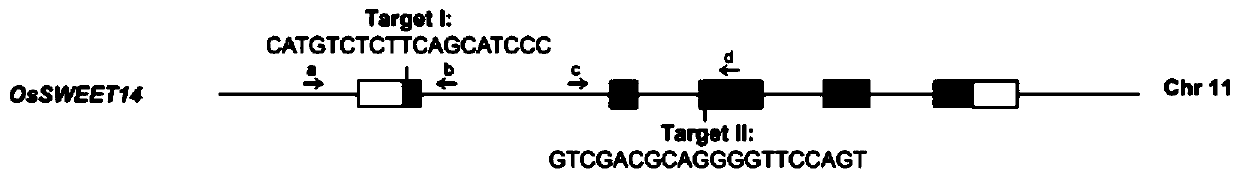
Method for breeding broad-spectrum bacterial blight-resistant rice by editing exon of OsSWEE14 gene
An anti-bacterial blight and exon technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of destroying the promoter region, low safety, variation and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] In this embodiment, a method for cultivating broad-spectrum bacterial blight-resistant rice by editing the exons of the OsSWEE14 gene comprises the following steps:
[0059] (1) Strain activation and plasmid extraction preparation: Strain culture the strain (TOP10F') carrying the pYLCRISPR / Cas9Pubi-H vector on a plate medium containing kanamycin (25 μg / ml) overnight, and the pYLsgRNA1 carrying pYLsgRNA1 - OsU3 / LacZ vector and pYLsgRNA2-OsU6b vector strains (DH10B) were streaked and cultured overnight on a plate medium containing ampicillin (50 μg / ml), and single colonies were picked to culture seed liquid, and then expanded for extraction plasmid;
[0060] (2) Construction of sgRNA1 expression cassette:
[0061] 1) The first round of PCR reaction: take 2-5ng pYLsgRNA1-OsU3 / LacZ plasmid as a template, and do two PCR reactions, one PCR reaction uses primers U-F and OsU3-S14E1, the concentration of primers in the reaction system is 0.2μM, and the product is a; another PC...
Embodiment 2
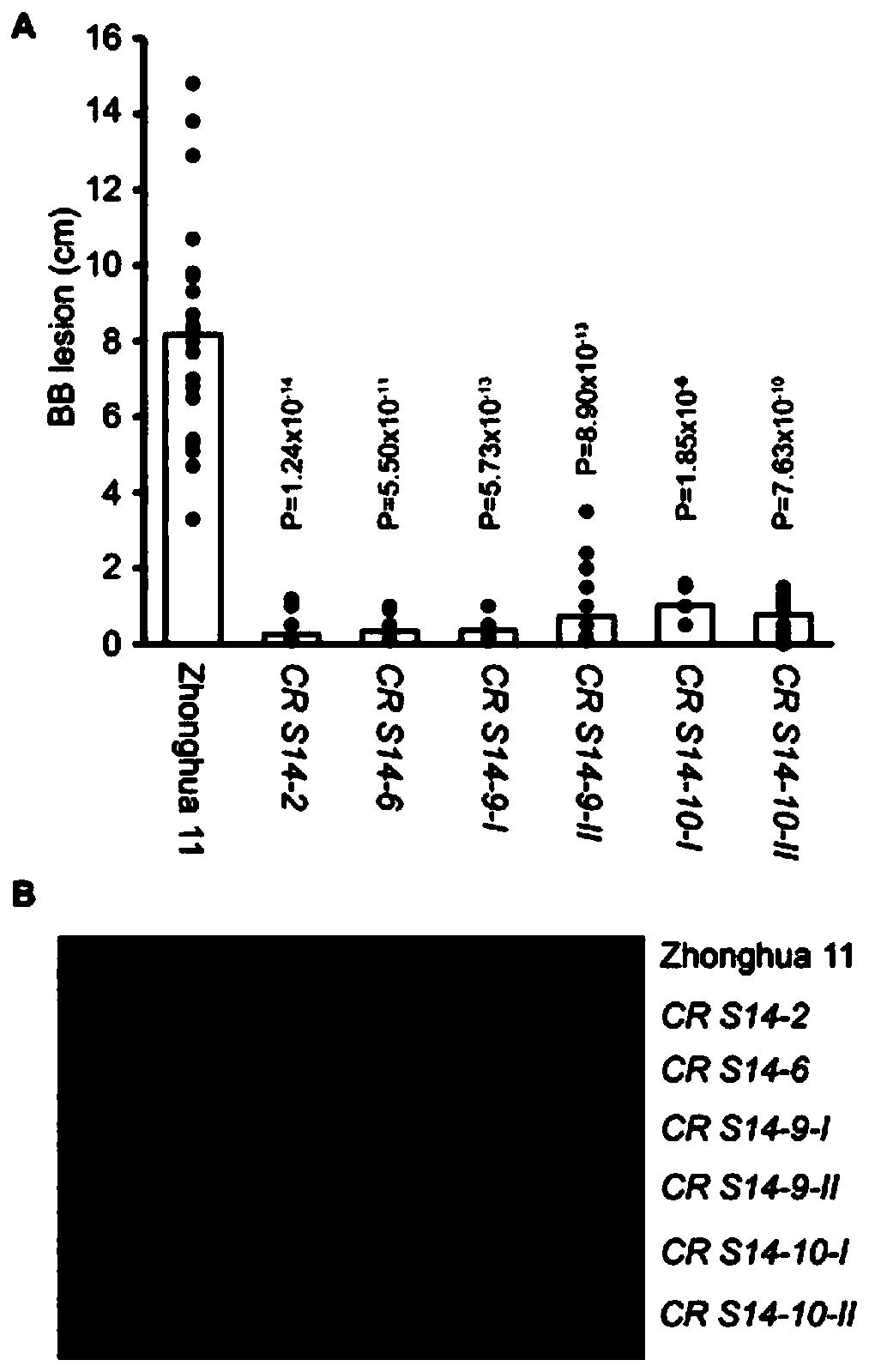
[0080] This example studies the resistance of CR S14-2, CR S14-6, CR S14-9-I, CR S14-9-II, CR S14-10-I and CRS14-10-II strains to bacterial blight PXO86 .
[0081] CR S14-2, CR S14-6, CR S14-9-Ⅰ, CR S14-9-Ⅱ, CR S14-10-Ⅰ, CRS14-10-Ⅱ strains and Zhonghua 11 rice wild strain was inoculated with PXO86 strain, and the lesion was measured and counted on the 14th day after inoculation.
[0082] The result is as figure 2 shown by figure 2 It can be seen that the lesions of CR S14-2, CR S14-6, CR S14-9-Ⅰ, CR S14-9-Ⅱ, CR S14-10-Ⅰ and CR S14-10-Ⅱ strains inoculated with PXO86 strain were significantly smaller than In the control group, Zhonghua No. 11 rice wild plant (corresponding figure 2 zhonghua 11), indicating that the above-mentioned strains are resistant to bacterial blight PXO86.
Embodiment 3
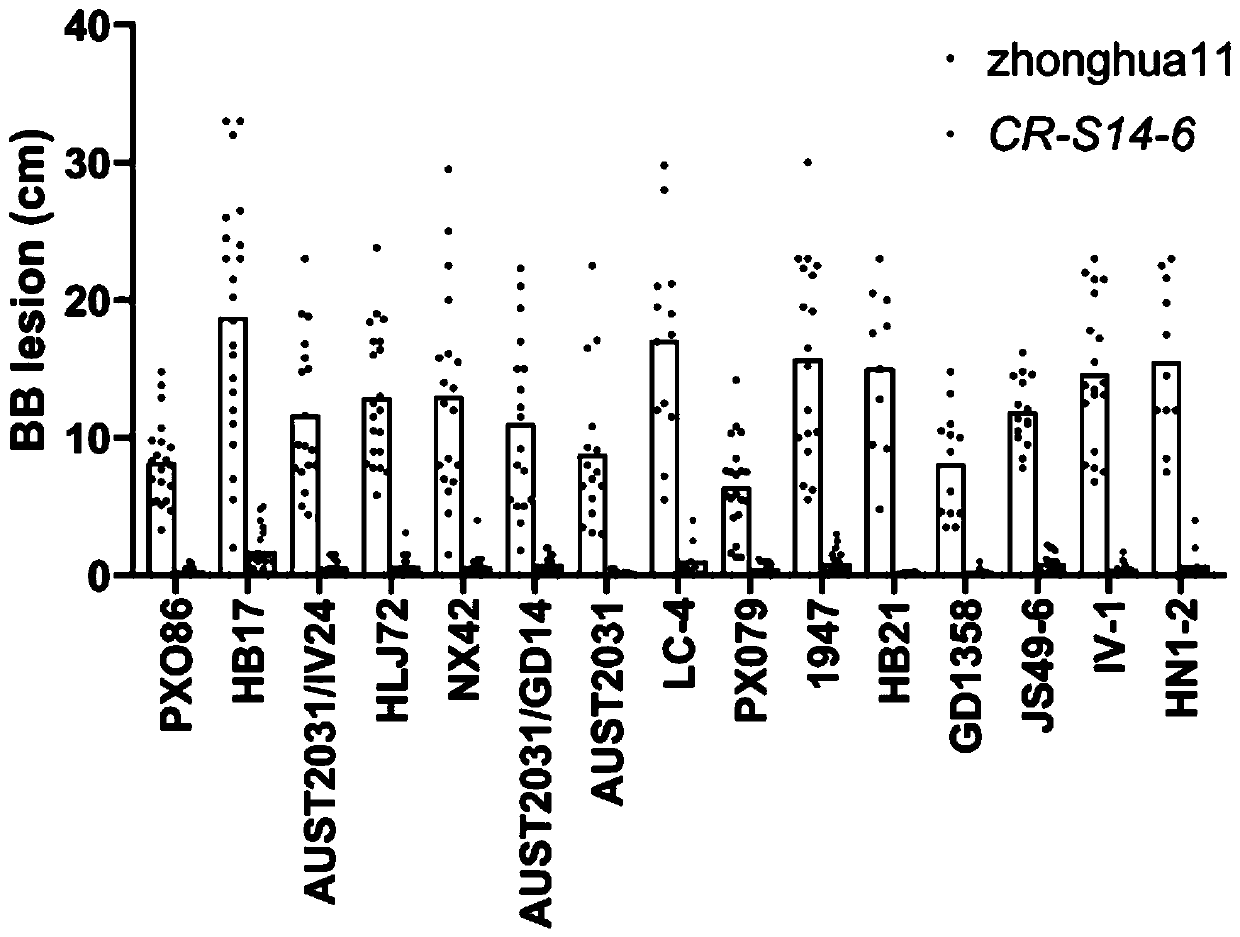
[0084] This example studies the resistance of the CR S14-6 strain to different bacterial blight bacteria.
[0085] The CR-S14-6 strain and Zhonghua 11 wild rice strain were inoculated with the following bacterial blight strains by leaf-cutting method: PXO86, HB17, AUST2031 / IV24, HLJ72, NX42, AUST2031 / GD14, AUST2031, LC-4, For PX079, 1947, HB21, GD1358, JS49-6, IV-1 and HN1-2, lesion spots were measured and counted on the 14th day after inoculation.
[0086] The result is as image 3 shown by image 3 It can be seen that the lesions of the CR-S14-6 strain inoculated with the above-mentioned bacterial blight strain were significantly smaller than the Zhonghua No. 11 wild rice strain inoculated with the above-mentioned bacterial blight strain (corresponding to image 3 zhonghua 11), indicating that the CR-S14-6 strain is resistant to the above-mentioned bacterial blight strains.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com