Method for quickly detecting rice bakanae pathogen F.fujikuroi based on RPA
A technology for Fusarium Fujikura and pathogenic bacteria, which is applied in the field of plant protection, can solve the problems of low detection result accuracy, long detection time, and dependence on sophisticated instruments and equipment, and achieves the effect of high specificity and sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Example 1, RPA detection nucleotide primer combination screening of rice bakanae pathogen Fusarium fujikura
[0061] 1. Primer design
[0062] 1. A large number of sequence analyzes and comparisons were carried out to obtain 6 primers (as shown in Table 1) for detecting the rice bakanae pathogen Fusarium fujikura.
[0063] Table 1 The sequence of RPA primers used to detect the rice bakanae pathogen Fusarium fujikura
[0064] Primer name Primer sequence (5'-3') F1 CCATTCAACACATACATCCGCCACCTCACT F2 CAACACATACATCCGCCACCTCACTGAACAAGAC F3 ACATACATCCGCCACCTCACTGAACAAGAC R1 CTAGGAGATGGTCGCTTAGAGTAGGTAGATCAAGG R2 TTCGTTGGATCGTATCTGTAGCCGAGGATTGGT R3 CTAGGAGATGGTCGCTTAGAGTAGGTAGATCAAGG
[0065] 2. Combine the 6 primers designed in step 1 into 3 pairs of primer combinations (as shown in Table 2).
[0066] Table 2 RPA primer combination and product size
[0067] Numbering Primer combination Product size (bp) ...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Embodiment 2, specificity
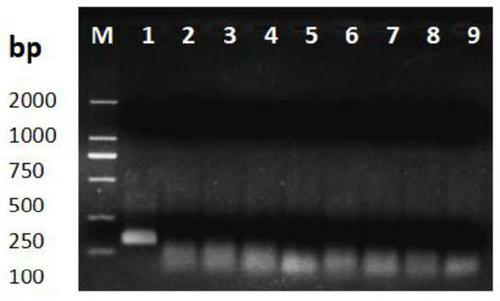
[0087] Tested strains: rice bakanae pathogen Fusarium fujikura, rice sheath blight Rhizoctonia solani, rice koji, rice blast fungus, wheat head blight fungus Fusarium graminearum and wheat equisetum.
[0088] 1. Inoculate the strain to be tested on a PDA plate, culture in the dark at 25°C for 7 days, scrape the mycelium with a sterile inoculation needle into a sterile centrifuge tube, and extract the DNA of the mycelium by CTAB method.
[0089] 2. Extract the total DNA of healthy rice leaves.
[0090] 3. Get the DNA sample that steps 1 and 2 obtain, take described DNA sample as template, adopt the primer that primer F and primer R form to carry out RPA reaction (reaction method sees step 2 and 3 of second part in embodiment 1) . Set to use ddH 2 0 as a negative control group for the template.
[0091] The result is as figure 1 shown. The results show that only the RPA amplification product corresponding to the rice bakanae pathogen Fusa...
Embodiment 3
[0092] Embodiment 3, sensitivity
[0093] 1. Inoculate the rice bakanae pathogen Fusarium Fujikura on a PDA plate, culture in the dark at 25°C for 7 days, scrape the mycelium with a sterile inoculation needle into a sterile centrifuge tube, and extract the DNA of the mycelium by CTAB method (the DNA concentration is 861.9 ng / μL).
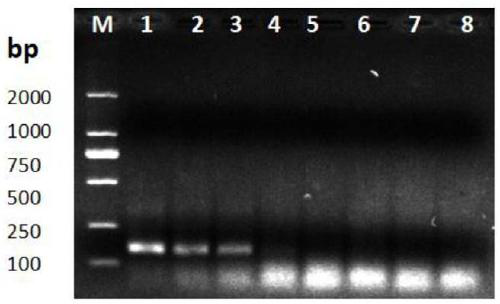
[0094] 2. The mycelia DNA obtained in step 1 was diluted step by step with a 10-fold gradient, respectively 10 -1 、10 -2 、10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 、10 -6 A total of 6 dilutions, resulting in concentrations of 86.19ng / μL, 8.619ng / μL, 8.619×10 -1 ng / μL, 8.619×10 -2 ng / μL, 8.619×10 -3 ng / μL and 8.619×10 -4 ng / μL DNA solution.
[0095] 3. Using the DNA samples that were diluted in different gradients in step 2 as a template, a primer pair consisting of primer F and primer R was used to perform RPA reaction (see steps 2 and 3 in the second part of Example 1 for the reaction method).
[0096] Set to use ddH 2 0 as a negative control group for the t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com