
Method for manufacturing high-strength aluminium-magnesium-slicon alloy wire
ActiveCN101200783AControl UniformityGuaranteed uniformityTemperature control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsSpectrum analyzerShaft furnace
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of Al-Mg-Si alloy line. The technological process is: selecting excellent aluminum ingot and putting the aluminum ingot in a vertical furnace to be melted; adding magnesium, silicon and iron; implementing the alloying treatment on aluminum liquid in a tilting holding furnace; using solid covering flux to cover the surface of the aluminum liquid after the refining through refining agent and standing for more than 30m; using a spectrum analyzer to detect main elements and regulating when the content is deviated; slowly dumping the aluminum solution by the tilting holding furnace; adding 0.03 to 0.5 percent of aluminum boron alloys when the dumped aluminum solution is refined through a chute and a continuous scouring device outside of the furnace; continuously casting with an aluminum alloy caster that is composed of an H-type wheeled crystal wheel into the aluminum alloy ingot; putting the aluminum alloy ingot in a two-roller with three-roller novel combined aluminum alloy continuous mill to mill the ingot into a Al-Mg-S alloy bar. The aluminum alloy bar is arranged at a sliding wire drawing machine to be drawn into aluminum alloy product line with required diameter and be stranded into line. The invention has the advantages of both ensuring the high strength and improving the conductivity simultaneously. The conductivity can reach to 53 percent IACS and the strength reaches to 315MPa.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHONGTIAN ALUMINUM WIRE
High-strenght aluminum alloy brazing sheet and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20120129003A1High strengthExcellent brazeabilityExhaust apparatusMachines/enginesFilling materialsImpurity
An aluminum alloy brazing sheet having a core material of an aluminum alloy, and a filler material cladded on the core is disclosed. The core material is an aluminum alloy having about 0.05 to about 1.2 mass Si, about 0.05-about 1.0 mass % Fe, about 0.05-about 1.2 mass % Cu, and about 0.6-about 1.8 mass % Mn, balance Al and the inevitable impurities. The filler material includes an aluminum alloy having about 2.5-about 13.0 mass % Si. Also, there is provided a method of manufacturing such an aluminum alloy brazing sheet.
Owner:FURUKAWA SKYALUMINUM
Heat treatment technology of high strength aluminium alloy
InactiveCN101956151AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove heat treatment processSolution treatmentQuenching
The invention relates to a heat treatment technology of high strength aluminium alloy. The technology performs solution treatment, primary quenching treatment, high temperature short time aging treatment, secondary quenching treatment, intermediate temperate short time aging treatment and low temperature long time aging treatment to high strength aluminium alloy in sequence. The technology improves the comprehensive mechanical property of alloy, increases the corrosion resistance and expands the application range of high strength aluminium alloy.
Owner:SICHUAN CITY TRACK TRAFFIC MATERIAL +1
Method for producing heat-resisting high-strength aluminium alloy wire
InactiveCN1941222ASatisfy the requirements of large-scale designSingle bars/rods/wires/strips conductorsCable/conductor manufactureElectricityRare earth
A method for producing high-intensity heat-resistant aluminum alloy line belongs to production technology field of materials applied to electrical engineering. It winnows component and content of alloy and controls technology to produce high-intensity aluminum alloy line. Select zirconium, copper, iron, silicon and rare earth with different percent of weigh and aluminum ingot into stove. The impurity content of aluminum ingot does not exceed 0.02%(besides silicon, iron, copper). Add alloying additive element and whisk, fine, component fast analyzing before entering stove. Put into continuous caster to produce aluminum alloy pole and draw into aluminum alloy line after tempered heat treatment and cooling to get production. In this method, the capability of production is satisfied the overhead designed demand for Three Gorges to serve the construct of transporting electrical power from west to east.
Owner:BEIJING ELECTRIC POWER CONSTR RES INST OF SGCC +1
Heat treatment method for improving obdurability of 7-series high strength aluminium alloy
InactiveCN101994072AImprove fracture toughnessIncrease supersaturationSolution treatmentRoom temperature
The invention relates to a heat treatment method for improving the obdurability of a 7-series high strength aluminium alloy, comprising the following steps: firstly carrying out double-stage forced solution treatment on the hot-processing 7***-series high strength aluminium alloy, namely, performing primary solution treatment for 2-4 hours at the temperature of 420-450 DEG C, and performing secondary reinforced solution treatment for 2-4 hours at the temperature of 450-490 DEG C; then quenching and cooling to room temperature, wherein the quenching medium is room temperature water; prestretching within 1-4 hours after quenching, wherein the prestretching distortion is 1-3%; performing high-temperature short-time ageing treatment, wherein the aging temperature is 120-180 DEG C and the aging time is 60-180min; quenching and cooling to room temperature after high-temperature short-time aging treatment, wherein the quenching medium is room temperature water; and finally carrying out low-temperature long-time aging treatment, wherein the aging temperature is 60-120 DEG C, and the aging time is 18-48 hours. The heat treatment method for improving the obdurability of a 7-series high strength aluminium alloy of the invention further improves the fracture toughness property of alloys and broadens the applied range of the aluminium alloys on the basis of maintaining the superhigh alloy strength.
Owner:苏州有色金属研究院有限公司
Formable, high strength aluminium-magnesium alloy material for application in welded structures
Owner:HASZLER ALFRED JOHANN PETER +3
High strength automobile aluminium alloy wheel rim
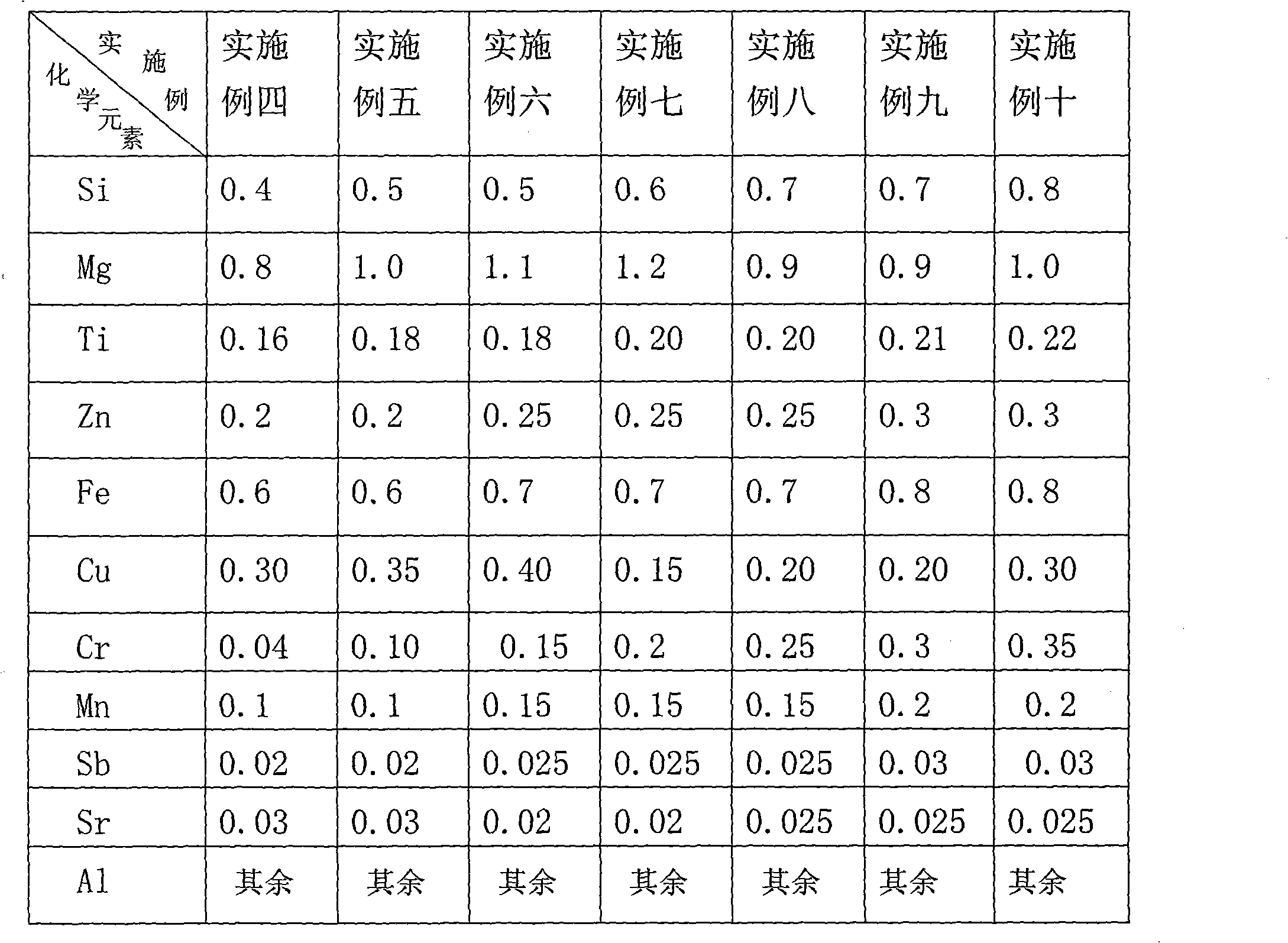
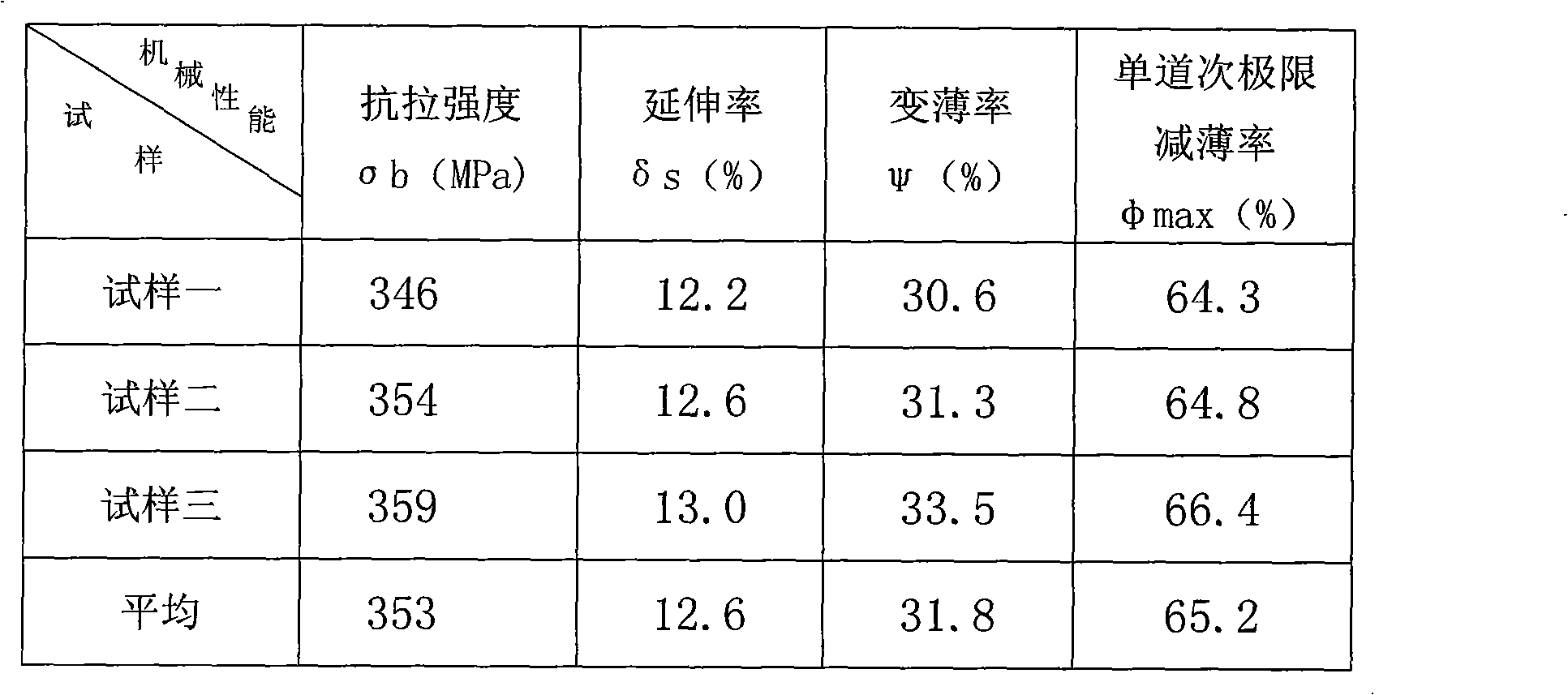
The invention relates to a high strength automobile aluminium alloy wheel rim, in particular to an automobile wheel rim matched with oversize vehicles. The high strength automobile aluminium alloy wheel rim is made of high strength aluminium alloy material which comprises main chemical elements with the mass percent: 0.4-0.8% of Si, 0.8-1.2% of Mg, 0.16-0.22% of Ti, 0.2-0.3% of Zn, 0.6-0.8% of Fe,0.15-0.4% of Cu, 0.04-0.35% of Cr, 0.1-0.2% of Mn, 0.02-0.03% of Sb, 0.02-0.03% of Sr and the rest of Al. The automobile aluminium alloy wheel rim has high tensile strength which is 10% higher than that of the existing aluminium alloy wheel rim produced by 6061-T6, is good in mechanical property, enhances the rotatable performance of alloy when the structure is refined, and has the advantages ofwide application scope, low production cost and easy popularization and use.
Owner:HECHI UNIV
High strength aluminium alloy brazing sheet
InactiveUS7514155B2High strengthHigh incipient melting pointFurnace typesHigh frequency current welding apparatusHigh intensityImpurity
Disclosed is a high strength aluminium alloy brazing sheet, including an Al—Cu core layer and at least one clad layer, the core layer having the following composition (in weight percent): Cu: 1.2-4.0, Mn: 0.06-1.5, Mg: 0.06-1.5, Si: up to 0.5, Zn: ≦0.4, Zr: ≦0.25, Fe: ≦0.5, Ti: ≦0.25, Cr: ≦0.25; V≦0.25; the balance substantially aluminium and impurities, the clad layer including an Al—Si based filler alloy and being applied on at least one side of the core layer. Also disclosed is a brazed assembly including the brazing sheet and the use of the brazing sheet for a brazing application such as a heat exchanger.
Owner:ALERIS ALUMINUM KOBLENZ GMBH
Combined welding technology of high-strength aluminium alloy laser-MIG
InactiveCN101947695AImprove absorption ratePlay a protective effectWelding apparatusPower flowShielding gas
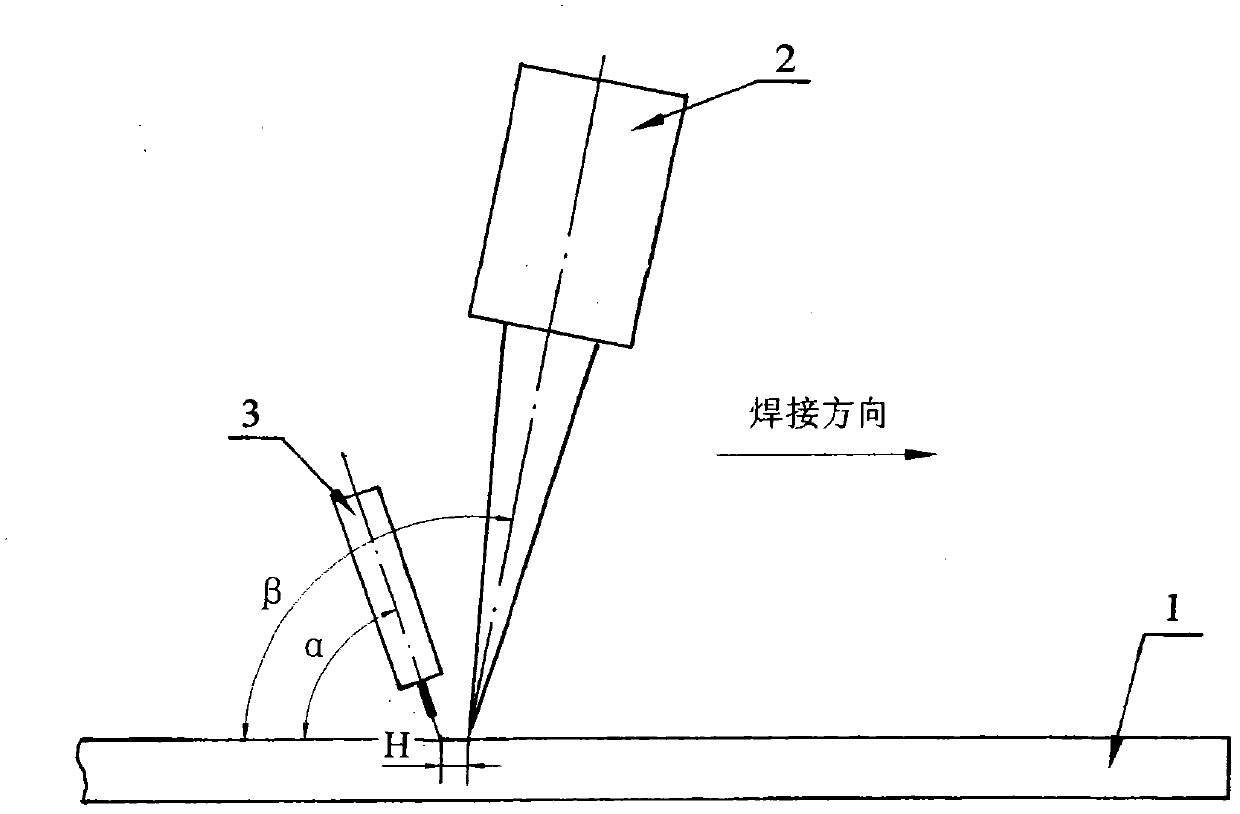
The invention discloses a combined welding technology of high-strength aluminium alloy laser-MIG, comprising the following steps: a. setting a combined mode and a welding gun angle; b. setting defocusing amount according to the thickness of a welding plate; c. setting combined welding protective gas as a mixed gas of helium and argon with a volume ratio of helium to argon of 1:4; d. according to welding speed, setting MIG welding air flow quantity; e. according to laser power and MIG current, setting MIG welding voltage value; f. according to the MIG welding voltage value and current value, setting the heat source interval between laser welding and MIG welding; and g. synchronously carrying out laser-MIG compound welding. The technology of the invention can obtain a welding line with clean and smooth welding surface, and the welding line has good shaping and does not have sag. The technology has the characteristics of big welding depth of fusion, high speed, small workpiece deformation, low assembly requirement, strong weld pool bridging ability and the like, is easy to integrate and can effectively control the problems of overlarge welding lines and base metal crystalline grain and the like caused by overheating in the aluminium alloy welding process.
Owner:NO 52 INST OF CHINA NORTH IND GRP CORP
High-strength aluminium, magnesium alloy equi-temperature extrusion method based on numerical simulation
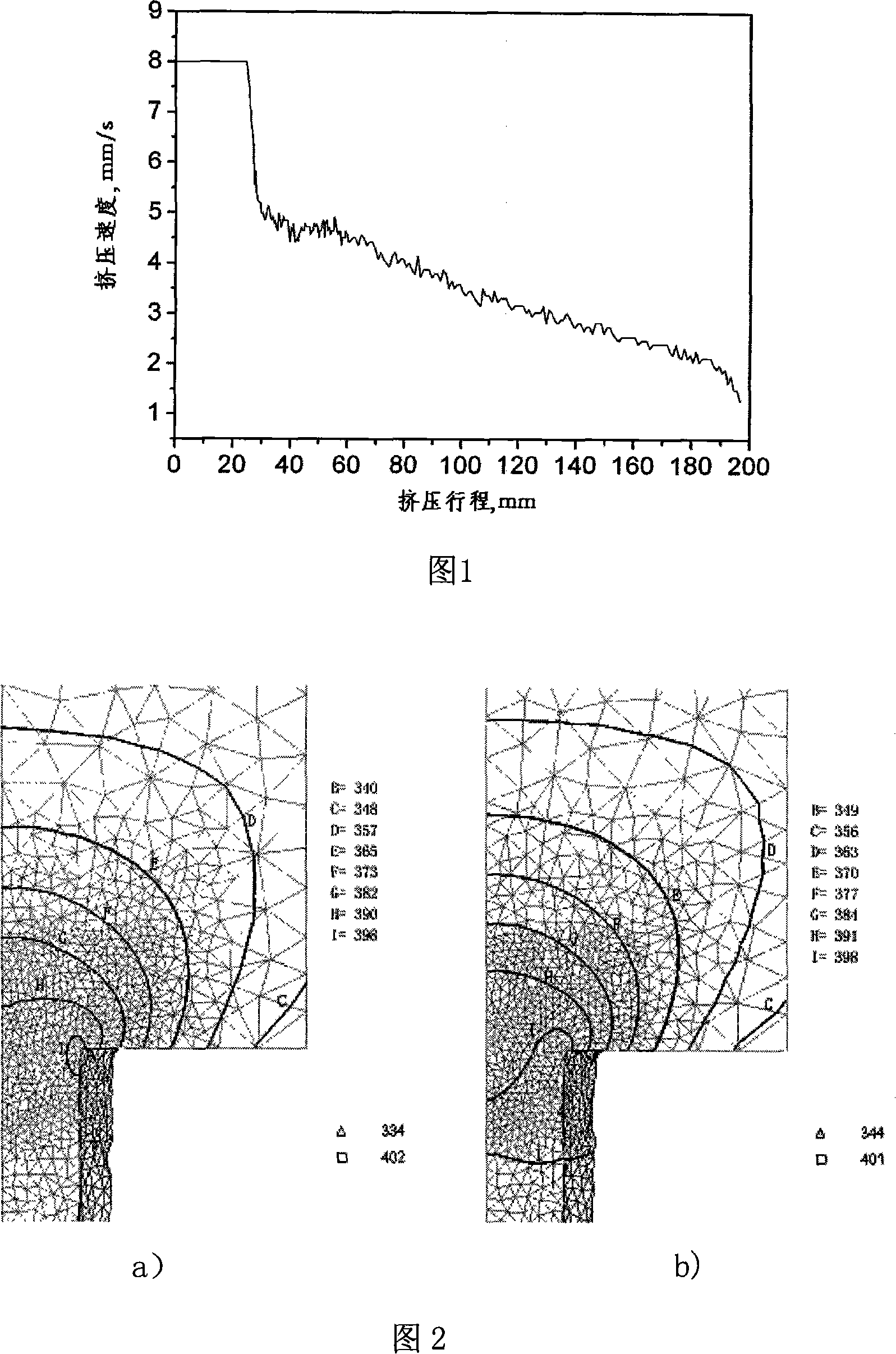
ActiveCN101069902AReduce warpageReduce stretch straightening deformationExtrusion control devicesControllers with particular characteristicsPlungerMagnesium alloy
The present invention provides a high-strength aluminium and magnesium alloy isothermal extrusion method based on numerical analog. Said method is characterized by that it utilizes PID control principle and makes it be applied for extrusion deformation finite element analog modeling, and utilizes once analogy of deformation process of workpiece to be machined to accurately and effectively obtain isothermal extrusion speed curve. According to the property of workpiece to be machined the workpiece outlet object outlet temperature, the extrusion speed can be regulated according to the PID control principle so as to obtain analog isothermal extrusion speed change curve correspondent to the described workpiece to be machined, and said isothermal extrusion speed change curve obtained by means of analogy can be inputted into the control system of extruding machine to control speed of main plunger of extruding machine so as to make extrusion outlet temperature retain constant.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Rolling method for ultrahigh-strength aluminum alloy plate
The invention discloses a rolling method for an ultrahigh-strength aluminum alloy plate. The rolling method comprises the following steps: A, a refined aluminum alloy ingot blank is annealed for 24-48 h uniformly at 450-550 DEG C; B, the annealing temperature is controlled to be 360-440 DEG C; single-pass 2-5% hot rolling pre-deformation is performed after inner temperature and outer temperature are uniform; temperature is continuously controlled to be 360-440 DEG C; then single-pass high reduction rolling deformation not less than 60% is performed, so that a thick plate blank is obtained; then water cooling or air cooling is performed; C, the cooled thick plate blank is subjected to 0.5-3h solid solution treatment at 450-550 DEG C, and then is subjected to water quenching; D, the water quenched thick plate blank is subjected to 6h of pre-aging treatment at 150-250 DEG C, and then is air-cooled to room temperature; and E, the thick plate blank which is air cooled to the room temperature is subjected to 40-60% of cold rolling deformation, and then is subjected to final-aging treatment at 120-200 DEG C. The plate made with the rolling method has ultrahigh strength, high damage-resistance and long service life.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing aluminium magnesium silicon alloy rod base and preparing high-strength aluminium magnesium silicon alloy conductor
The invention belongs to the field of electrotechnics, and provides a method for preparing an aluminium magnesium silicon alloy rod base and preparing a high-strength aluminium magnesium silicon alloy conductor. Through a smelting technique and refining especially the control of a rolling technique, an aluminium magnesium silicon alloy rod base with a specific state is prepared, and can be directly pulled, after the natural aging, to obtain an aluminium magnesium silicon alloy wire that accords with LHA1 and LHA2 requirements. As compared with a conventional technique, the aluminium magnesiumsilicon alloy rod base prepared by the method provided by the invention is stable in performance, and the aluminium magnesium silicon alloy wire prepared by the aluminium magnesium silicon alloy rod is stable in linearity without any artificial aging treating, thereby substantially reducing the cost for producing the aluminium magnesium silicon alloy wire and fully meeting the requirement of an aluminium alloy wire used for an overhead twisted wire.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRIC CABLE RES INST
High strength aluminium alloy and producing process
The high strength alloy for building section consists of Al in 95.75-96.5 wt% and M in 2.95-3.7, with M being Mg, Si, Cu and Fe. The production process of the alloy includes the following key steps: compounding based on the formulation, smelting, semi-continuous casting, hot extruding to form, on-line water quenching, and artificial ageing. The Al alloy thus produced has tensile and compression strength over 320 MPa, yield strength over 270 MPa, elongation over 10 %, and excellent corrosion resistance, extrusion performance and weldability.
Owner:BAIFURUI MATERIAL HUNAN
A production method of high-strength large-elongation aluminum-clad steel wire
InactiveCN108986989AChange heat treatment temperatureHigh tensile strengthSingle bars/rods/wires/strips conductorsApparatus for heat treatmentWire rodHigh carbon
The invention relates to a production method of high-strength large-elongation aluminum-clad steel wire, comprising the following steps: 1) hot-drawing high-carbon steel wire rod to different wire diameters through cold drawing; 2) carry out lead bath quenching treatment on that steel wire, and carry out on-line pickling and rinsing to obtain a pretreated steel wire; 3) uniformly cover an outer lay of that pretreated steel wire with a layer of aluminum to form a cladding blank; 4) that coat blank is drawn into a super-high-strength aluminum clad steel wire semi-finished product through multiple passes of a bimetal synchronous deformation wire draw machine; 5) age that semi-finished product of the high-strength aluminum-clad steel wire through a high-temperature box. The method of the invention changes the traditional lead bath heat treatment temperature, The tensile strength of Al-clad steel wire is increased by multi-pass synchronous deformation and drawing with small compression ratio, and the elongation of Al-clad steel wire is increased by high temperature aging treatment. The ultimate tensile strength >= 1700 MPa, elongation >= 3. 0%, and other indexes are in accordance with the requirements of Al-clad steel GB / T17937-2009 standard, thereby meeting the requirements of high strength and high elongation and meeting the application requirements.
Owner:HUBEI LONGSKY COMM TECH
Directly extrusion cast high strength aluminium alloy
The present invention relates to aluminum alloy material, and is especially one kind of directly extrusion cast high strength aluminum alloy. The aluminum alloy consists of Cu 4.0-5.0 wt%, Mg 1.0-2.0 wt%, Mn 0.4-0.8 wt%, trace alloy elements including Ti 0.05-0.25 wt%, B 0.01-0.05 wt%, V 0.05-0.20 wt% and Zr 0.05-0.20 wt%, and mixed RE 0.05-0.15 wt% except Al and inevitable impurities, including Fe less than 0.2 wt% and Si less than 0.1 wt%. The aluminum alloy is prepared through direct extrusion casting, quenching and perfect artificially ageing process, has the features of capacity of being heat treated to reinforce, high strength, low cost, etc, and is suitable for use in making heavy bearing aluminum alloy structures.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
High-strength aluminum alloy plate and process for producing the same
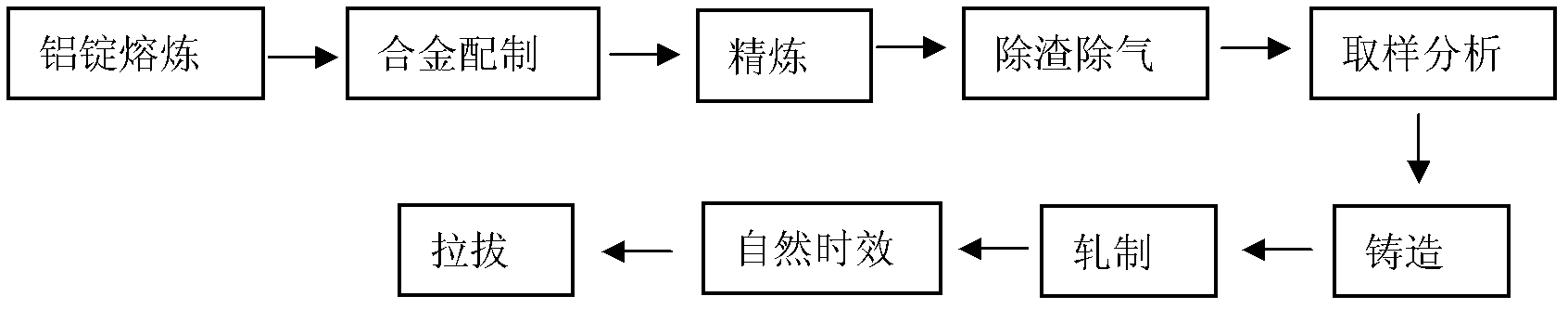
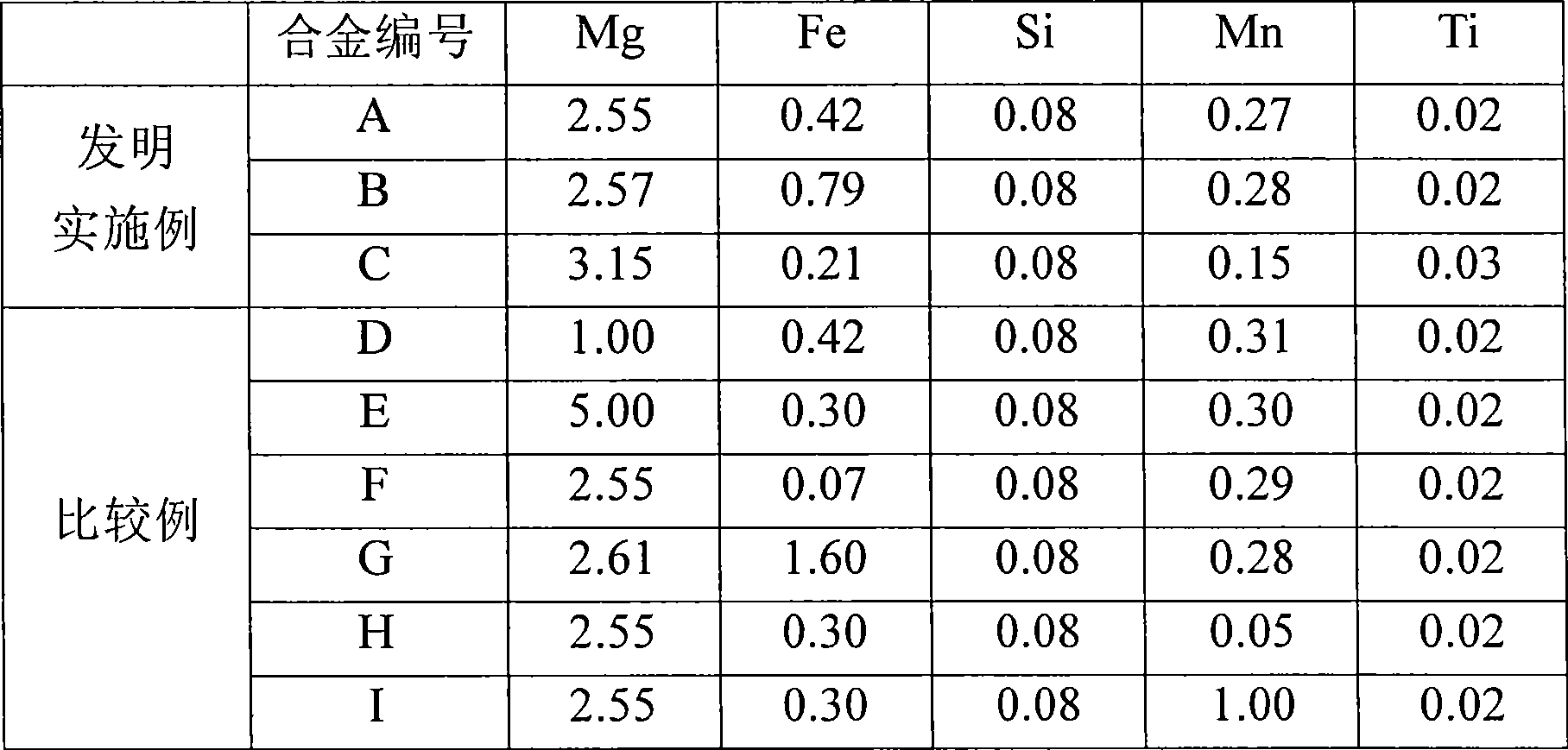
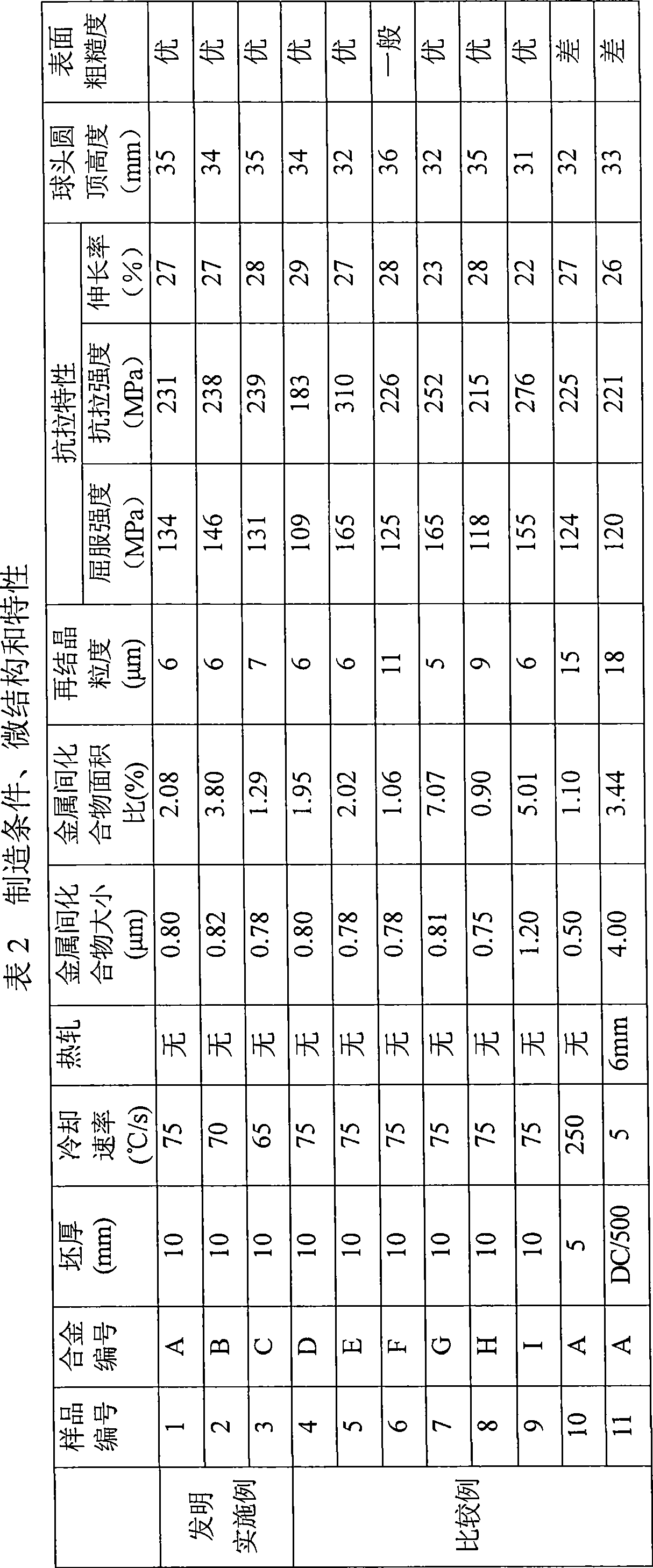
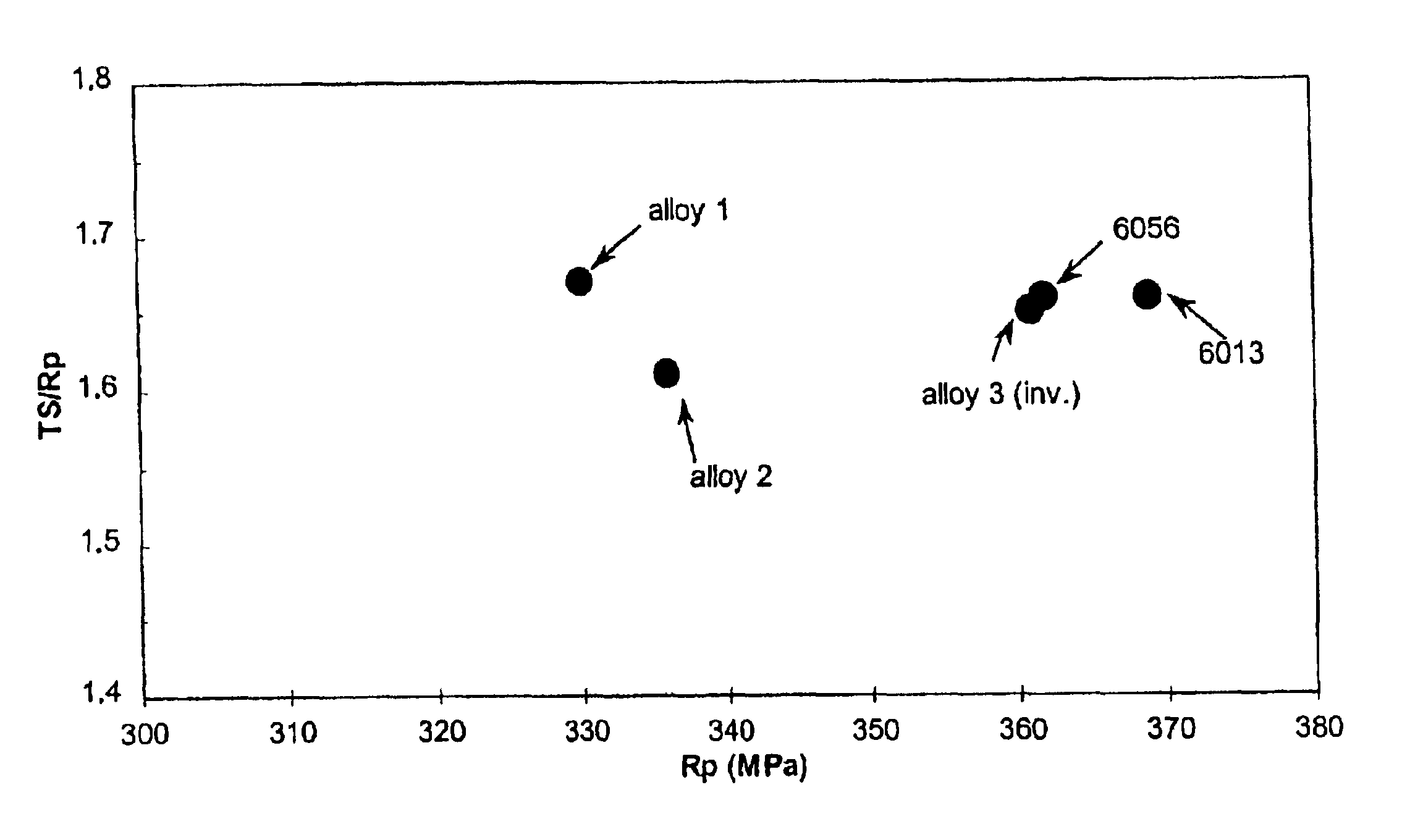
ActiveCN101490291AHigh strengthImprove surface roughnessThin material handlingMetal rolling arrangementsChemical compositionSurface roughness
The invention provides a high-strength aluminum alloy plate which is suitable for use as structural materials such as ones for domestic electrical appliances and exterior automotive sheets and combines excellent unsusceptibility to surface roughening and formability; and a process for producing the plate. The high-strength aluminum alloy plate has a chemical composition containing 2.0-3.3 mass% Mg, 0.1-0.5 mass% Mn, and 0.2-1.0 mass% Fe, the remainder being unavoidable impurities and Al and the unavoidable impurities containing less than 0.20 mass% Si. In the plate, intermetallic compounds have an average diameter in terms of equivalent-circle diameter of 1 mum or smaller and an areal proportion of 1.2% or higher, recrystallized grains have an average grain diameter of 10 mum or smaller, and the tensile strength is 220 MPa or higher. An aluminum alloy melt having the chemical composition is poured into a twin-belt casting machine to continuously produce, by casting, a thin slab having a thickness of 6-15 mm at a cooling rate of 50-200 DEG C / sec as measured in a position corresponding to 1 / 4 the slab thickness. The cast is wound into a coil and then cold-rolled at a cold rolling reduction of 60-98%. The resultant plate is subjected to final annealing with a continuous annealing furnace in which the plate is heated at a rate of 100 DEG C / min or higher and held at a temperature of 400-520 DEG C for a period of 5 minutes or shorter to produce the high-strength aluminum alloy plate.
Owner:NIPPON LIGHT METAL CO LTD
High-strength aluminum alloy
The invention discloses a high-strength aluminum alloy which is an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu aluminum alloy. The high-strength aluminum alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 7.0-9.0 percent of Zn, 1.3-2.0 percent of Mg, 1.5-3.0 percent of Cu, no more than 0.1 percent of Si, 0.1-0.3 percent of Mn, no more than 0.3 percent of Fe and the balance of Al and inevitable trace elements, wherein the ratio of Zn to Mg is 3.0-3.5. In such a way, the specific strength, the hardness, the corrosion resistance, the toughness, the machining performance, the welding performance and the like of the aluminum alloy can be improved.
Owner:昆山市源丰铝业有限公司
Weldable high strenght Al-Mg-Si alloy
InactiveUS6939416B2Improve balanceImprove toughnessThin material handlingMetal layered productsMisch metalSilumin
The invention relates to a weldable, high-strength aluminium alloy wrought product, which may be in the form of a rolled, extruded or forged form, containing the elements, in weight percent, Si 0.8 to 1.3, Cu 0.2 to 1.0, Mn 0.5 to 1.1, Mg 0.45 to 1.0, Ce 0.01 to 0.25, and preferably added in the form of a Misch Metal, Fe 0.01 to 0.3, Zr<0.25, Cr<0.25, Zn<1.4, Ti<0.25, V<0.25, others each <0.05 and total <0.15, balance aluminium. The invention relates also to a method of manufacturing such an aluminium alloy product.
Owner:ALERIS ALUMINUM KOBLENZ GMBH
High-strength aluminium alloy
The invention provides a high-strength 5052 aluminum alloy. Wherein, optimizing and adjusting the chemical intergradient and content within GB / T3190-1996; letting the alloy achieve final index: tensile strength ªÊbí¦300MPa, yield strength ªÊsí¦240MPa, and specific elongation í¦10%. This product has wide application.
Owner:CHINA NON-FERROUS METALS PROCESSING TECH CO LTD
Ultra-low loss and ultra-low temperature OPGW (optical fiber composite overhead ground wire) and production method thereof
The invention relates to an ultra-low loss and ultra-low temperature OPGW (optical fiber composite overhead ground wire) and a production method thereof, which are particularly applicable to remote large-capacity low-loss EHV (extra-high voltage) long-distance power transmission networks, and can be used in the filed of communications in various severe environments with high elevation, severe lowtemperature, dry and changeable and windy weather and the like. The OPGW comprises ultra-low loss fibers, G652D fibers, low-temperature fiber paste, first stainless steel tubes, second stainless steel tubes, internal high-strength aluminium sheathed steel wires and external high-strength aluminium sheathed steel wires; the inside of the first stainless steel tube is provided with the ultra-low loss fibers and uniformly filled with the low-temperature fiber paste so as to form a first stainless steel fiber unit; and the inside of the second stainless steel tube is provided with the G652D fibers and uniformly filled with the low-temperature fiber paste so as to form a second stainless steel fiber unit; the first and second stainless steel fiber units are synchronously stranded with the internal aluminium sheathed steel wires and uniformly daubed with the fiber paste; the external high-strength aluminium sheathed steel wires are stranded at the outer layer of the obtained product, and thus a double-layer armored ultra-low loss and ultra-low temperature OPGW.
Owner:ZHONGTIAN ELECTRIC POWER OPTICAL CABLES CO LTD
3D printing process method of high-strength aluminum-magnesium alloy
ActiveCN111872386ALow costImprove qualityAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packaging3D modelingMaterials science
The invention relates to a 3D printing process method of a high-strength aluminum-magnesium alloy, and belongs to the technical field of 3D printing. Firstly, high-strength aluminum-magnesium alloy raw materials are mixed evenly through heating and melting; then high-quality aluminum-magnesium alloy powder is prepared from the high-strength aluminum-magnesium alloy in a molten state through a gasatomization technology, and aluminum-magnesium alloy powder for 3D printing is obtained after drying; and printing parameters are adjusted, 3D printing is carried out according to 3D model data of parts in printing equipment with inert gas introduced, and a 3D printing product with the high-strength aluminum-magnesium alloy as a raw material is obtained. Compared with the prior art, as for the product printed through the process method, the relative density can reach 99% or above, the Vickers hardness can reach 110 HV or above, the tensile strength can reach 430 MPa or above, the elongation can reach 21%, through proper heat treatment, the Vickers hardness of a sample can reach 150 HV or above, the tensile strength can be further increased to 520 MPa or above, and the elongation is maintained at 17% or above.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com