Corneal epithelial cells and corneal stent, and preparation methods and applications thereof
A corneal epithelial cell, cornea technology, applied in epidermal cells/skin cells, embryonic cells, animal cells, etc., can solve the problems of corneal shortage, immune rejection, obstacles, etc., achieve continuous cell transparency, reduce immune rejection obstacles, low immunity original effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
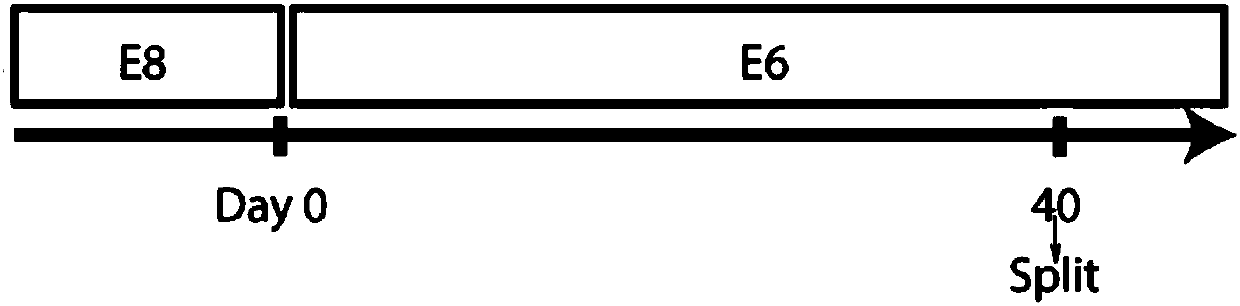
[0045] hESCs were induced to differentiate into CECs in defined and albumin-free E6 medium
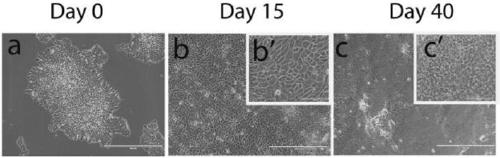
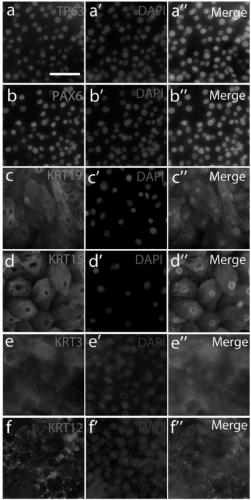
[0046] H9hESCs routinely cultured in E8 were differentiated into CECs in E6 according to the flow chart (Fig. 1A). By day 15 of differentiation, the cells mostly developed an epithelial morphology, some of which had a polygonal morphology typical of CECs (Fig. 1B). In this example, the cells were subcultured on day 40, and the cells were immunostained within one week after subculture. Most cells were positive for the CEC progenitor markers TP63 and PAX6, another CEC progenitor keratin-19 (KRT19), and the basal CEC marker KRT15. After 20 days of culture in E6 medium, many cells were also positive for two terminally differentiated CEC markers, KRT3 and KRT12 (Fig. 1C).
[0047] Gene expression was analyzed by RT-qPCR, and differentiated hESCs were collected every two weeks to study the expression of lineage-specific marker genes. The expression of the pluripotency marker OCT4 was down...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Gene expression profiles of hESCs differentiated into CECs
[0051] As expected, expression of pluripotency genes was significantly reduced at week 2 of differentiation and remained low. In this example, the expression of surface ectoderm markers was detected to increase at the 2nd week and the 4th week, and the expression of LSC and embryonic CEC markers were detected at the 6th and 8th weeks. Meanwhile, expression of neural and retinal markers increased at week 2, peaked at week 4, and then gradually decreased, whereas expression of lens progenitor cell markers continued to increase during all 8 weeks of differentiation. However, expression of adult CEC markers remained low in differentiated cells. These data demonstrate that the expression of eye development genes, particularly those associated with epidermal ectoderm and embryonic CEC, is induced in E6 differentiated cells and that the multistep differentiation process somehow recapitulates the embryonic process of...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Proliferation capacity of hESC-derived CECs
[0054] LSCs first differentiate into CEC progenitors, migrate to the basal layer of the cornea, and terminally differentiate into CECs during corneal regeneration and homeostasis [42] . One of the characteristics of CEC progenitor cells is their ability to proliferate rapidly. Therefore, this example analyzes whether hESC-derived CECs are proliferative. First, in this example, the proliferative ability of CECs differentiated from H9 and CT3 hESCs was monitored respectively. Although neither CEC line proliferated as rapidly as the parental hESCs, CECs still proliferated at a relatively high rate throughout the 3-day observation period (Fig. 3A). Second, cell cycle assays showed that approximately 40% of CECs were in S and G2 / M phases ( Figure 3-B1~Figure 3-B3 ). Third, nearly half of the CECs from H9 or CT3 were KRT15 + Cells are Ki67 + (Fig. 3C and 3D). All these data indicate the proliferative nature of the cells. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com