Hybrid excitation multi-phase reluctance motor and power generation system
A technology of hybrid excitation and reluctance motors, which is applied in the direction of motors, synchronous machines, electric vehicles, etc., and can solve the problem of narrow magnetic field adjustment range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
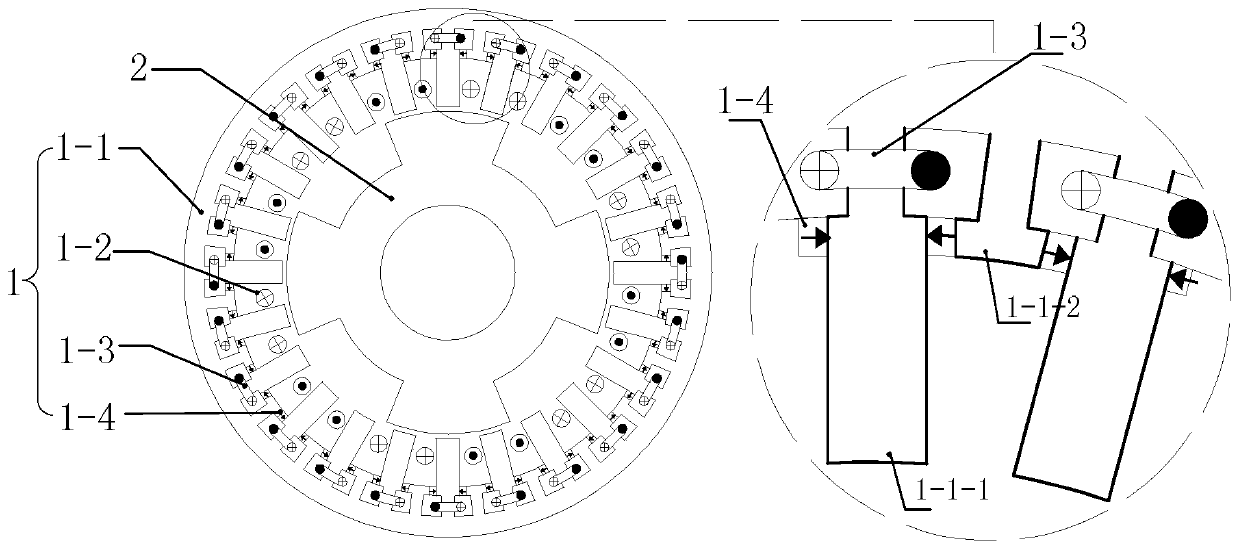
[0125] see figure 1 Describe this embodiment 1. The hybrid excitation multiphase reluctance motor described in this embodiment includes a stator 1 and a rotor 2, both of which are coaxial and have an air gap, and the rotor 2 is located in the stator 1;
[0126] The rotor 2 is composed of a rotor core, slotted in the axial direction on the air gap side of the rotor core, and the formed teeth and slots are arranged alternately along the circumferential direction;
[0127] The stator 1 is composed of a stator core 1-1, an m-symmetrical armature winding 1-2, an excitation winding and a permanent magnet 1-4; wherein, m is the number of phases of the motor;
[0128] The stator core 1-1 is a cylindrical structure, slotted in the axial direction on the air gap side, and the formed teeth and slots are arranged alternately along the circumferential direction; a total of 4Pmk teeth are formed on the air gap side of the stator core 1-1, and 4Pmk teeth are composed of 2Pmk long teeth 1-1...
Embodiment 2
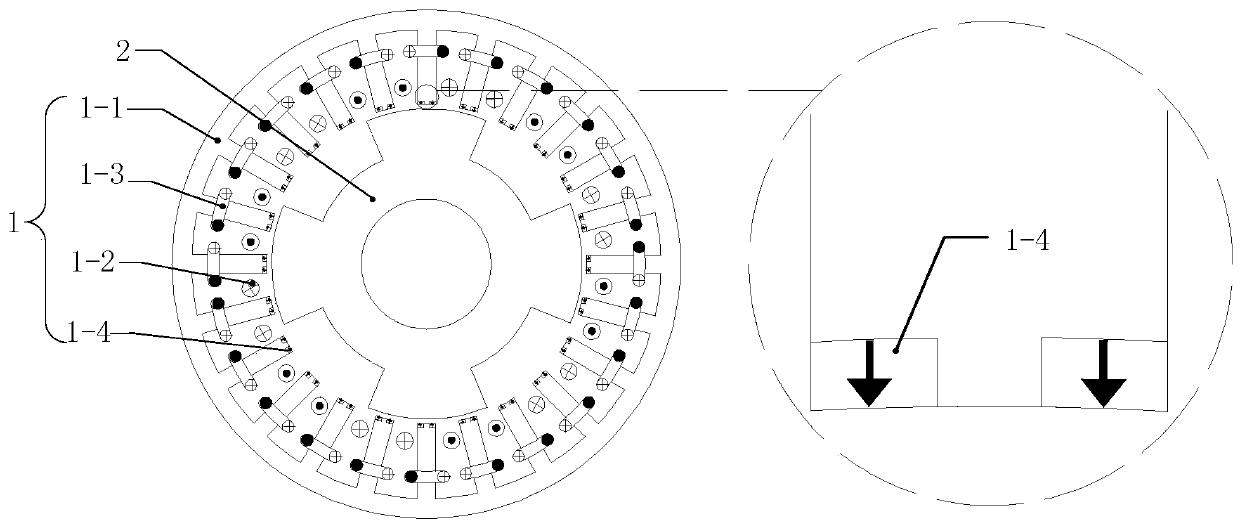
[0137] see figure 1 Describe this embodiment 2. The hybrid excitation multiphase reluctance motor described in this embodiment includes a stator 1 and a rotor 2, both of which are coaxial and have an air gap, and the rotor 2 is located in the stator 1;
[0138] The rotor 2 is composed of a rotor core, slotted in the axial direction on the air gap side of the rotor core, and the formed teeth and slots are arranged alternately along the circumferential direction;
[0139] The stator 1 is composed of a stator core 1-1, an m-symmetrical armature winding 1-2, an excitation winding and a permanent magnet 1-4; wherein, m is the number of phases of the motor;
[0140] The stator core 1-1 is a cylindrical structure, slotted in the axial direction on the air gap side, and the formed teeth and slots are arranged alternately along the circumferential direction;
[0141] A total of 2Pmk teeth are formed on the air gap side of the stator core 1-1, and an excitation coil 1-3 is wound on ea...
Embodiment 3
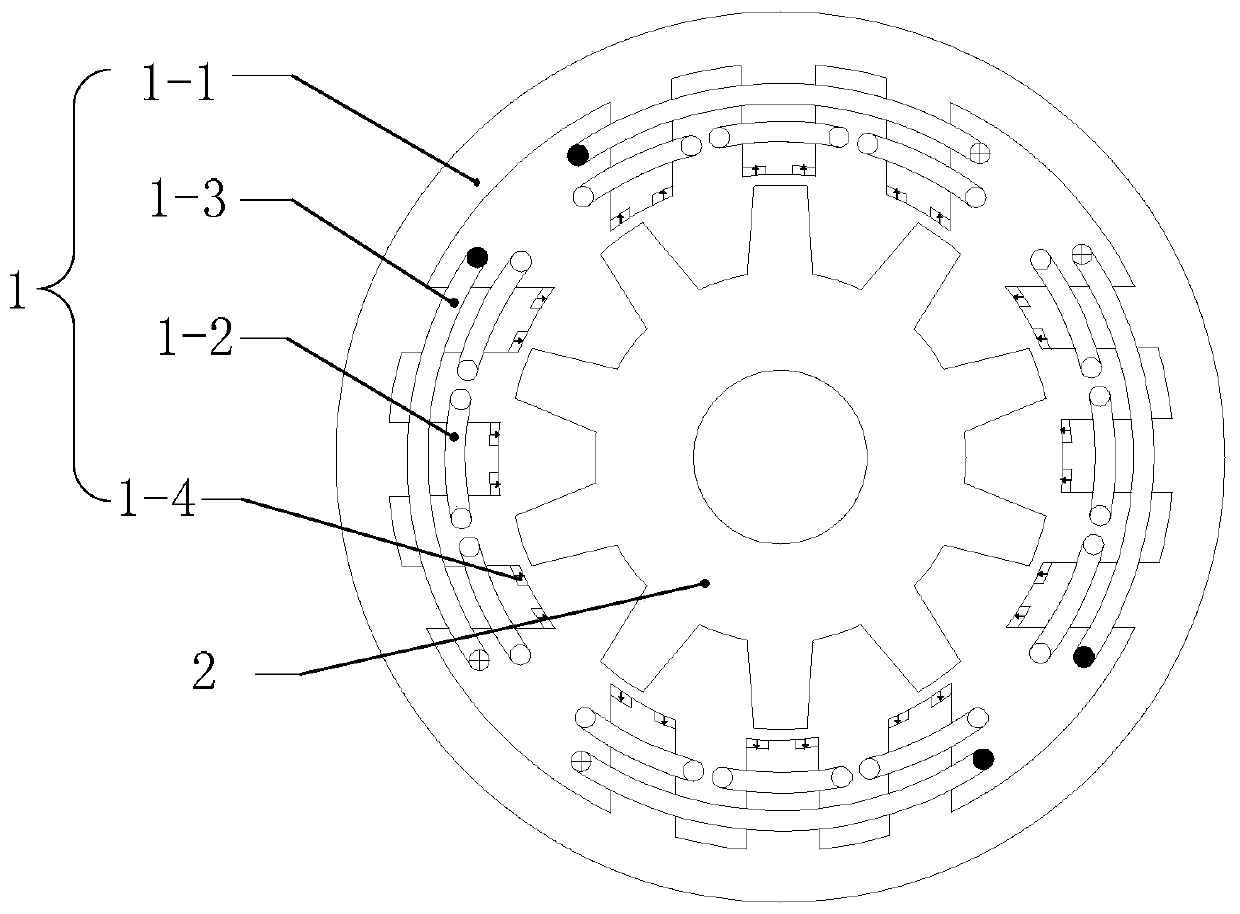
[0151] see image 3 with Figure 4 Describe this embodiment 3. The hybrid excitation multiphase reluctance motor described in this embodiment includes a stator 1 and a rotor 2, both of which are coaxial and have an air gap, and the rotor 2 is located in the stator 1;
[0152] The rotor 2 is composed of a rotor core, slotted in the axial direction on the air gap side of the rotor core, and the formed teeth and slots are arranged alternately along the circumferential direction;
[0153] The stator 1 is composed of a stator core 1-1, an m-symmetrical armature winding 1-2, an excitation winding and a permanent magnet 1-4; wherein, m is the number of phases of the motor;
[0154] The stator core 1-1 is a cylindrical structure, slotted in the axial direction on the air gap side, and the formed teeth and slots are arranged alternately along the circumferential direction;
[0155] A total of 2Pmk teeth are formed on the air gap side of the stator core 1-1, and an excitation coil 1-3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com