Biological information analysis method for human single-gene genetic disease detection
A genetic disease and biological information technology, applied in the field of biological information analysis for the detection of human single-gene genetic diseases, to achieve the effect of simple and clear analysis steps and comprehensive analysis content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
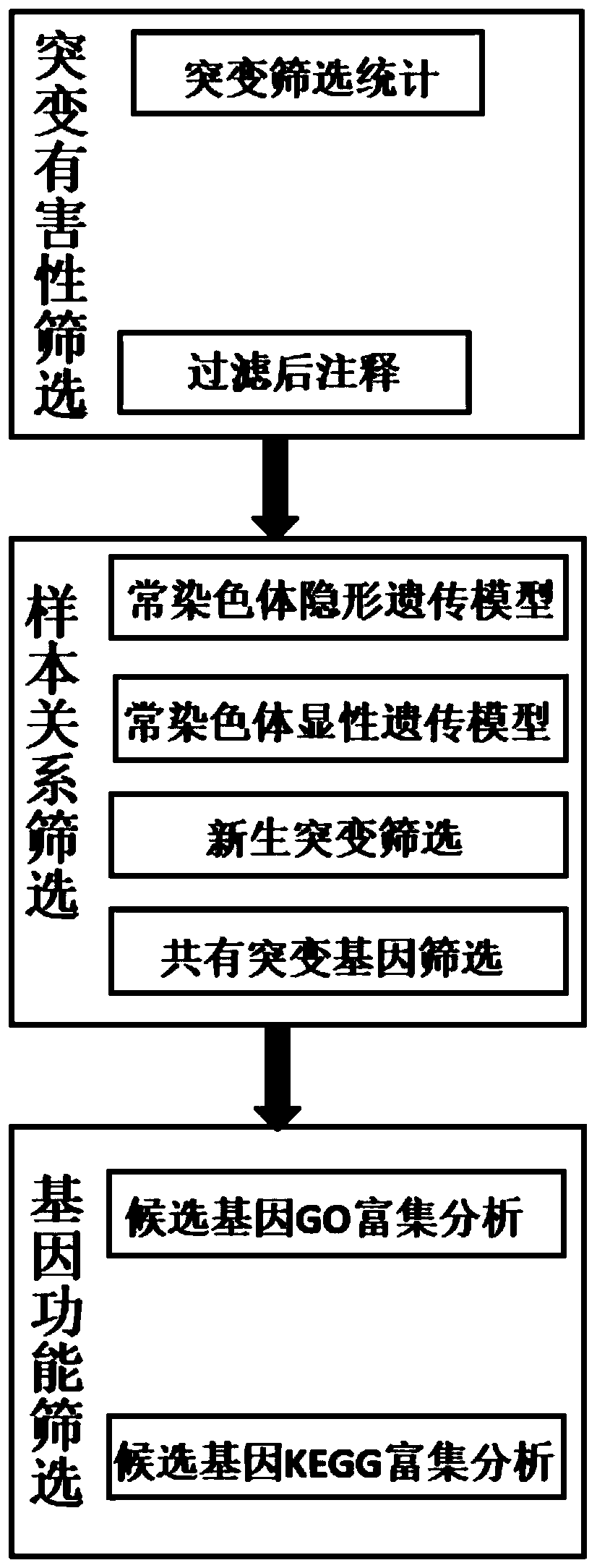
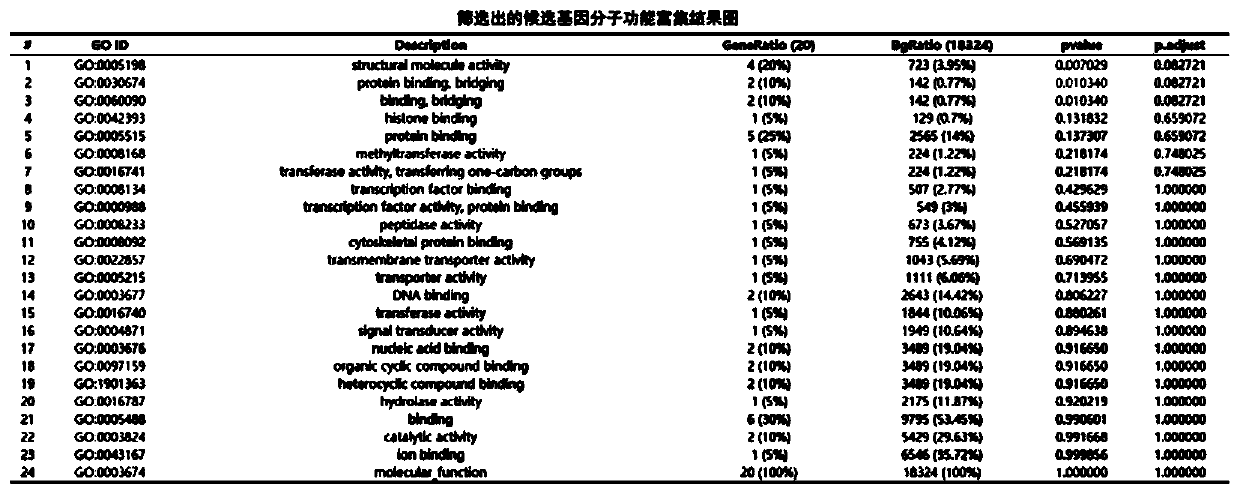
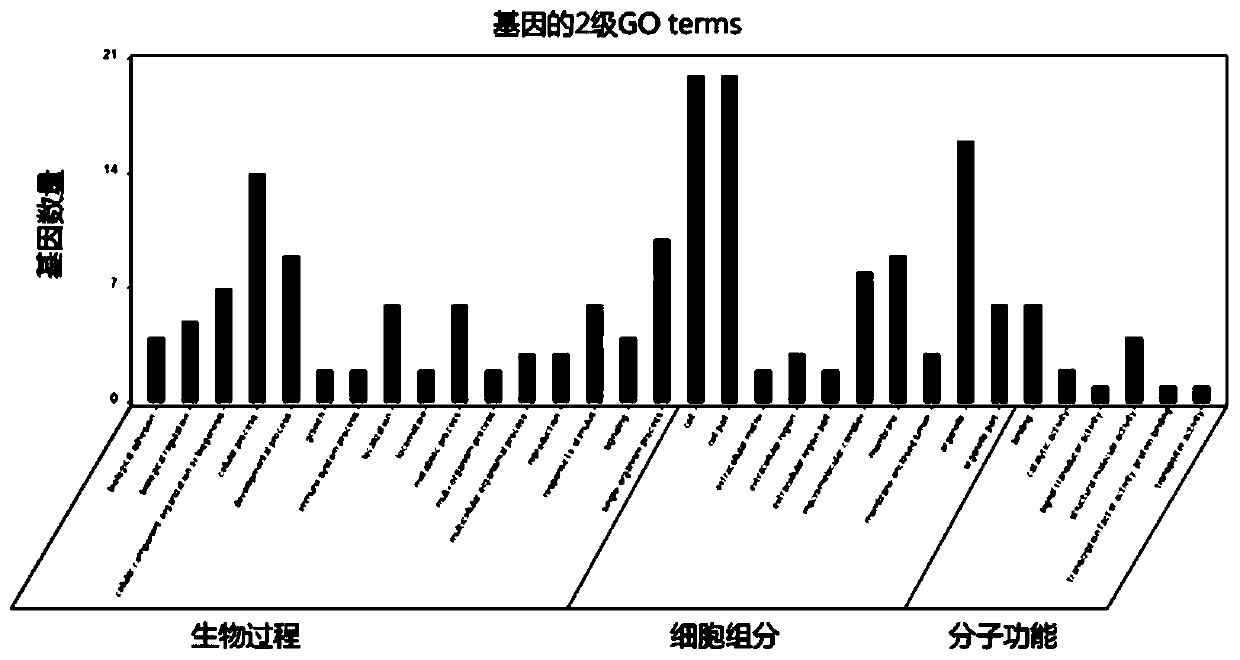
[0021] The exome sequencing data of human samples with renal hypoplasia (including 3 normal samples and 1 diseased sample) were analyzed. The reference genome was hg19, and the normal samples were: S1881-16, S1882-16 and S0405- 16. The diseased sample is: S0401-16. The family information is: S1881-16, S1882-16, S0405-16 and S0401-16. like figure 1 As shown, a bioinformatics analysis method for detecting human single-gene genetic diseases based on exon sequencing technology, the specific steps are as follows:
[0022] Step S1, screening of mutation deleterious sites: the specific screening steps are as follows:
[0023] 1. Filter the variant sites in the Thousand Genomes Database (frequency greater than 0.01 in the population);
[0024] 2. Filter the mutation sites whose frequency is greater than 0.01 in the database ExAC and ESP6500;
[0025] 3. Retain mutations in exonic or splicing regions;
[0026] 4. Filter synonymous mutations and retain non-synonymous mutations;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com