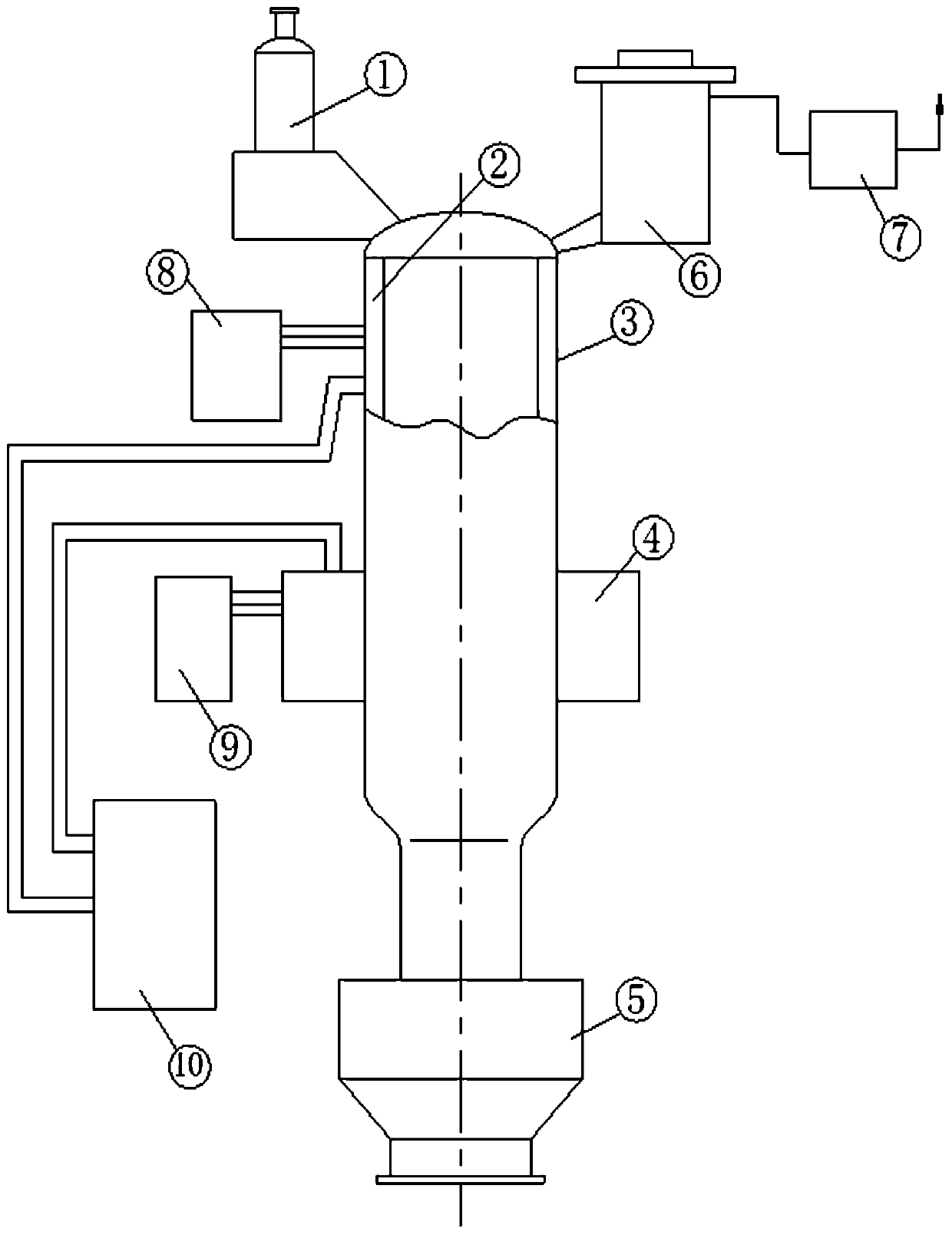
Vacuum smelting furnace for reducing magnesium metal
A technology of vacuum smelting and metal magnesium, applied in the field of light metals, can solve the problems of increasing energy consumption, high labor intensity, and high pressure on environmental protection, and achieve the effects of improving work efficiency, reducing labor intensity and saving energy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The present invention will be described in detail below in combination with specific embodiments.
[0030] Such as figure 1 As shown, the vacuum smelting furnace for reducing metal magnesium of the present invention includes: vacuum feeding device 1, induction heater 2, furnace body 3, microwave heater 4, vacuum discharge device 5, condensation tank and crystallizer 6, Vacuum system 7, induction heater power supply 8, microwave heater power supply 9, cooling circulating water system 10. Induction heater power supply 8 provides suitable heating energy for induction heater 2; microwave heater power supply 9 provides suitable heating energy for microwave heater 4; cooling circulating water system 10 guarantees induction heater 2 and microwave heater 4 in suitable Working at high temperature; the vacuum feeding device 1, induction heater 2, furnace body 3, microwave heater 4, vacuum discharge device 5, condensation tank and crystallizer 6, vacuum system 7, induction heater...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com