Method for mining relevance of species in micro-organisms
A technology of microbiota and association, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve the problems of complex microbial network, large amount of metagenomics data, insufficient to restore the true relationship of bacterial communities, etc., to achieve the effect of deepening understanding and ensuring comprehensiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1 FS-Weight method
[0034] (1) Sampling and sequencing
[0035] In the MG-Rast database, a healthy Chinese youth human gut data set numbered MGP 15838 was obtained (this data set contains 16s rRNA samples of intestinal flora of 314 healthy people, covering 8 ethnic groups in 7 provinces of China samples), use the species annotation software QIIME (version 1.91) for species annotation and relative abundance calculation, count the obtained species to the genus level, and take the genera with an average abundance greater than 0.01% at the genus level for network construction.
[0036] DNA was extracted, and 5,102,015 high-quality metagenomic sequences were generated by high-throughput sequencing. The quality control software Mothur was used to control the quality of the sequences, and 24,125 microbial OTUs were obtained, and the species annotation and relative abundance were performed using the species annotation software QIIME (version 1.91). degree calculati...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Embodiment 2PCA-PMI method
[0055] (1) Sampling and sequencing
[0056] Step is with embodiment 1;
[0057] (2) Loose Definition algorithm to process data
[0058] Step is with embodiment 1
[0059] (3) Relevance Mining
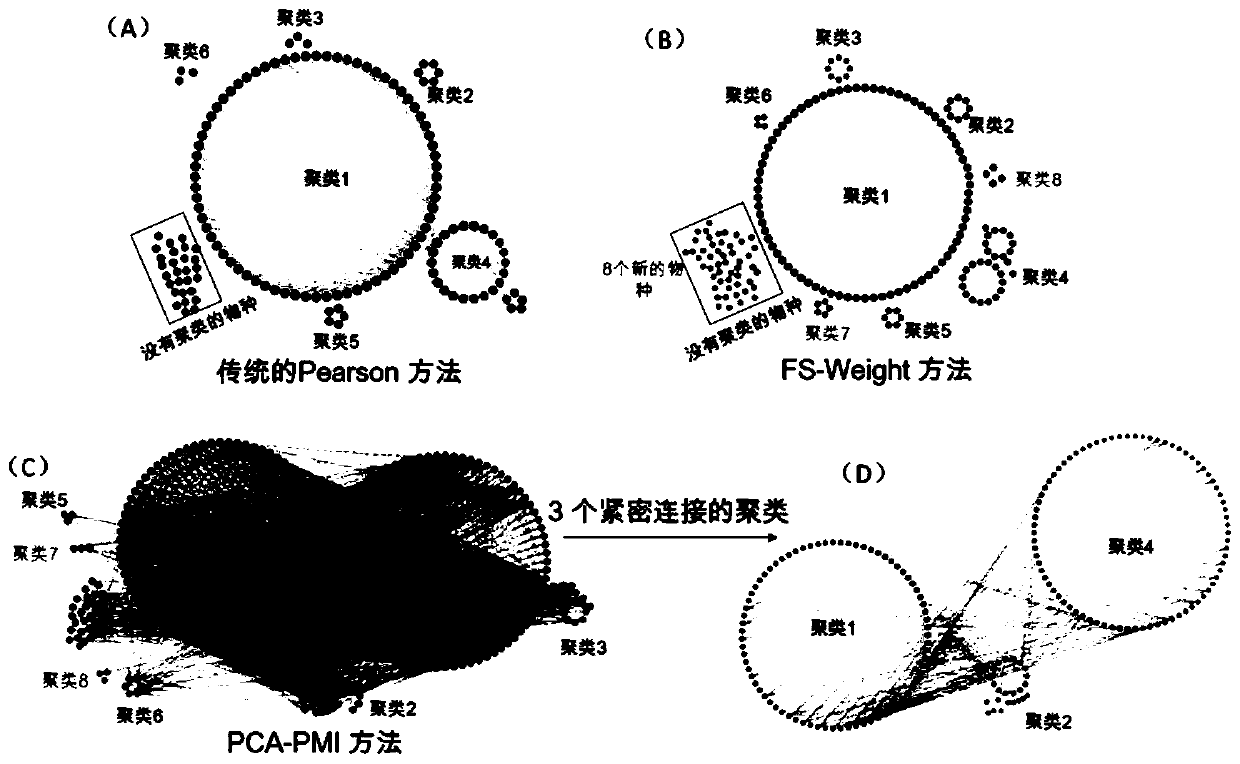
[0060] Using the concept of entropy in information theory, the partial mutual information (PCA-PMI) algorithm adjusted by the road consistency algorithm is used to calculate the linear and nonlinear correlation of the network.
[0061] The steps to mine linear and nonlinear relationships are divided into 3 steps:
[0062] 1) Calculate the entropy between any two species using mutual information;
[0063] 2) On the basis of mutual information, for any two species, consider other species connected to the two species, and calculate the partial mutual information of the two species;
[0064] 3) On the basis of the mutual information threshold (80%) given by the user, the road consistency algorithm is used to screen the mutual information. The road ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Embodiment 3 Loose Definition method
[0069] (1) Sampling and sequencing
[0070] Step is with embodiment 1;
[0071] (2) Loose Definition algorithm to process data
[0072] Step is with embodiment 1
[0073] (3) Relevance Mining
[0074] Co-occurrence networks were constructed using the traditional Pearson algorithm. The Pearson correlation coefficient is a linear correlation coefficient, which is used to reflect the statistics of the degree of linear correlation between two variables. The larger the absolute value of the Pearson correlation coefficient, the stronger the correlation.
[0075] (4) Calculation and detection
[0076] For the constructed network, the cytoscape software was used for visualization, and the MCODE clustering algorithm was used to detect potential clusters; cluster members were aligned according to taxonomic or functional annotation databases; the most connected nodes were calculated as candidates for hub nodes, and these nodes were sele...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com