A constant current control module, non-isolated step-down circuit and constant current control method
A technology of constant current control and rectification module, applied in energy-saving control technology, electric light source, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, large number of peripheral components, and high difficulty in assembling peripheral circuits, so as to reduce system cost and facilitate PCB routing. line, to achieve the effect of LED open circuit protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
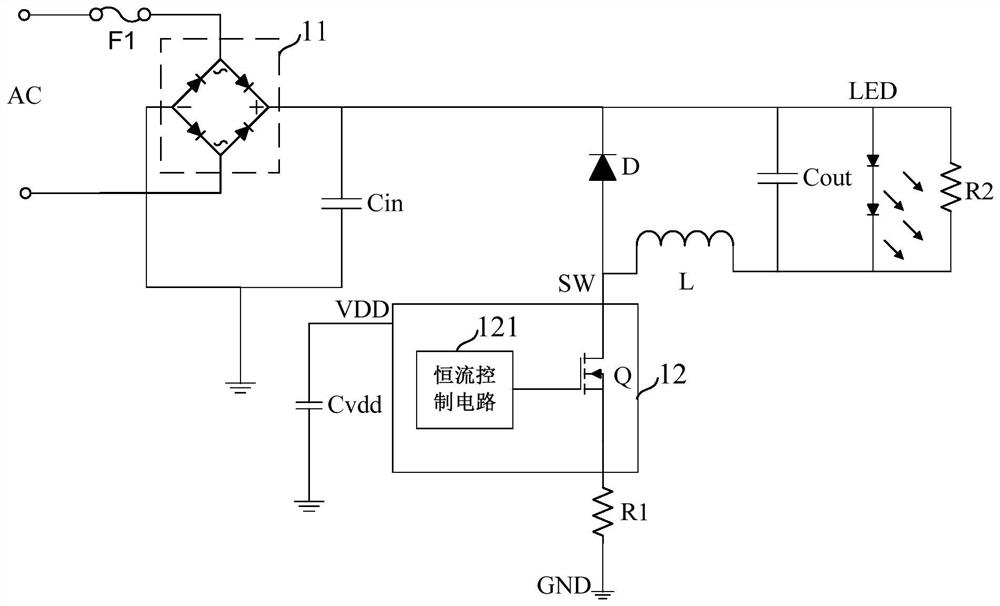
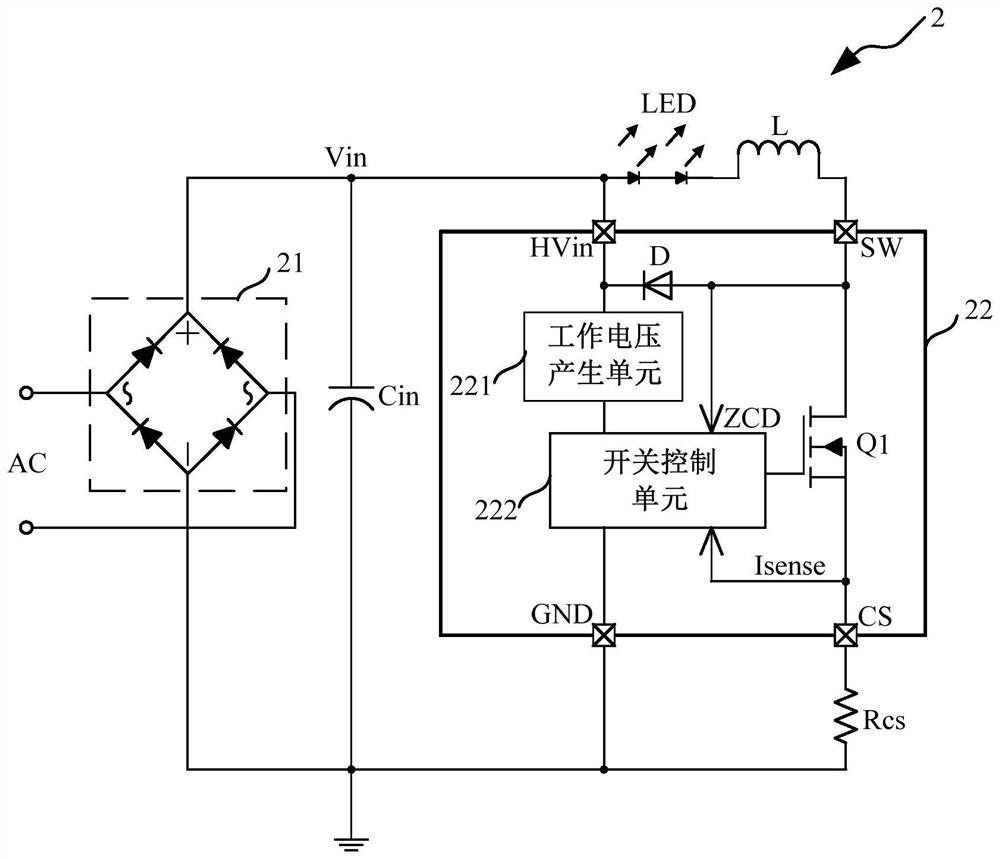
[0056] Such as image 3 As shown, this embodiment provides a non-isolated step-down circuit 2, and the non-isolated step-down circuit 2 at least includes:
[0057] A rectifier module 21 , an input capacitor Cin, a load, an inductor L, a sampling resistor Rcs and a constant current control module 22 .
[0058] Such as image 3 As shown, the rectification module 21 converts the AC signal AC into a DC input voltage Vin.
[0059] Specifically, the rectification module 21 is a rectification bridge, including two parallel diode groups, each diode group includes two diodes connected in series, and the two poles of the AC signal AC are respectively connected between the two diodes of each diode group.
[0060] Such as image 3 As shown, the input capacitor Cin is connected in parallel with the two ends of the rectification module 21 for stabilizing the input voltage Vin.
[0061] Specifically, the upper plate of the input capacitor Cin is connected to the input voltage Vin, and th...
Embodiment 2
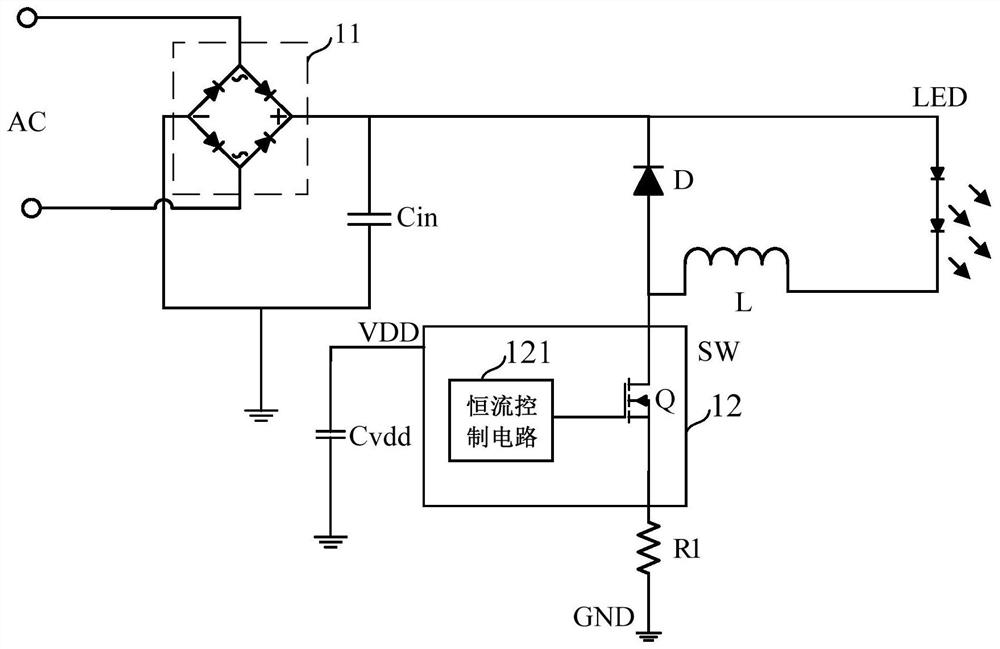
[0078] Such as Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment provides a non-isolated step-down circuit 2. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the drain terminal of the first switching transistor Q1 of this embodiment is connected to the freewheeling diode D A detection resistor R is also connected between the positive electrodes.
[0079] Specifically, such as Figure 4 As shown, the connection node between the detection resistor R and the freewheeling diode D is connected to the switch control unit 222 . The detection resistor R detects the current flowing through the freewheeling diode D, and outputs the detected signal to the switch control unit 222. When the current flowing through the freewheeling diode D is zero, the inductor The current on L just crosses zero, and the switch control unit 222 can directly obtain the demagnetization time Toff of the inductor L accordingly, so as to avoid the influence of the zero-crossing detection time TQR in the quas...
Embodiment 3
[0081] This embodiment provides a non-isolated step-down circuit 2. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that this embodiment uses a second switching tube Q2 to replace the freewheeling diode D in Embodiment 1.
[0082] Specifically, the drain terminal of the second switching transistor Q2 is connected to the output terminal of the rectification module 21, the source terminal is connected to the drain terminal of the first switching transistor Q1, and the gate terminal is connected to the switch control unit 222, through the The switch control unit 222 controls the second switch tube Q2 to realize synchronous rectification and improve the overall efficiency of the system. The connection relationship and principles of other modules and devices of the non-isolated step-down circuit 2 in this embodiment are the same as those in the first embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com