Laser amplification method based on disc crystal and solid laser amplifier
A solid-state laser and amplifier technology, applied in the field of lasers, can solve the problems of low amplification times of seed light and poor beam quality, and achieve the effects of avoiding excessive peak power, increasing the times of amplification, and improving the utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
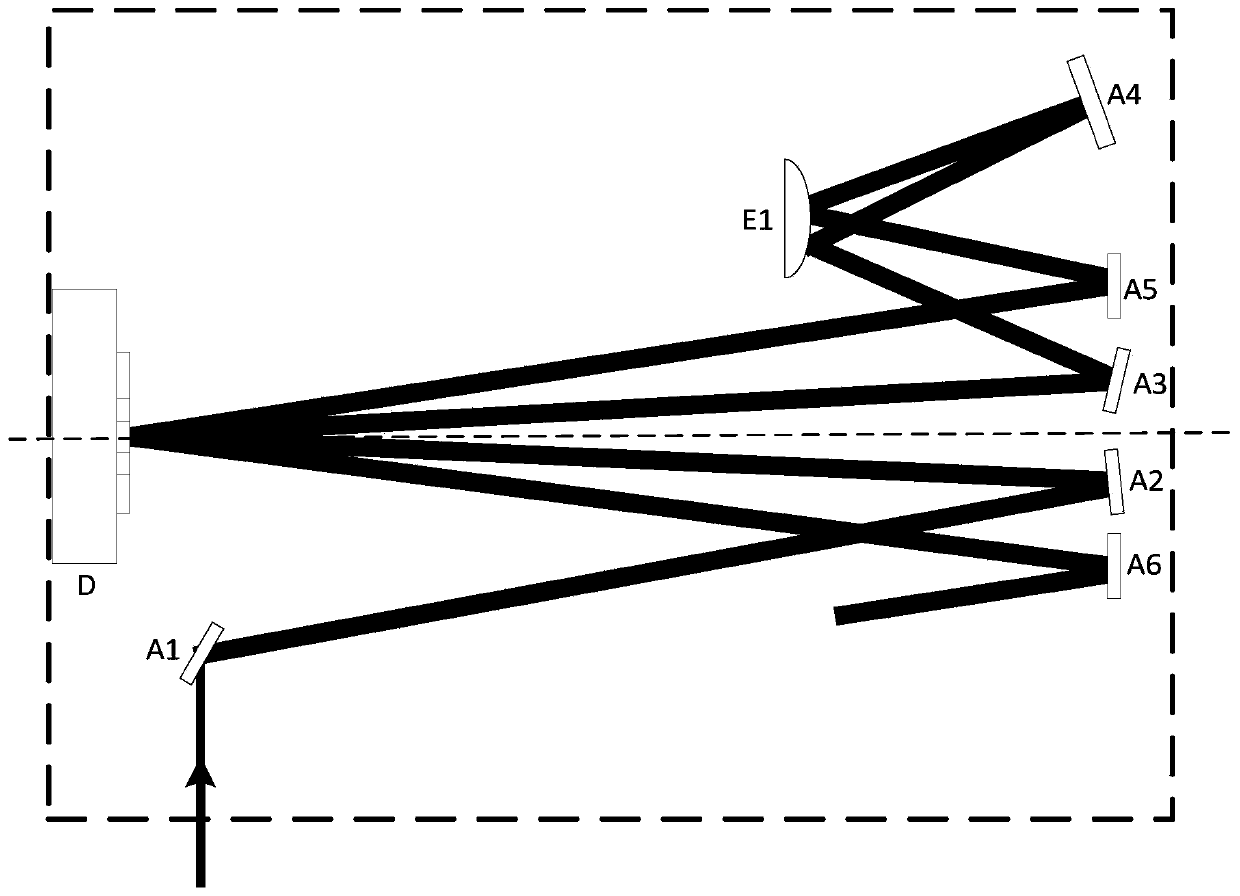
[0060] Please refer to Figure 4 , in this embodiment, both the first amplifying unit and the second amplifying unit are multi-pass amplifying units. Among them, the first amplification unit of the inner cavity adopts figure 2 As shown in the structure, the second amplification unit of the external cavity adopts figure 1 structure shown. The concave mirror E2 and the convex lens E3 form a collimating beam expansion unit, and the plane mirrors A1, A6 and A7 are auxiliary reflection units.
[0061] In this embodiment, the seed light is reflected by A1, enters the inner cavity and is transmitted to A2, then reflected to the disc crystal D, reflected to A3 through the disc crystal, then to the convex mirror E1, reflected to A4 and then to E1 , the seed light is transmitted to A5, then transmitted to the disc crystal again, reflected to A6 and then reflected by A6 into the collimator beam expander unit, then passed through the concave mirror E2 and convex lens E3 in turn to be ...
Embodiment 2
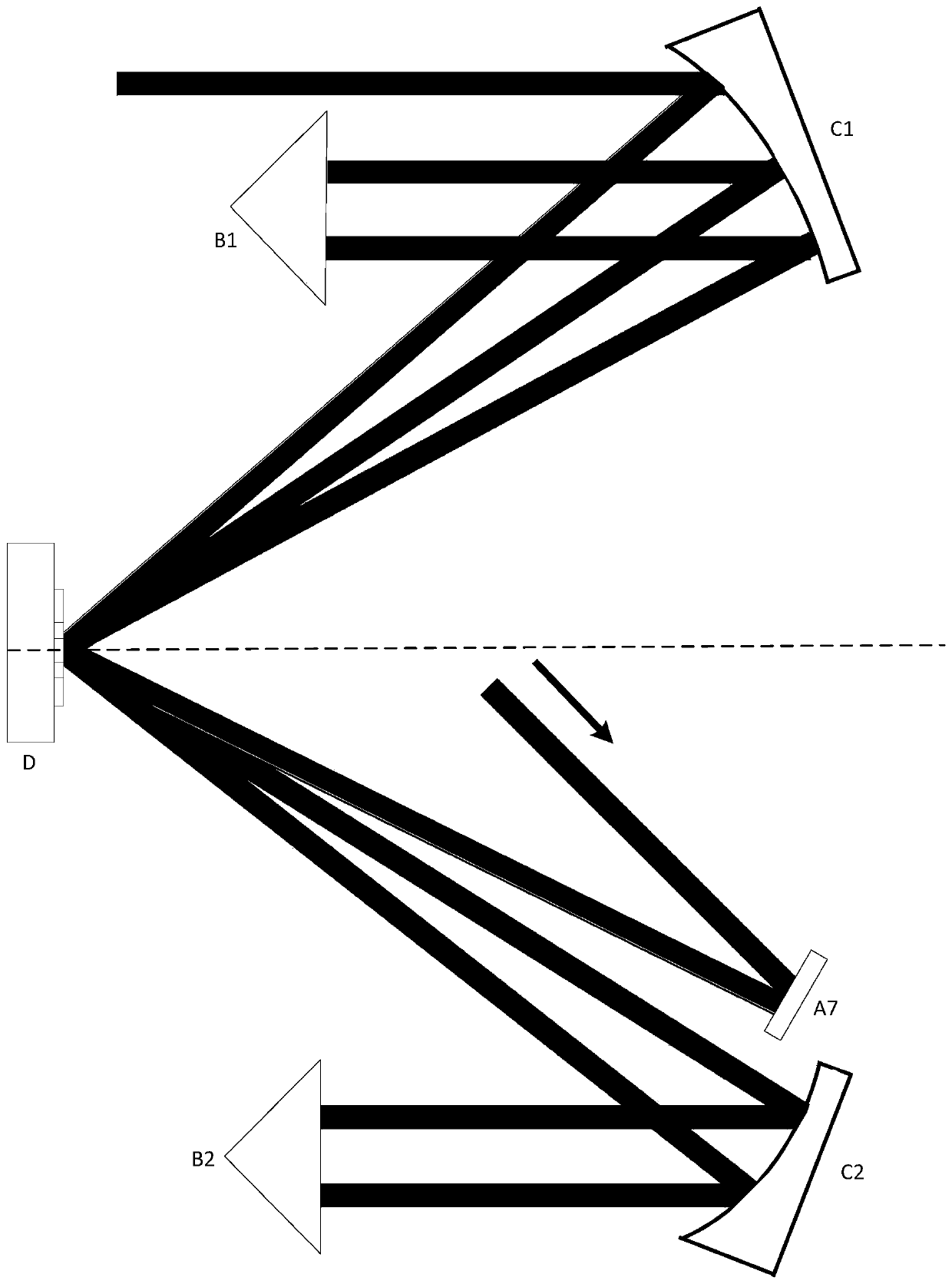
[0064] Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of a solid-state laser amplifier with a parabolic mirror-right-angle prism assembly inside and outside the cavity; the inner cavity and the outer cavity both use a parabolic mirror-right-angle prism combination, and both are multi-pass amplification units. Similarly, E2 and E3 form a collimating beam expansion unit, and A8, A9 and A10 are auxiliary reflection units.
[0065] The seed propagation path is similar to the path of the outer cavity in Example 1. The incident light is first reflected into the inner cavity through A8, transmitted to C3, then focused to D, reflected by D and transmitted to C4 in parallel (in the case of the disc crystal method line) out. Next, similar to the outer cavity of Example 1, the light is transmitted to C4 again through B4, and then focused to D, the light is reflected to C3, and then transmitted to C3 again through B3, and then focused to D, transmitted to C4 and transmitted by C4 Reflected out of ...
Embodiment 3
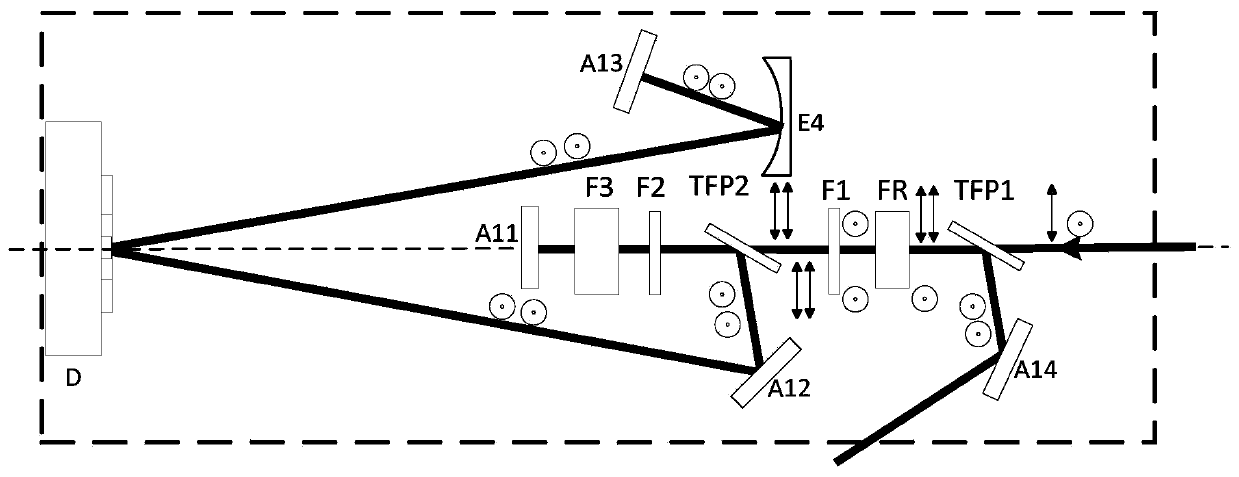
[0068] Image 6 It is a schematic diagram of a laser amplifier where the inner cavity is a regenerative amplification unit and the outer cavity is a parabolic mirror-right-angle prism assembly; in this embodiment, the inner cavity uses a regenerative amplification unit, and the outer cavity uses a parabolic mirror-right-angle prism assembly, which is actually multi-pass amplification and regenerative amplification The same combination of E2 and E3 constitutes a collimating beam expander unit, and A15 is an auxiliary reflection unit.
[0069] The polarization state of the incident light includes p light (arrow) and s light (center point). After passing through TFP1, only p light passes through. After passing through FR from right to left, the polarization state changes and becomes s light, and then passes through the half-wave plate. The s light turns into p light, and then passes through TFP2 again, and then passes through F2; F3 does not work at this time, the light passes th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com