Target extraction method of symmetric supervision model based on mixed loss function
A technology of mixed loss and loss function, applied in image data processing, 3D image processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of manpower and material resources, low efficiency, etc., and achieve the effect of improving efficiency and solving manpower and material resources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0029] Specific implementation mode 1: The specific process of the target extraction method based on the symmetric supervision model of the mixed loss function in this implementation mode is as follows:
[0030] Step 1. Obtain cardiac magnetic resonance image data and label them;
[0031] Step 2. Preprocessing the labeled cardiac MRI image data obtained in step 1, the preprocessing includes operations such as obtaining two-dimensional slices, cropping, scaling, and data normalization;
[0032] Step 3, using the cardiac MRI image data preprocessed in step 2 as the input of the symmetric supervision model;
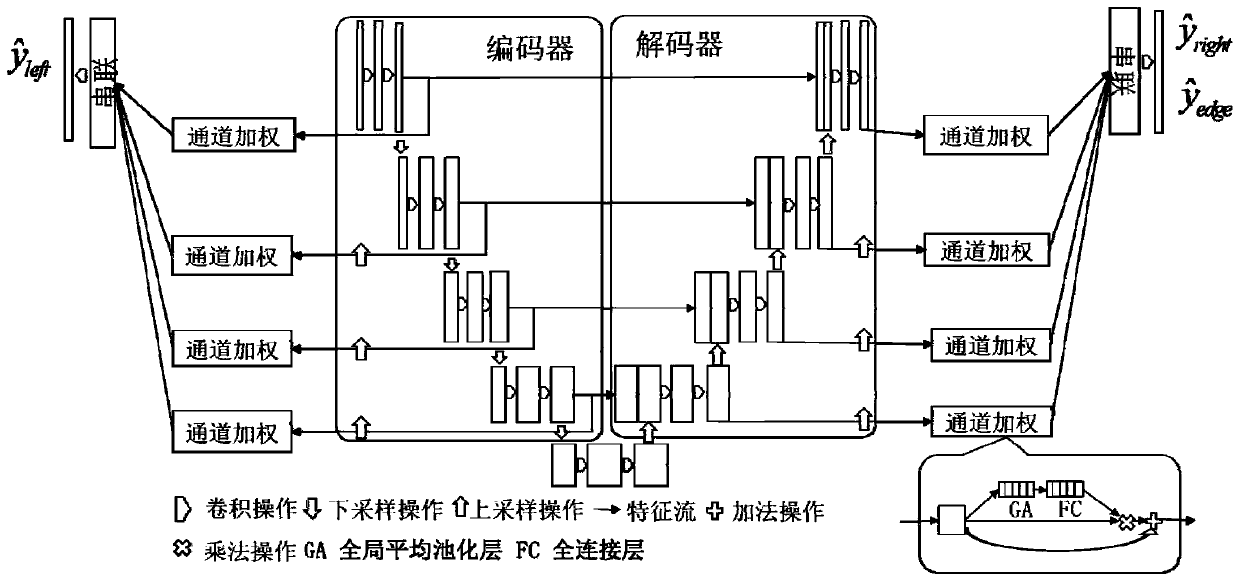
[0033] The symmetric supervised model consists of two parts: an encoder and a decoder. The encoder includes an input layer, a convolutional layer, a normalization layer, a maximum pooling layer, and an output layer. The decoder includes a convolutional layer, a deconvolutional layer, and a normalization layer. Oneization layer, Dropout layer and output layer;
[0034] The ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0041] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that in the step 1, cardiac MRI image data is acquired and marked; the specific process is:
[0042] Step 11, manually mark the left atrium area and the background area, wherein the left atrium area is marked as 1, and the background area is marked as 0, and this type of mark is stored as the label of the extraction model;
[0043] Step 12, use the Canny operator to extract boundaries on the left atrium region and background region binary images extracted in step 11, mark the boundaries as 1, and mark other regions as 0, and store such marks as labels for boundary detection.
[0044] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0045] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that in the step 2, the labeled cardiac MRI image data obtained in step 1 is preprocessed, and the preprocessing includes obtaining two-dimensional slices, cutting , scaling, and data normalization operations; the specific process is:
[0046] In the training phase, random rotation within the specified range and horizontal and vertical flip operations will be performed on the labeled cardiac MRI image data obtained in step 1 to achieve data amplification to avoid overfitting;
[0047] Two-dimensional slices are extracted from the marked cardiac MRI image data obtained in step 1 through the long axis (the MRI is scanned in the direction from head to toe of the person, in fact, a slice is scanned at each moment, and then reconstructed into 3D It is stored as a 3D array, and this extraction is converted into a 2D slice in the direction of the long axis according to the o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com