Bilaterally-excited tangential magnetic steel hybrid excited brushless motor
A hybrid excitation and brushless motor technology, applied to synchronous motors with stationary armature and rotating magnets, magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, etc., can solve the limitation of magnetic modulation efficiency and power density , low space utilization, low power density, serious geometric constraints of the stator, etc., to achieve the effect of high excitation efficiency, simple structure, simple and reliable brushless AC excitation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
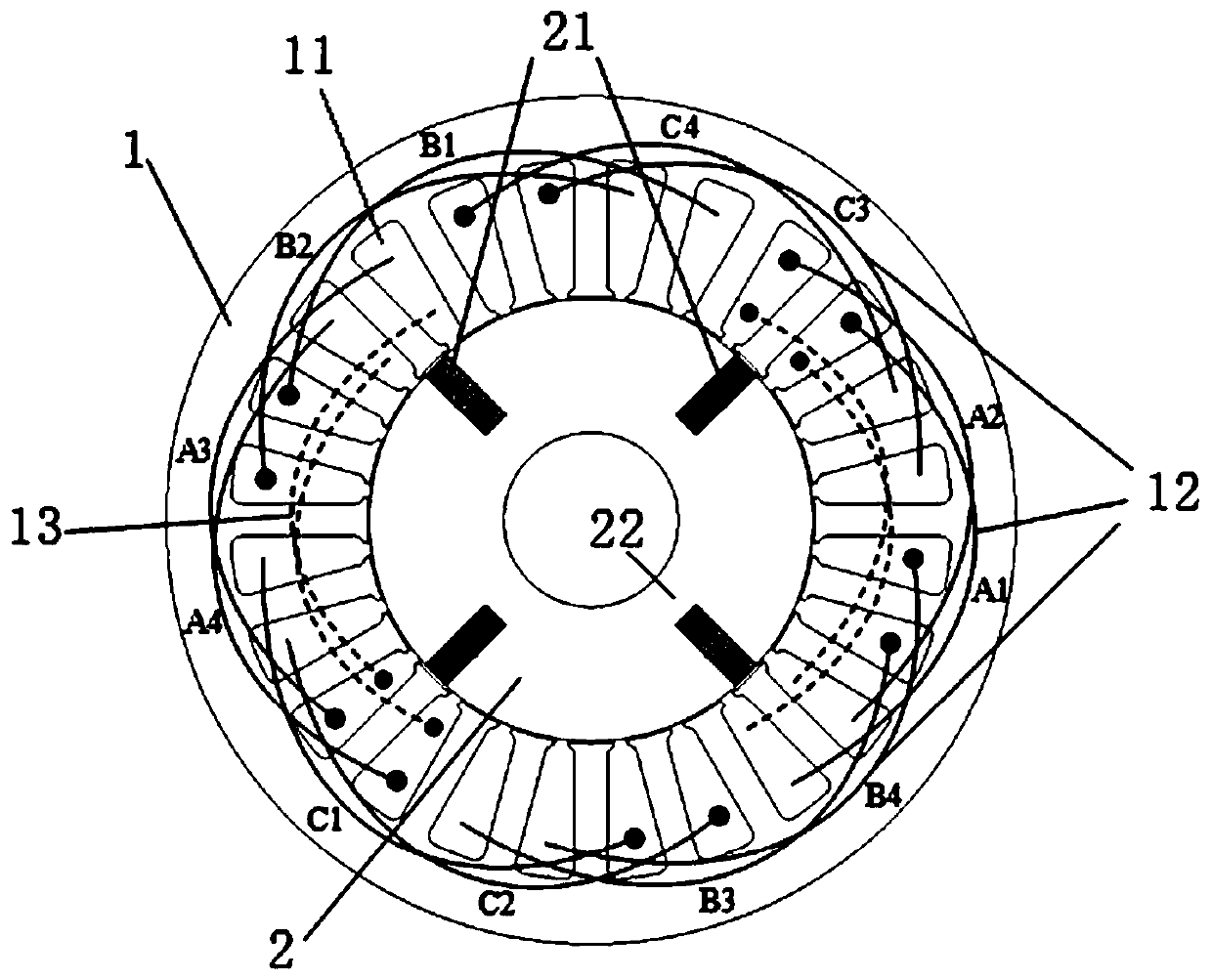
[0049] With three-phase inner rotor motor m=3, N s =24, p =3 as an example, where m represents the number of motor phases, N s Indicates the number of stator slots, and p indicates the number of rotor pole pairs.
[0050] Such as figure 1 As shown, a bilateral excitation type tangential magnetic steel hybrid excitation brushless motor includes a stator 1, a rotor, a tangential magnetic steel 21, a magnetic bridge 22, an armature winding 12 and an excitation winding 13; between the stator and the rotor there is gap.
[0051] In this embodiment, both the stator and the rotor core are preferably made of magnetically permeable materials.
[0052] Both the armature winding and the field winding are AC windings, which are respectively wound on both sides of the stator slot in the stator. The relative winding positions of the armature winding and the field winding can be exchanged, that is, the field winding is outside the slot when the armature winding is inside the slot, or ...
Embodiment 2
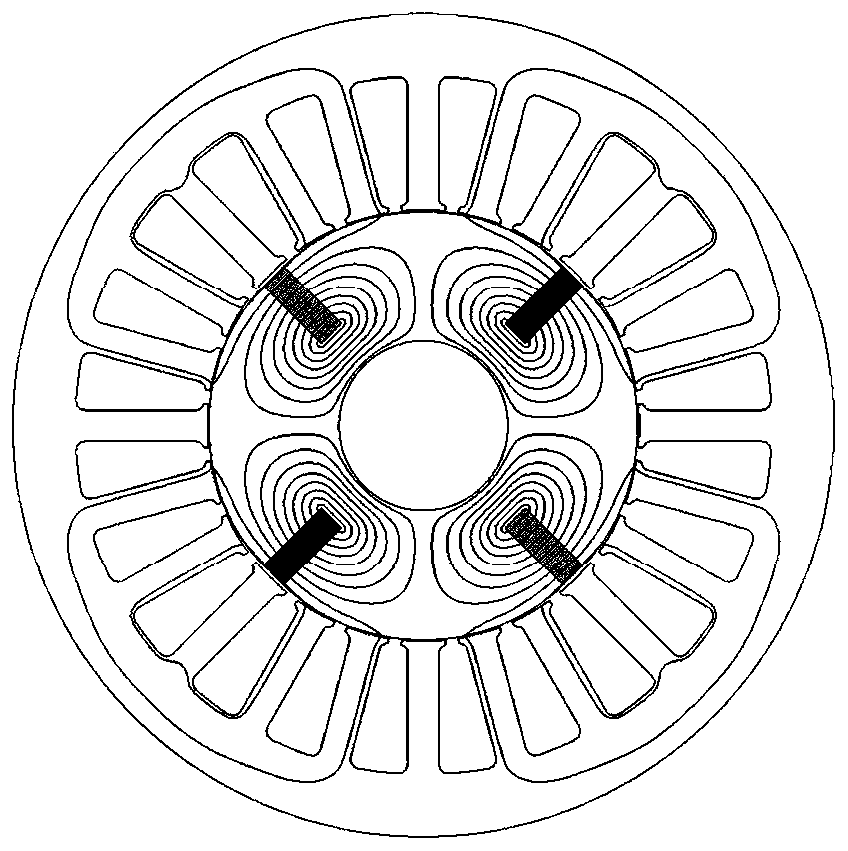
[0064] In Embodiment 1, a magnetic barrier is set on the quadrature-axis magnetic circuit of the rotor to increase the reluctance of the quadrature-axis magnetic circuit, which can reduce the influence of the armature reaction on the AC excitation magnetic field and the permanent magnetic field, thereby improving the output capacity of the motor.
[0065] The magnetic barrier can be a surface quadrature magnetic barrier 23 or a built-in quadrature magnetic barrier. Both the surface quadrature magnetic barrier and the built-in quadrature magnetic barrier are preferably air gaps or non-magnetically conductive materials.
[0066] The magnetic barrier in Embodiment 2 is a surface cross-axis magnetic barrier, which is arranged on the outer surface of the rotor, preferably on the outer surface of the rotor corresponding to the position of the tangential magnetic steel, that is, to increase the air gap of the cross-axis magnetic circuit, as Figure 4 shown.
Embodiment 3
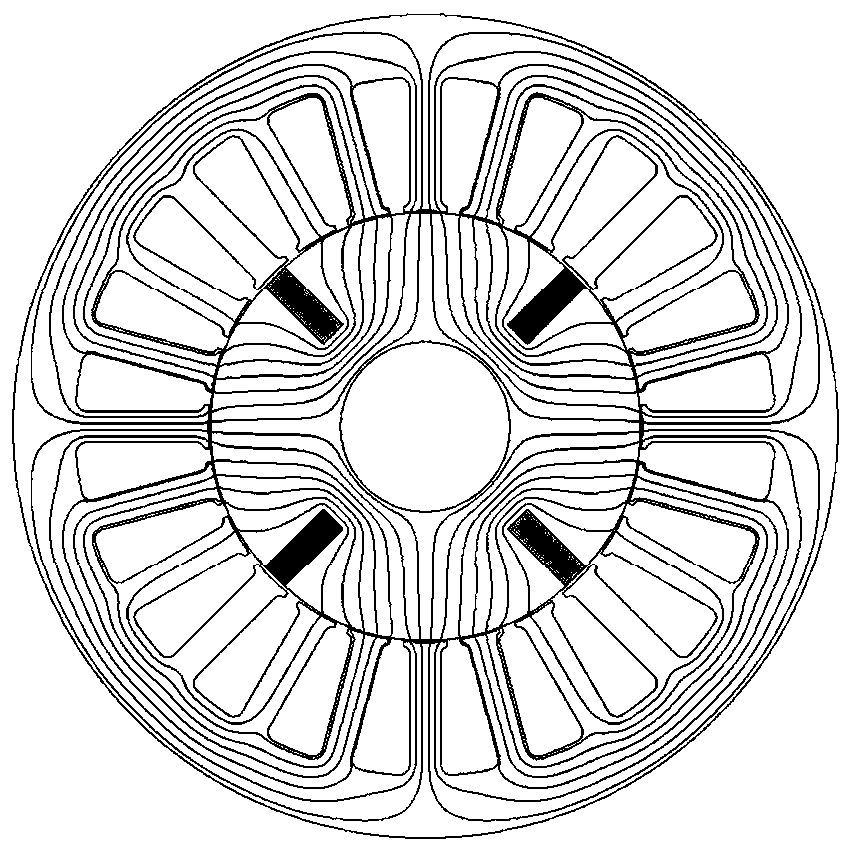
[0068] The magnetic barrier includes both the surface quadrature-axis magnetic barrier and the built-in quadrature-axis magnetic barrier, that is, on the basis of embodiment 2, the built-in quadrature-axis magnetic barrier inside the iron core is added, such as Figure 5 As shown, it is set on the rotor core between two adjacent tangential magnetic steels. Alternatively, the magnetic barrier can also be only a built-in quadrature axis magnetic barrier.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com