Application of three components of scutellaria baicalensis to synergistically improving cell proliferation enhancement of FGF2 (fibroblast growth factors 2)
A technology of FGF2- and baicalin, applied in the field of molecular biology, to achieve the effect of clear target
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1 Preparation of Radix Scutellariae Extract
[0029] Purchase dried scutellaria baicalensis slices from pharmacies, remove impurities, grind the dried scutellaria baicalensis into a uniform powder, weigh 2 g of the powder and add 20 mL of methanol for ultrasonic extraction, extract 3 times, each time for 20 min, filter and combine the extracts, pass through 0.22 μm The filter membrane was blown with nitrogen, concentrated and dried, redissolved in ultrapure water, passed through a 0.22 μm filter membrane, and stored at 4°C until use.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2 Screening the components that bind to FGF2 in the extract of Scutellaria baicalensis
[0031] 1. Preparation of FGF2-Scutellaria baicalensis active ingredient complex
[0032] FGF2 lyophilized powder was dissolved in 10 mM pH6.8 ammonium acetate buffer to obtain FGF2 ammonium acetate solution; according to the ratio of FGF2 ammonium acetate solution: Scutellaria baicalensis extract (v:v) = 1:1, mix to form FGF2-Scutellaria baicalensis extract liquid mixture; incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes to make the active ingredient in the Scutellaria baicalensis extract combine with FGF2 to form a complex of FGF2-Scutellaria baicalensis active ingredient;
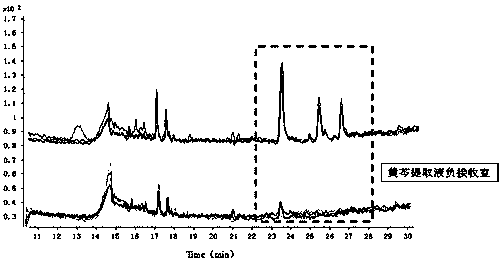
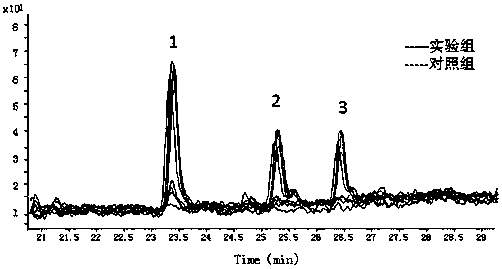
[0033] 2. Multi-chamber electrophoresis separation
[0034] The hatched FGF2-scutellaria baicalensis extract mixture is used as the sample solution, and the scutellaria baicalensis extract is used as the control solution, which are respectively the experimental group and the control group; multi-chamber electrophoresis...
Embodiment 3
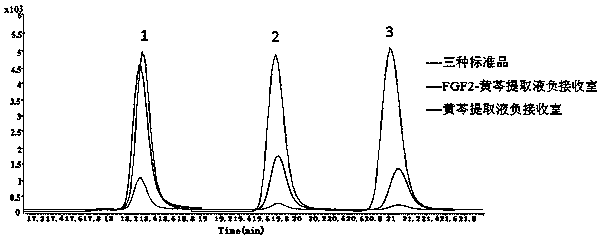
[0048] Example 3 Qualitative analysis of active components of Scutellaria baicalensis combined with FGF2
[0049] 1. The solution in the receiving chamber after the dissociation of Example 2 is subjected to HPLC high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum analysis;
[0050] Chromatographic conditions:
[0051] Chromatographic column: C18 (4.6 mm×150 mm, 5 μm)
[0052] Mobile phase: 0.1% formic acid aqueous solution (A), 0.1% formic acid acetonitrile solution (B)
[0053] Injection volume: 5μL
[0054] Flow rate: 0.5 mL min -1
[0055] Gradient elution procedure:
[0056] Time (min) Mobile phase B (%)
[0057] 0 0
[0058] 7 0
[0059] 10 25
[0060] 20 40
[0061] 30 65
[0062] 40 80
[0063] Mass Spectrometry Conditions:
[0064] Electrospray ion source, negative ion mode, using full scan mode; spray gas pressure: 30 psi; dry gas (N 2 ) flow rate: 13.0 L / min, drying gas temperature: 300°C; capillary vo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com