Immunology functions and purpose of GPR174
A kind of use, B cell technology, applied in the field of GPR174 immunological function and its use, can solve the lack of in-depth molecular mechanism and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
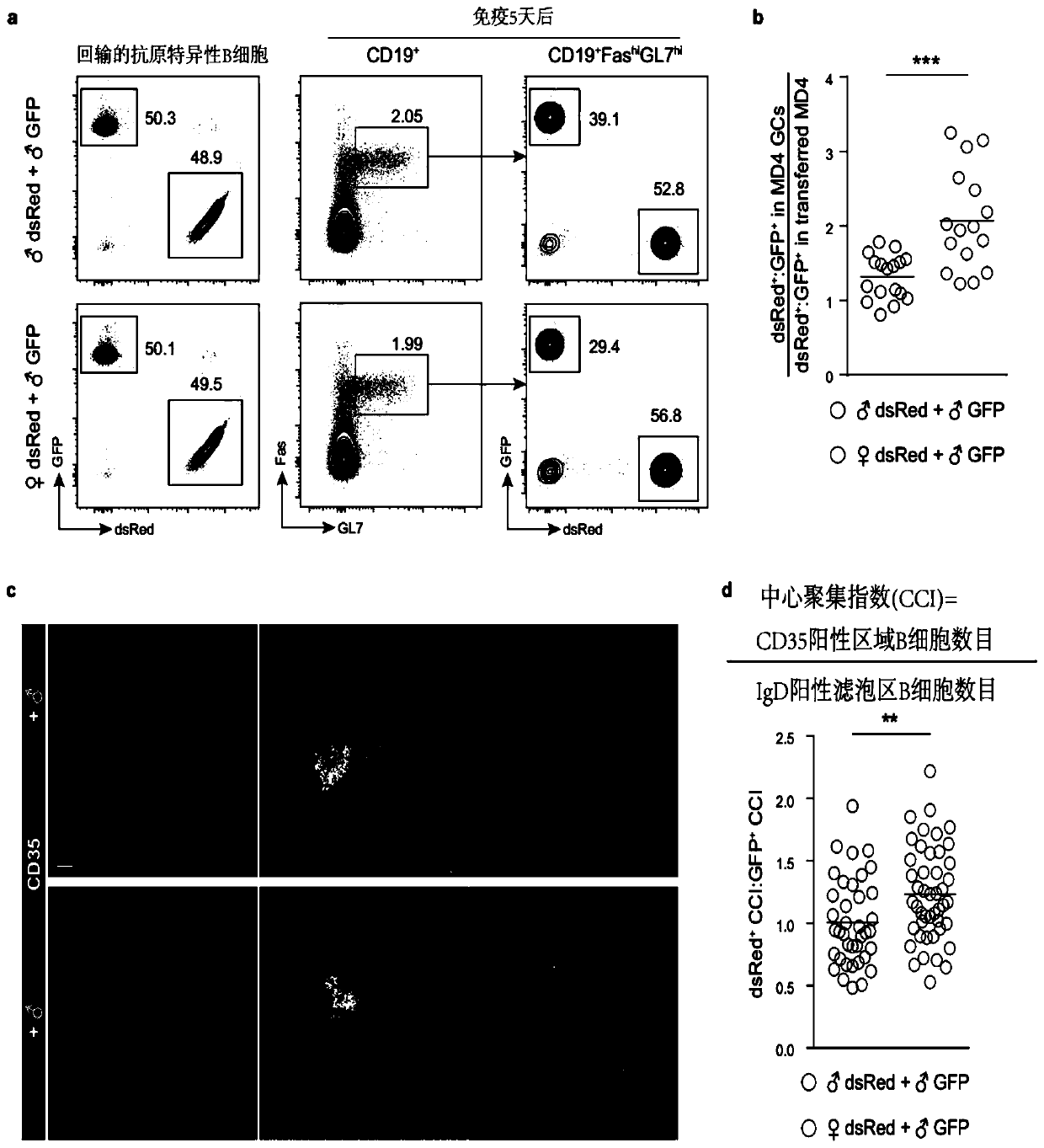
[0166] Example 1 Intrinsic Differences in Germinal Center Formation Between Male B Cells and Female B Cells
[0167] In this example, the inventors detailed the inherent differences in the size of the germinal center and the inherent difference in dynamic positioning before the formation of the germinal center response between male and female B cells.
[0168] To investigate whether there are inherent differences in the ability of male and female B cells to form germinal centers, the inventors constructed a system for the co-infusion of antigen-specific male and female B cells: the same amount of male or female antigen Specific MD4 B cells (dsRed-red fluorescent protein marker) were mixed with the same number of male antigen-specific MD4B cells (GFP-green fluorescent protein marker) and then reinfused into male recipient mice ( figure 1 a Longitudinal first column), and at the same time, a certain number of male antigen-specific OT2 T cells were reinfused as helper T cells to ...
Embodiment 2
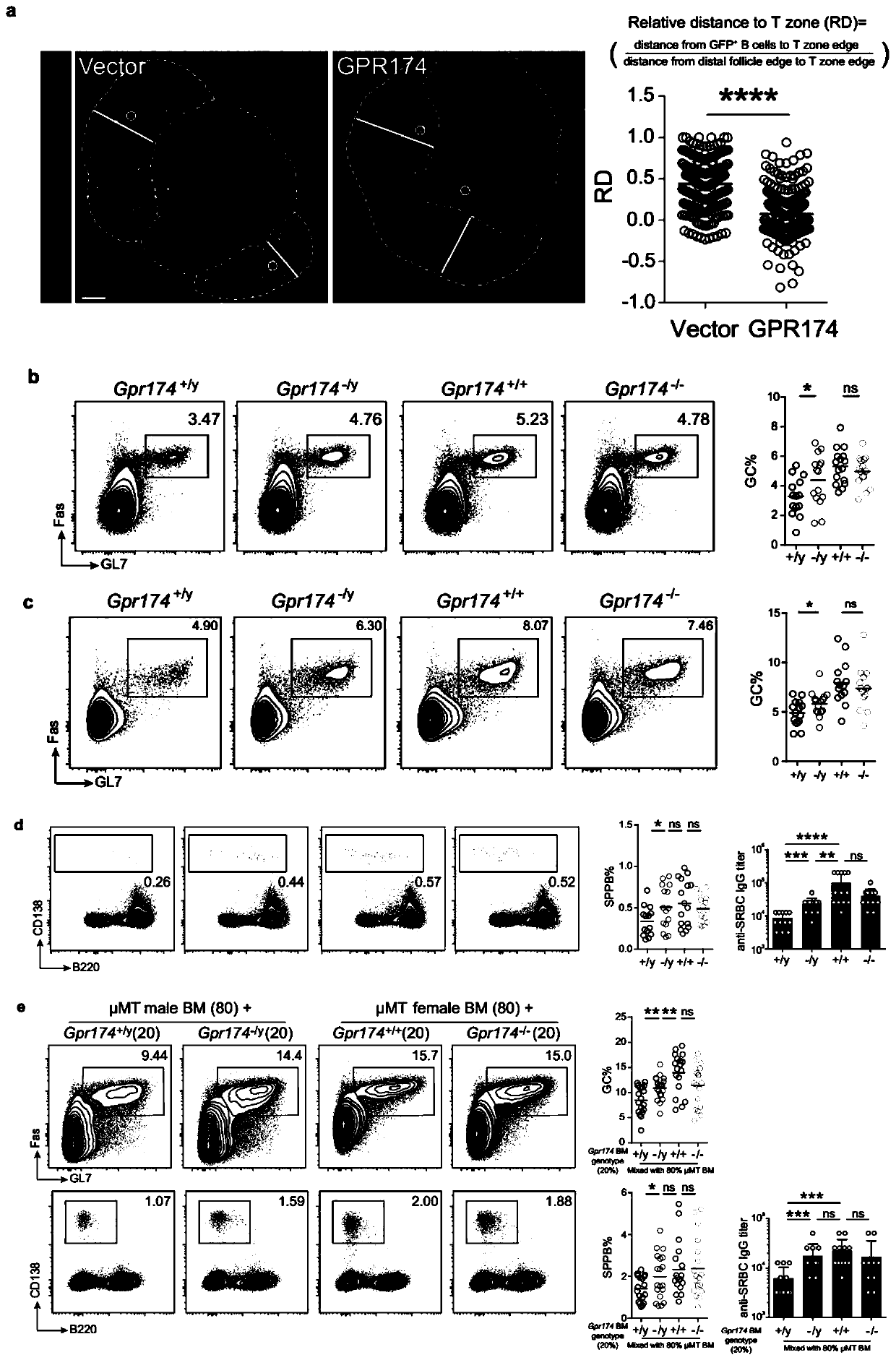
[0170] Example 2 GPR174 regulates the dynamic localization of B cells activated by antigen stimulation and inhibits the germinal center response in male non-female mice
[0171] In this example, the inventors introduced in detail that the newly discovered G protein-coupled receptor GPR174 can regulate the dynamic localization of B cells in vivo and its influence on the germinal center response.
[0172] In order to explore why male B cells and female B cells have inherent differences in the ability to accumulate to the follicular center region before forming a germinal center reaction, the inventors first discovered that a new G protein-coupled receptor GPR174 can act as a chemotactic receptor to regulate B Dynamic localization of cells in vivo. The inventors used GFP fluorescence-labeled retroviral vectors to overexpress GPR174 to activated B cells in vitro, and then reinfused them into mice, and found that a large number of B cells overexpressing GPR174 were obviously gather...
Embodiment 3
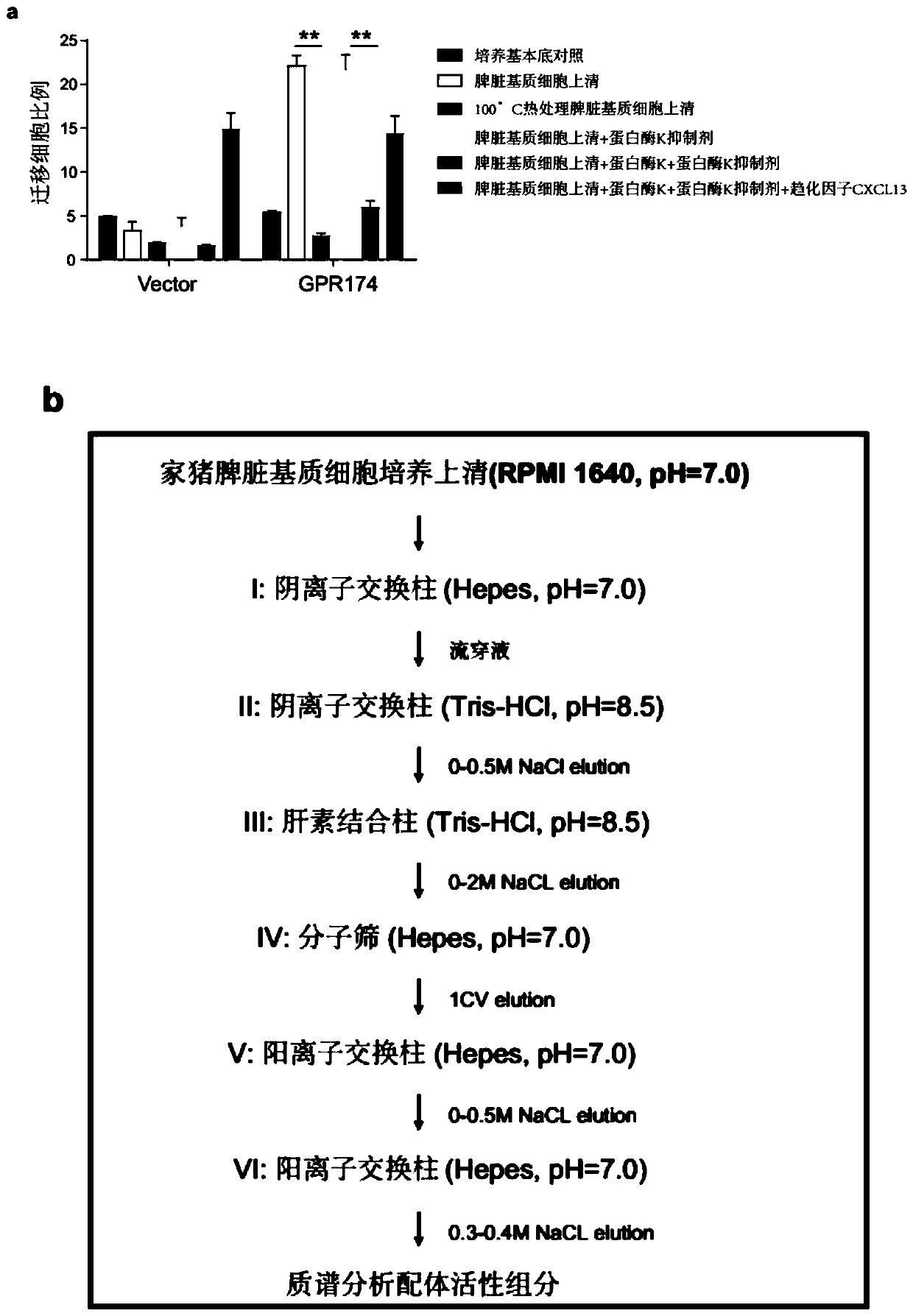
[0175] Example 3 GPR174 is the receptor of chemokines CCL21 and CCL19 and regulates the differential chemotactic migration of male and female B cells in vitro and in vivo
[0176] In this example, the inventors introduced in detail that the newly discovered G protein-coupled receptor GPR174 is actually a chemokine receptor that recognizes chemokines CCL21 and CCL19, and explained that GPR174-CCL21 / CCL19 mediates male Differences in in vitro chemotaxis assays and in vivo dynamic localization of B cells and female B cells.
[0177] To further explain why GPR174 affects germinal center responses in male non-female mice, the inventors first started by identifying a ligand that interacts with GPR174. Since most of the chemokines in existing studies are secreted by spleen stromal cells, the inventors prepared the supernatant of mouse spleen stromal cells cultured in vitro, and detected that it contained strong B cells that activated in vitro Ligand properties of GPR174-dependent ch...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com