Method for catalytic degradation of antibiotics by nitrogen-doped modified nano titanium dioxide and evaluation method
A nano-titanium dioxide, catalytic degradation technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete removal of ciprofloxacin and secondary pollution, and achieve no secondary pollution. , good stability, the effect of reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] 1. Experimental materials
[0040] 1.1 Experimental reagents
[0041] Table 1-1 Main chemical reagents
[0042]
[0043] 1.2 Experimental instruments and equipment
[0044] Table 1-2 Main instruments and equipment
[0045]
[0046] 2. Experimental part
[0047] S01 dissolves 5 mg of ciprofloxacin in pure water to prepare a 5 mg / L ciprofloxacin solution;
[0048] S02 Take out 1L of the ciprofloxacin solution in step S01, adjust the pH value to 7.5, and calcinate the nano-TiO in a muffle furnace at 500°C with a mass ratio of urea / titanium dioxide of 1:1. 2 Add the photocatalyst to the ciprofloxacin solution, and turn on the magnetic stirrer to stir at the same time. The stirring time is 30min, and the reaction temperature is 25°C, so that the catalyst and the target pollutant reach the adsorption-desorption equilibrium. After the degradation is completed, the nano-TiO is recovered by filtration. 2 Photocatalyst and cleaning wastewater. Ciprofloxacin in clean w...
Embodiment 2
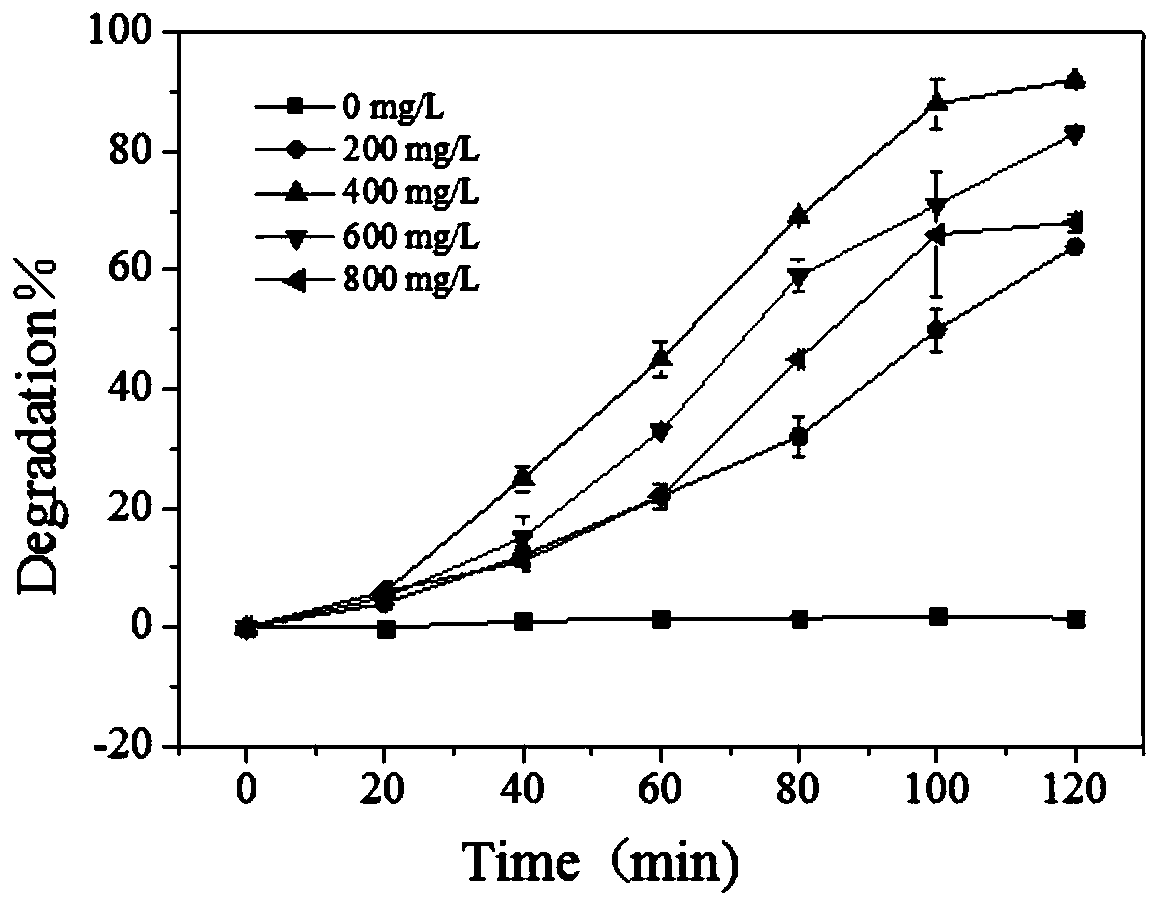
[0050] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that for nano-TiO 2 The effect of the dosage on photocatalytic degradation was investigated:
[0051] By studying different nano-TiO 2 Dosage (0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8g.L -1 ) in the photocatalytic degradation experiment under the condition of nano-TiO 2 The effect of dosage on the reaction rate. The experimental conditions are as follows: the temperature is 25° C., the concentration of ciprofloxacin is 5 mg / L, and the initial pH of the reaction solution is 7.5.
[0052] The results of the study were:
[0053] Nano-TiO 2The dosage is 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8g / L respectively. Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that when no photocatalyst is added, ciprofloxacin basically does not decrease, indicating that the degradation effect of the other four groups is mainly due to the nano-TiO 2 . Among the other four groups, the catalyst dosage of 0.4g / L had the best degradation effect. The reason may be that when the dos...
Embodiment 3
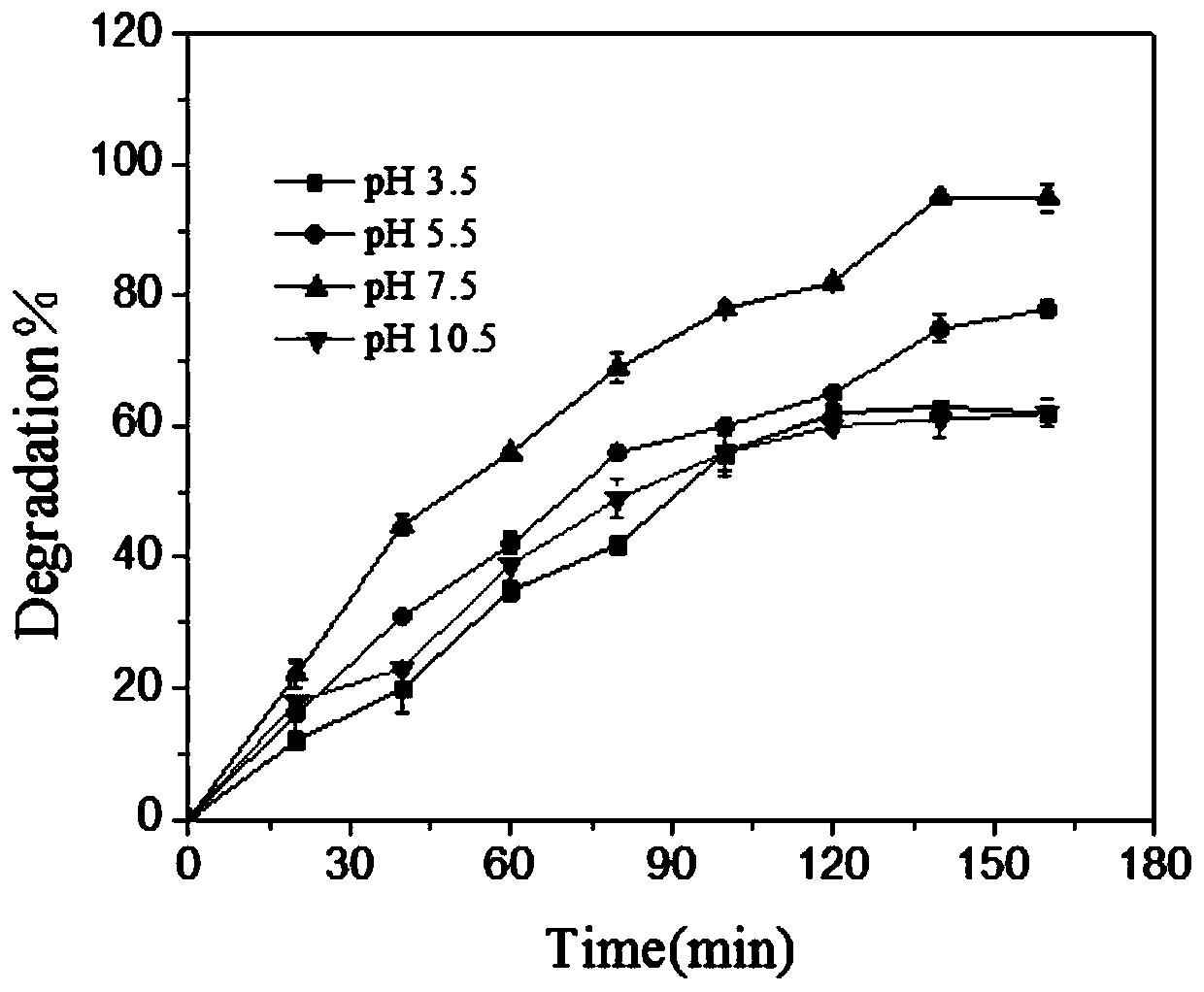
[0055] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is that the initial pH of the solution is investigated on the influence of the photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin:
[0056] The effect of pH value on the reaction rate was studied in the catalytic degradation experiments under the conditions of different initial pH (3.5, 5.5, 7.5, 10.5) of the solution. The test conditions are as follows: the temperature is 25°C, the dosage is 0.4g / L, and the concentration of ciprofloxacin is 5mg / L.
[0057] The result is:
[0058] Regulating the initial pH of ciprofloxacin solution is 3.5,5.5,7.5,10.5, and the dosage of catalyst is 0.4g / L, figure 2 Indicates the effect of materials on the photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin under different initial pH conditions. Such as figure 2 As shown, the initial pH of the solution increased continuously, but the degradation rate first increased and then decreased. And when the pH of the initial solution of ciprofloxacin is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com