Fault tree based initial event frequency evaluation method and device and computer-readable storage medium
A fault tree and basic event technology, applied in the field of nuclear safety, can solve problems such as difficulty in determining the frequency of initiating events, and achieve the effects of easy engineering implementation, good compatibility, and easy acceptance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
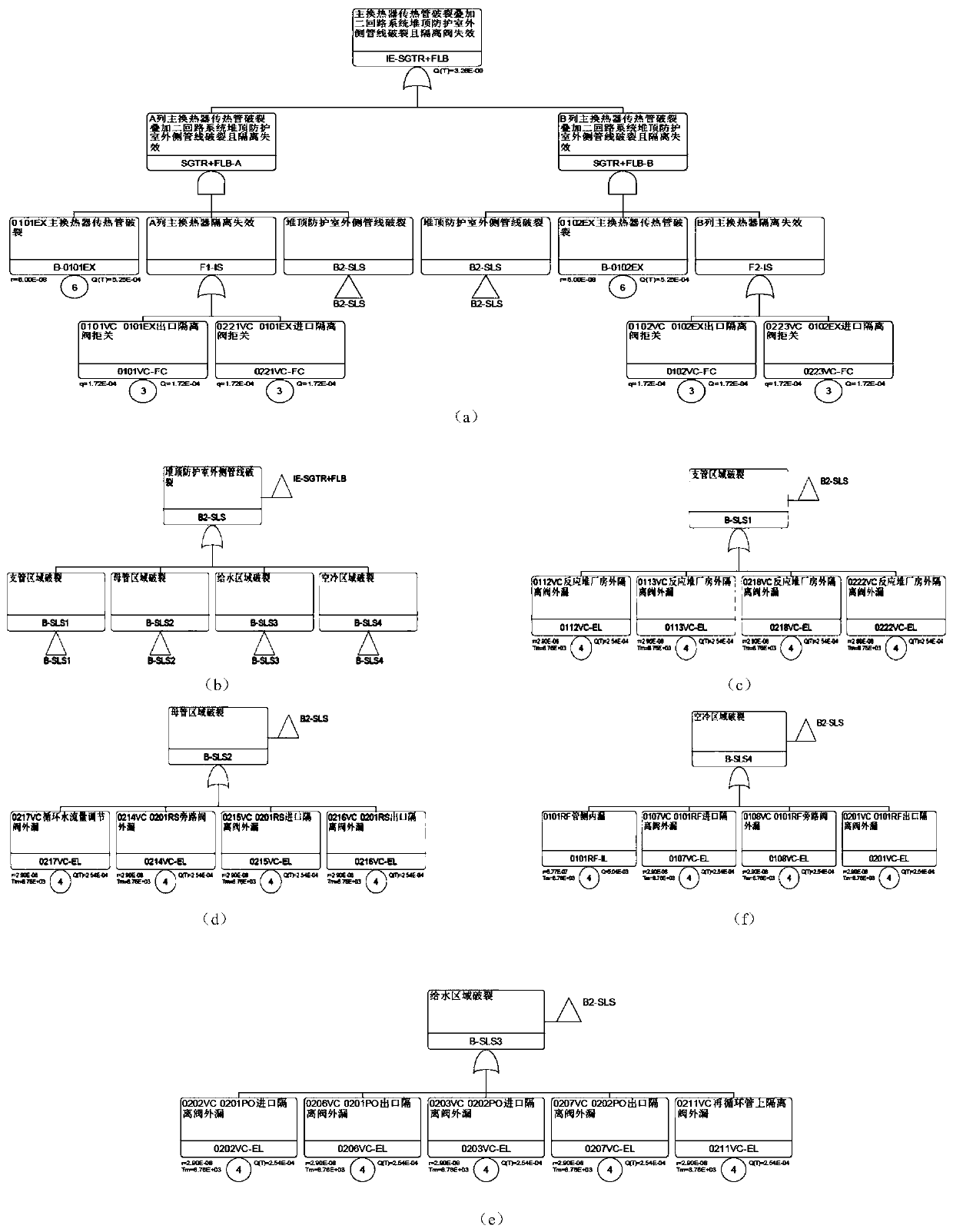
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
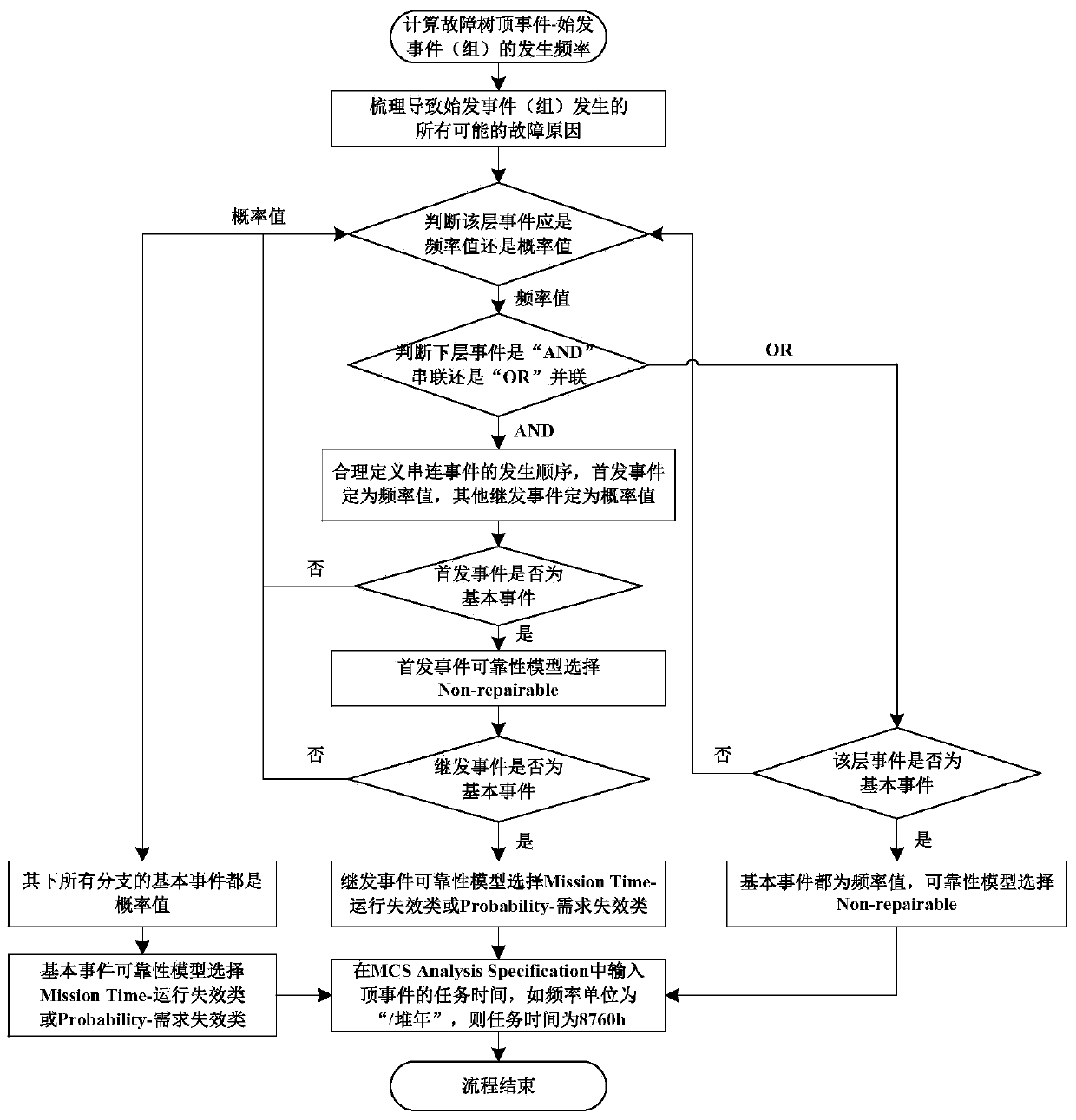
[0034] Such as figure 1 As shown, the flow chart of the method for evaluating the frequency of initiating events based on the fault tree provided by the present invention. The evaluation method includes the following steps:
[0035] Step S1, determine the initiating event to be evaluated and all fault causes leading to the initiating event, and jump to step S2 with the initiating event as the current layer event;
[0036] Step S2, judging whether the fault cause of the current layer event is a frequency value or a probability value;
[0037] Step S3, if the failure cause of the event at the current layer is a probability value, then all basic events at the lower layer are probability values, select Mission Time-operating failure class or Probability-requirement failure class as the reliability model, and jump to step S8; if The fault cause of the current layer event is the frequency value, judge whether the lower layer events are logical OR connection (that is, "OR" parallel...
Embodiment 2
[0062] This embodiment provides a computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored, and when the program is executed by a processor, the evaluation method provided in Embodiment 1 is realized.
[0063] In particular, any combination of one or more computer readable medium(s) may be utilized. The computer readable medium may be a computer readable signal medium or a computer readable storage medium. A computer readable storage medium may be, for example, but not limited to, an electrical, magnetic, optical, electromagnetic, infrared, or semiconductor system, apparatus, or device, or any combination thereof. More specific examples (non-exhaustive list) of computer readable storage media include: electrical connections with one or more leads, portable computer disks, hard disks, random access memory (RAM), read only memory (ROM), Erasable programmable read-only memory (EPROM or flash memory), optical fiber, portable compact disk read-only memory (CD-ROM), ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com