Sintering method of sintered neodymium-iron-boron permanent magnet material
A sintering method and permanent magnet material technology, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, magnetic objects, inductance/transformer/magnet manufacturing, etc., can solve the problem of unexpected improvement of coercive force, solid phase sintering, grain growth, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of inhibiting grain growth, ensuring grain refinement, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
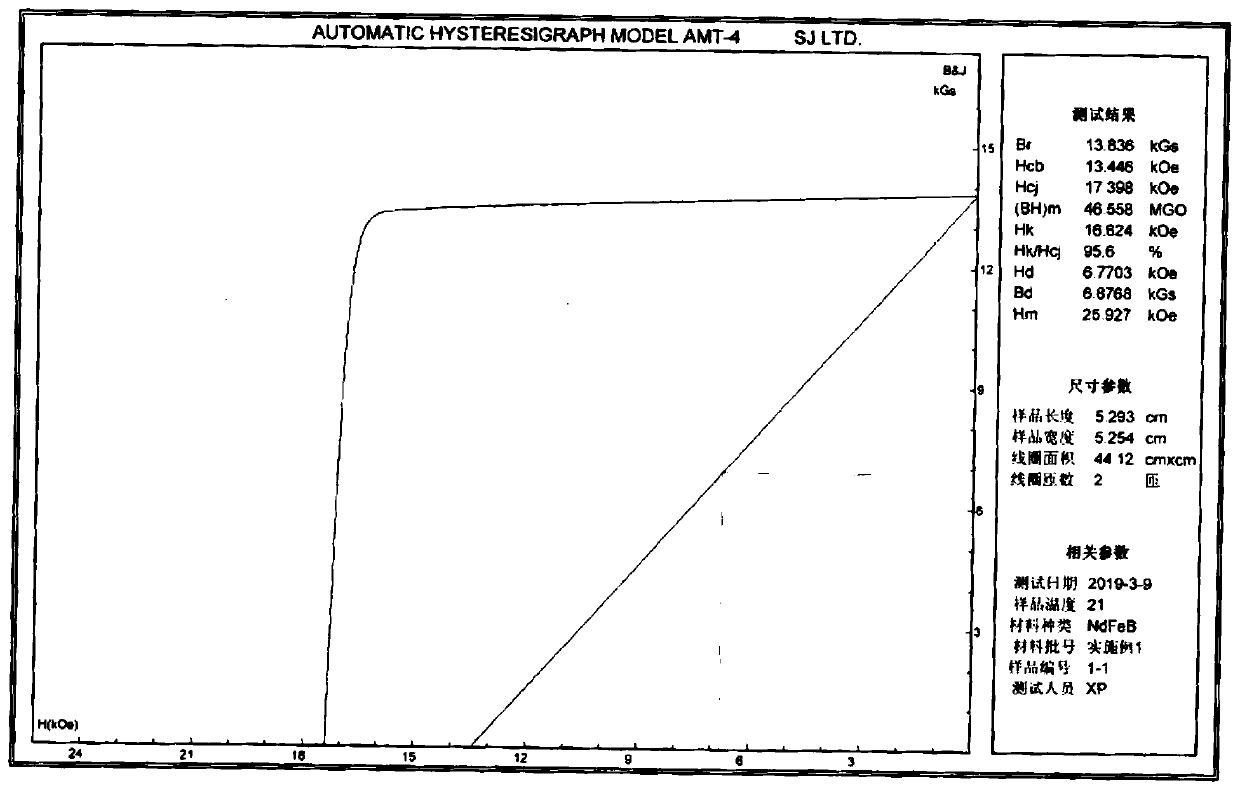
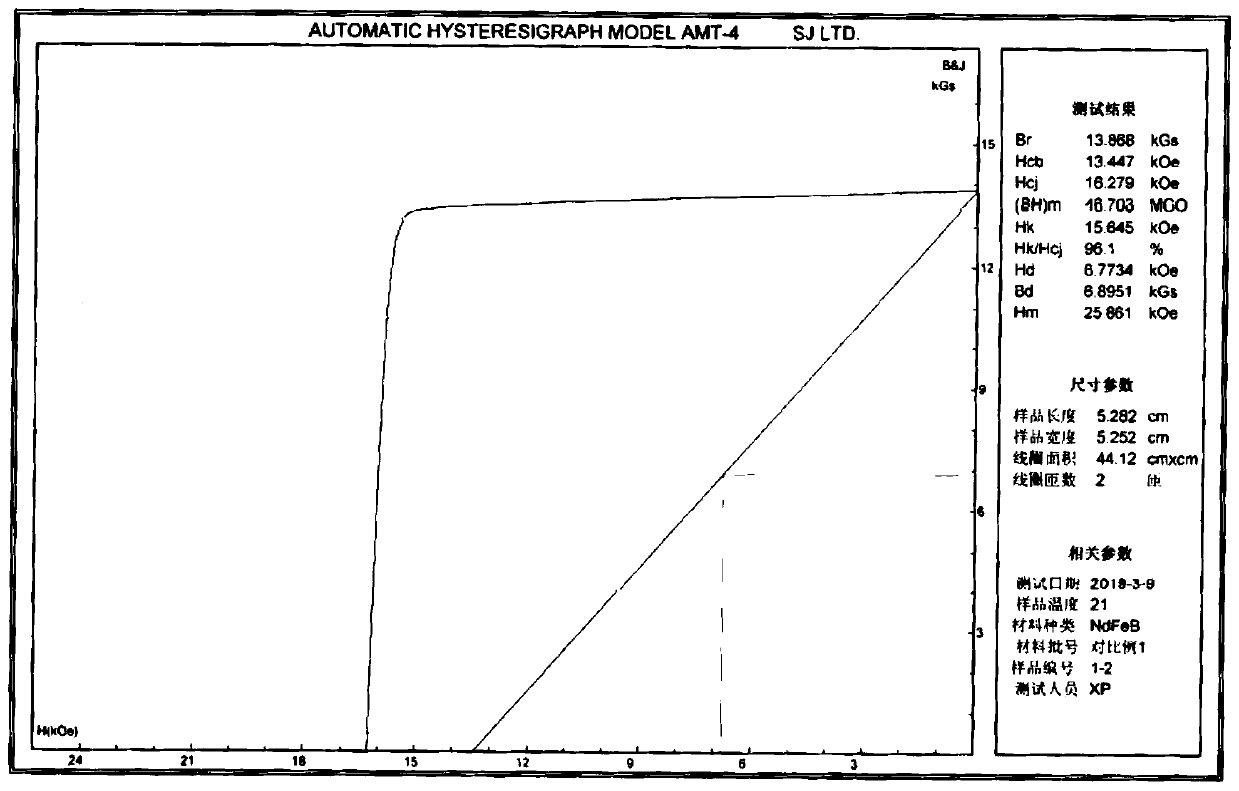
[0027] will be composed as Nd 10.2 PR 3.5 Dy 0.4 co 1.0 Cu 0.2 Al 0.2 Ga 0.1 Zr 0.1 B 5.7 Fe 78.6 (Atomic percentage) for batching, melting under the protection of inert gas, and then casting into cast pieces. The cast piece is coarsely crushed by the hydrogen crushing process, and then ground into a fine powder with a particle size of 4.0um (particle size: D50) by a jet mill, oriented and pressed into a compact in a molding press under the protection of nitrogen, and then sent to sintering furnace for sintering. The sintering process is as follows: from room temperature to 300°C, hold for 1 hour, then heat up to 600°C, hold for 2 hours, then heat up to 800°C, hold for 3 hours; when the temperature is 20°C lower than the optimum sintering temperature (the optimum sintering temperature is 1060°C) , that is, 1040°C, hold for 5h, and finally raise the temperature to the optimum sintering temperature of 1060°C, hold for 1.5h. After sintering, it is filled with argon gas...
Embodiment 2
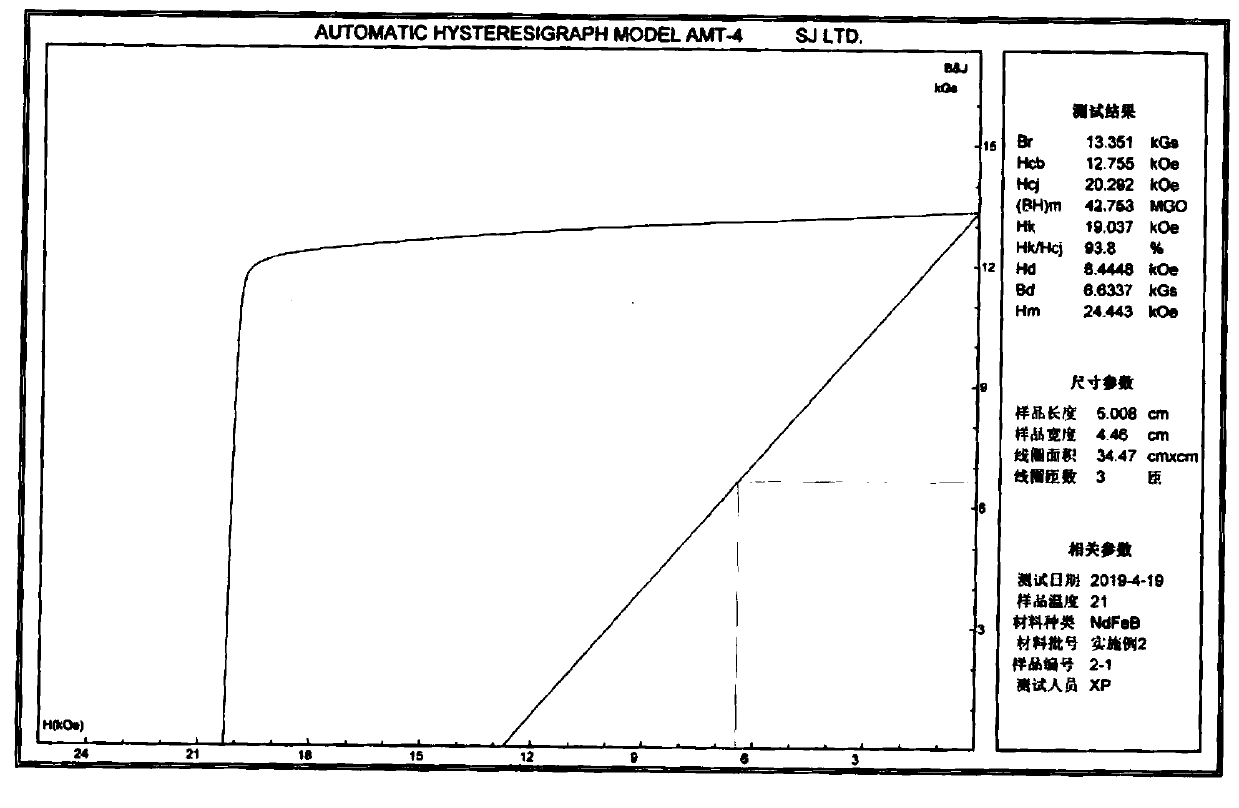
[0034] will be composed as Nd 10.3 PR 3.5 Dy 0.4 Tb 0.2 co 1.1 Cu 0.2 Al 1.0 Ga 0.2 Zr 0.1 B 5.7 Fe 77.3 (Atomic percentage) for batching, melting under the protection of inert gas, and then casting into cast pieces. The cast piece is coarsely crushed by the hydrogen crushing process, then ground into a fine powder with a particle size of 3.8um (particle size D50) by a jet mill, oriented and pressed in a molding press under the protection of nitrogen to form a compact, and then sent to sintering furnace for sintering. The sintering process is as follows: from room temperature to 300°C, hold for 1 hour, then heat up to 600°C, hold for 2 hours, then heat up to 800°C, hold for 3 hours; when the temperature is 20°C lower than the optimum sintering temperature (the optimum sintering temperature is 1065°C) , that is, 1050°C, hold for 5h, and finally raise the temperature to the optimum sintering temperature of 1065°C, hold for 2h. After sintering, it is filled with argon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com