Method for treating dye wastewater by Fe<0>/PDS system
A dye wastewater, treatment method technology, applied in the oxidation water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of difficult treatment, complex components, difficult organic pollutants, etc. Reduce cost, improve degradation rate, improve degradation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
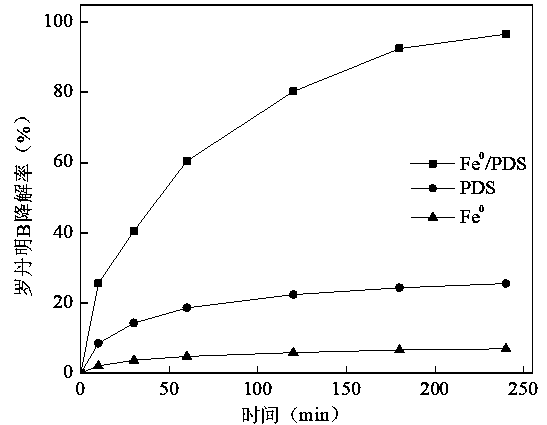
[0015] Experimental conditions: the initial pH is 7, Fe 0 The dosage is 0.5 g / L, the dosage of PDS is 2 g / L, and the reaction temperature is 25°C. Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that when zero-valent iron is added alone, the degradation rate of rhodamine B is only 6.9%, basically no removal, which shows that zero-valent iron has a poor adsorption effect on rhodamine B and cannot effectively degrade rhodamine B.
[0016] When PDS was added alone, the degradation rate of rhodamine B was 25.6%. PDS itself has a certain oxidation ability. When PDS is dissolved in aqueous solution, a hydrolysis reaction will occur to generate persulfate (S 2 o 8 2- ), its oxidation-reduction potential is 2.01 V, which can effectively oxidize some pollutants, but its oxidation ability is relatively weak. Therefore, the degradation rate of rhodamine B in the reaction system is not high.
[0017] Fe 0 The degradation rate of rhodamine B in the / PDS system was 96.2%, compared with that of Fe ...
Embodiment 2
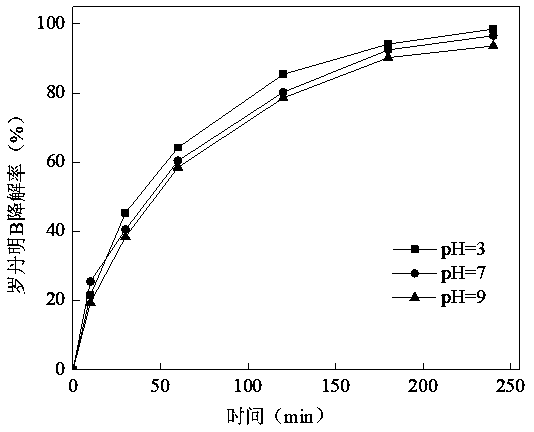
[0019] Experimental conditions: Fe 0 The dosage was 0.5 g / L, the dosage of PDS was 2 g / L, the reaction temperature was 25 ℃, and the initial pH were 3, 7, and 9, respectively.
[0020] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that under acidic, neutral and alkaline conditions, Fe 0 The / PDS system has a high degradation rate for rhodamine B dye wastewater, but the degradation rate is slightly different. After 30 min of reaction, the degradation rate reached 45.4 % under acidic conditions, 40.5 % under neutral conditions, and 38.4 % under alkaline conditions.
Embodiment 3
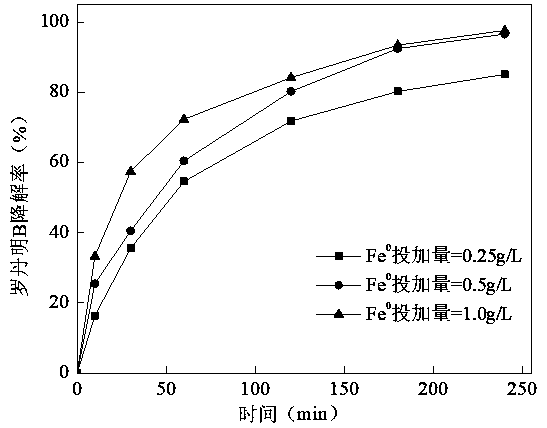
[0022] Experimental conditions: PDS dosage is 2 g / L, initial pH is 7, reaction temperature is 25 °C, Fe 0 The dosage is 0.25, 0.5, 1.0 g / L respectively. Depend on image 3 It can be seen that when Fe 0 When the dosage increased from 0.25 g / L to 0.5 g / L, the degradation rate of Rhodamine B also increased from 85.1 % to 96.6 %, but when Fe 0 When the dosage was increased to 1 g / L, the removal rate did not increase significantly.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com