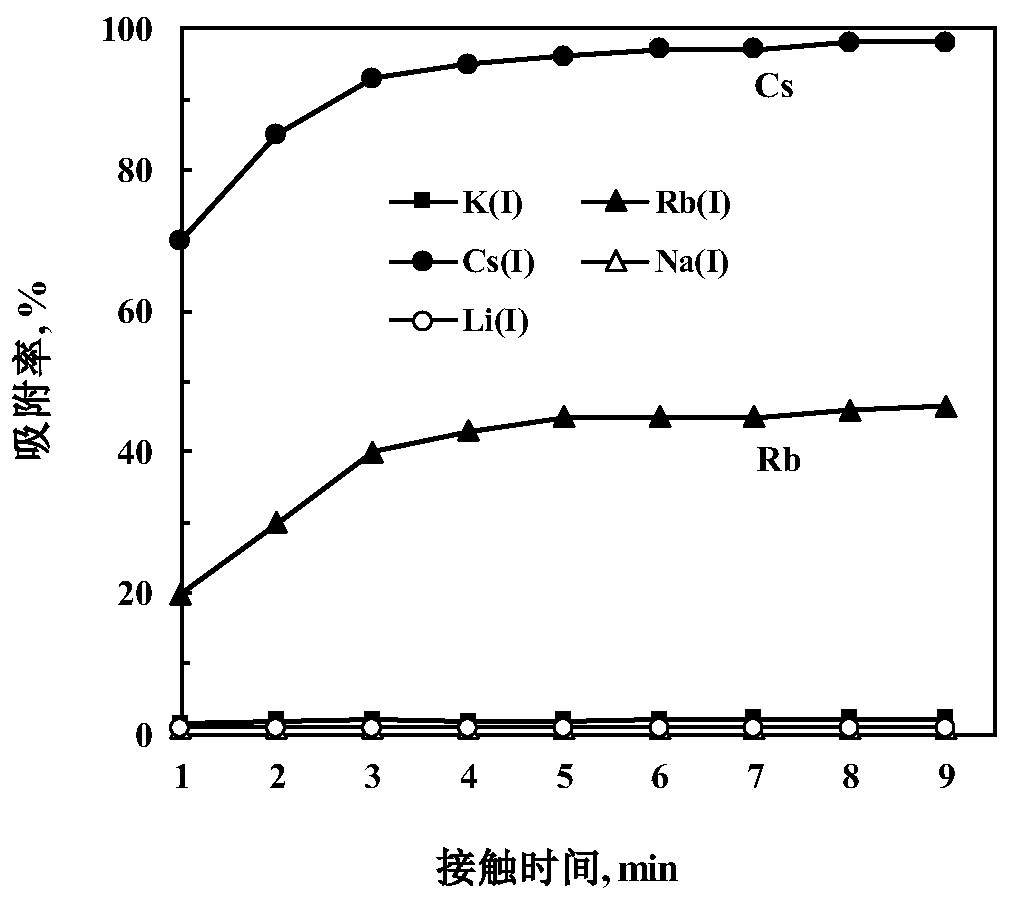
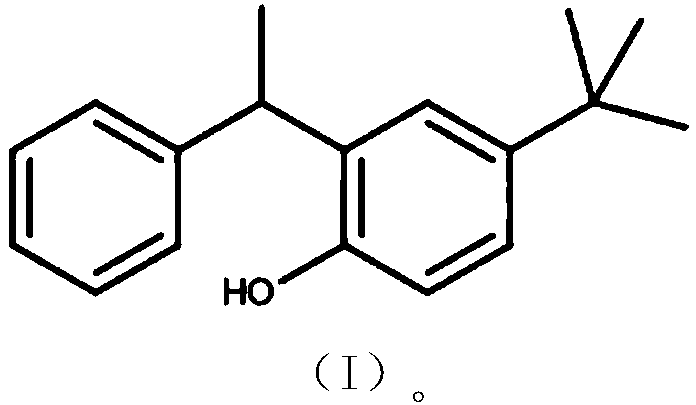
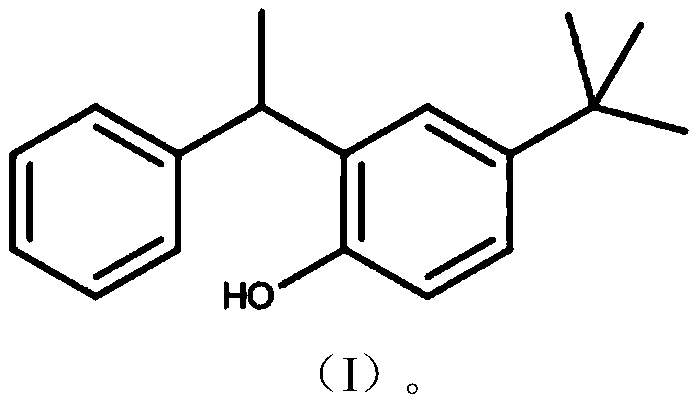
Method of adsorbing and separating rubidium and caesium
An adsorption separation and adsorbent technology, applied in the field of element separation, can solve the problems of difficult separation process, low selectivity, rubidium and cesium separation, etc., and achieve the effect of easy promotion, good selectivity and fast separation speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] 1g is dissolved in the compound shown in structural formula (I) in 100.0mL dichloromethane, fully dissolves, and adds 10.0gSiO in the gained solution 2 -P Stir well to make SiO 2 -P is mixed evenly with the compound shown in the structural formula (I), and most of the dichloromethane is volatilized by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure until the material is in a near-dry state, and the organic molecules enter SiO under capillary action and physical adsorption. 2 -P pores, and then vacuum-dry the nearly dry material at 45°C for 24 hours to obtain an adsorbent.
Embodiment 2
[0033] 0.5g of the compound shown in the structural formula (I) was dissolved in 75.0mL of dichloromethane, fully dissolved, and 3.0g of SiO was added in the resulting solution 2 -P Stir well to make SiO 2 -P is mixed evenly with the compound shown in the structural formula (I), and most of the dichloromethane is volatilized by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure until the material is in a near-dry state, and the organic molecules enter SiO under capillary action and physical adsorption. 2 -P pores, and then vacuum-dry the nearly dry material at 50°C for 24 hours to obtain an adsorbent.
Embodiment 3
[0035] 0.7g of the compound shown in the structural formula (I) was dissolved in 80.0mL of dichloromethane, fully dissolved, and 5.0g of SiO was added in the resulting solution 2 -P Stir well to make SiO 2 -P is mixed evenly with the compound shown in the structural formula (I), and most of the dichloromethane is volatilized by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure until the material is in a near-dry state, and the organic molecules enter SiO under capillary action and physical adsorption. 2 -P pore size, and then vacuum-dry the nearly dry material at 55° C. for 24 hours to obtain an adsorbent.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap