Methods for gender determination of avian embryos in unhatched eggs and means thereof
An avian, sex technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, other methods of inserting foreign genetic material, determination/inspection of microorganisms, etc., can solve the effective and non-invasive method without sex identification, no detectable signal, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0500] Use different color lasers and filters for fluorescence analysis to identify the sex of poultry
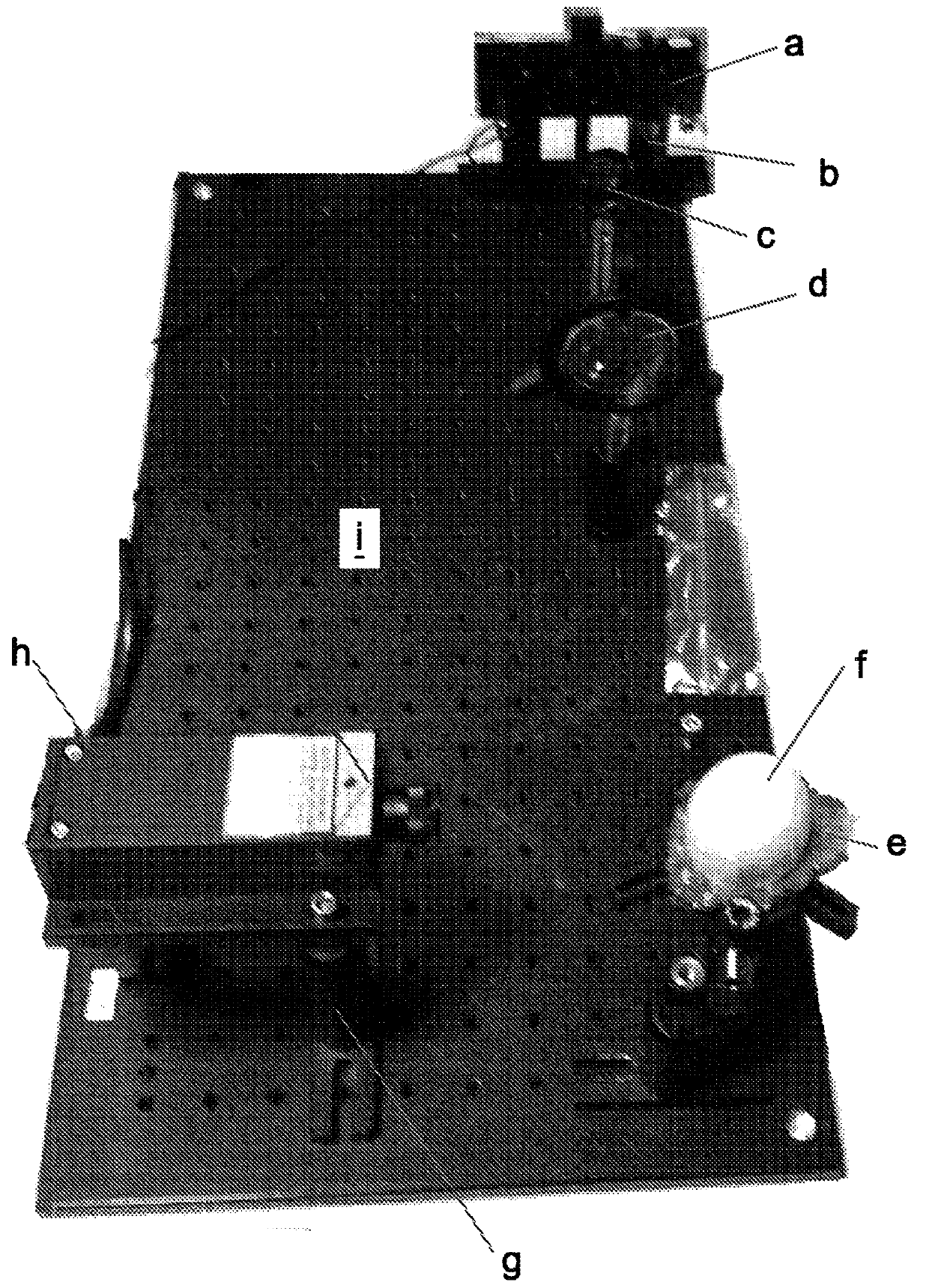
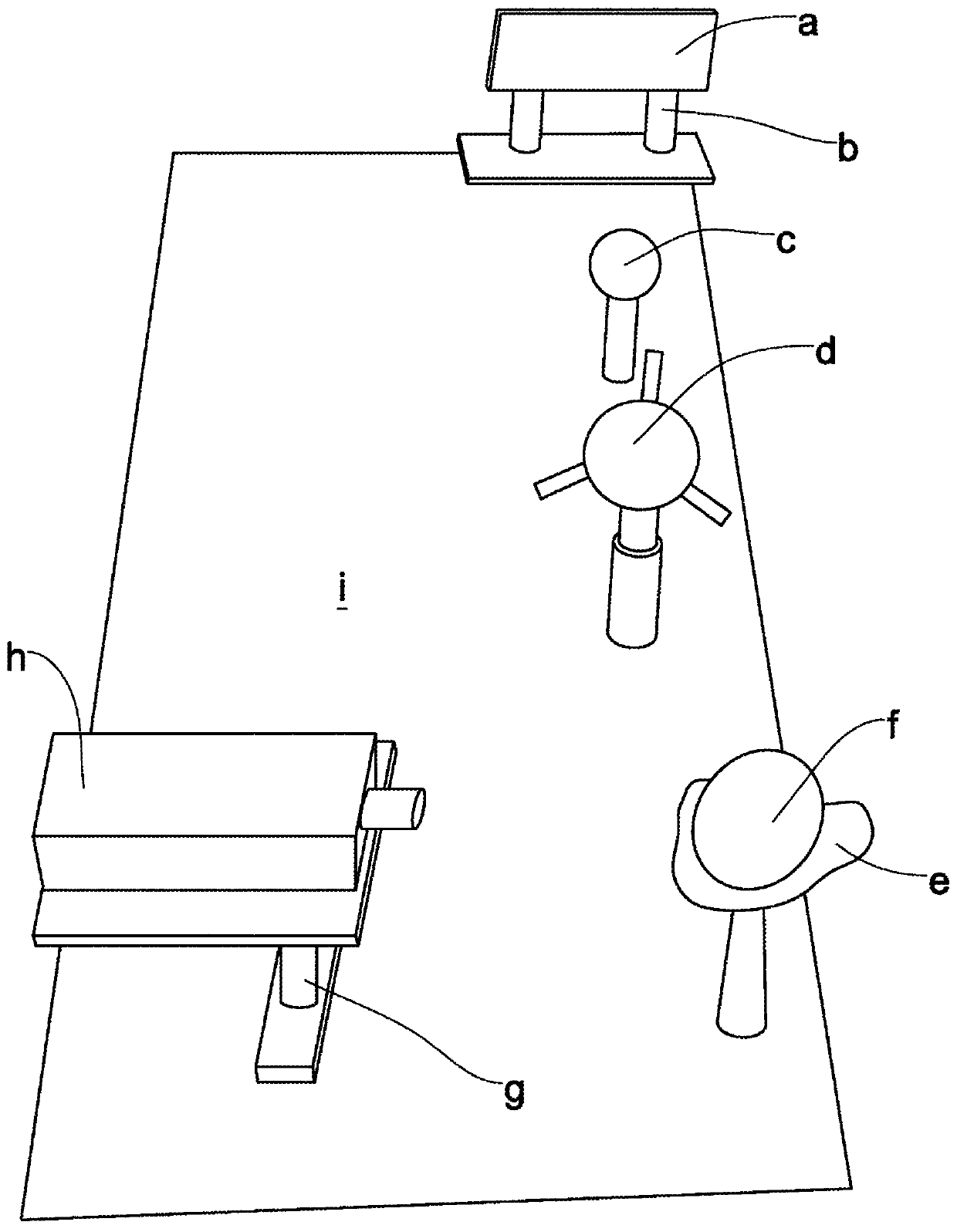
[0501] Optical fluorescence system
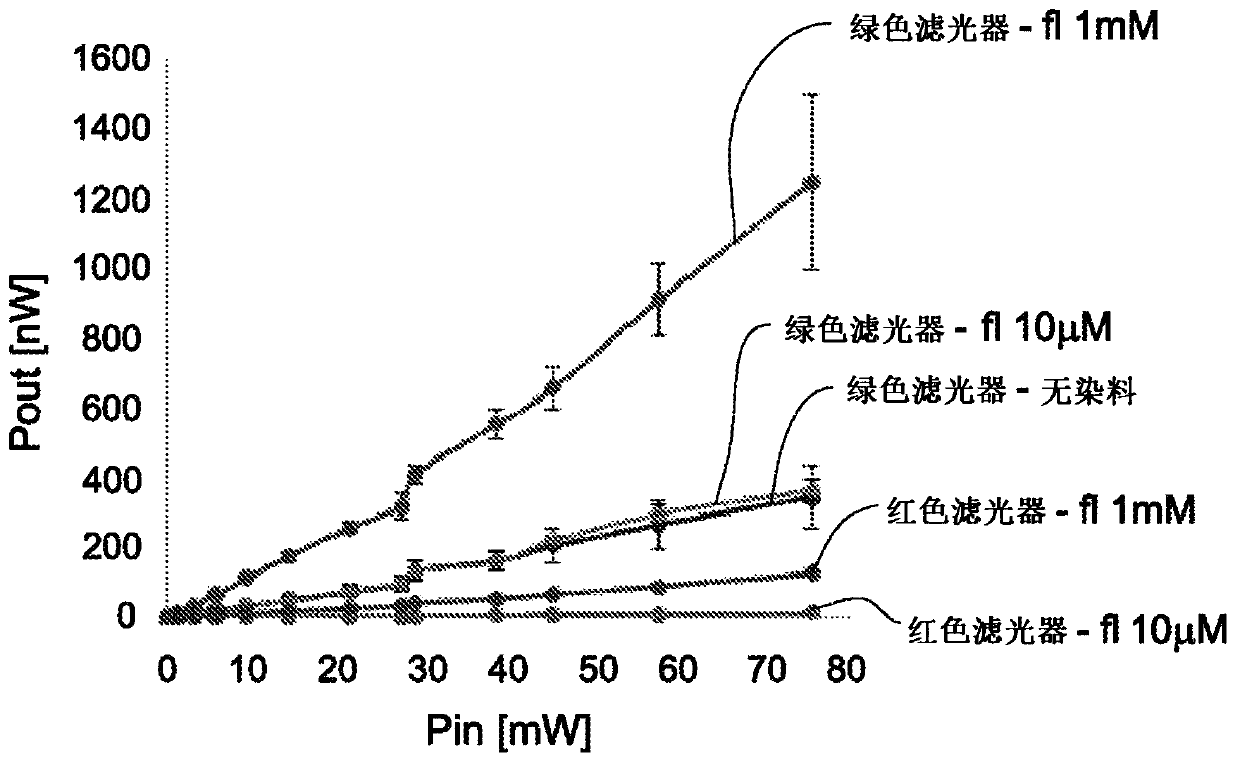
[0502] In order to demonstrate the feasibility of visually identifying the sex of poultry in eggs, the use of green fluorescence was evaluated compared to blue fluorescence or red fluorescence reporter genes.
[0503] Use blue laser, green laser or red laser to determine the white fluorescence of whole eggs or eggs separated into white, yolk and shell. Comparison of empty eggs (shells) and whole eggs showed no significant difference in the level of autofluorescence (data not shown).
[0504] Table 6 describes the scattering and autofluorescence intensity of the different components of the egg.
[0505] It is important to note that the background noise (without laser) is about 4nW, and in the presence of laser (532nm), due to light scattering around the filter (passing a low-pass filter above 660nm), the background The noise is about 12nW.
[050...
Embodiment 2
[0515] Fluorescence of cells transfected with RFP or GFP added to the egg
[0516] To illustrate the feasibility of detecting RFP-expressing cells in eggs, the present inventors next checked whether the cells can be detected after injecting fluorescent protein (especially RFP or GFP) transfected cells into intact eggs.
[0517] More specifically, as described in the experimental procedure, HEK cells were transfected with GFP or RFP vectors. After excitation, the fluorescence of GFP and RFP transfected cells was checked. Image 6 (GFP) and Figure 7 (RFP) clearly shows that both GFP and RFP are expressed by the transfected cells, and a fluorescent signal can be observed. Then the HEK-transfected cells were injected into fresh eggs as described in the experimental procedure, and the fluorescence intensity of the eggs was measured.
[0518] First, the fluorescence intensity of eggs with or without cells expressing red fluorescent protein RFP is characterized by excitation of the eggs w...
Embodiment 3
[0541] Design of guide RNA vector
[0542] In order to incorporate the RFP reporter gene into the sex chromosome W or Z, the CRISPR Cas9-mediated HDR method was selected. Then look for related gRNA sites from the two sex chromosomes.
[0543] Female Z chromosome integration
[0544] For the female chicken Z chromosome, the region represented by SEQ ID NO: 15 is 9156874-9161874, the region represented by SEQ ID NO: 16 is 27764943-27769943, the region represented by SEQ ID NO: 17 is 42172748-42177748, and the region represented by SEQ ID NO: 18 The region 78777477-78782477 represented by 63363656-63368656 and SEQ ID NO: 19 was analyzed for guide RNA. More specifically, in order to guide the integration of RFP into the Z chromosome, a gRNA called gRNA7 of the Z chromosome locus chrZ_42174515_-1 was prepared next, which contains the nucleic acid sequence GTAATACAGAGCTAAACCAG, which is also represented by SEQ ID NO:26.
[0545] This step is performed according to the "PrecisionV Cas9 Sm...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com