A PID-type iterative learning control method based on neural network
A technology of iterative learning control and neural network, applied in the field of PID iterative learning control based on neural network, to achieve good precision and efficient iterative learning and tracking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
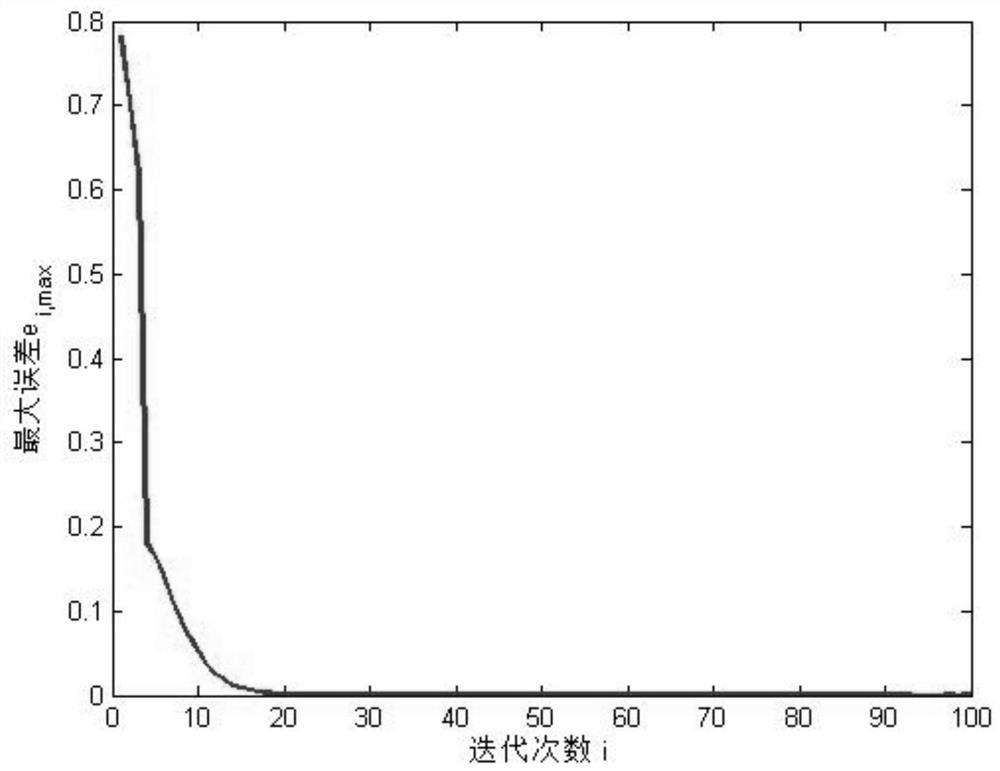
[0079] Consider the following system:
[0080]
[0081] Obviously, this is a non-affine nonlinear system. The expected output trajectory in the iterative learning task is:
[0082] the y d (t)=0.5×(-1) round(t / 10) t∈I[1,100]
[0083] We adopt the iterative learning scheme formula (17) proposed in the present invention to control the system, and now we pre-set the structure of the neural network and the initial values of the parameters. The three neural networks used to estimate the gain of the PID controller all use a hidden layer with three nodes, and the inputs of the three neural networks are:
[0084]
[0085] For all i∈I[1,+∞), t∈I[1,T], we set the radial basis function center of the neural network to be [0 0 0] T , with a width of 100; for all t∈I[1,T], the input of the first iterative neural network is set to z S,1 (t)=[0 0 0] T . The weight of the first iteration is w P,1 (t) = [0.2 0 0] T ,w I,1 (t)=[0 0 0] T ,w D,1 (t) = [0 00] T ; For all t∈I[...
Embodiment 2
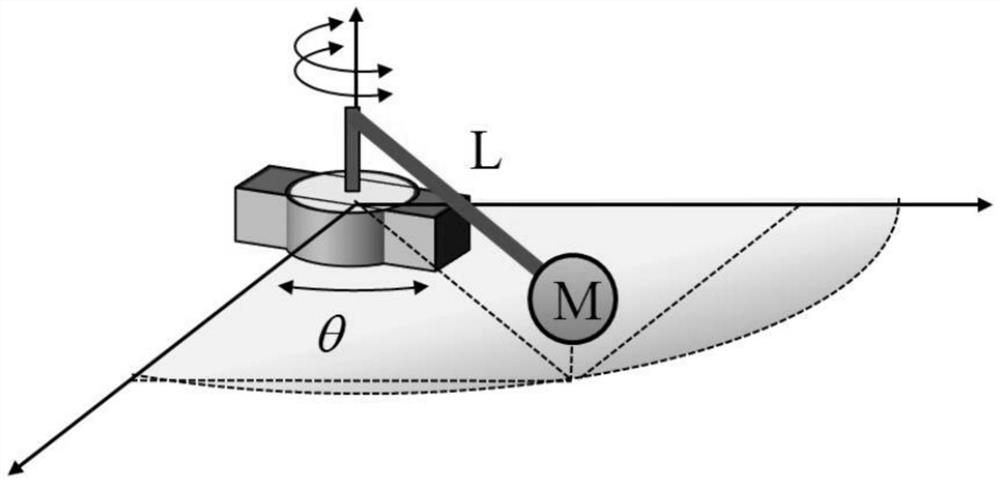
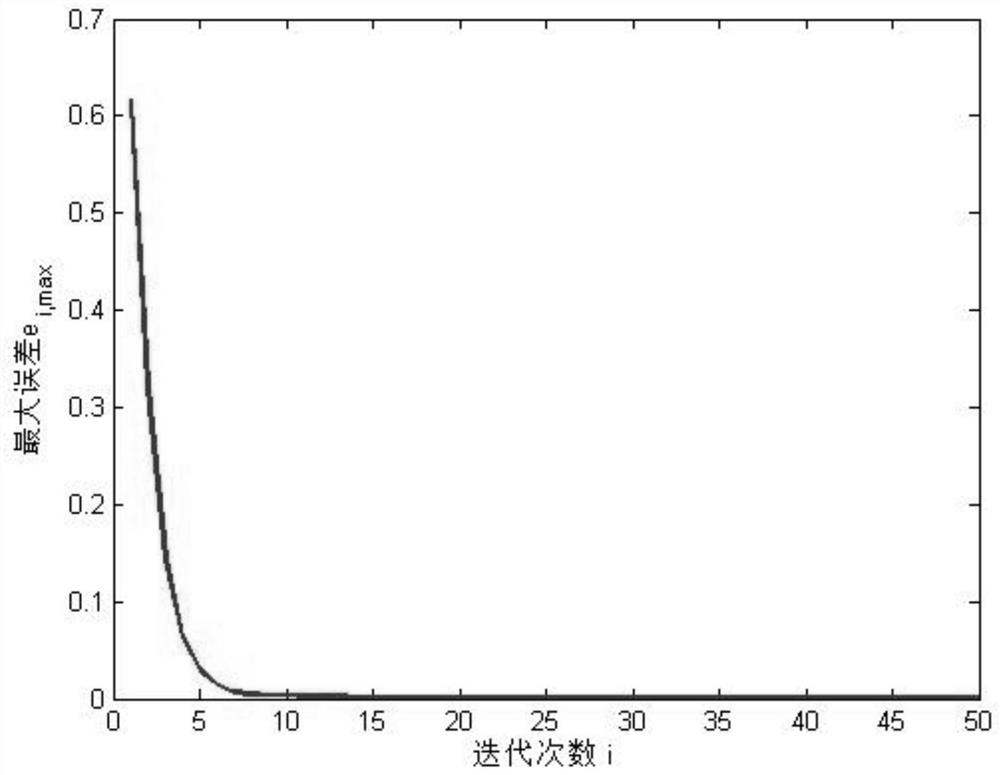
[0088] Such as figure 2 is a pick-and-place robot model (refer to non-patent literature 2: Liu N. Learning identification and control for repetitive linear time-varying systems [D]. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2014.), for the rotation angle θ of the manipulator, we get the state variable x 1 = θ and And taking the angular velocity as the system output, the following second-order linear mathematical model can be obtained:
[0089]
[0090] Where β=2Nm / rad is the viscous friction coefficient, K t =100 is the gain of the actuator, M(t) is the mass at the bottom of the time-varying manipulator, and L=0.1m is the length of the manipulator. During the pick-and-place process of the robotic arm, the heavy object is grasped in the 5th second and put down in the 10th second. The mass of M(t) also changes from 1kg to 10kg and then back to 1kg.
[0091] Take the sampling time T s =0.01s, the discretization model (19) in the time interval [1,10] can obtain the fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com