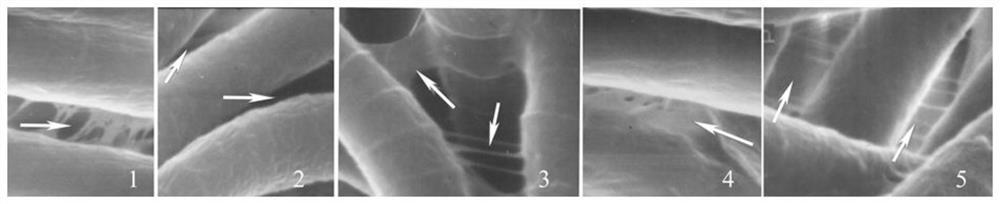
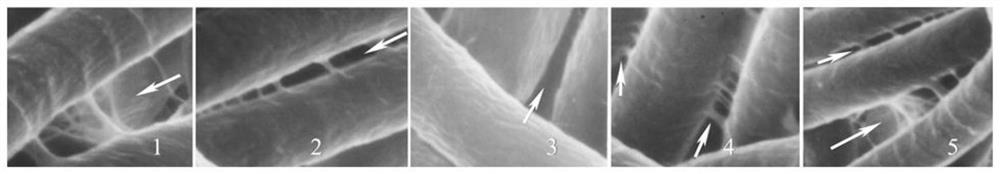
A method for identifying the drainage performance of spirulina algae filaments using scanning electron microscopy
An electron microscope, spirulina technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, determination/inspection of microorganisms, material analysis using wave/particle radiation, etc. low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The technical solutions of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific implementation examples.
[0022] 1. Selection of sample materials: 2 well-known Spirulina platensis strains Sp-3 and Sp-15 that are widely used in large-scale production and cultivation are also preserved in the Institute of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences of Zhejiang University affiliated to the applicant. The applicant guarantees that samples can be provided to the public as needed during the validity period of the patent.
[0023] 2. Reagents and instruments: The filter paper used for filtration is produced by Hangzhou Wohua Filter Paper Co., Ltd.; the chemical reagents are all domestic analytical grades; the BX-53 optical microscope with DP-73 from Japan Olympus Company is used to observe and measure the morphology of algal filaments; the scanning electron microscope AMRAY / KYKY-1000B scanning electron microscope produced by Beijing Analytical Instrument Fac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com