Laser scanning electrode structure and laser scanning control system
A technology of laser scanning and electrode structure, applied in the field of microelectronics and optics, can solve the problems of changing the refraction constant of liquid crystal, the scanning frequency is limited, and affecting the laser propagation path, etc., to achieve precise control, realize large-angle regulation, and increase the angle. The effect of control accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Example 1:
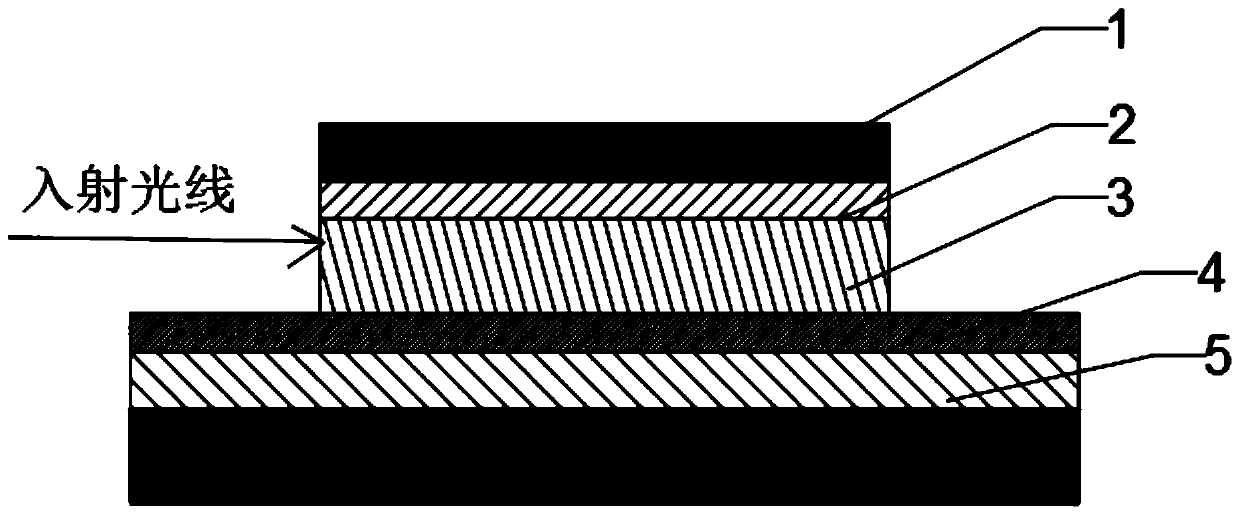
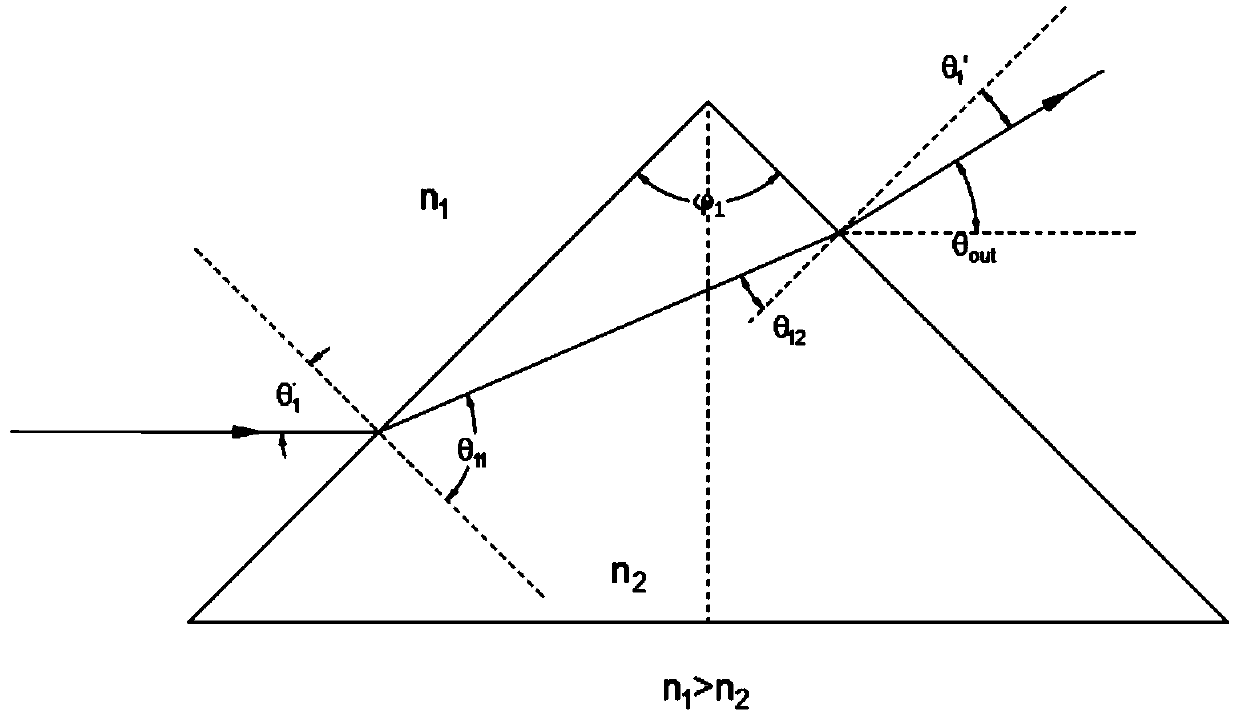
[0060] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 , a laser scanning electrode structure, comprising a liquid crystal layer 3, an electrode driving layer 2 is arranged above the liquid crystal layer 3, an electrode driving device is arranged on the electrode driving layer, and the electrode driving device includes a laser emission angle control part, the The laser emission angle control unit includes an incident side and an outgoing side, both of which are straight sides and intersect each other or their extension lines, and the electrode driving device is electrically connected to the liquid crystal layer. The base of the triangle formed by the intersection of the incident side and the outgoing side is parallel to the laser incident direction. The laser emission angle control part is configured as an isosceles triangle or an isosceles trapezoid, and the incident side and the emitting side are respectively configured as two waist sides of an isosceles triangle or an is...
Embodiment 2
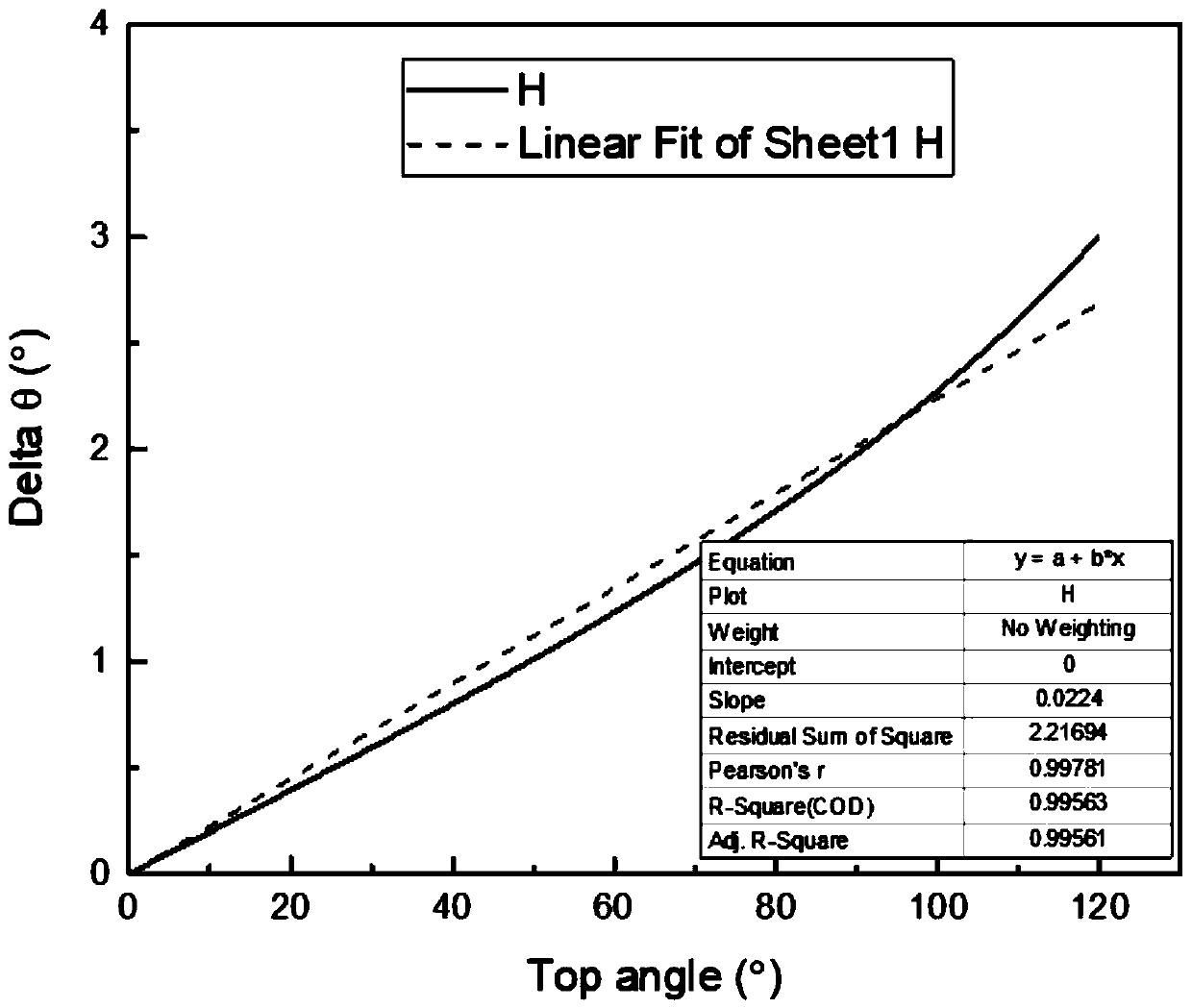
[0074] Such as Figure 4 , in embodiment 2, we can realize a laser deflection device for laser scanning up and down deflection by using this single laser scanning electrode structure combination, and isolate the ITO layer (electrode driving layer) above the liquid crystal layer into several mutually independent non-conductive regions (area S). The discrete electrodes can be roughly divided into U series of upper bias electrodes and D series of lower bias electrodes. Each level of electrodes is controlled independently of each other, and is numbered as the zeroth level electrode U from left to right. 0 , the first-stage electrode U 1 , the second electrode U 2 .....Wait. In order to better illustrate the effect of this embodiment, the upper deflection electrode U series and the lower deflection electrode D series are set in this embodiment, which can expand the laser scanning angle. In this embodiment, in order to facilitate the angle calculation, the upper and lower deflec...
Embodiment 3
[0080] In Embodiment 3, it is also possible to set different electrodes to deflect at different angles, such as setting a large-angle deflection as the main, and a small-angle deflection as a supplementary way, such as setting the front deflection angle to 5° deflection, and the small electrode at the back It is set to 3° deflection, and the most edge deflection angle is set to 2° or 1° deflection. Of course, different angles can also be selected in other embodiments. In this way, it is better than setting each laser deflection to the same angle. For the angle of deflection, different electrodes are selected for further regulation, but this is more computationally intensive.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com