A magnetic field modulated permanent magnet linear generator with composite armature structure
A permanent magnet linear and magnetic field modulation technology, which is applied in the shape/style/structure of winding conductors, electrical components, electromechanical devices, etc., which can solve the requirement of improving the comprehensive performance of linear generators, and it is difficult to obtain thrust characteristics and dynamic performance. Motor scheme and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
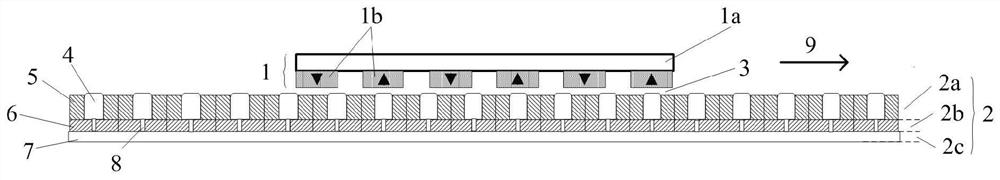
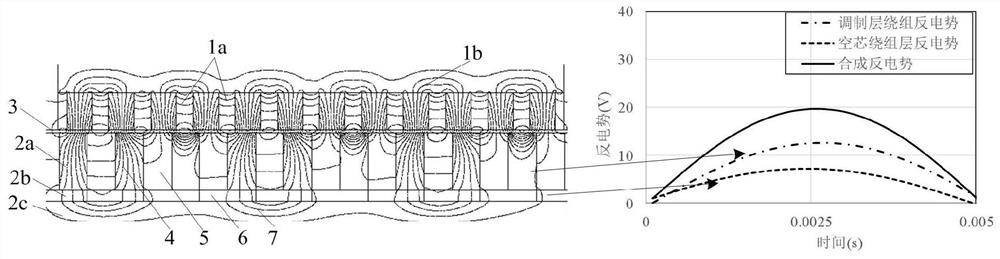
[0033] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, a magnetic field modulation permanent magnet linear generator with a compound armature structure is composed of a secondary 1, a primary armature 2, and an air gap 3 between the primary armature 2 and the secondary 1; the secondary is composed of The yoke plate 1a and the permanent magnet array 1b are composed; and the primary armature 2 is provided with a multi-layer composite structure composed of a modulation layer 2a, an air core winding layer 2b and an iron core layer 2c.
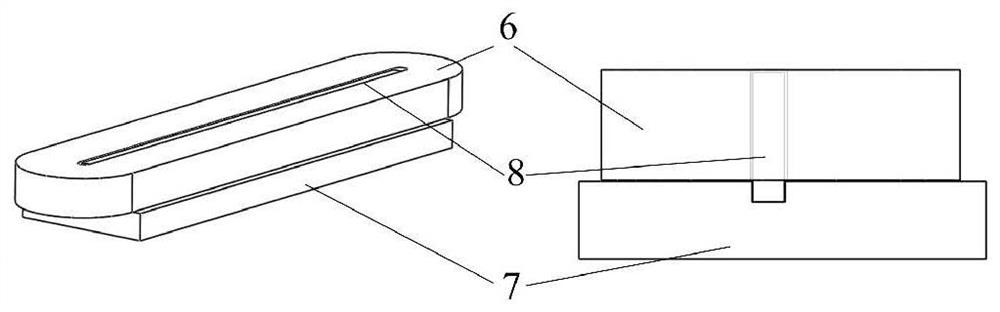
[0034] The modulation layer 2a is the upper layer, including the magnetic modulation block 4 and the modulation layer winding 5 . The magnetic adjustment block 4 adopts high magnetic permeability material and is arranged equidistantly along the moving direction of the motor. Number of pole pairs p of secondary 1 permanent magnet array 1b 1 , the number Z of the modulation block 4 and the pole pair number p of the traveling wave magnetic field generated by th...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: as Figure 4a As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the side of the magnetic adjustment block 4 facing the air gap 3 is chamfered, which can obtain the same electromagnetic effect as the rounded corner treatment method, effectively suppressing the positioning force of the motor, but the process Implementation is simpler. Distance and angle α of chamfer 11 1 and alpha 2 Choose according to the specific number of poles and slots. The distance of the chamfer 11 should not be too large, otherwise the thrust of the motor will drop rapidly.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3: as Figure 4b As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 is that the modulation block 4 cuts out a groove shape with a wide top and a narrow bottom on the side facing the air gap 3 to form trapezoidal small teeth 12 . The uniform trapezoidal small teeth 12 can alleviate the sudden change of the motor air-gap flux permeability, thereby suppressing the positioning force of the motor. The tooth height of the trapezoidal small tooth 12 is also not easy to be too large, and should be within several millimeters.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com