Lever-cutting shock wave energy passive measurement sensor
A passive measurement and shock wave technology, applied in the direction of blasting force measurement, can solve the problems of difficult wiring, electromagnetic interference, cumbersome processing procedures, etc., and achieve the effect of rapid quantitative passive measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] In order to facilitate those skilled in the art to understand and implement the patent of the present invention, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
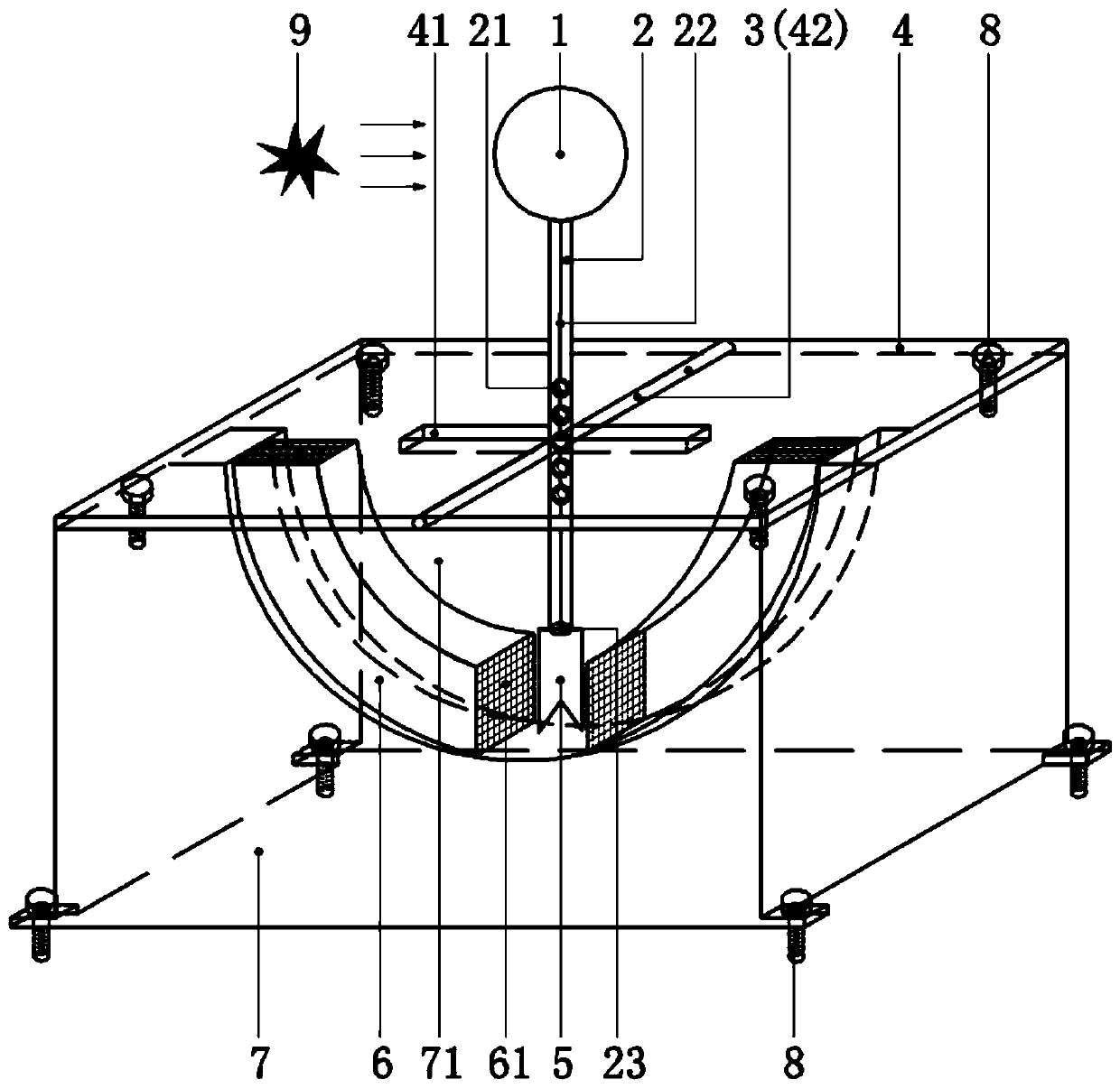
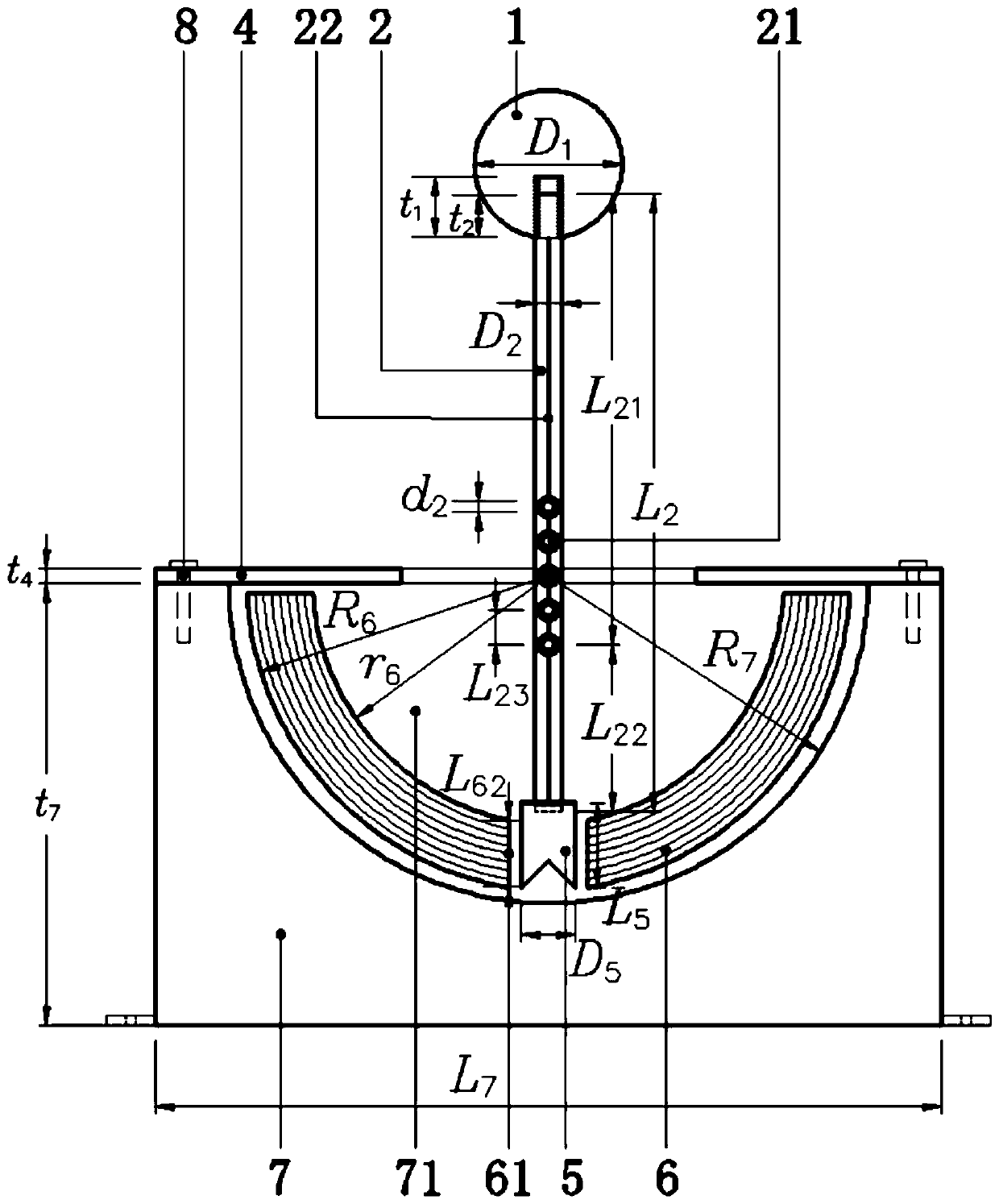
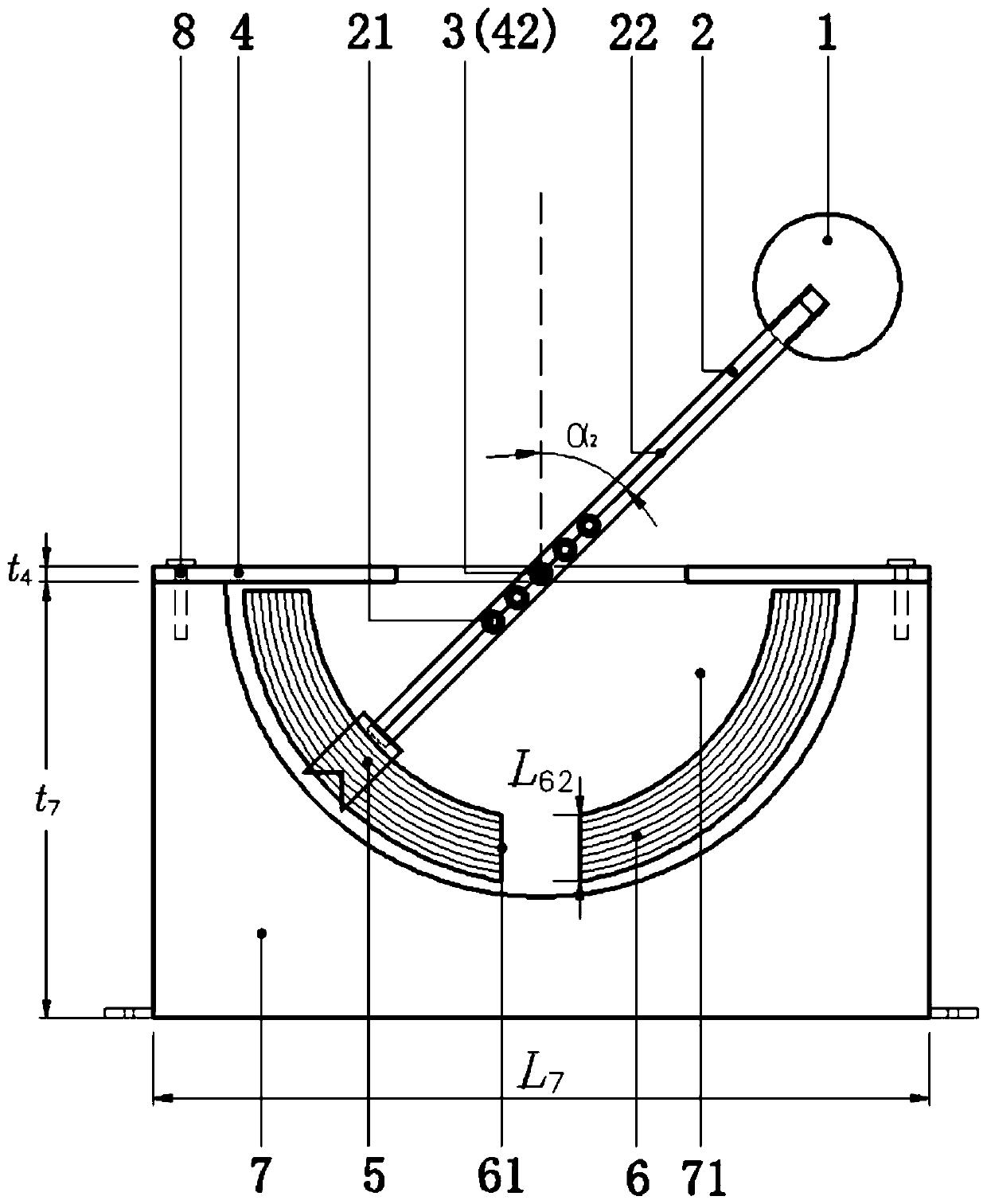
[0040] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the overall structure of the present invention. Such as figure 1As shown, the present invention is made up of windward ball 1, rocking bar 2, support rod 3, cover plate 4, blade 5, energy-absorbing member 6, base 7, movable bolt 8. The end that defines the present invention near explosion point 9 is the left end, and the end that defines the present invention away from explosion point 9 is the right end. The windward ball 1 is fixed on the top of the rocker 2 through the screw hole and the thread, the blade 5 is fixed on the bottom of the rocker 2 through the slot 23, the rocker 2 is connected with the support rod 3 through the rolling bearing 21, and the support rod 3 is inser...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com