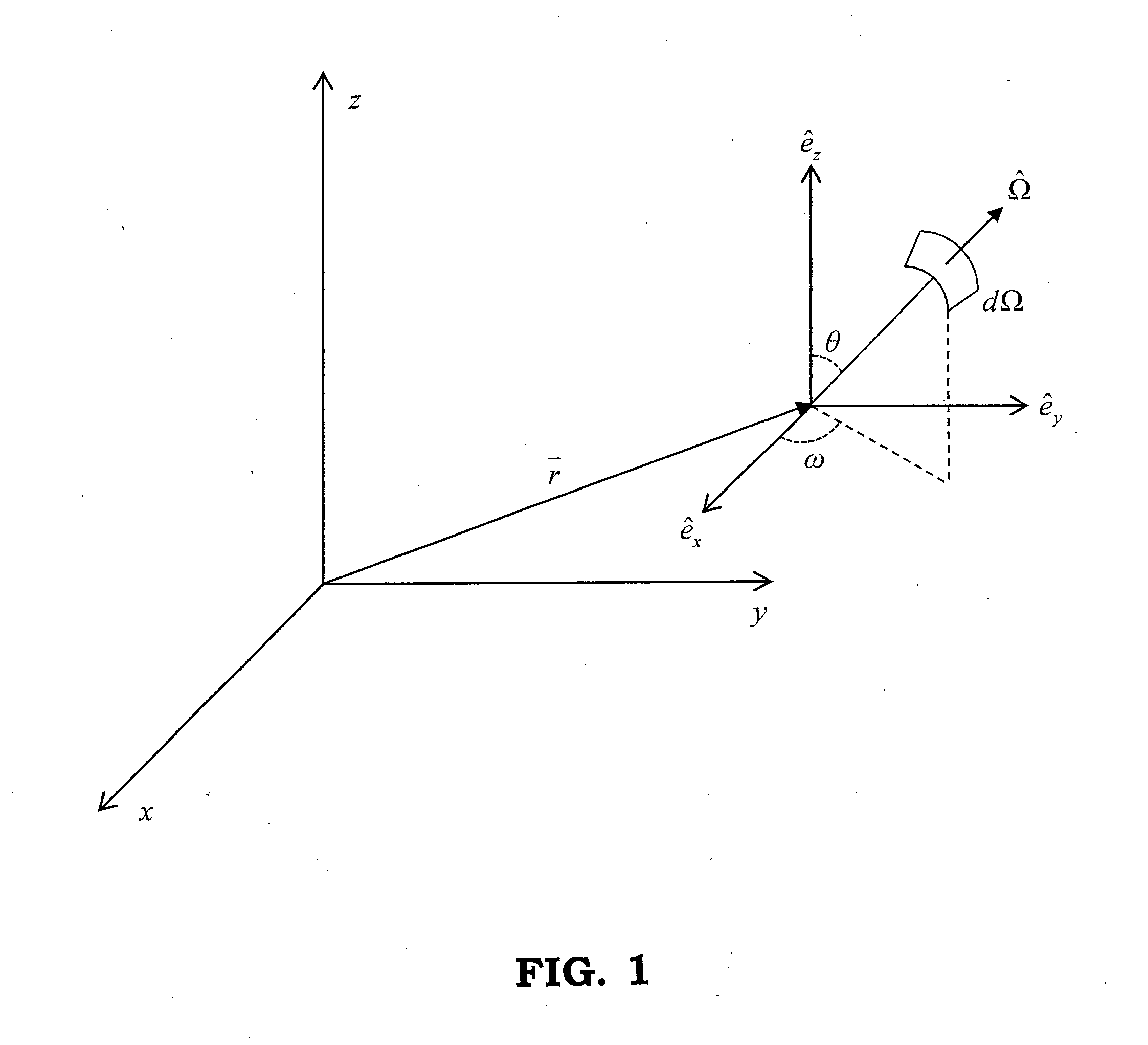
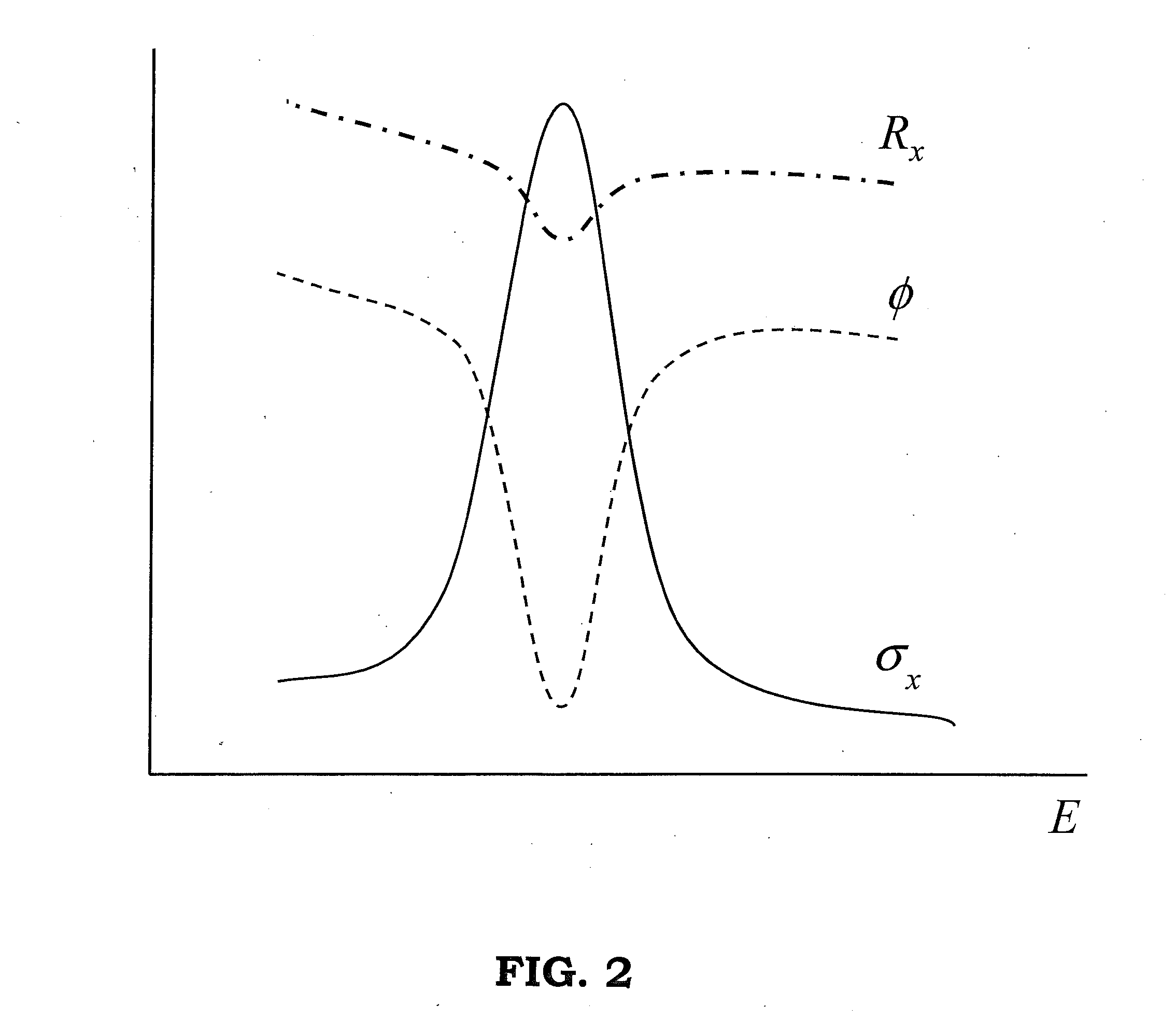
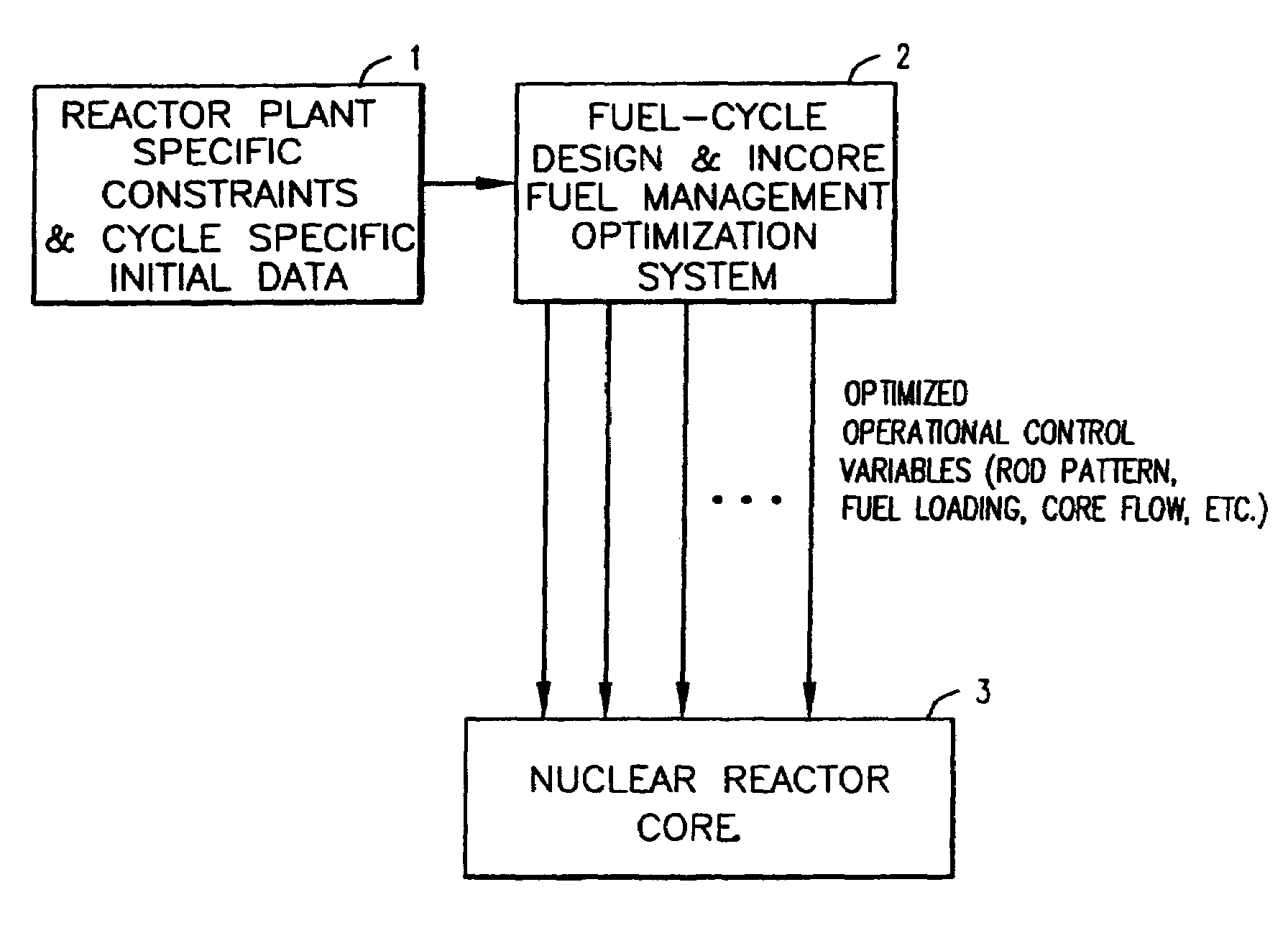
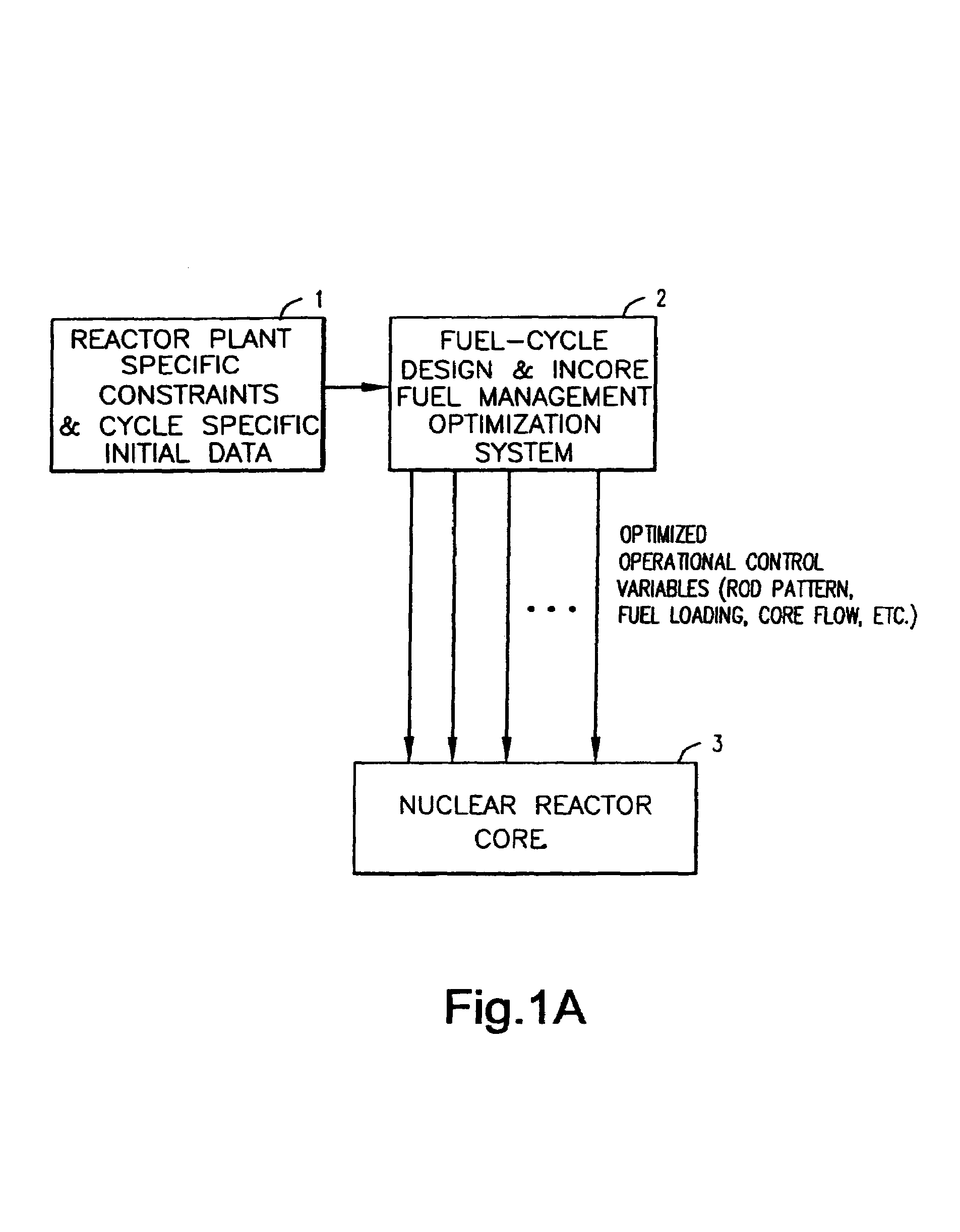
Patents
Literature
505results about "Computer implemented nuclear control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
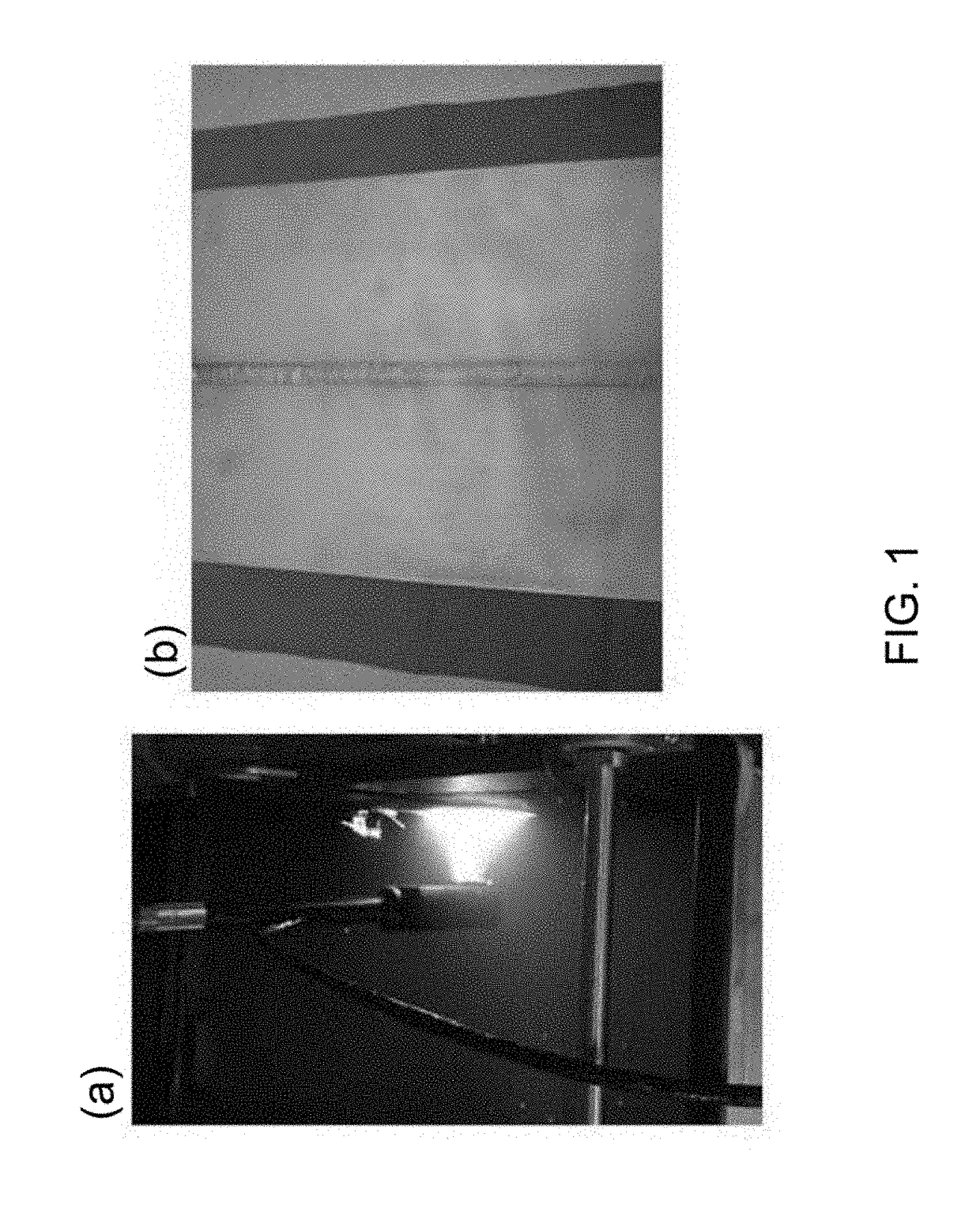
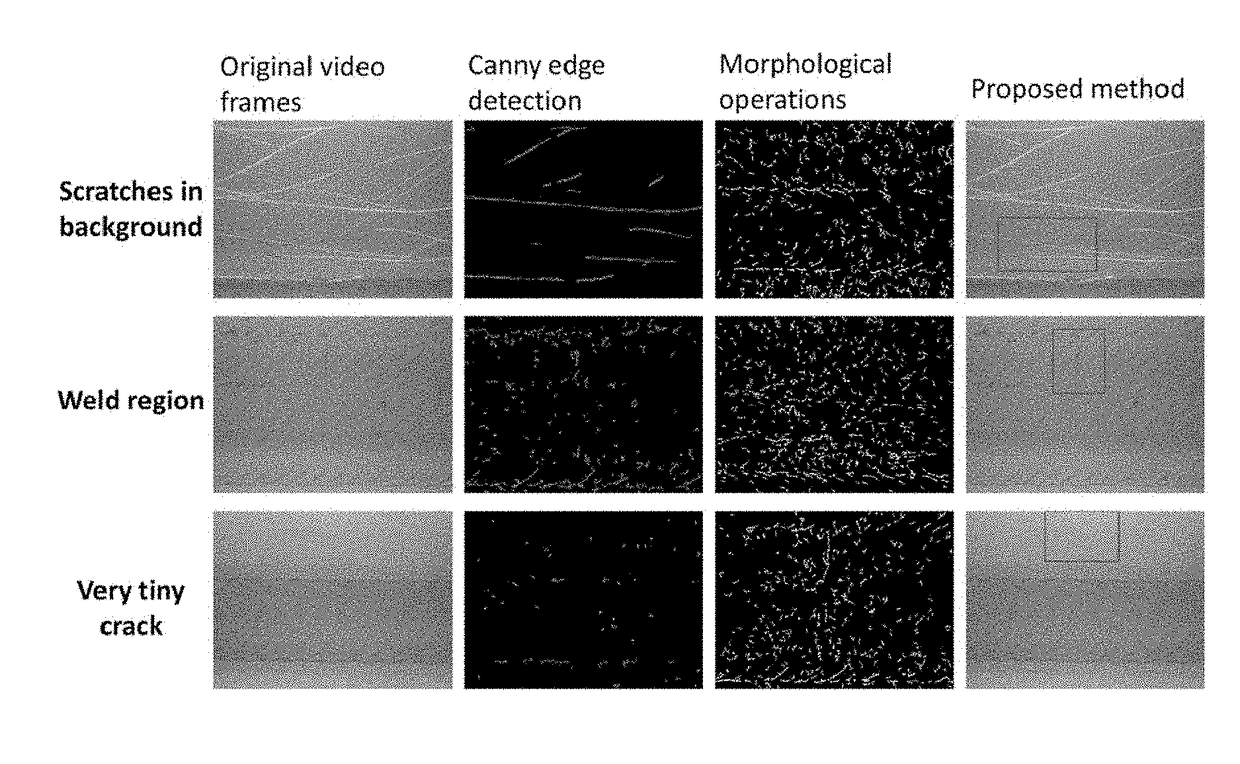
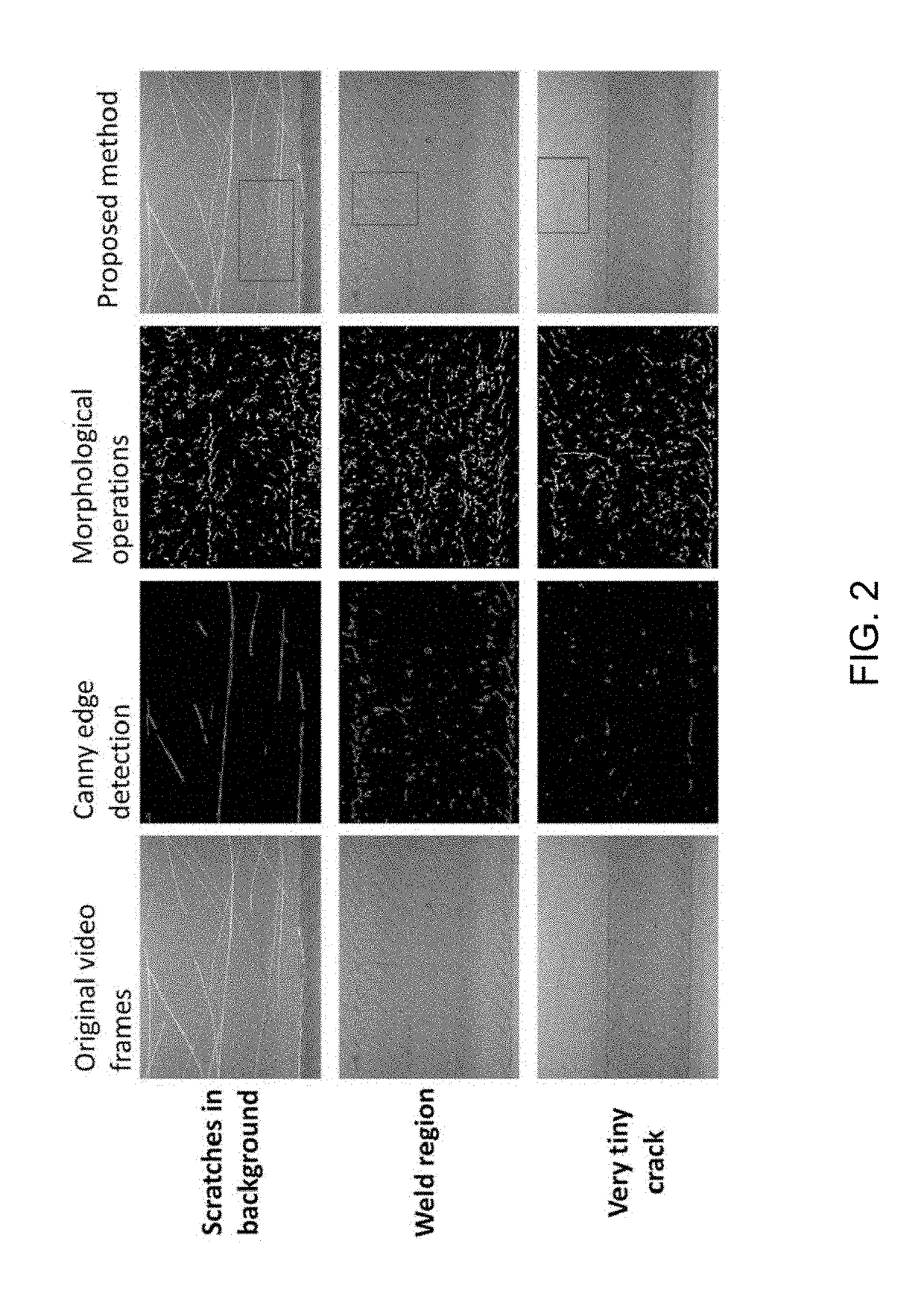
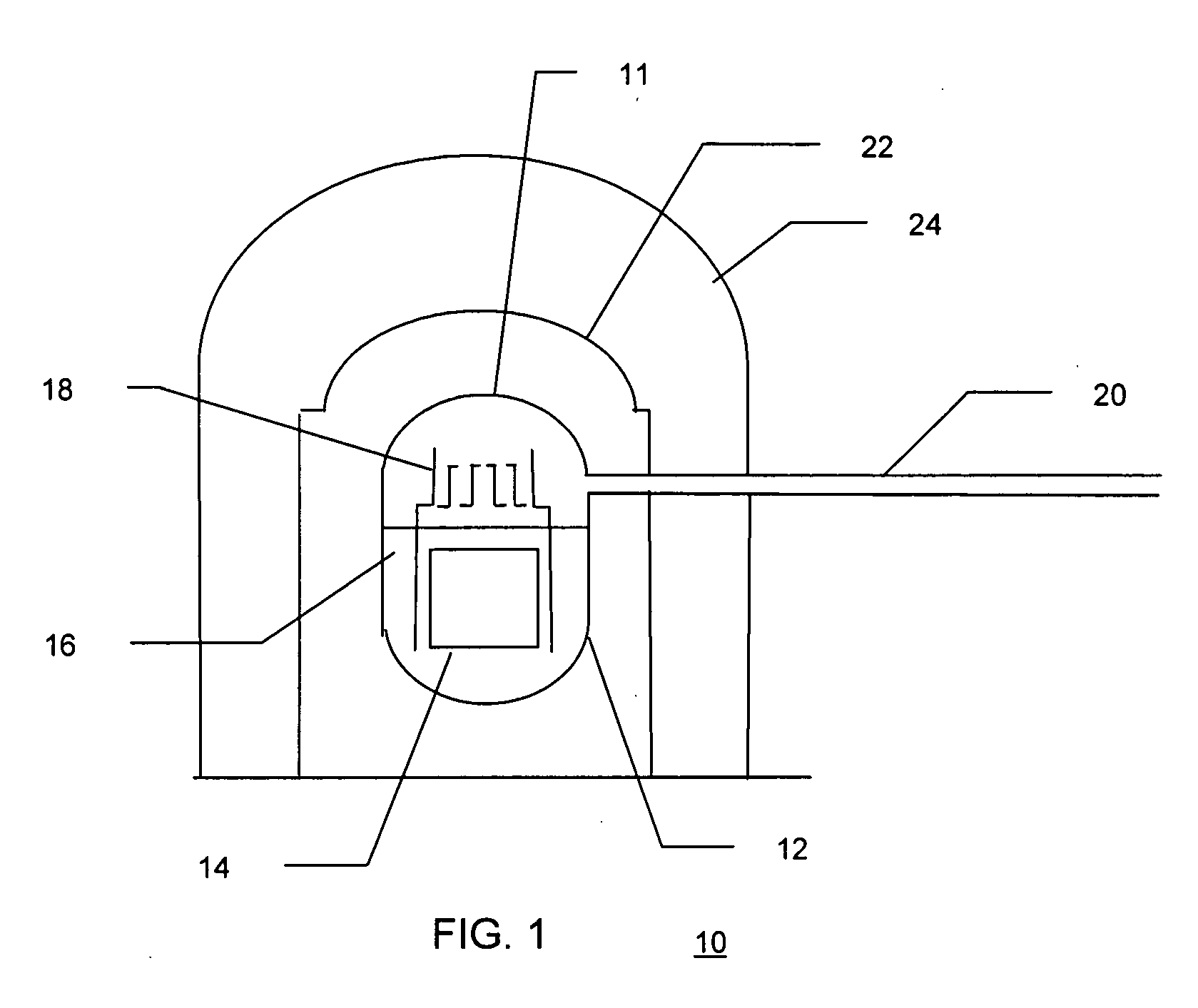
Methods and systems for crack detection
Systems and methods suitable for capable of autonomous crack detection in surfaces by analyzing video of the surface. The systems and methods include the capability to produce a video of the surfaces, the capability to analyze individual frames of the video to obtain surface texture feature data for areas of the surfaces depicted in each of the individual frames, the capability to analyze the surface texture feature data to detect surface texture features in the areas of the surfaces depicted in each of the individual frames, the capability of tracking the motion of the detected surface texture features in the individual frames to produce tracking data, and the capability of using the tracking data to filter non-crack surface texture features from the detected surface texture features in the individual frames.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
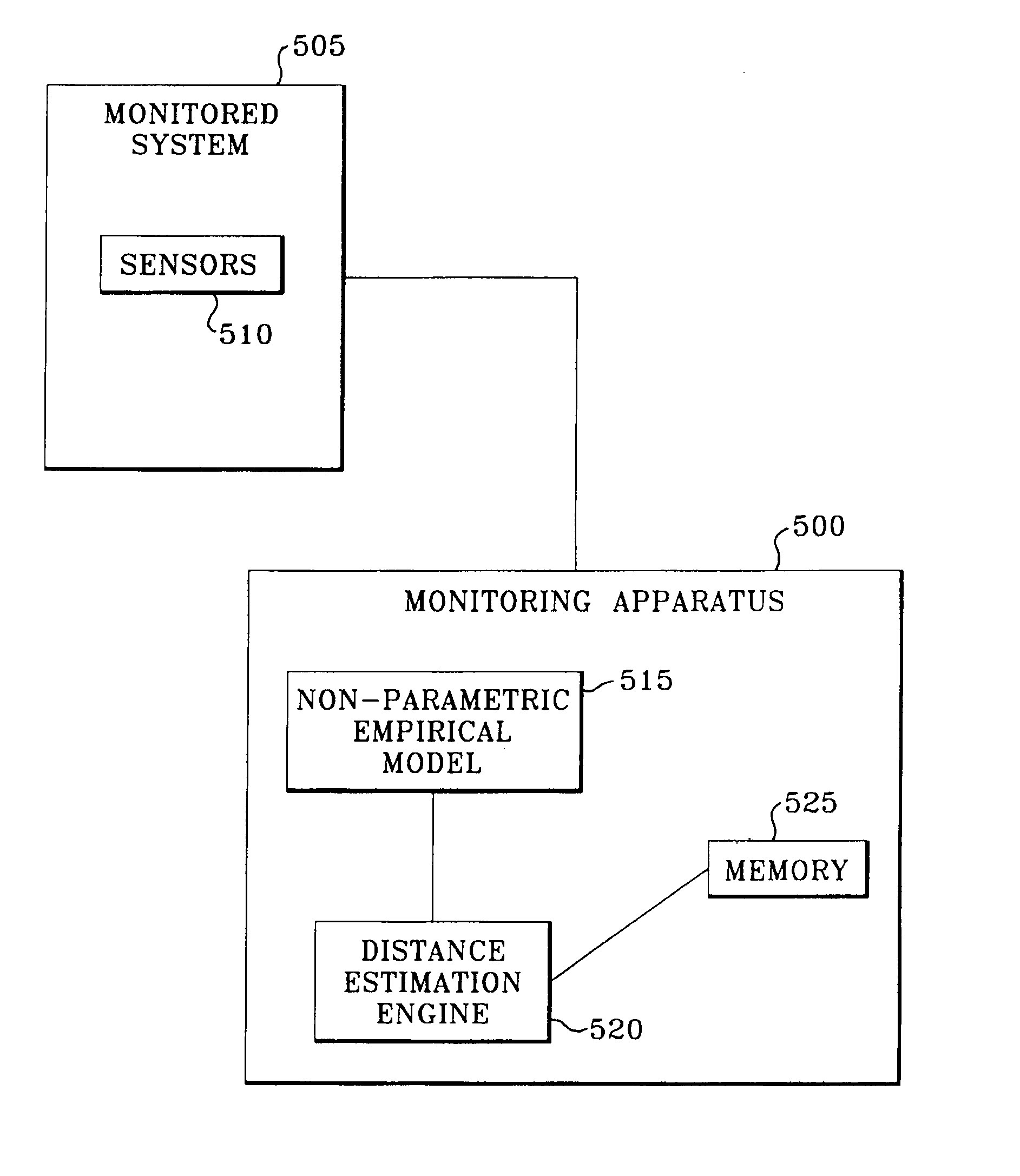
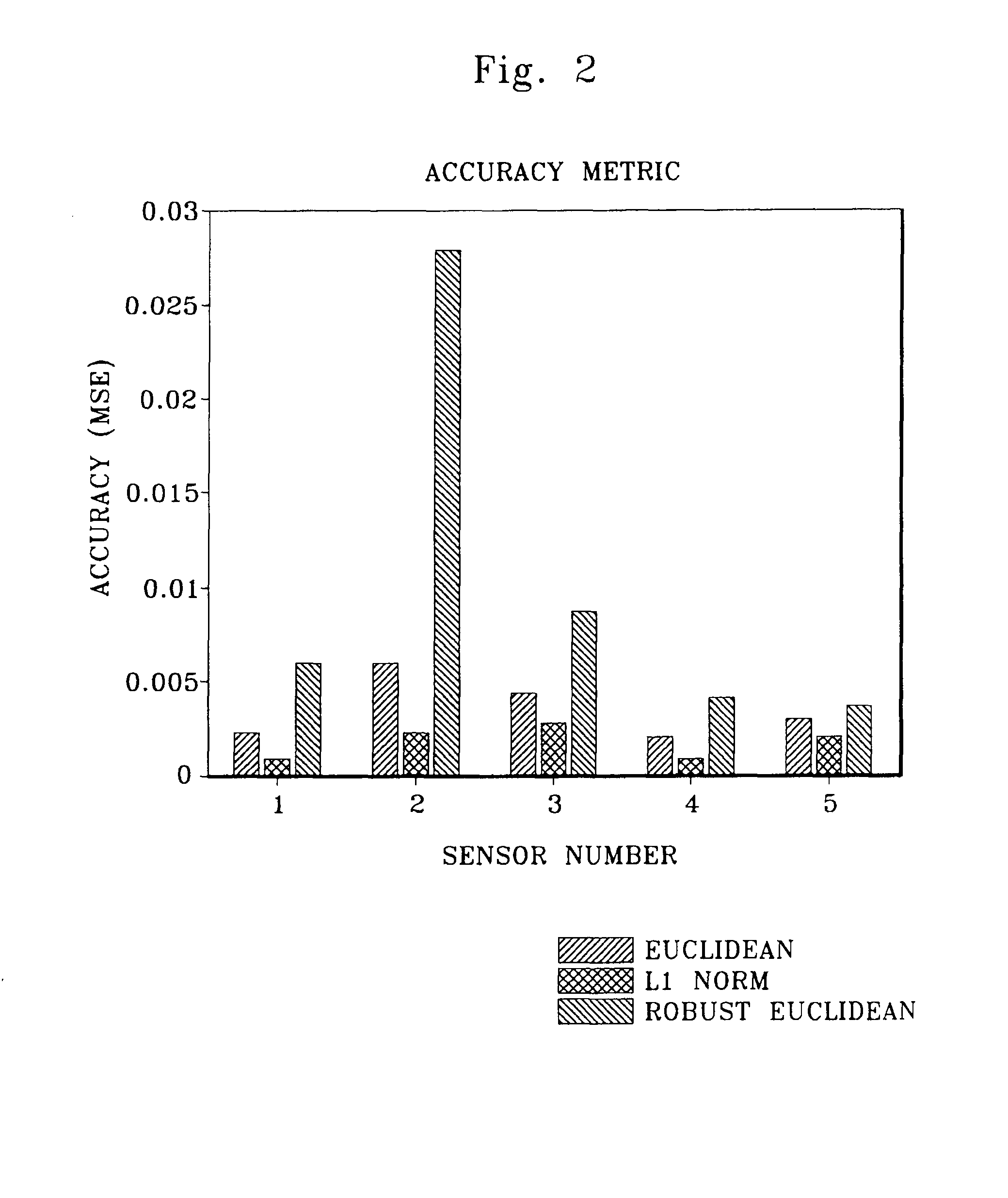
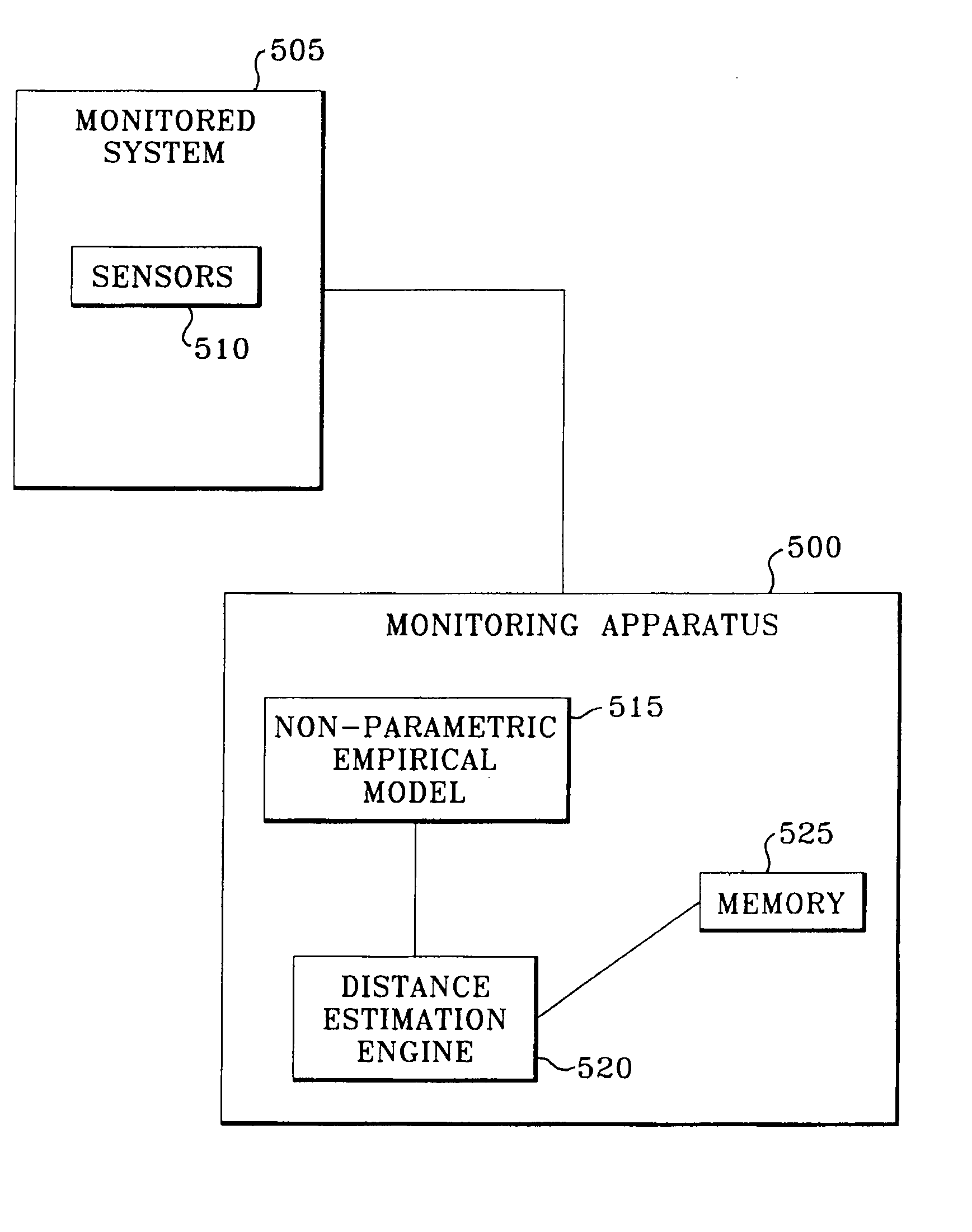
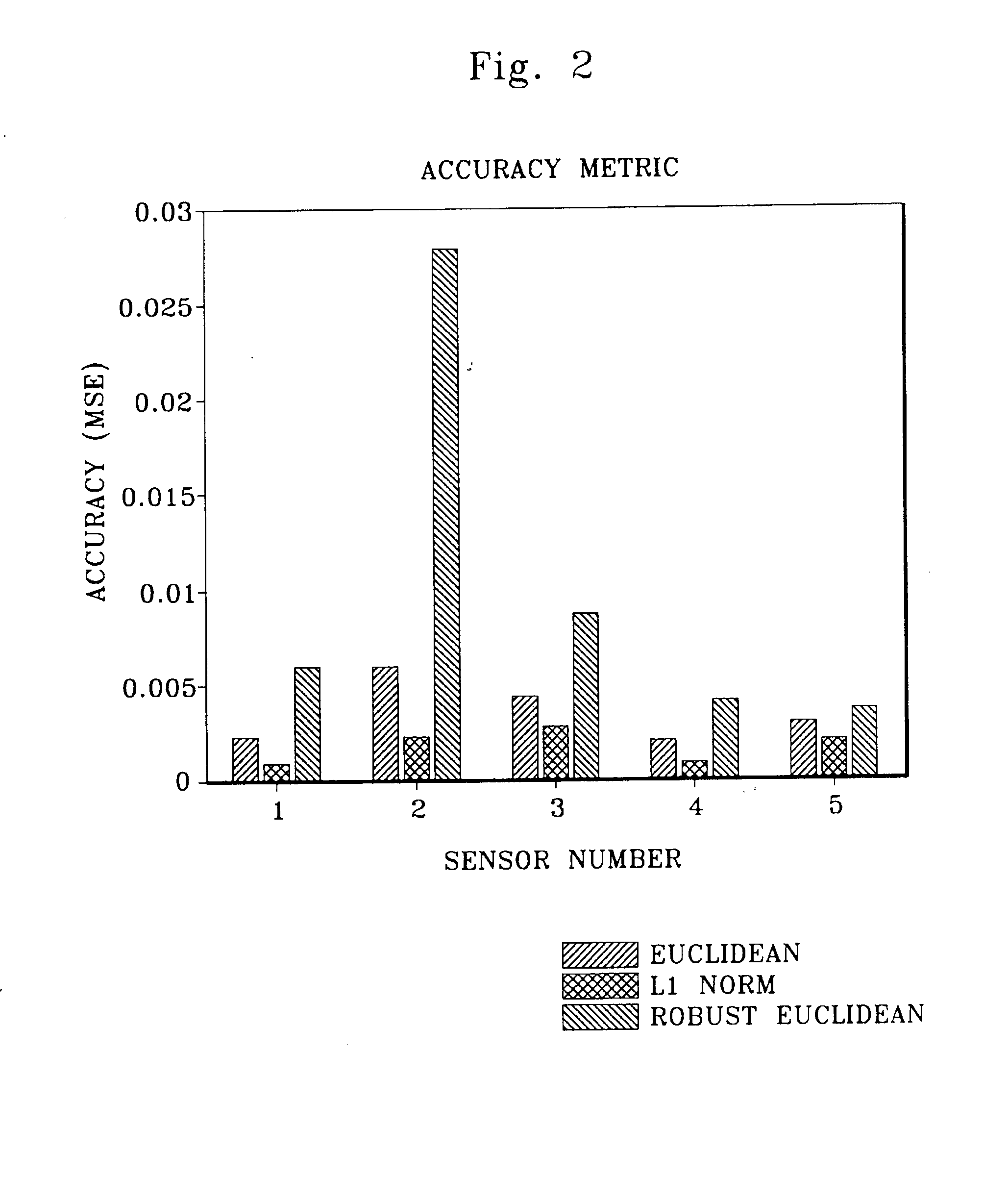
Robust distance measures for on-line monitoring
ActiveUS8311774B2Improve model performanceRobust distance metricNuclear energy generationSimulator controlComputer scienceDistance measurement
An apparatus and associated method are utilized for monitoring an operation of a system characterized by operational parameters. A non-parametric empirical model generates estimates of parameter values in response to receiving a query vector of monitored parameters for a model characterizing the system. A distance estimation engine (a) determines robust distances between the query vector and each of a set of predetermined historical vectors for the non-parametric empirical model based on an implementation of an elemental kernel function; (b) determines weights for the monitored parameters based on the robust distances; and (c) combining the weights with the predetermined historical vectors to make predictions for the system.
Owner:SMARTSIGNAL CORP
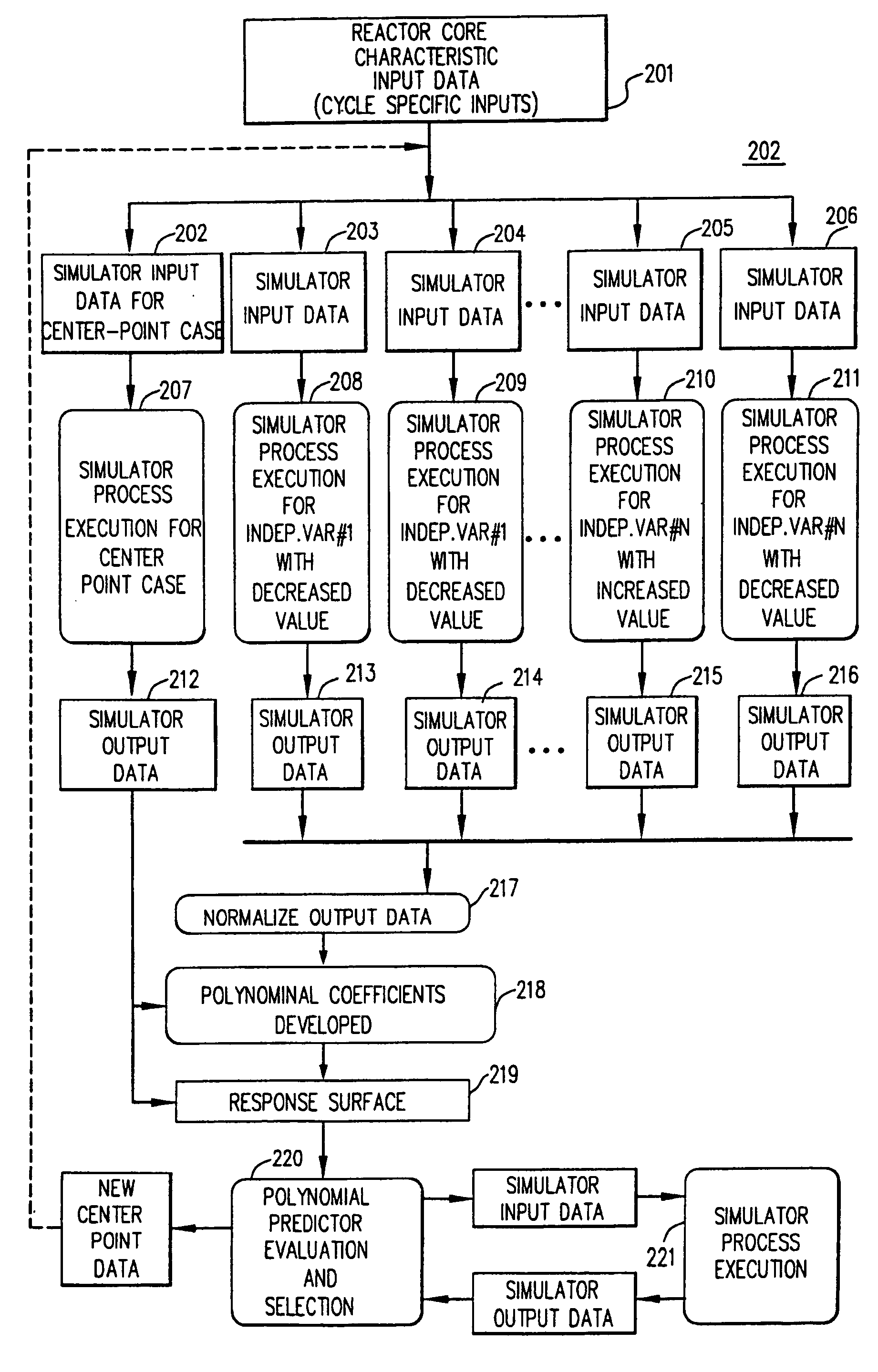
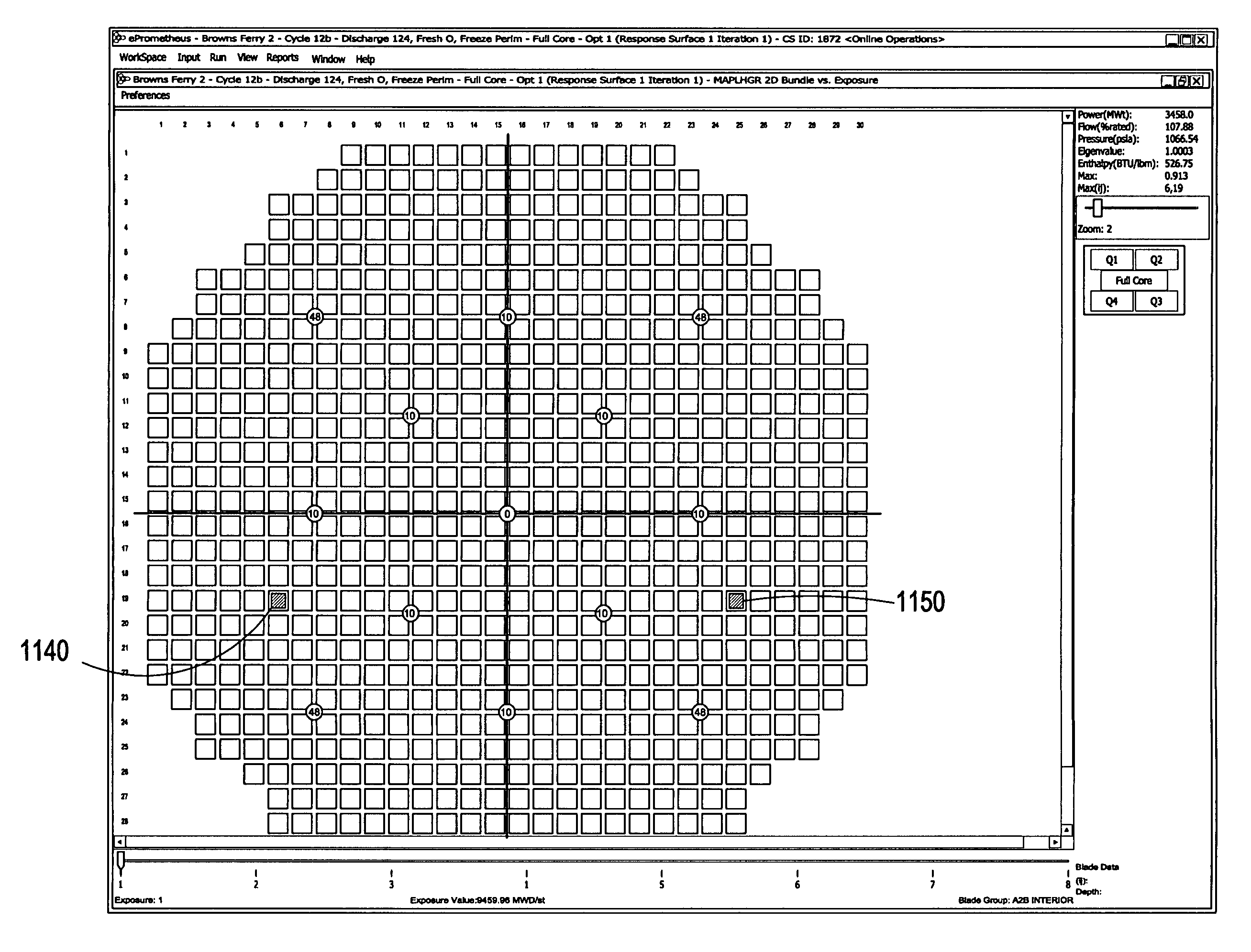
Method for predicted reactor simulation
ActiveUS20050089831A1Cosmonautic condition simulationsPlant parameters regulationEngineeringDefining relationship
In the method for reactor simulation, a user modifies one or more design inputs used in creating a response surface. The response surface defines relationships between the design inputs and operational outputs of at least one or more aspects of a core design. A reactor simulation is then generated based on the response surface for the core design and the modified design input.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
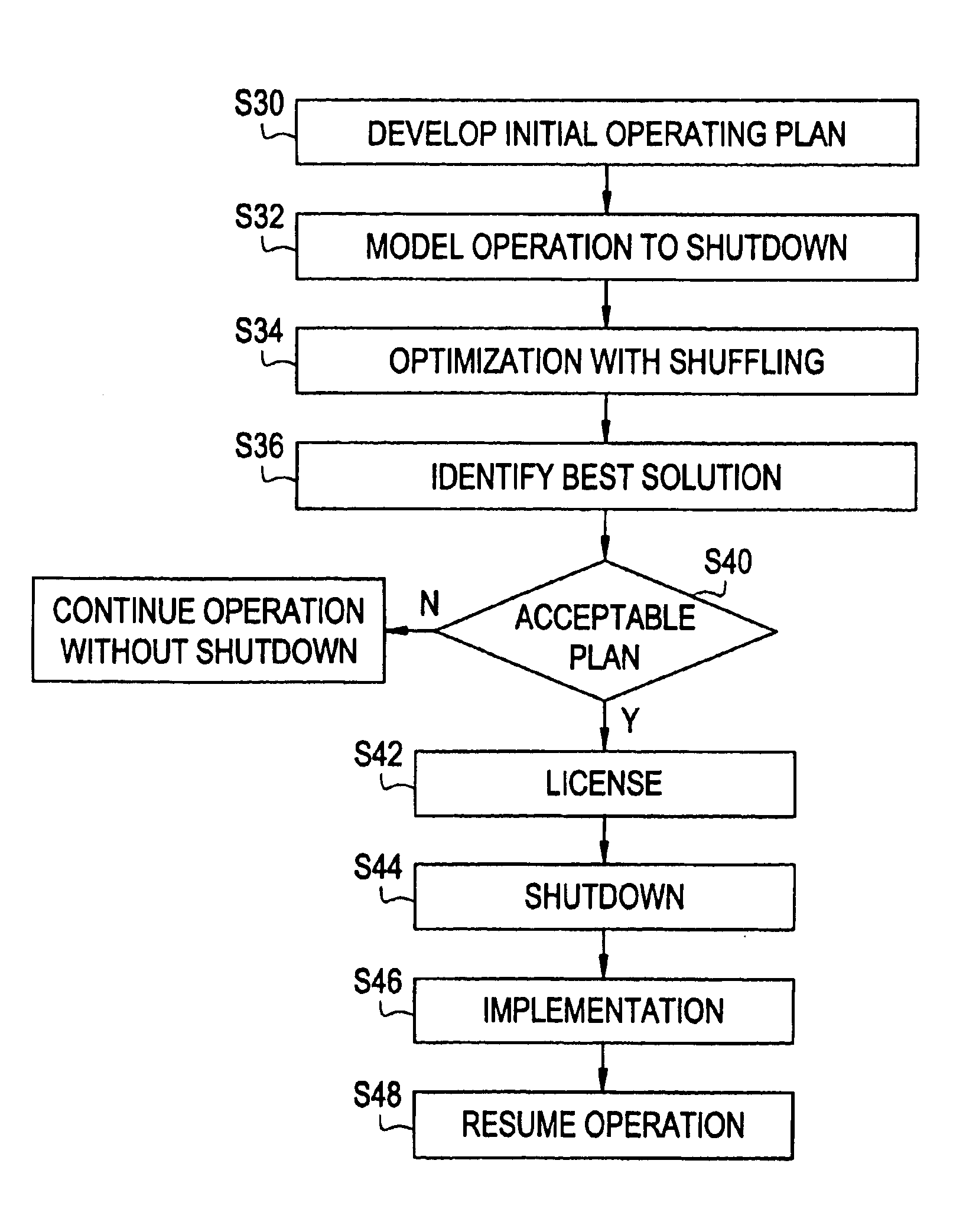
In-cycle shuffle
ActiveUS6862329B1Increase energy outputLimit thermal performanceNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear engineeringTotal energy
According to the method, a reactor core is shut down during the operation cycle. One or more fuel bundles of the reactor core are then moved to new positions within the reactor core to increase a total energy, output of the reactor core as compared to continuing operation of the reactor core without the shutting down and moving steps.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
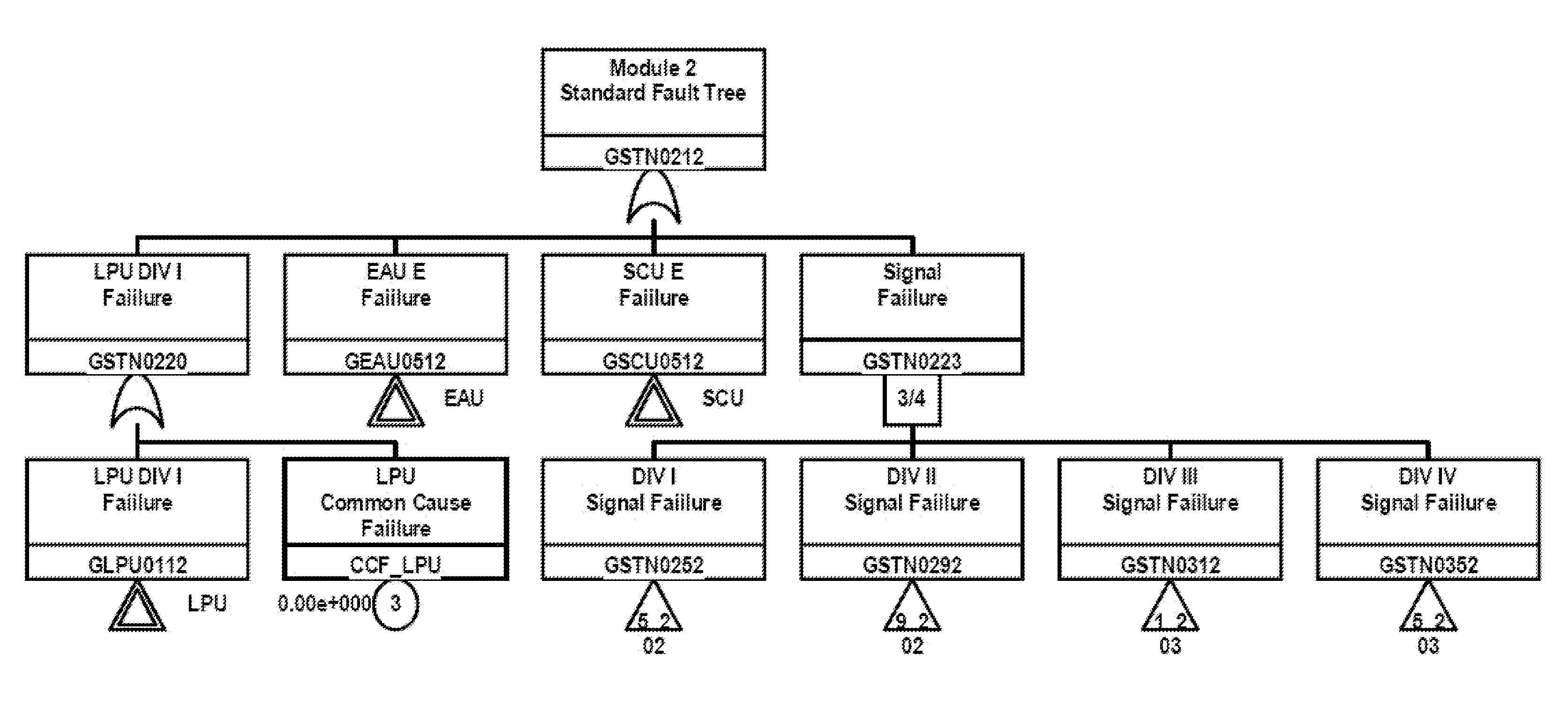
Fault Tree Analysis System for the Instrument Control Process for Nuclear Power Plant with Advanced Boiling Water Reactor Background
InactiveUS20100100251A1Fast and accurate to establishLevel controlAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsProbabilistic risk assessmentBiology
The invention relates to the fault tree analysis system for a nuclear power plant with advanced boiling water reactor. The full digital instrument control system uses six different modes to simulate the transmission of the digital signals and the analog signals from the detection units. It is to develop the fault tree for various signal transmission modes to support the nuclear power plant in probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) and meet requirements for simulated signal detection, transmission, logic operation and equipment actuation. Thus, the digital instrument control flow process can fit into PRA model and properly reflect its importance in risk assessment.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
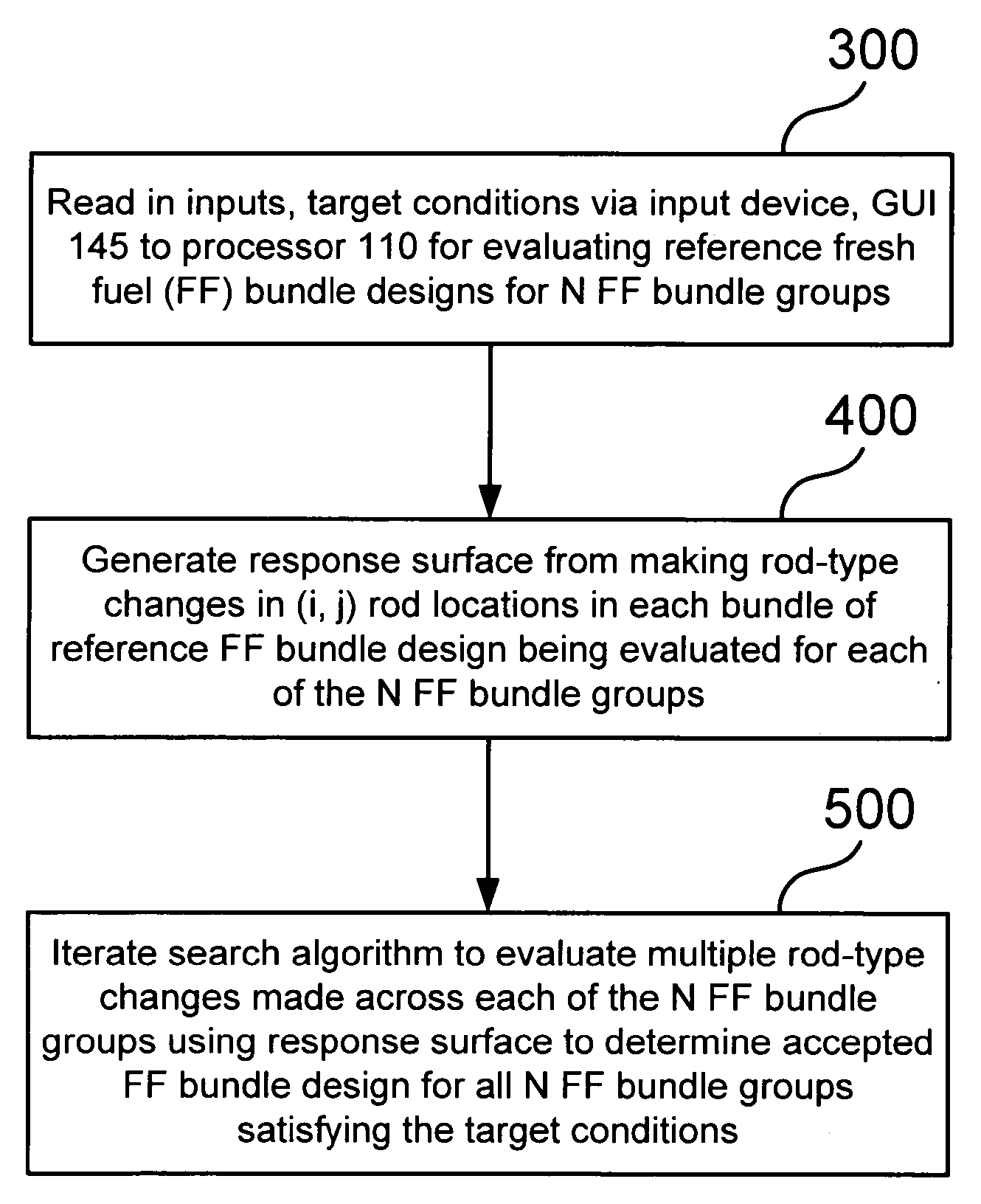
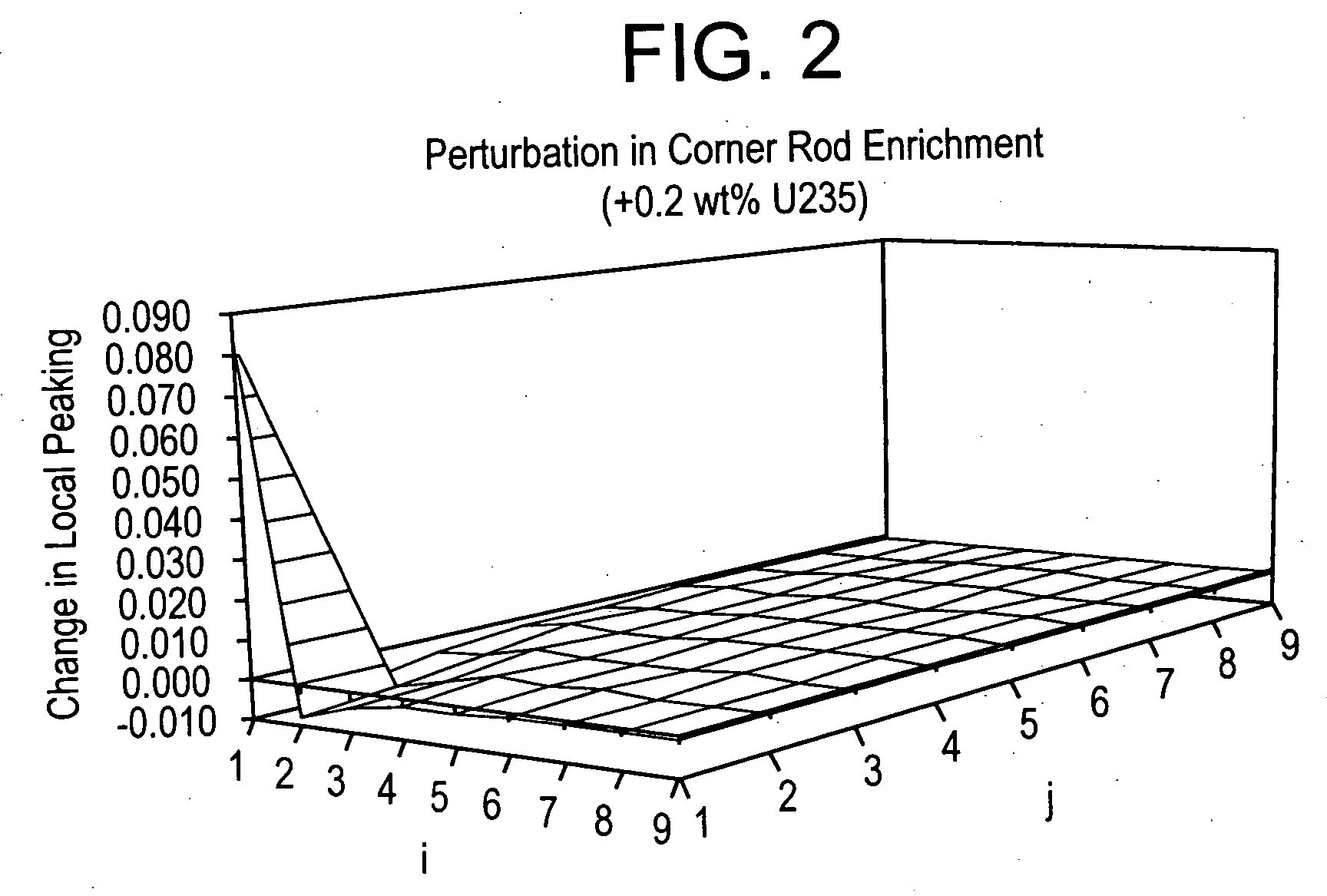
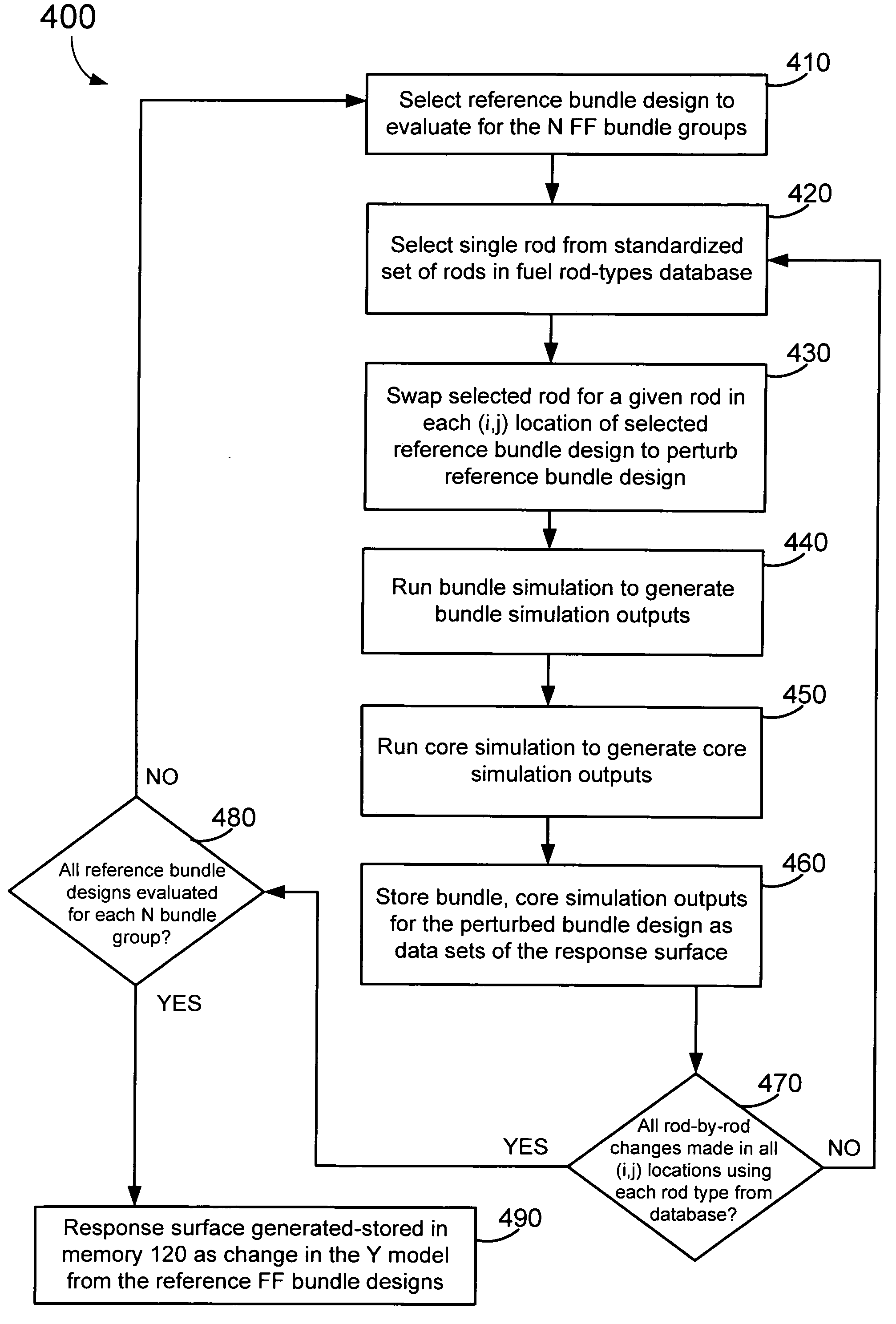
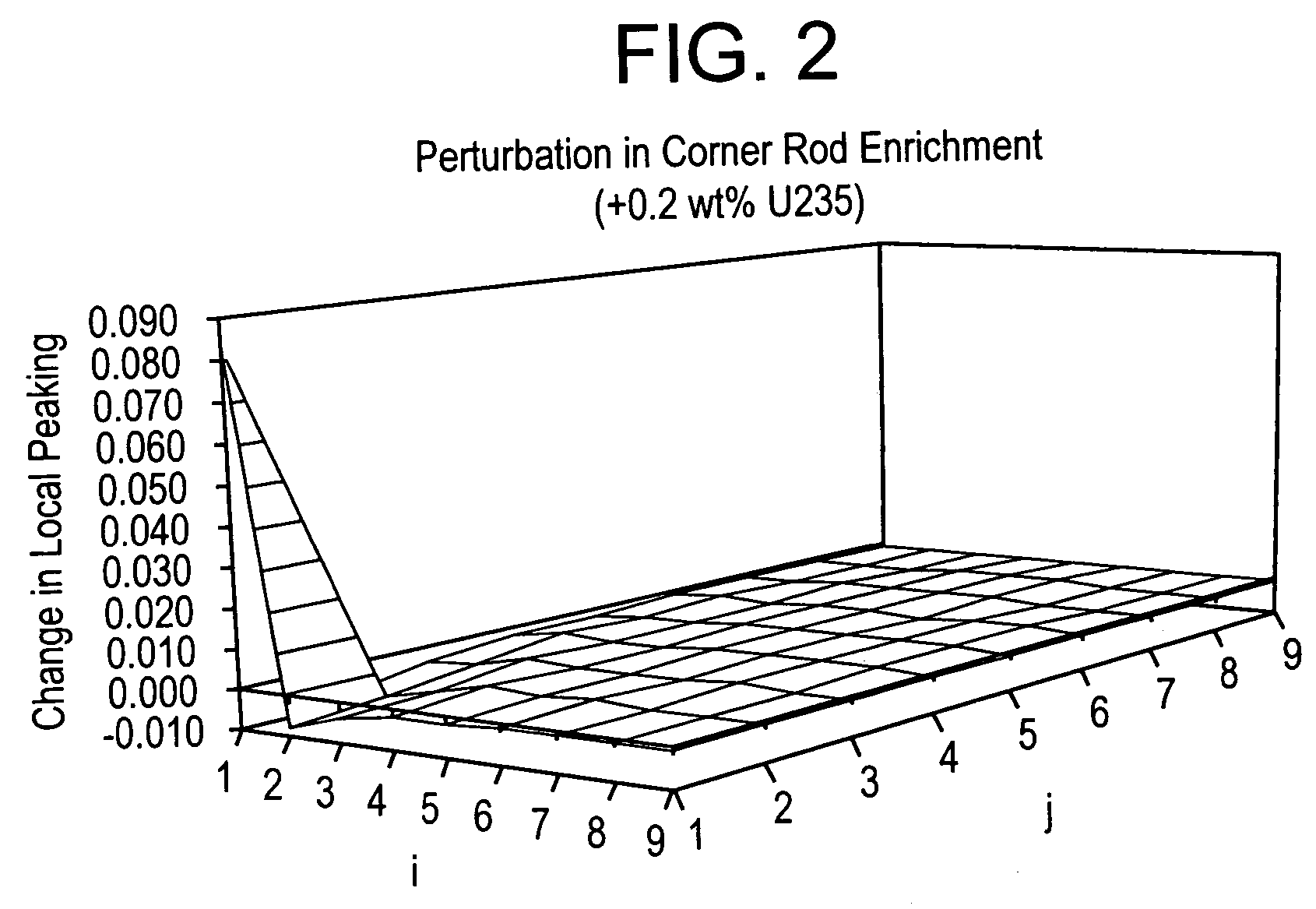
Method of determining a fresh fuel bundle design for a core of a nuclear reactor
InactiveUS20060149514A1Cosmonautic condition simulationsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A method for determining a fresh fuel bundle design for a core of a nuclear reactor may include defining a plurality of inputs including user-defined target conditions for evaluating one or more reference fresh fuel bundle designs for each of N bundle groups, and generating a response surface based on making single rod-type changes in each (i,j) rod location of each bundle of a given reference bundle design being evaluated for each of the N bundle groups. A search algorithm may be iterated to evaluate a given combination of multiple rod-type changes made simultaneously across each of the N bundle groups using the generated response surface to determine an accepted fuel bundle design for each of the N bundle groups that satisfies the user-defined target conditions.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
Method of determining a fresh fuel bundle design for a core of a nuclear reactor
InactiveUS7574337B2Cosmonautic condition simulationsComputation using non-contact making devicesNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A method for determining a fresh fuel bundle design for a core of a nuclear reactor may include defining a plurality of inputs including user-defined target conditions for evaluating one or more reference fresh fuel bundle designs for each of N bundle groups, and generating a response surface based on making single rod-type changes in each (i,j) rod location of each bundle of a given reference bundle design being evaluated for each of the N bundle groups. A search algorithm may be iterated to evaluate a given combination of multiple rod-type changes made simultaneously across each of the N bundle groups using the generated response surface to determine an accepted fuel bundle design for each of the N bundle groups that satisfies the user-defined target conditions.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
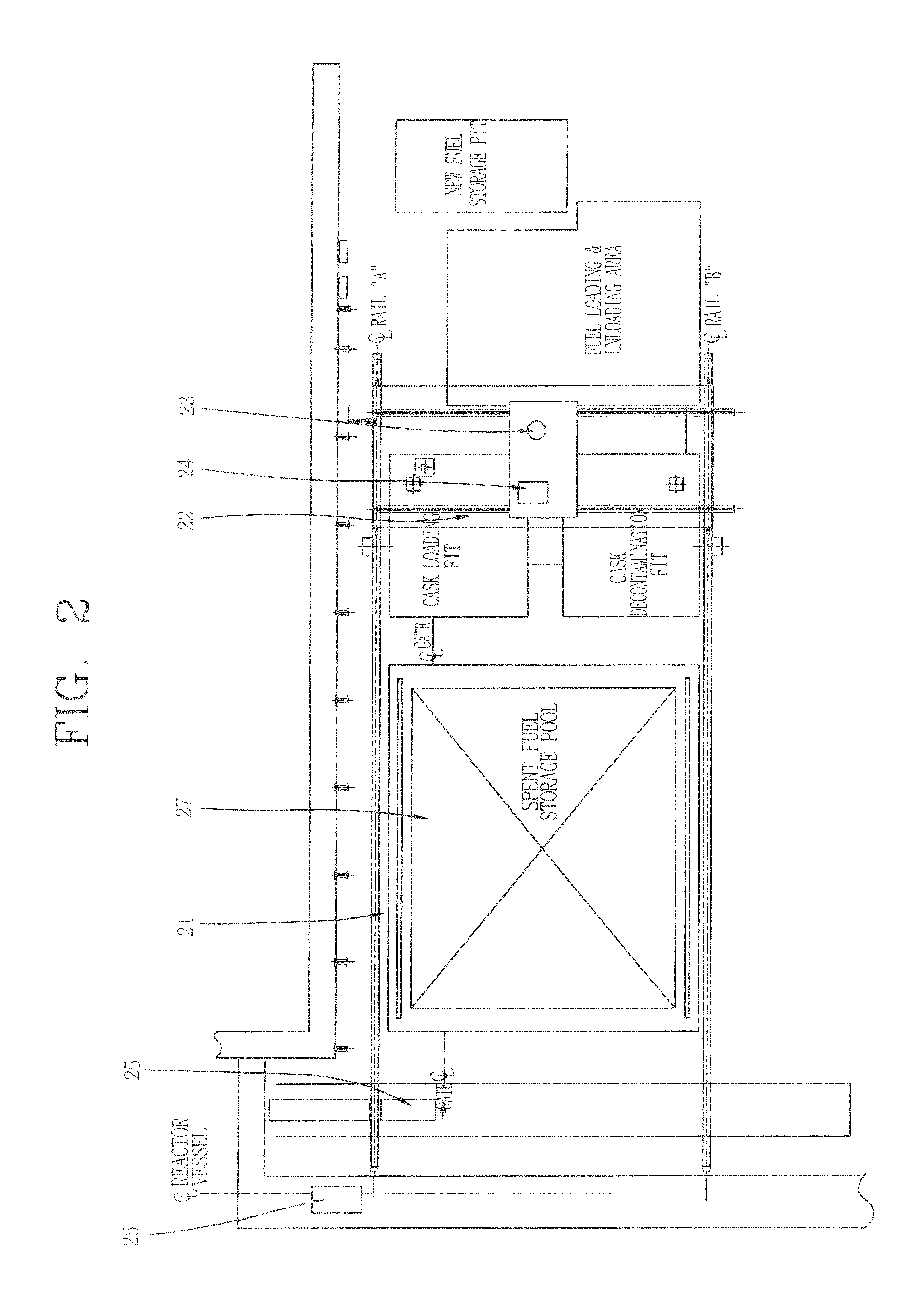
Remote control system for the fuel handling system of nuclear power plant
InactiveUS20120128113A1Reduce exposurePrevent exposure to radioactivity and dropping of foreign substanceMan-machine nuclear interfaceNuclear energy generationHuman–machine interfaceProgrammable logic controller
Disclosed is a remote control system for a fuel handling system of a nuclear power plant, in which the system includes a remote control console; a programmable logic controller (PLC) unit; a servo motor drive; and a human-machine interface (HMI) unit.
Owner:DOOSAN HEAVY IND & CONSTR CO LTD
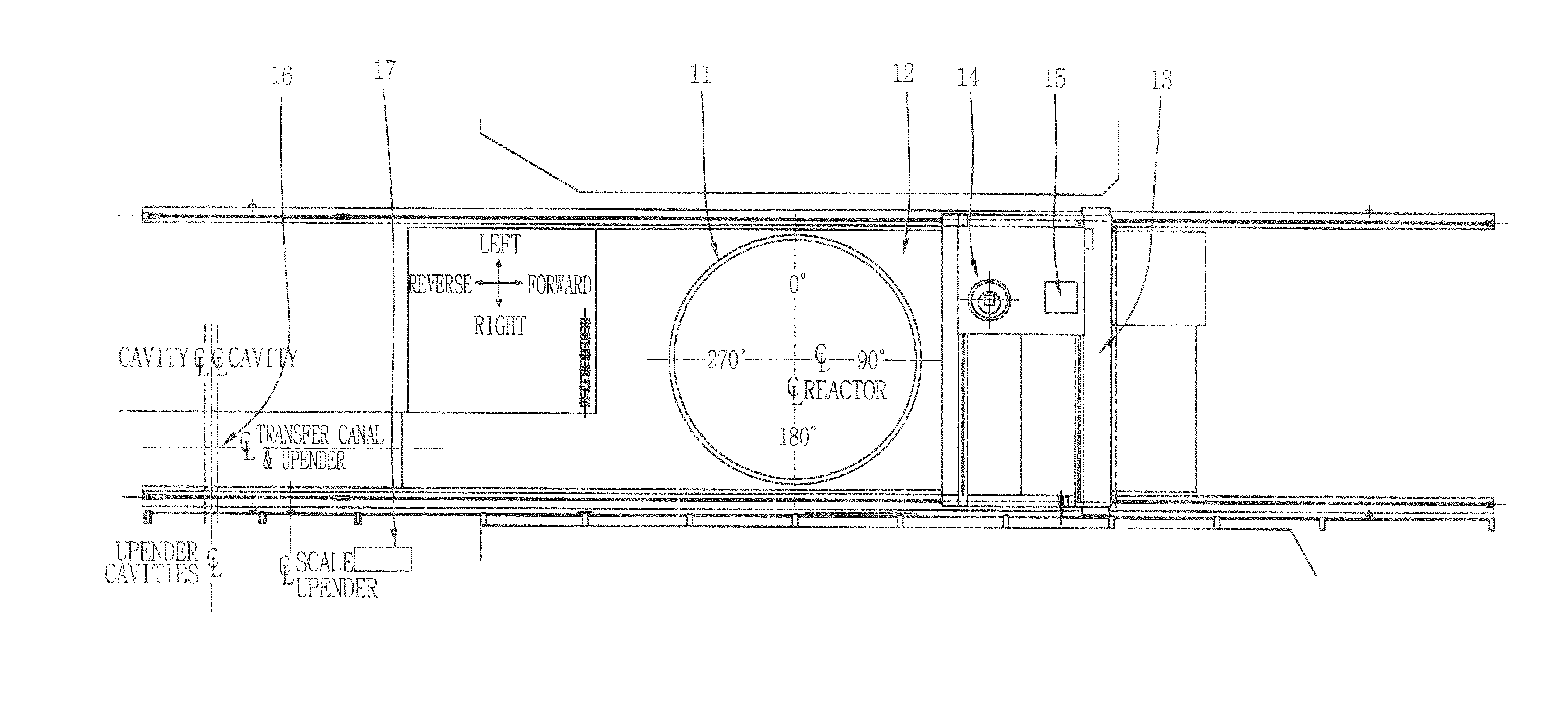
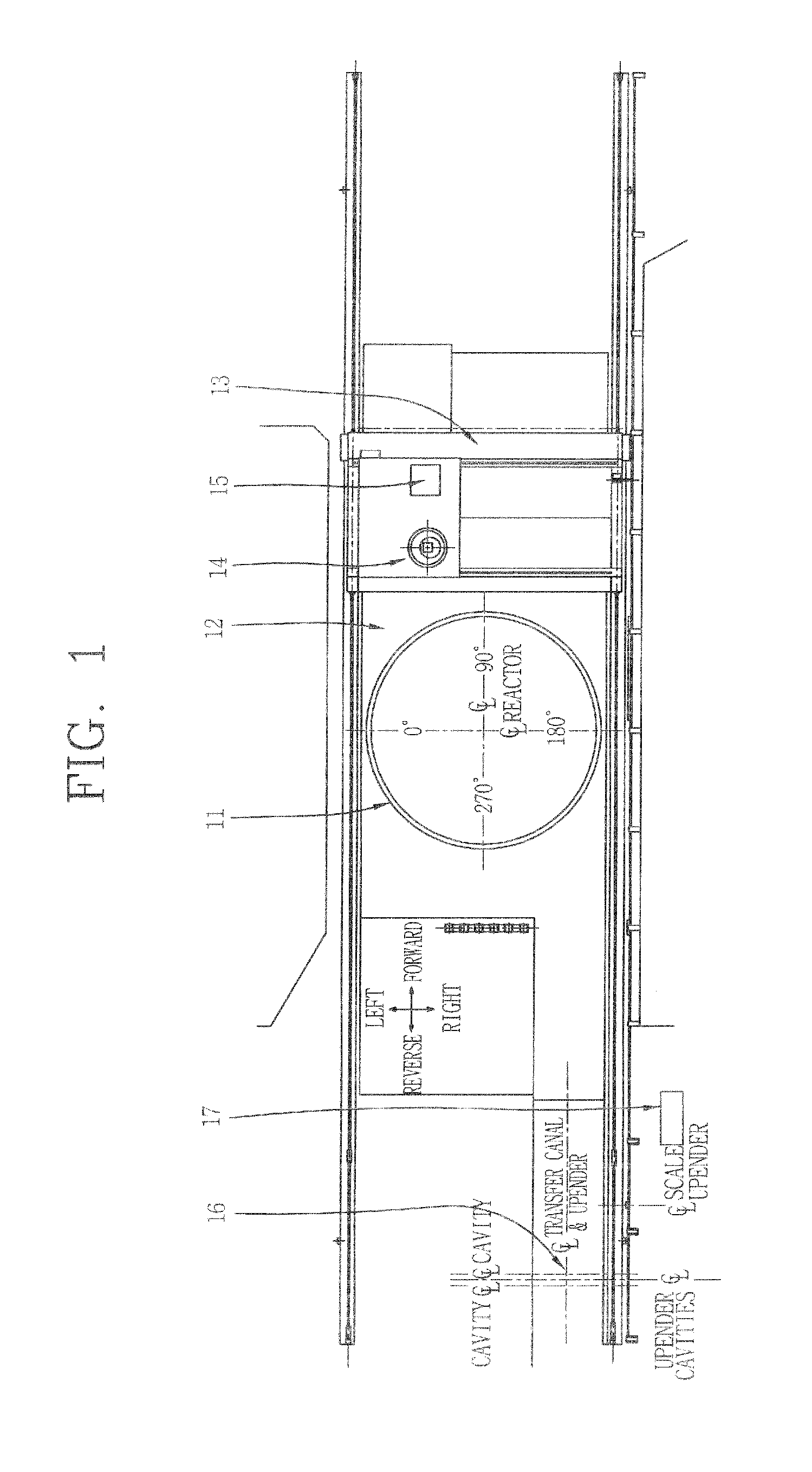
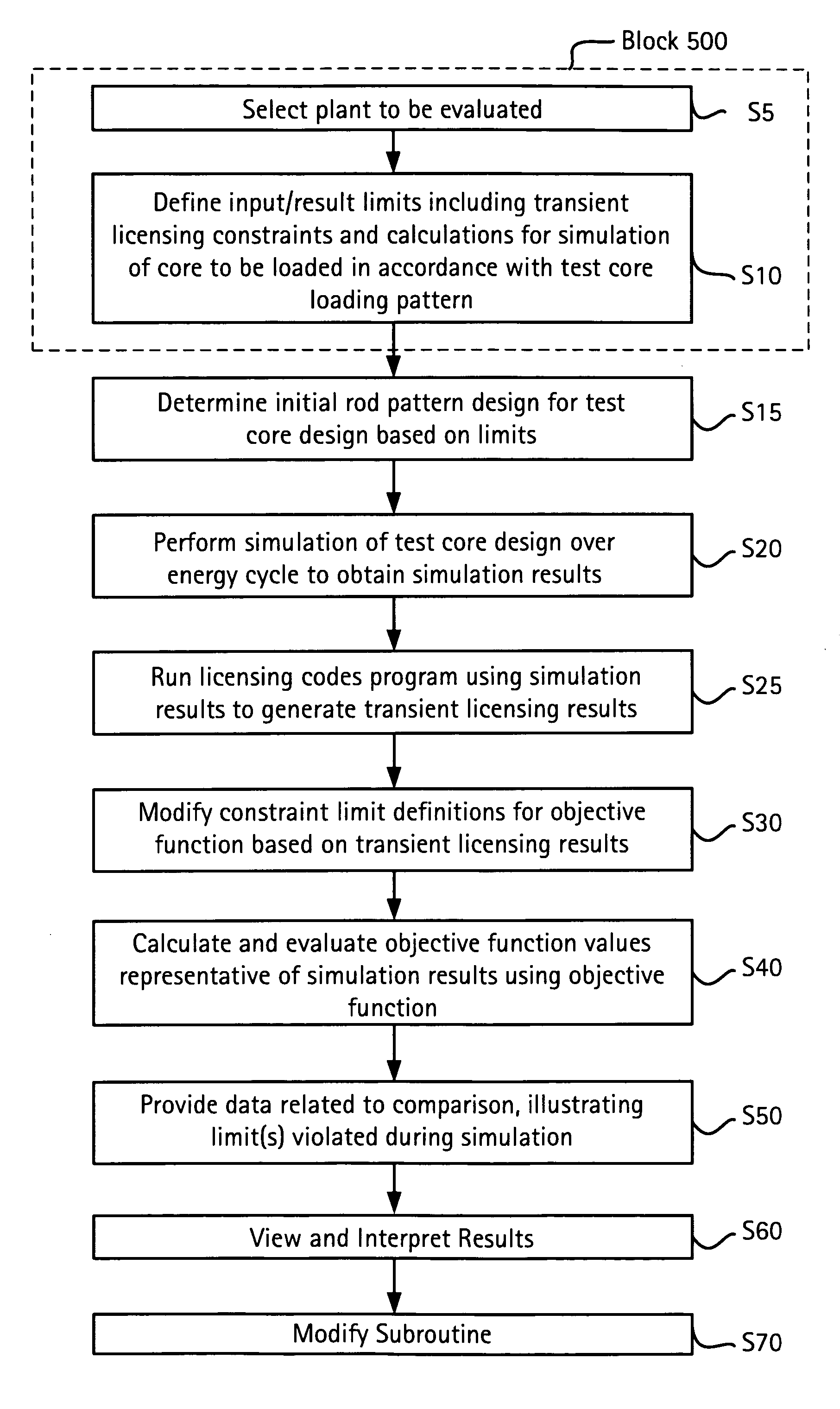
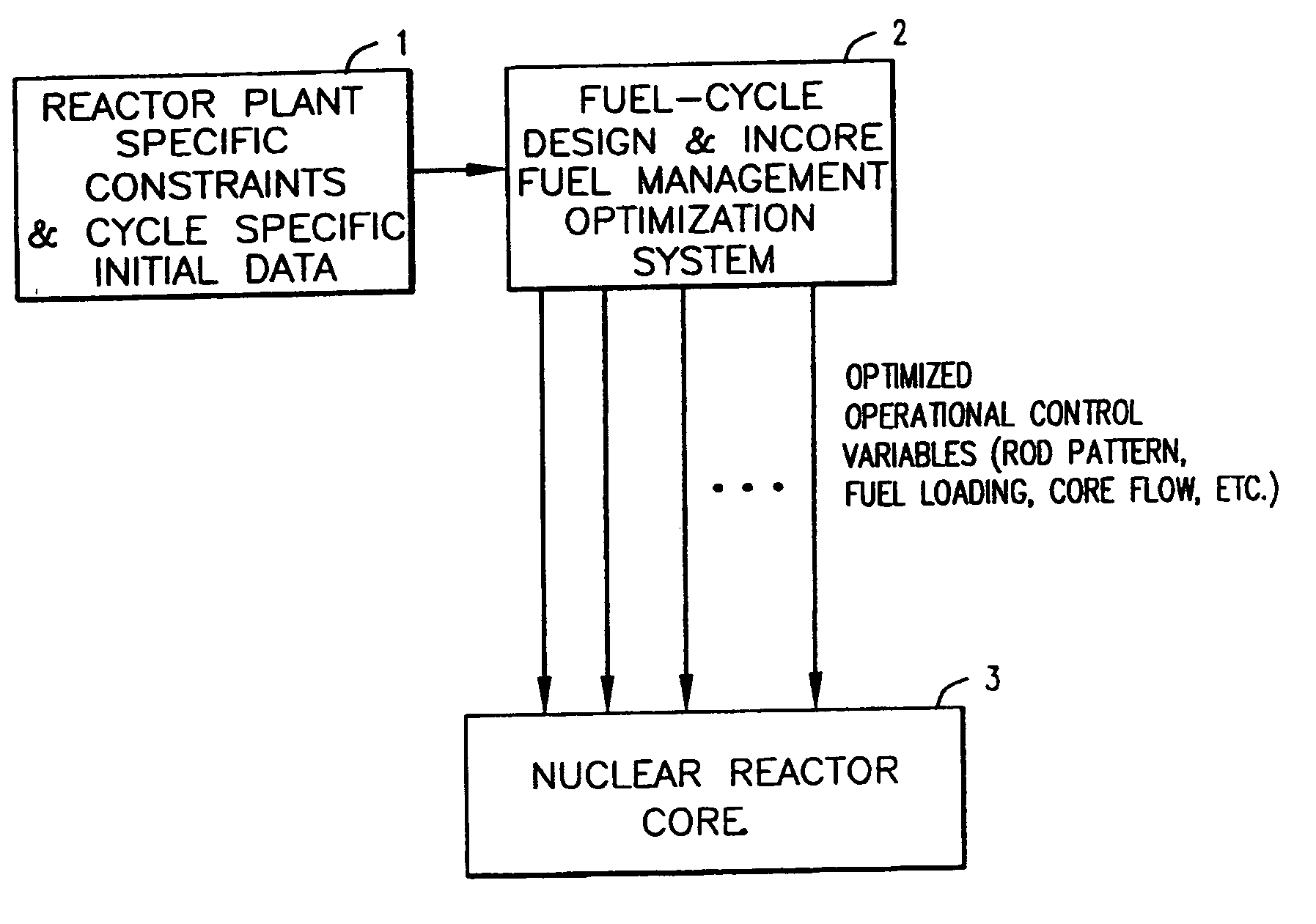
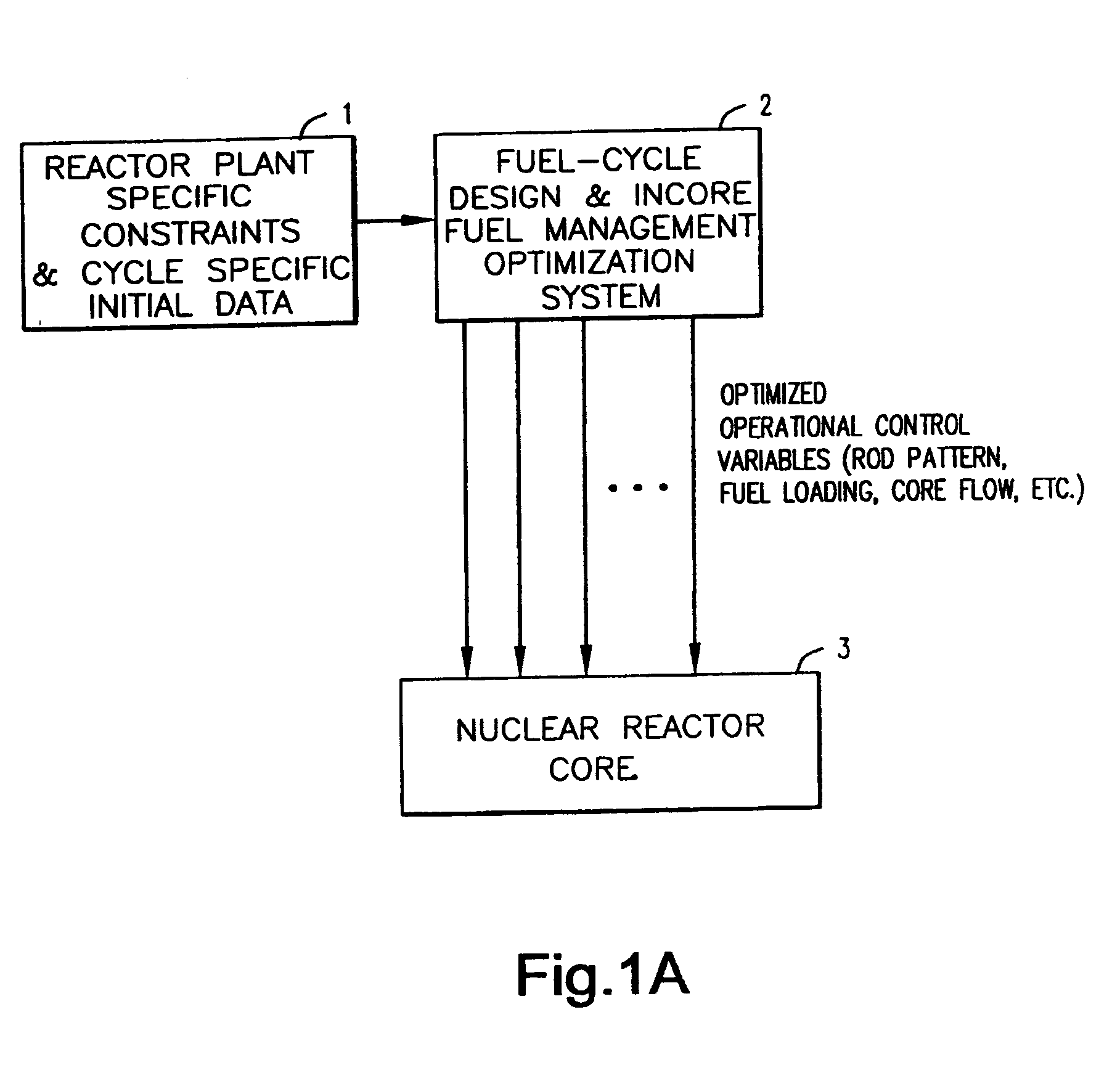
Computer-implemented method and system for designing a nuclear reactor core which satisfies licensing criteria
ActiveUS20070213959A1Power plant safety arrangementPlant parameters regulationNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
In a computer-implemented method of designing a nuclear reactor of a given reactor plant, an initial, test reactor core design is generated for the given plant based on a plurality of limits input by a user. The limits include a plurality of transient licensing constraints to be satisfied for operating the given plant. The method includes selecting, from a set of automated tools, one or more automated tools to evaluate the test core design, and operating one of more of selected automated tools to output data for display to the user. The displayed data is related to a core design that satisfies the limits inclusive of the transient licensing constraints.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
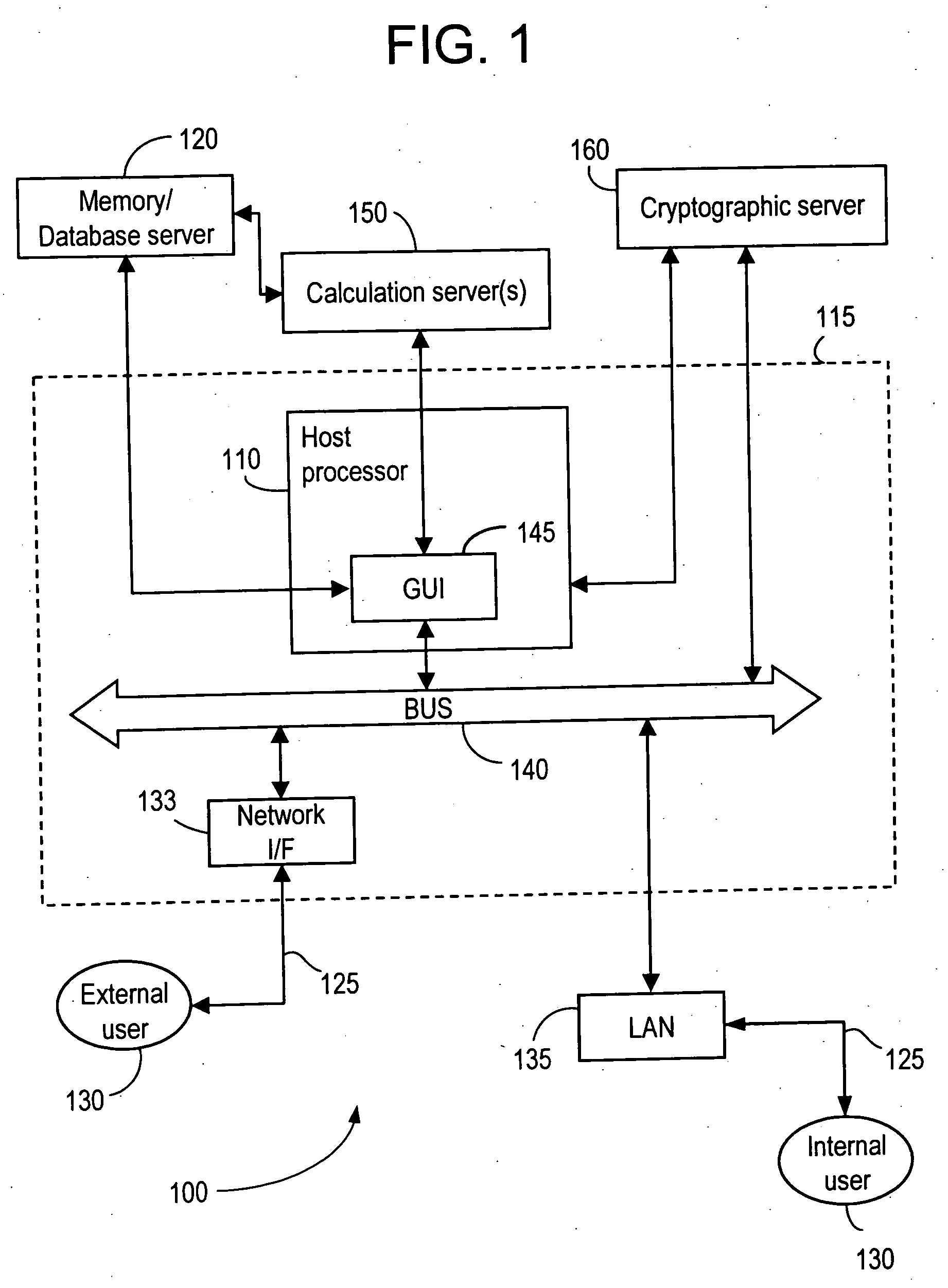
Method and apparatus for evaluating robustness of proposed solution to constraint problem and considering robustness in developing a constraint problem solution
ActiveUS20070179919A1Nuclear energy generationAnalogue computers for electric apparatusGraphicsGraphical user interface
In an embodiment of a method of evaluating robustness of a proposed solution to a constraint problem, operational output data for at least first and second modified versions of the proposed solution is generated. The first modified version has at least one control variable of the proposed solution perturbed in a first direction and the second modified version has the at least one control variable of the proposed solution perturbed in a second direction. At least a portion of the generated operation output data is then presented such as on a graphical user interface.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Incore instrument core performance verification method
InactiveUS20110002432A1Increase power levelEnhances accuracy and safety and convenienceNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringValidation methodsEngineering
A subcritical physics testing program which utilizes vanadium self-powered incore instrumentation thimble assemblies to provide an actual measured powered distribution that is used to confirm that the core will operate as designed. The signals received from the incore detector elements are integrated until a fractional uncertainty is less than a specified level. The measured power distribution is then compared against a predicted power distribution for a given rod position or temperature difference. If the measured power distribution is within a specified tolerance to the predicted power distribution, then the core is expected to behave as predicted.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
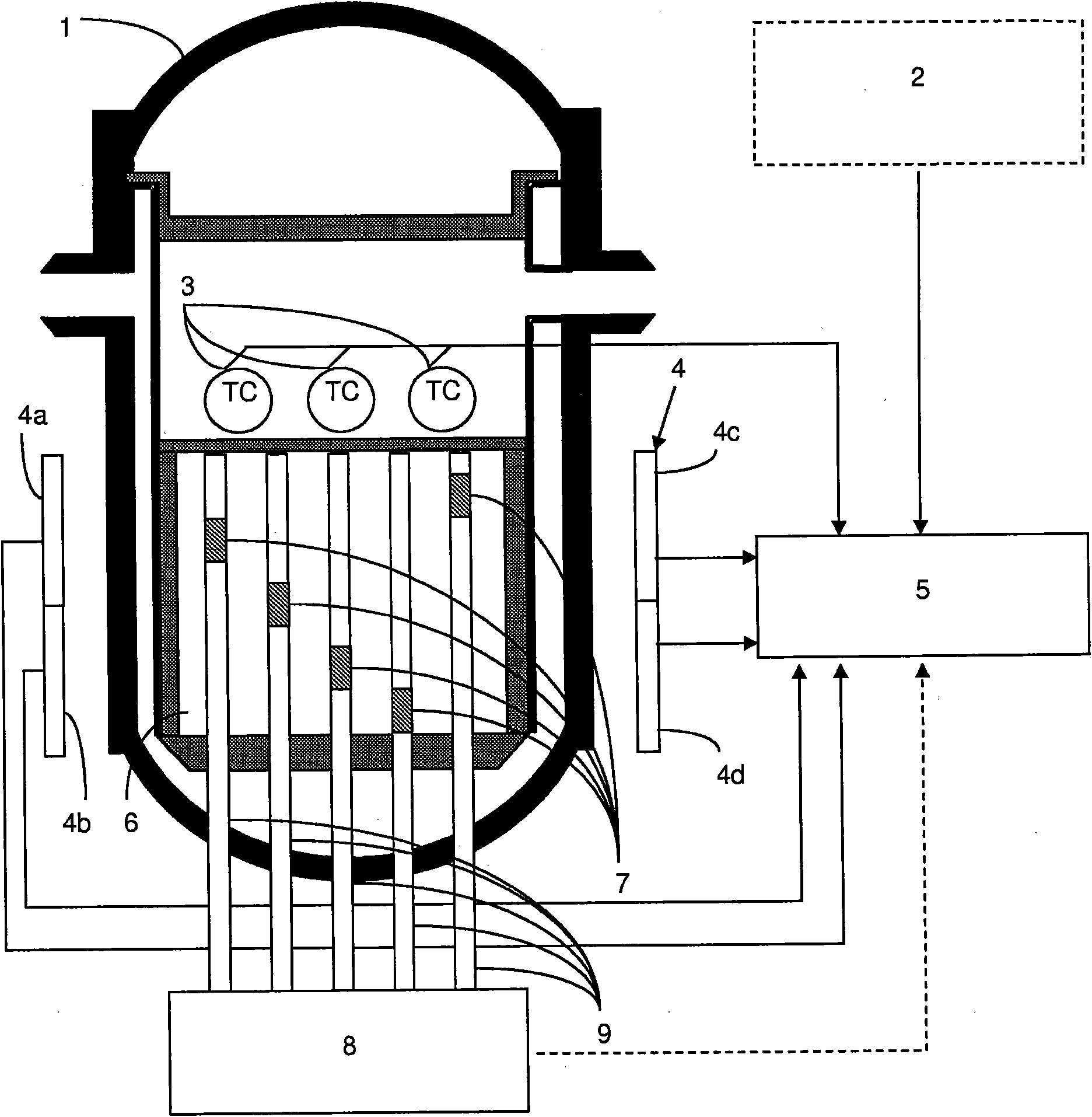
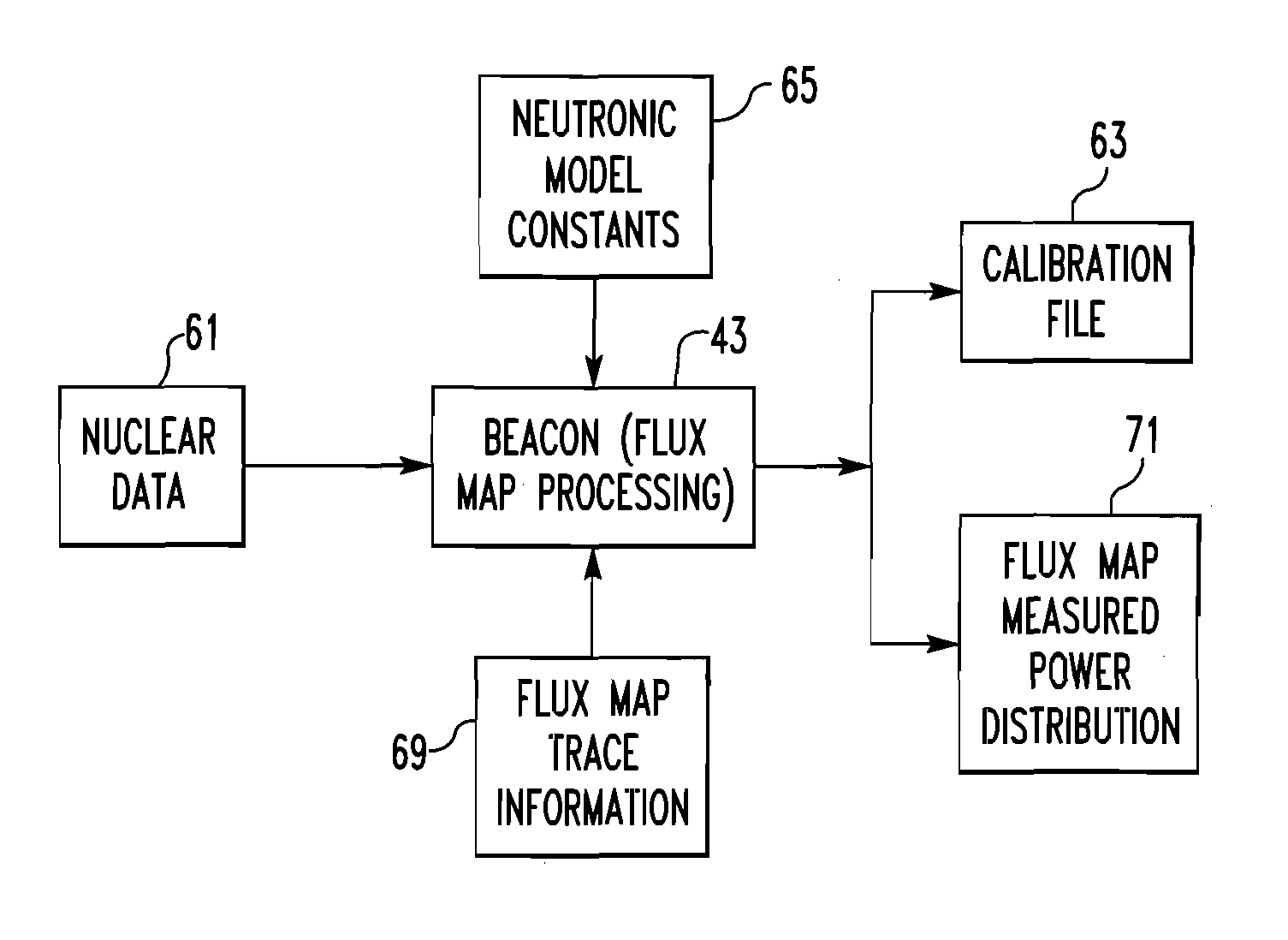
Method for determining the volumetric power distribution of the core of a nuclear reactor
ActiveCN101669176AAccurate and effective monitoringOptimizing TransientsNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
The invention relates to a method for determining (30) the volumetric power distribution of the core of a nuclear reactor using a set of detectors for measuring a neutronic flow provided outside the reactor vessel, and a set of probes for measuring the temperature of the coolant at the outlet of the fuel assemblies. The method (30) comprises the step of determining a first volumetric power distribution using a neutronic calculation code (40) instantaneously solving the diffusion equation and updating the isotopic balance of the core during the fuel depletion based on values of the core operation parameters, and the step of determining a new volumetric power distribution by adjusting (60 and 90) the first volumetric power distribution using the measures provided by the sensors for measuringthe neutronic flow and provided outside the reactor vessel (80) and by the temperature measuring probes (100).
Owner:FRAMATOME ANP
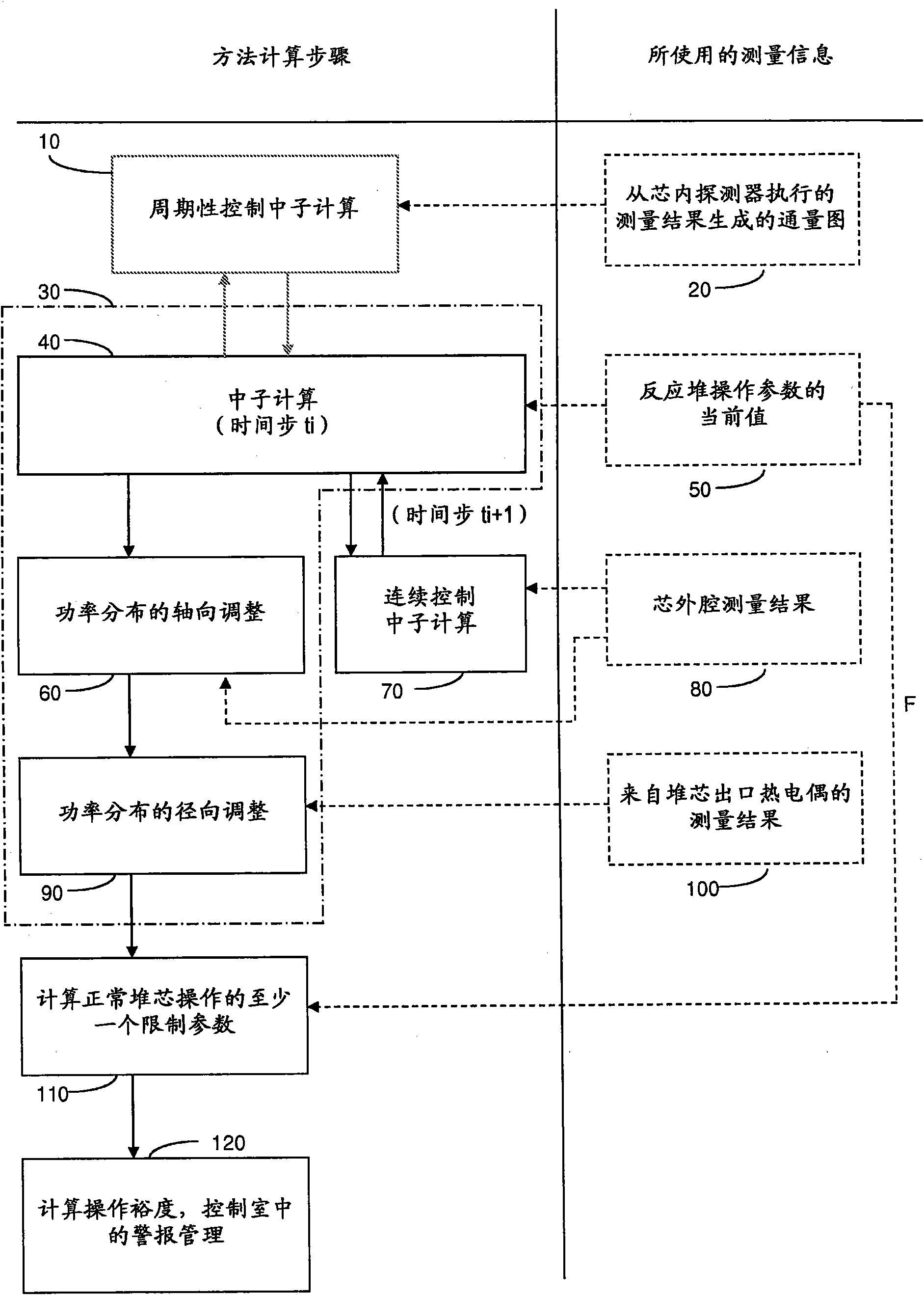
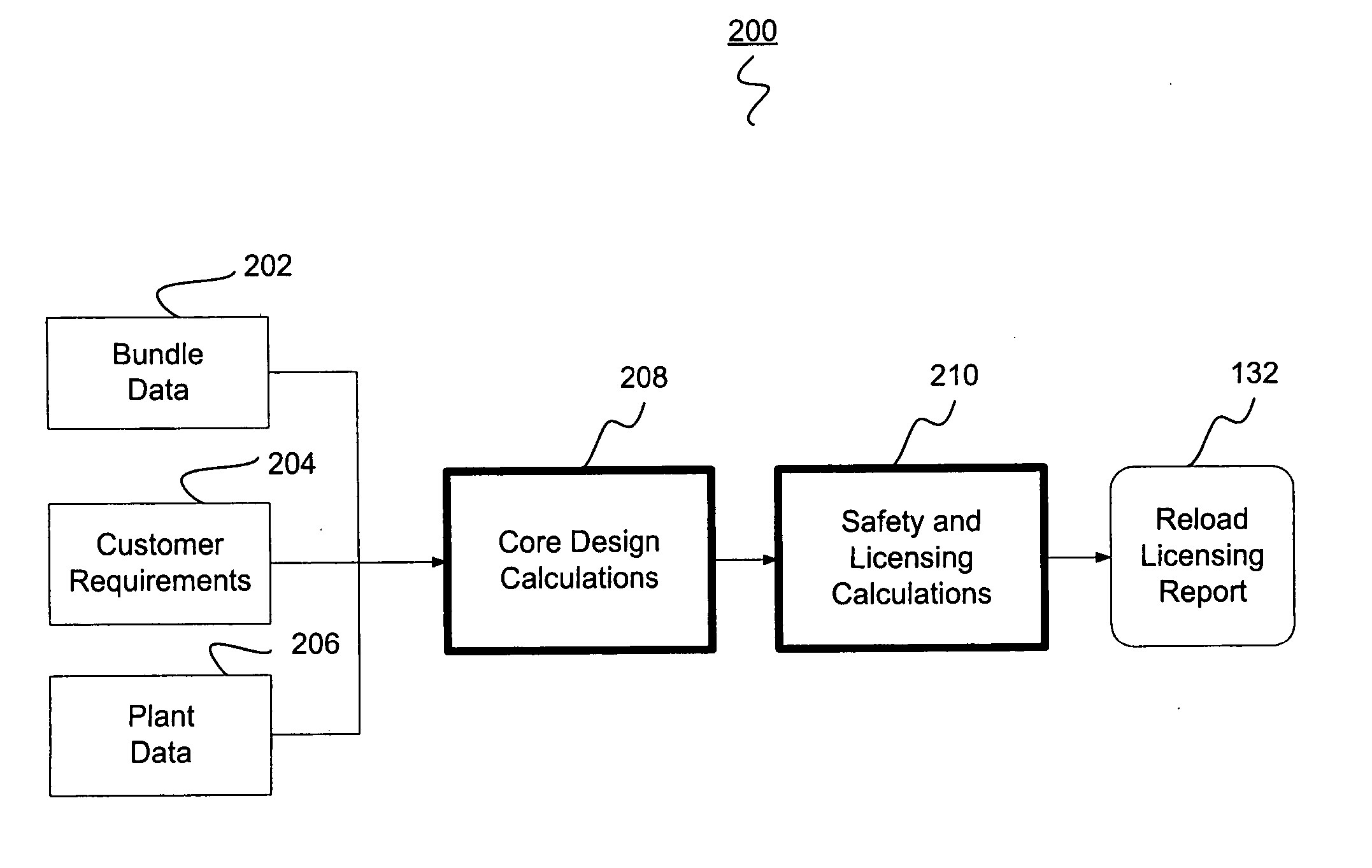
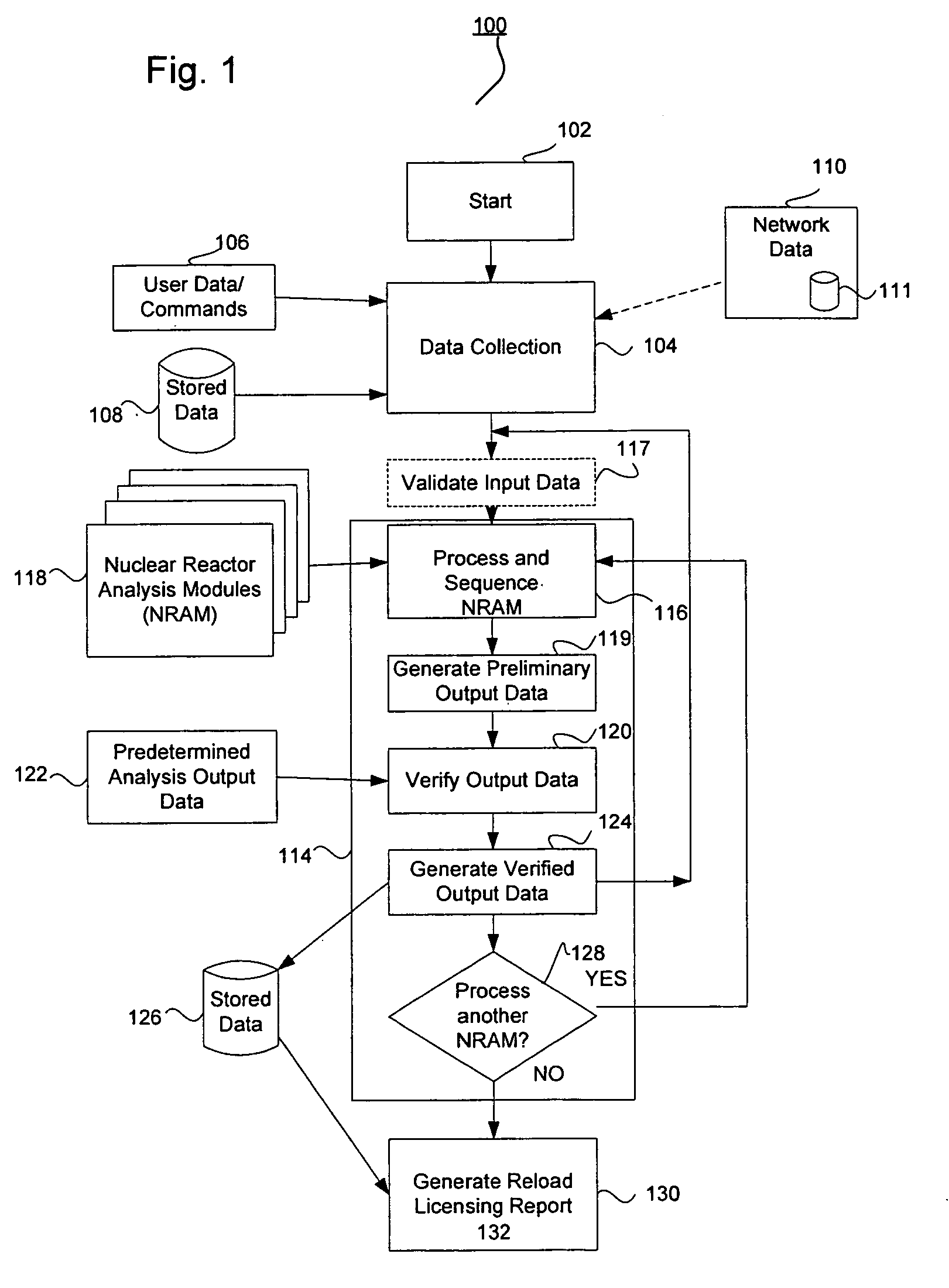
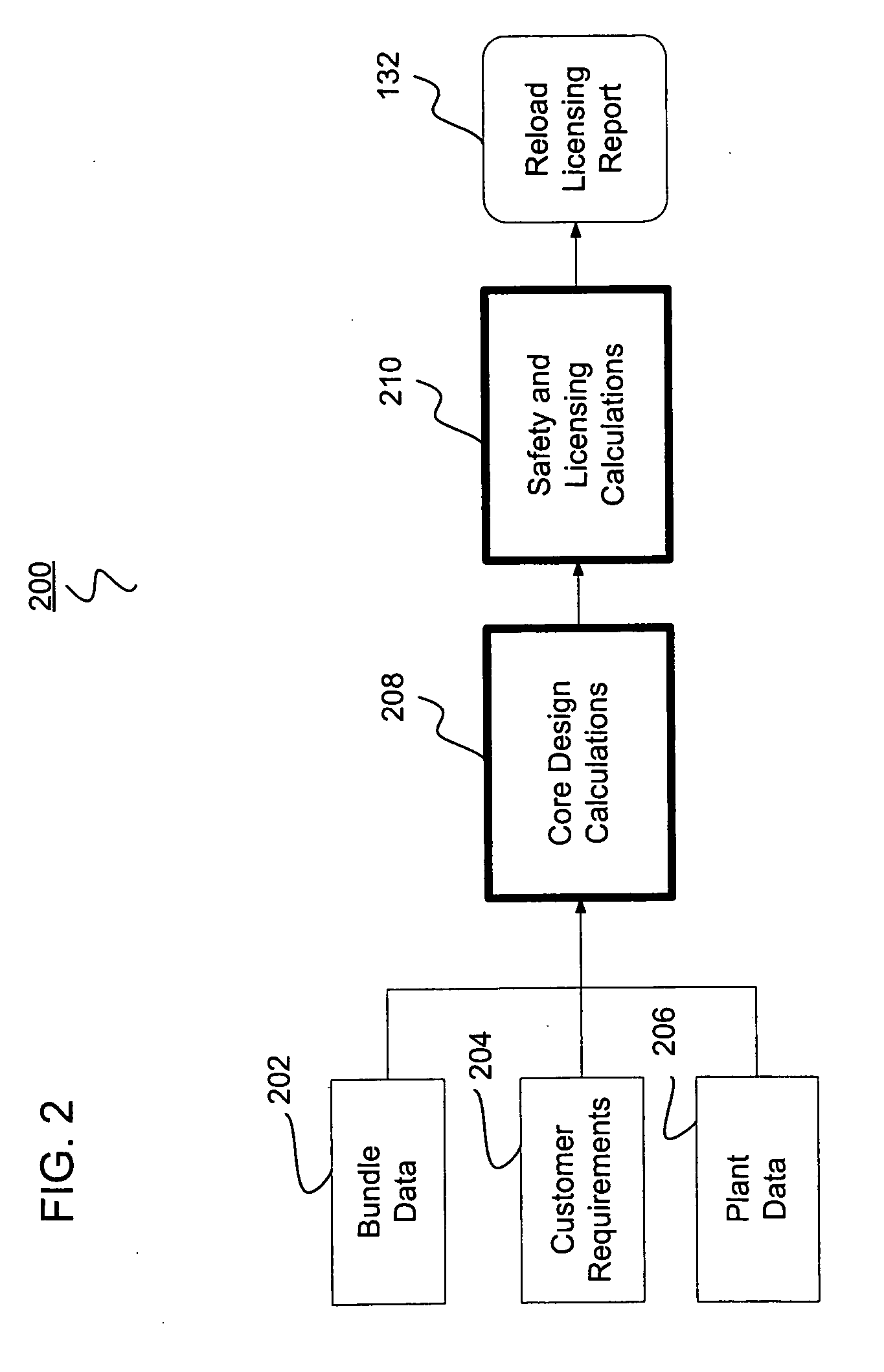
Nuclear reactor reload licensing analysis system and method
ActiveUS20060149515A1Shorten the timeReduction in resourceNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactorData profiling
A system and computer implemented method for automatically performing reload licensing analysis of a nuclear reactor and preparing and generating a reload licensing report. The system and method include collecting input data and processing a plurality of nuclear reactor analysis modules. Each of the nuclear reactor analysis modules receives analysis module input data and generates analysis output data. The analysis module input data is based at least in part on the collected input data. The method also includes verifying at least one analysis output data from one nuclear reactor analysis module by comparing the analysis output data to predetermined analysis output data for the one nuclear reactor analysis module. The method further includes generating a reload licensing report for the nuclear reactor as a function of the analysis output data from two or more nuclear reactor analysis modules.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
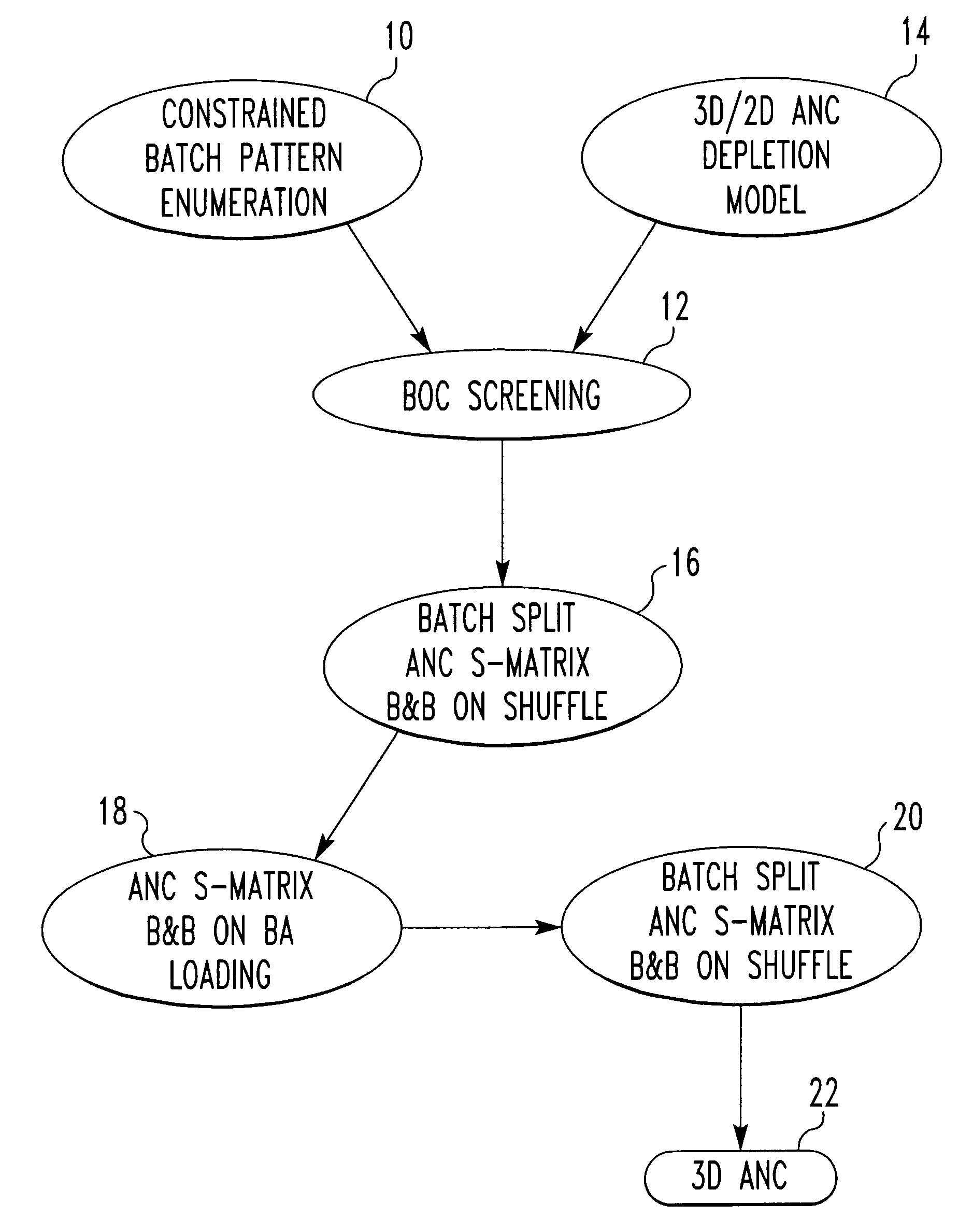
Method of establishing a nuclear reactor core fuel assembly loading pattern
ActiveUS6931090B2Satisfies requirementBetter meetingCosmonautic condition simulationsAnimal housingNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
All possible loading patterns for a nuclear reactor core are searched and optimized for compliance with design constraints. The fuel inventory is divided into a few batches according to coarse levels of reactivity. A recursive enumeration process identifies patterns meeting selected core position constraints, which can be user modified to adjust the search space size. For the batch loading patterns satisfying the constraints, the batches are divided into several smaller batches. A sensitivity matrix linearizing the relationship between fuel assembly position and the depletion model is processed through mixed integer linear programming with branching and bounding to identify an optimal daughter loading pattern. The process is repeated through several levels of batch refinement and selection of optimal daughter patterns, including a level where burnable absorbers are assigned to feed assemblies, until the individual fuel assembly level is reached. The multiple optimal patterns remaining provide a range of solutions.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
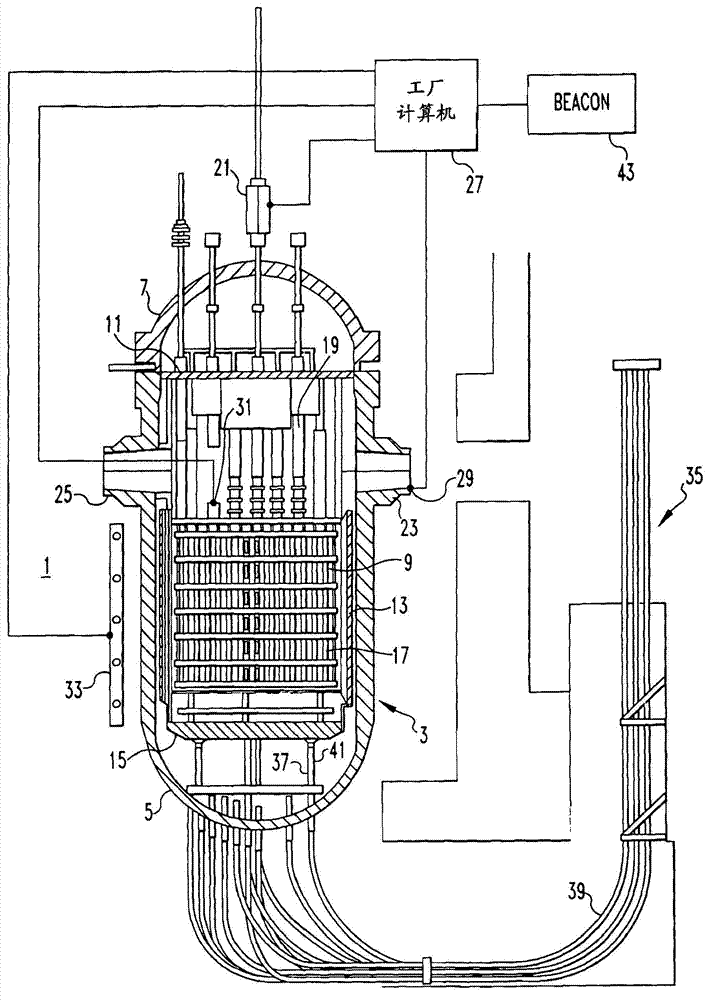
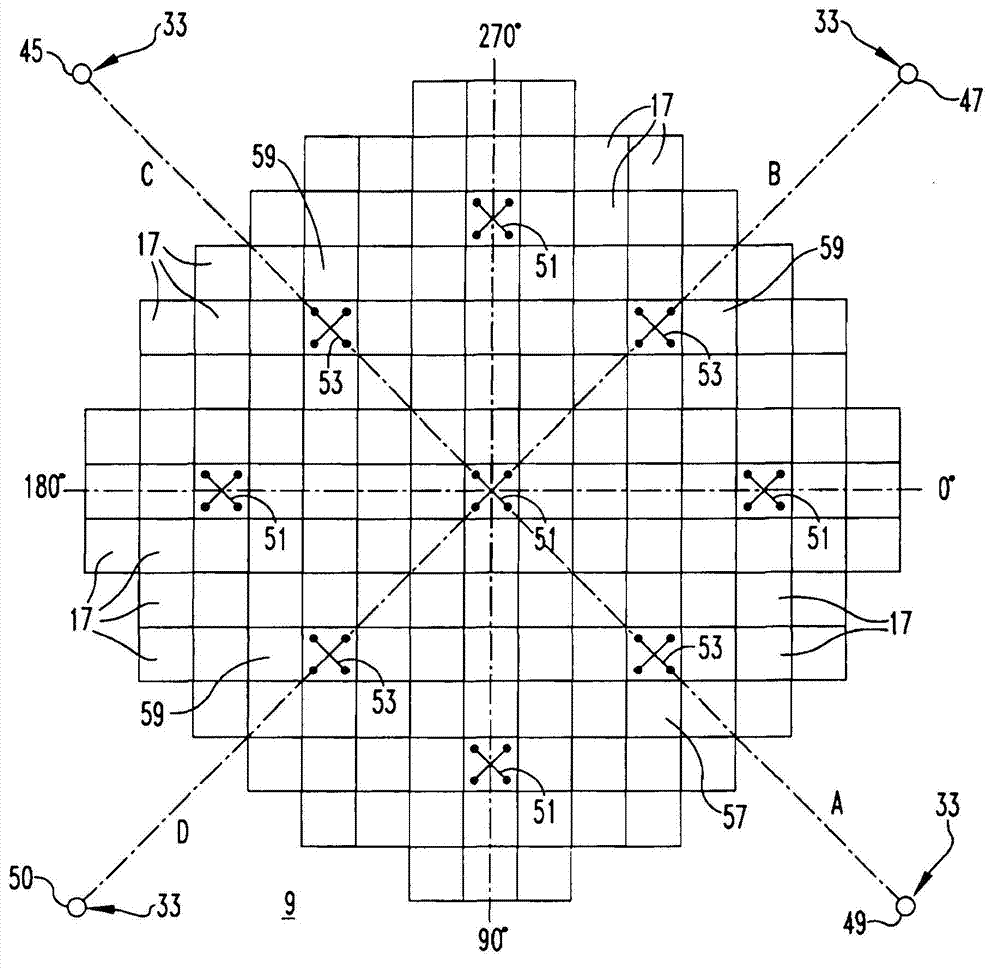
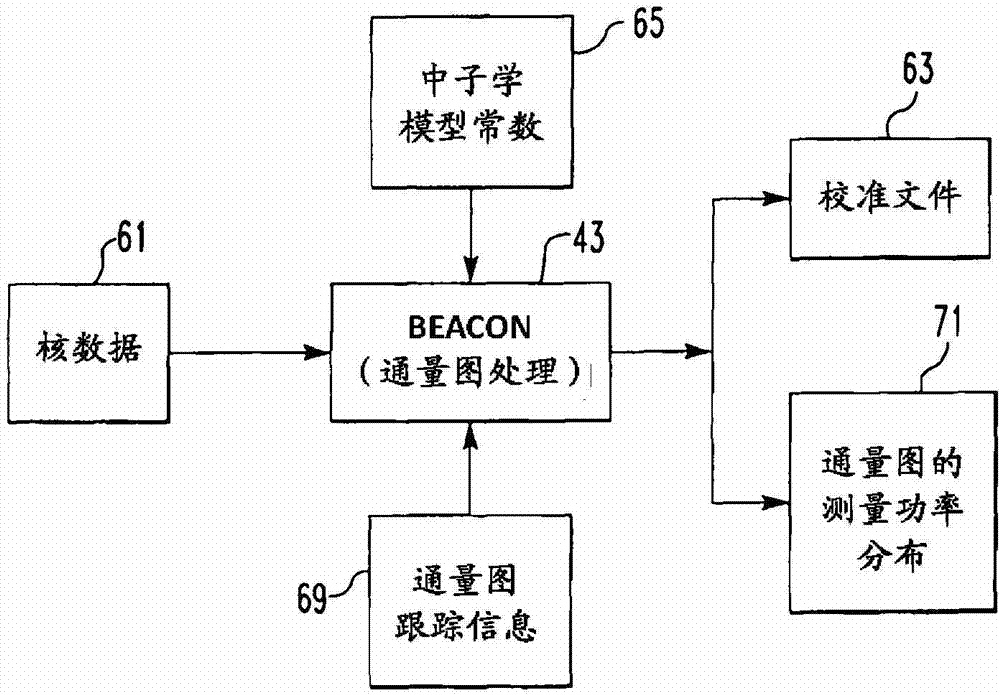
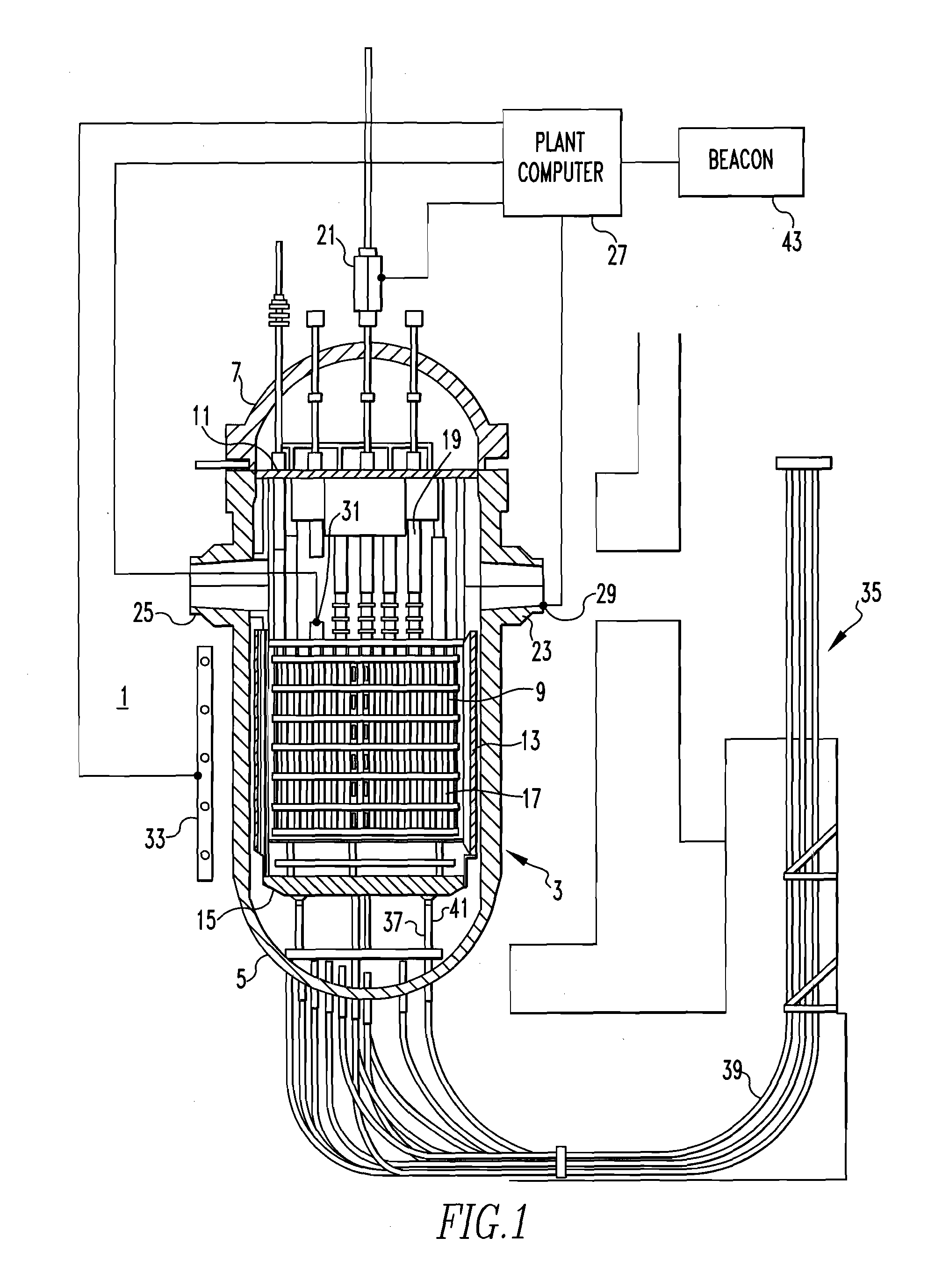
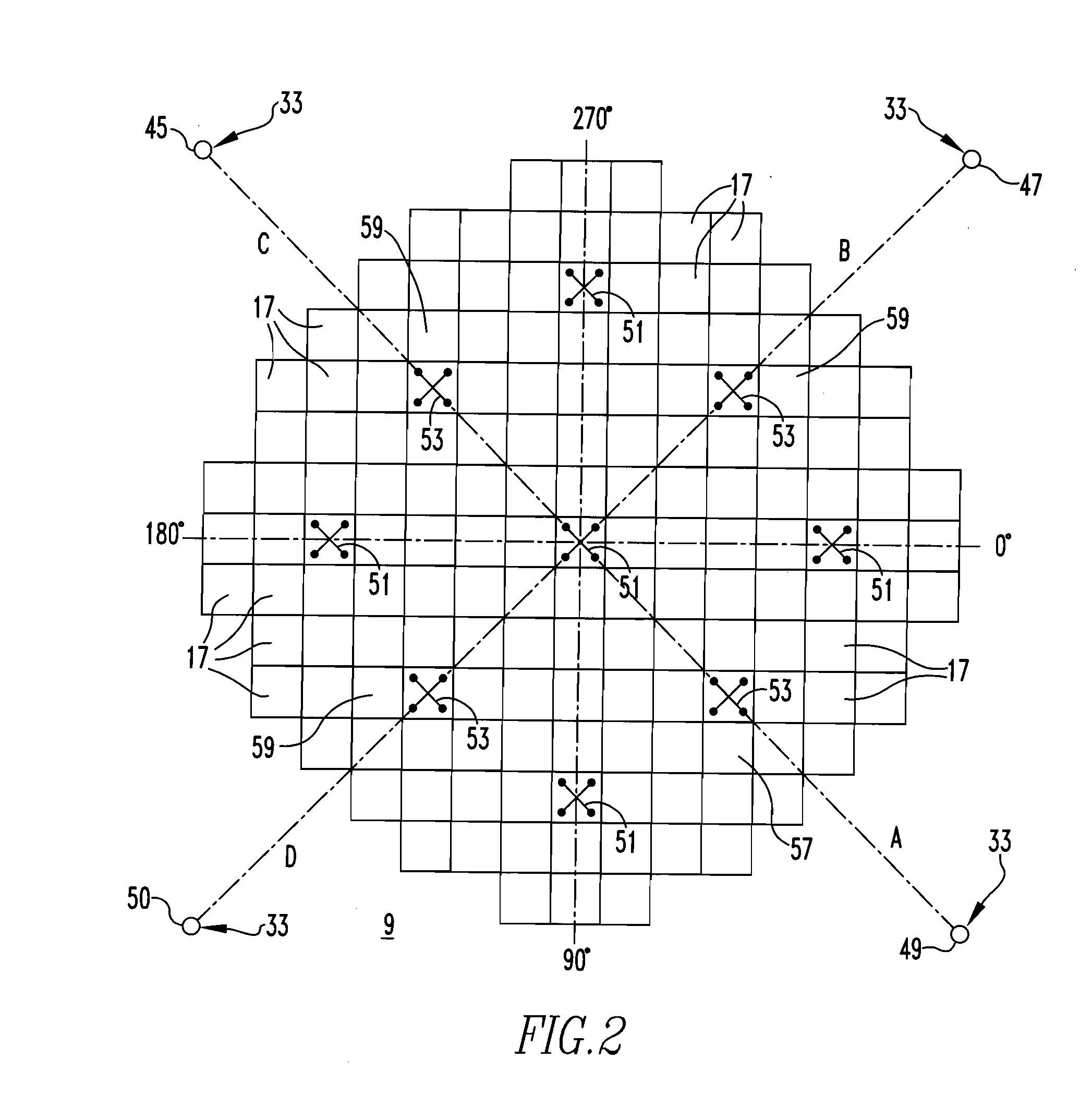
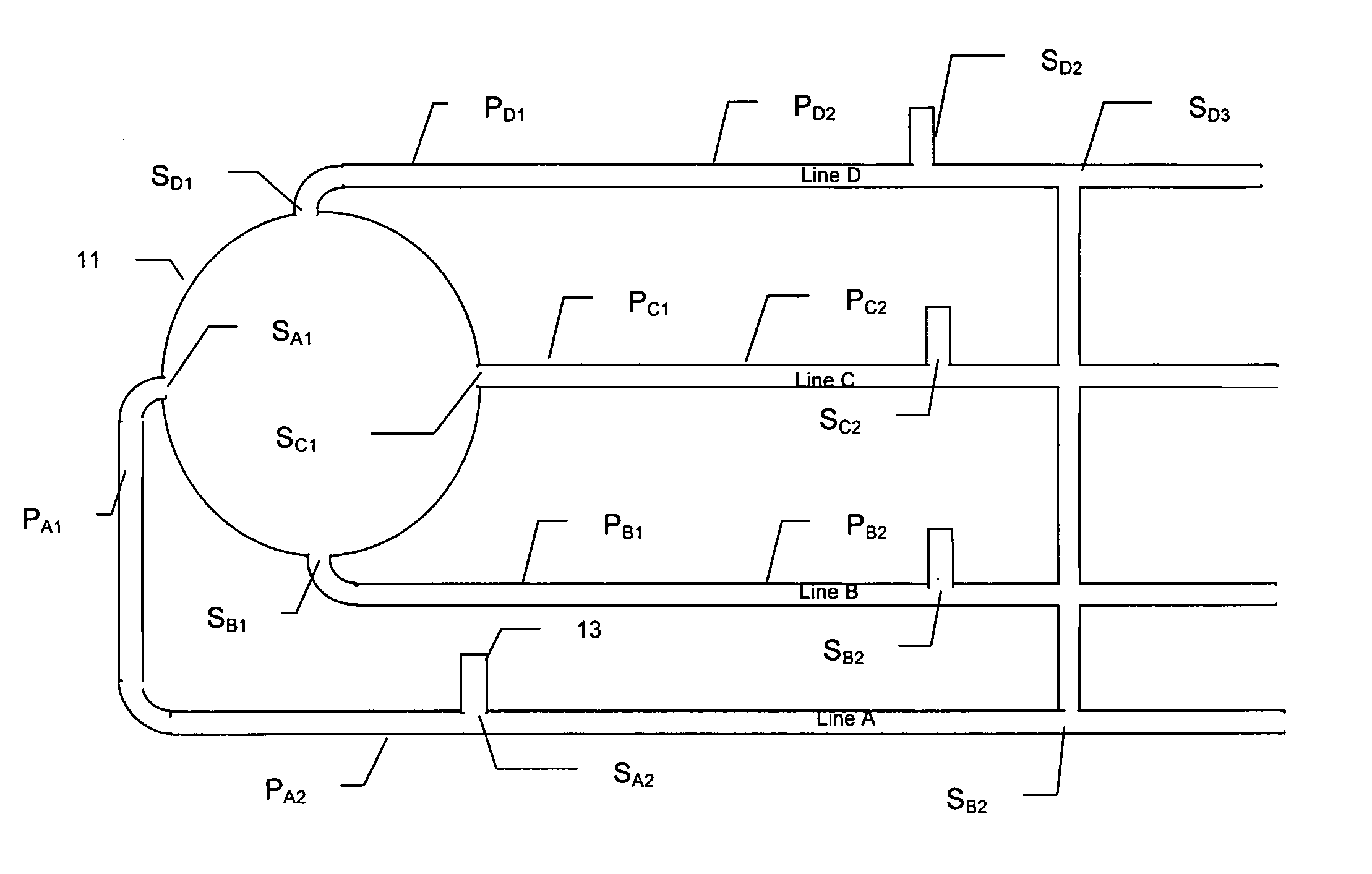
Method of calibrating excore detectors in a nuclear reactor
A method of calibrating excore detectors for a pressurized water reactor (PWR) (1) includes: measuring peripheral core flux signals using excore detectors (33) disposed at a plurality of locations spaced about the periphery of the core (9), and using the measured power distribution from either a core monitoring system (43) or in-core flux measurement (69). Calibration of the excore detectors (33) is broken into two parts: (1) the relation between the excore detector signal and weighted peripheral assembly axial offset, and (2) the relation between weighted peripheral assembly axial offset and core average axial offset. Relation (2) can be determined by a representative neutronics model. Accuracy of the neutronics solution is improved by applying (83) nodal calibration factors, which represent the ratio of the measured three-dimensional power distribution (75) to the nodal predicted three- dimensional power distribution and correct the neutronic results to match what would be measured if predictive scenarios were actually performed in the actual reactor core (9).
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
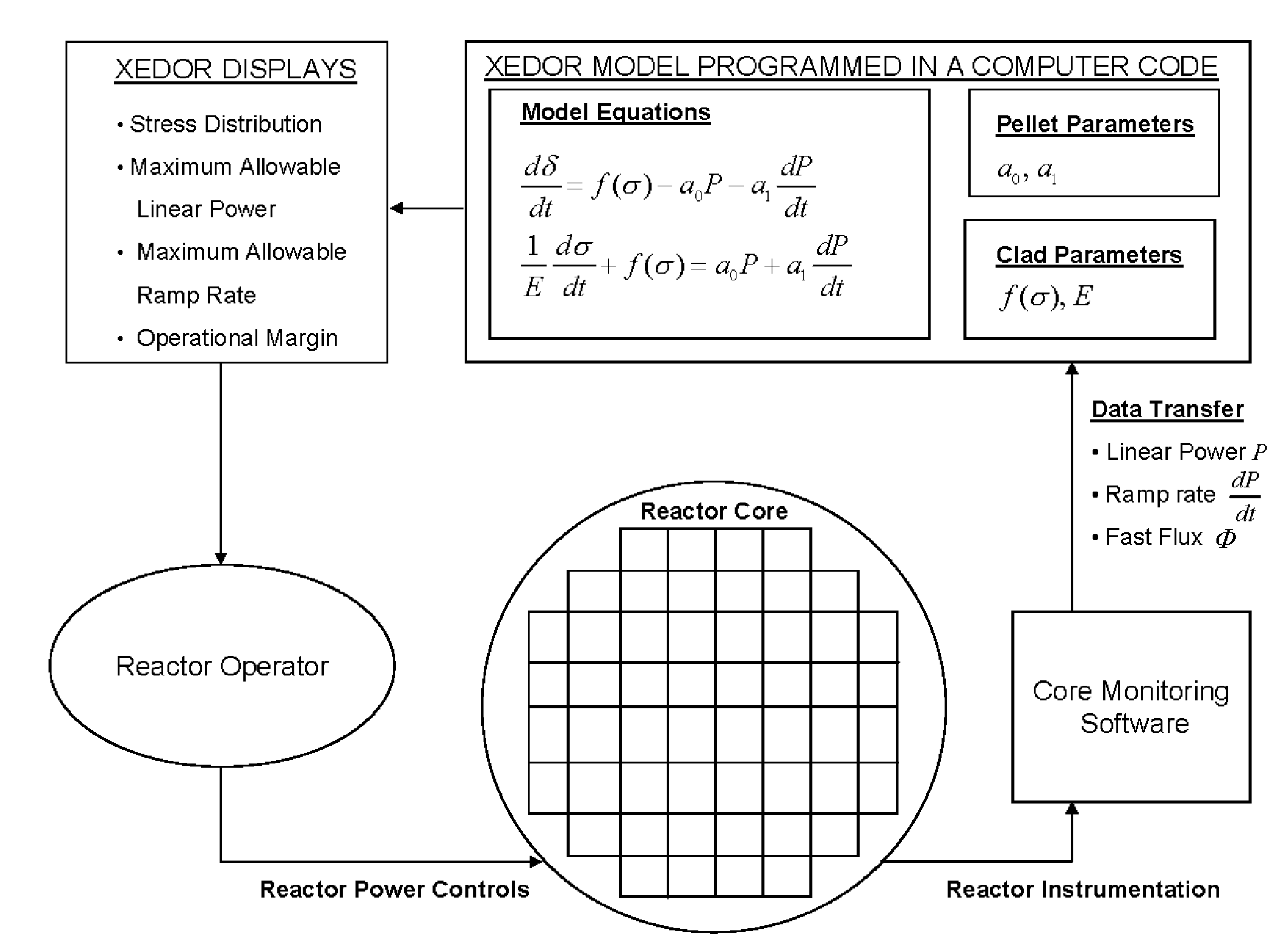
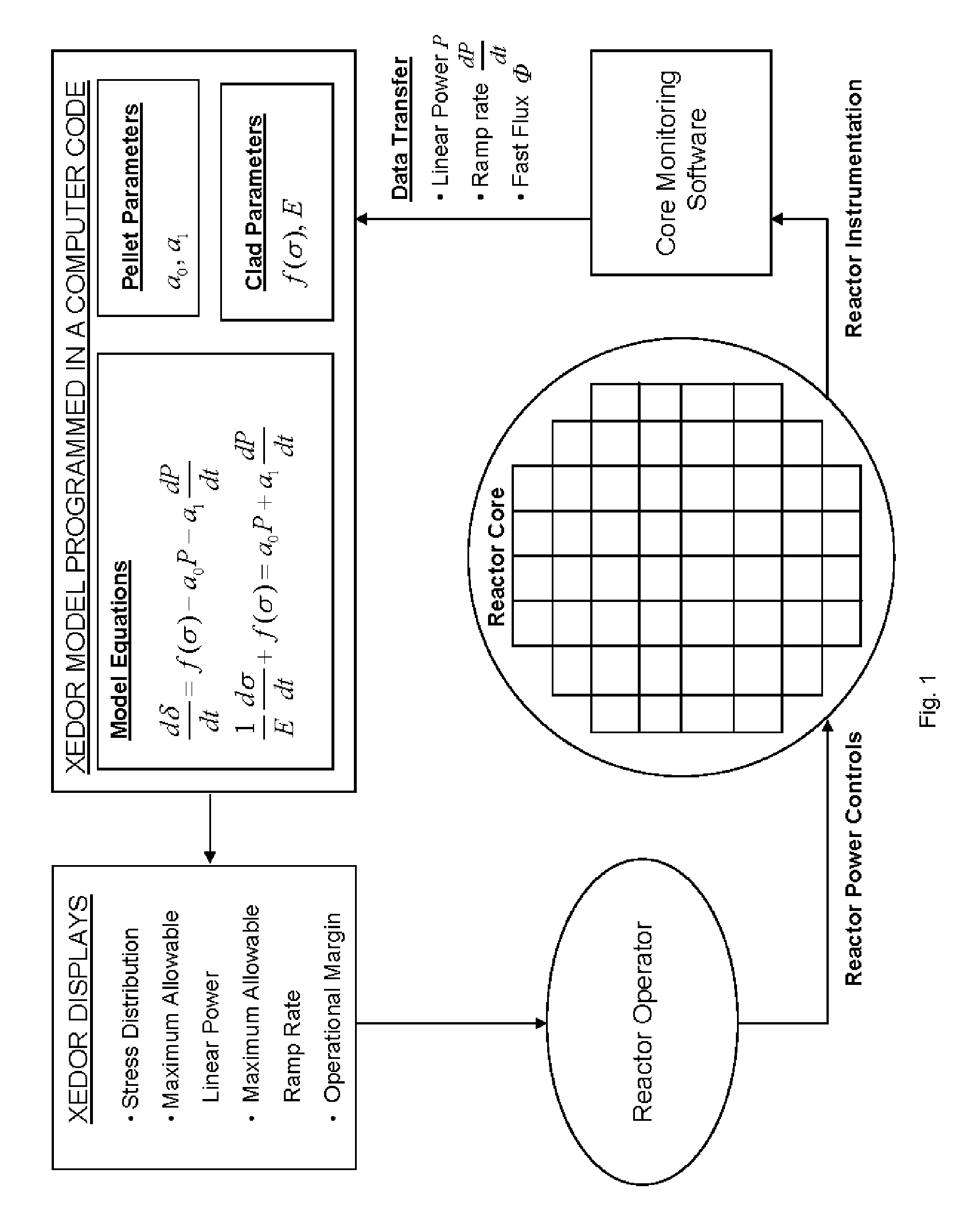
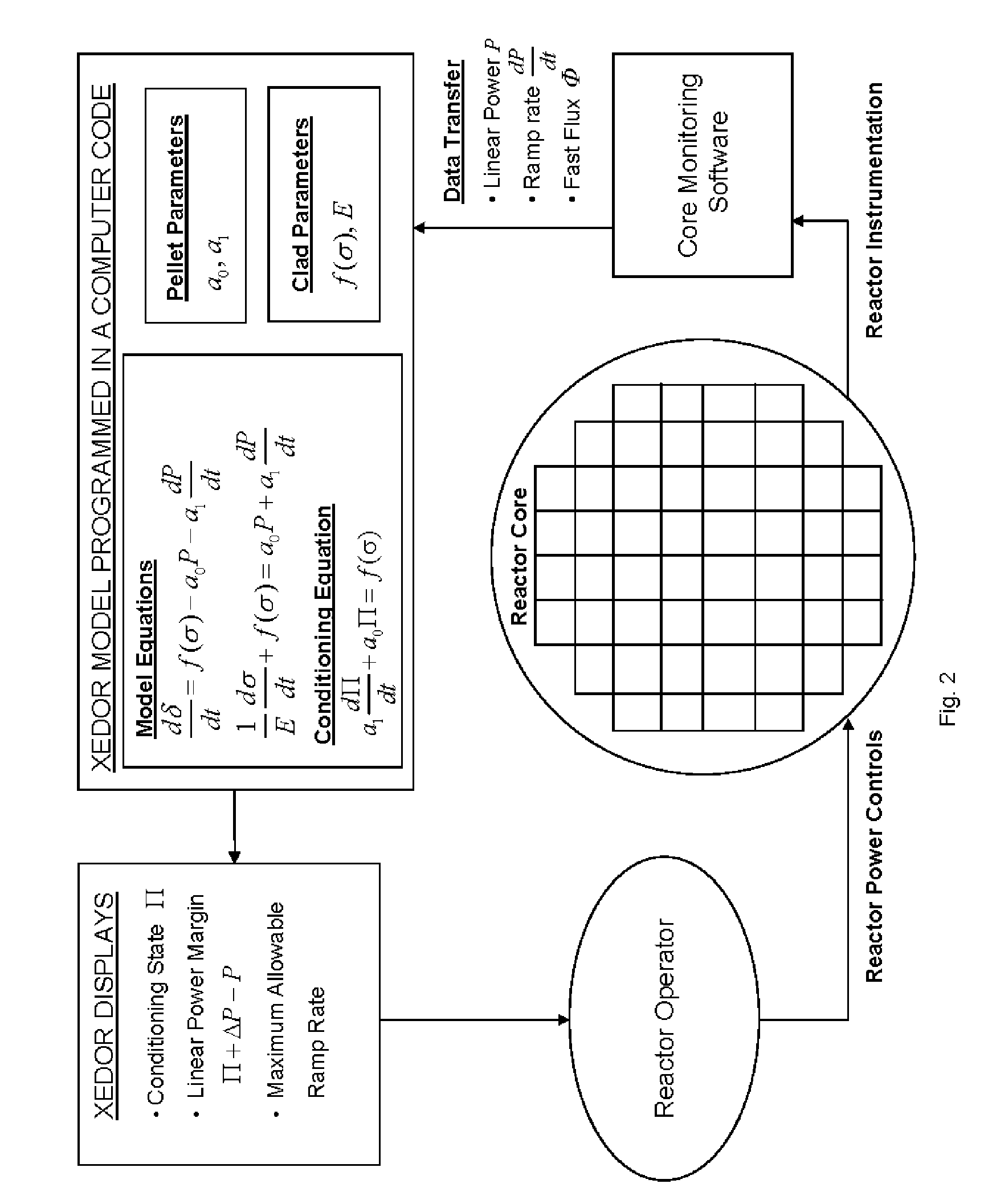
Reduced Order Stress Model for Online Maneuvering, Diagnostics of Fuel Failure and Design of Core Loading Patterns of Light Water Reactors
ActiveUS20090080585A1Nuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringStress corrosion crackingReduced order
The invention is principally directed to a reduced order model, XEDOR, facilitating the prediction of and the diagnostics of pellet-clad interaction stress-corrosion-cracking failure of nuclear fuel rods. The invention more particularly relates to assessment of susceptibility to PCI failure for guidance in the design of fuel loading in nuclear reactors. The invention additionally relates to the protection against PCI failure by providing operational information to operators of a nuclear reactor during power maneuvering, including predictive calculations prior to executing power maneuvers. Additionally, the invention relates to the diagnostics of an event suggesting a possible PCI cladding failure.
Owner:AREVA NP SAS
Robust distance measures for on-line monitoring
ActiveUS20080183425A1Improved kernel-based model performanceRobust distance metricNuclear energy generationSimulator controlComputer scienceDistance measurement
An apparatus and associated method are utilized for monitoring an operation of a system characterized by operational parameters. A non-parametric empirical model generates estimates of parameter values in response to receiving a query vector of monitored parameters for a model characterizing the system. A distance estimation engine (a) determines robust distances between the query vector and each of a set of predetermined historical vectors for the non-parametric empirical model based on an implementation of an elemental kernel function; (b) determines weights for the monitored parameters based on the robust distances; and (c) combining the weights with the predetermined historical vectors to make predictions for the system.
Owner:SMARTSIGNAL CORP
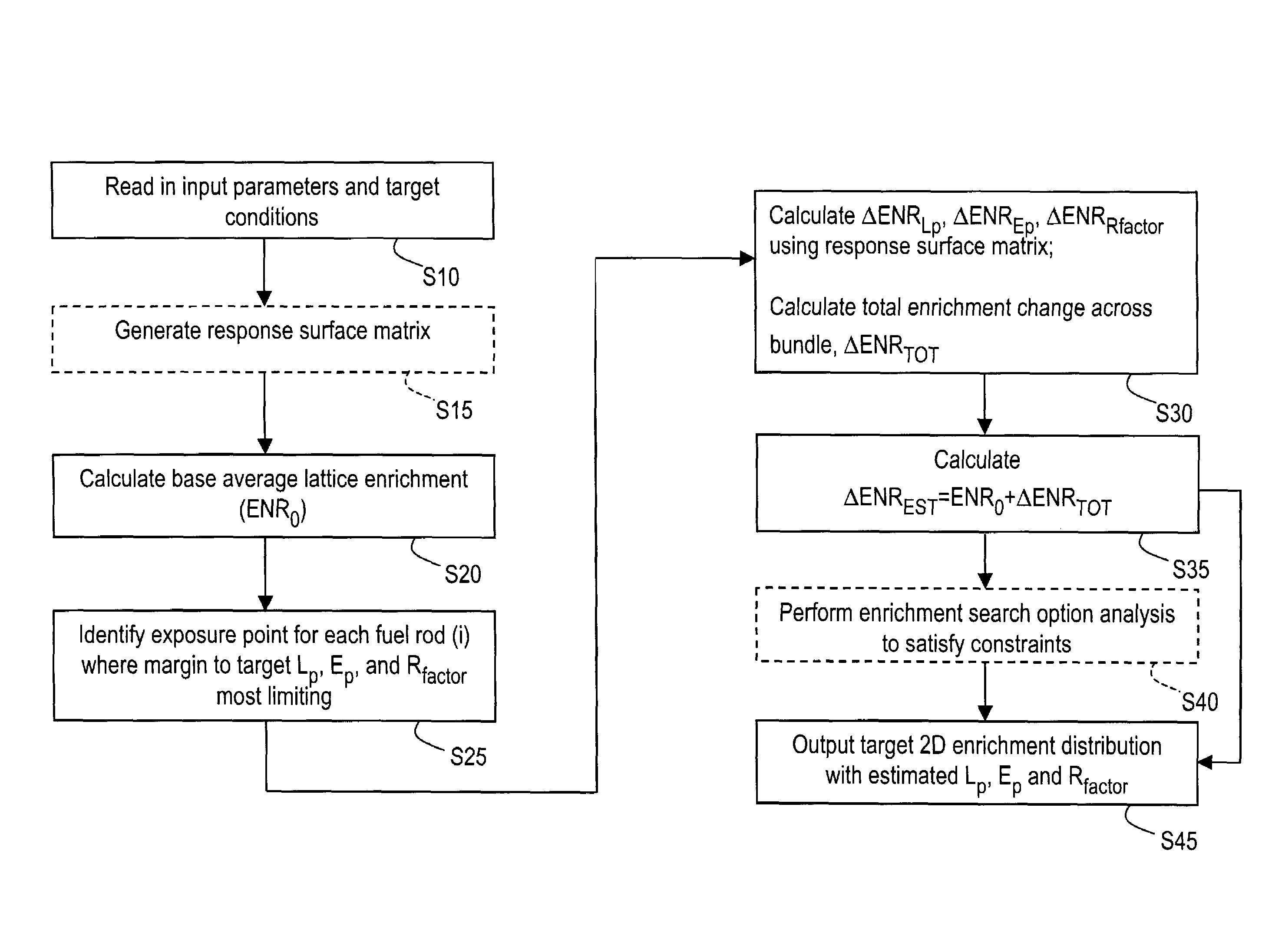
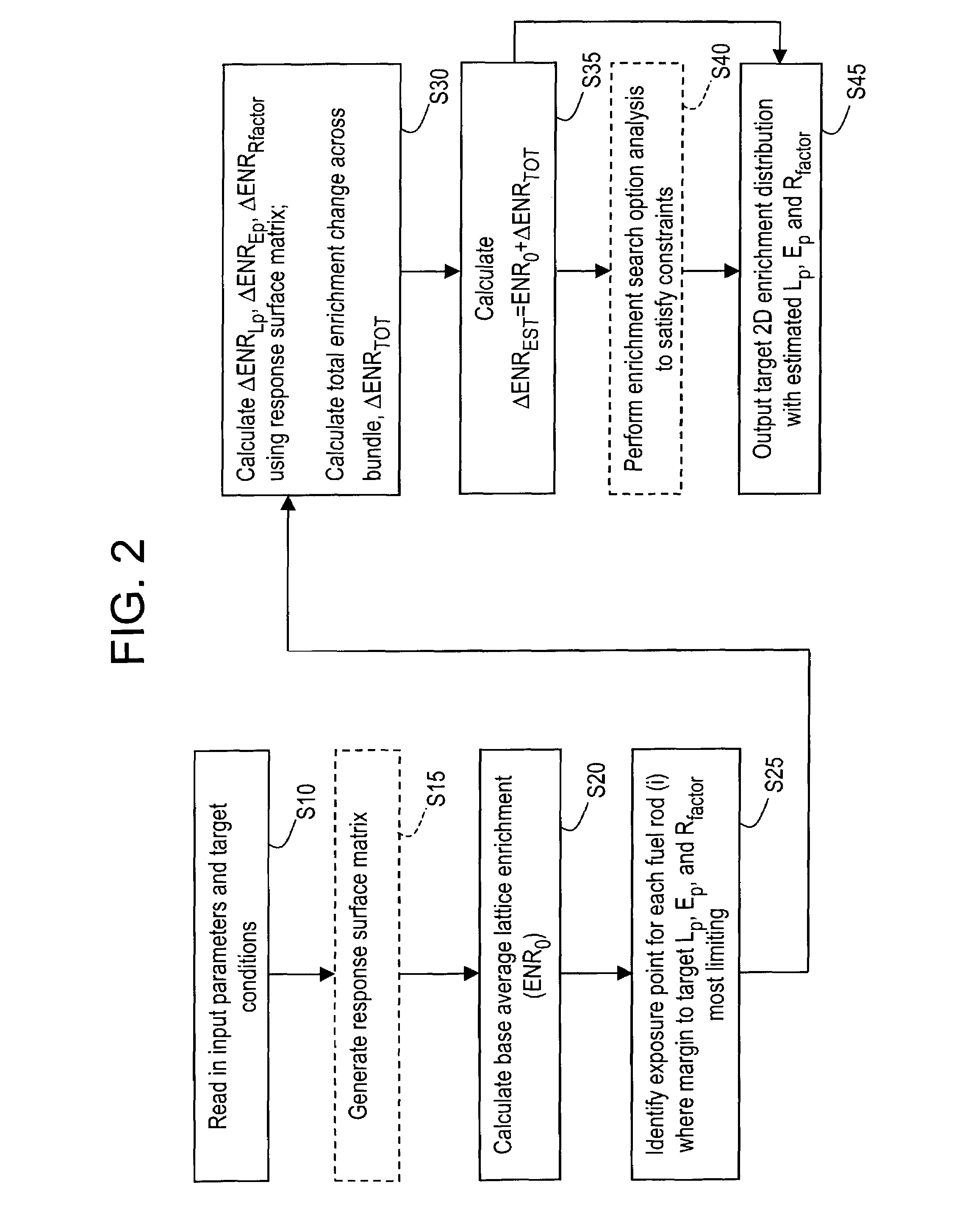
Method and arrangement for determining pin enrichments in fuel bundle of nuclear reactor
A method and arrangement of determining pin enrichments for a fuel bundle of a nuclear reactor, where a plurality of input parameters and target conditions may be input and enrichment changes, to be made across the fuel bundle, may be calculated using response matrix technology. Fuel bundle pin enrichment data may be output that satisfies the target conditions. The method and arrangement may enable production of fuel bundles having a desired local peaking, exposure peaking and R-factor performance. Consequently, given fuel cycles typically may be loaded and operated such that less fuel may be needed for identical cycle lengths, potentially resulting in improved fuel cycle economics. Additionally, because fuel bundle development may require fewer iterations, there may be a substantial cycle time reduction in the bundle design process, potentially reducing cost and enhancing profitability.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
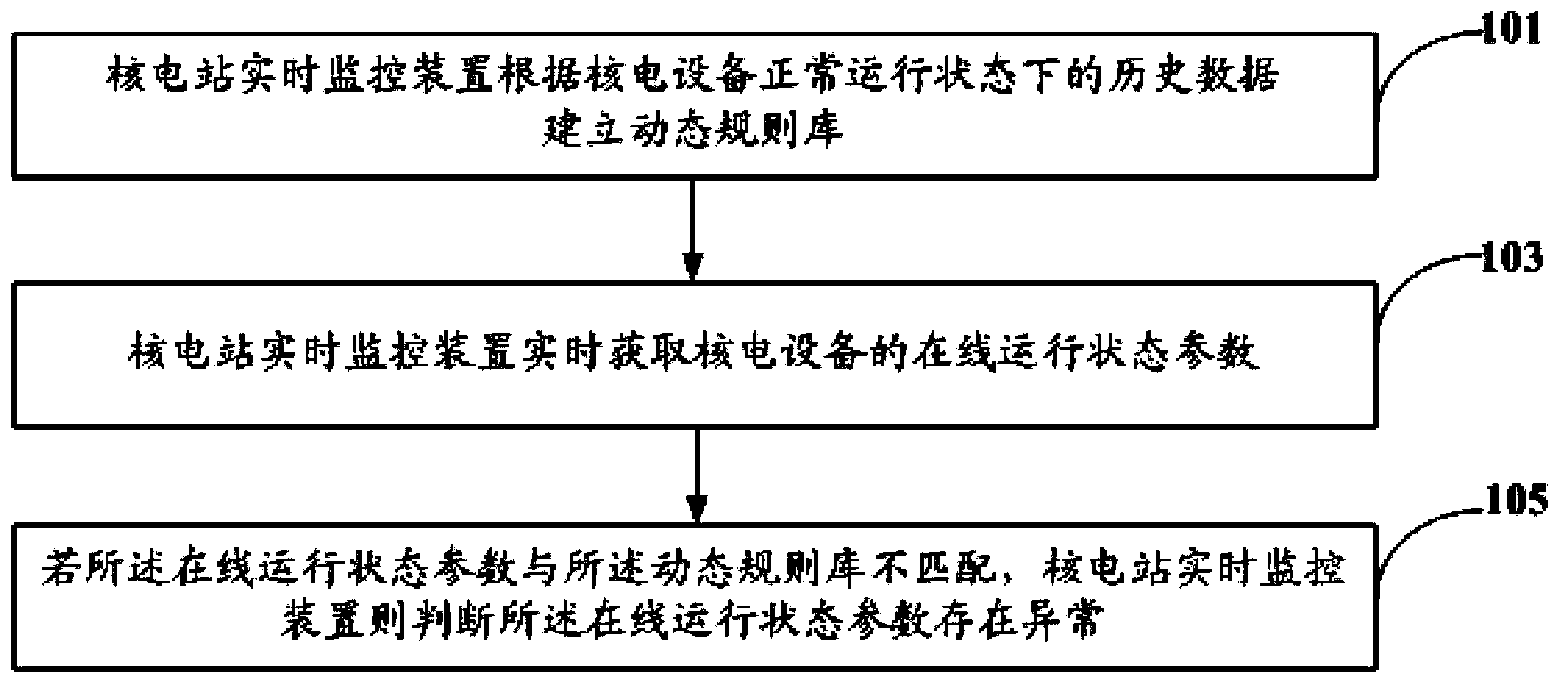
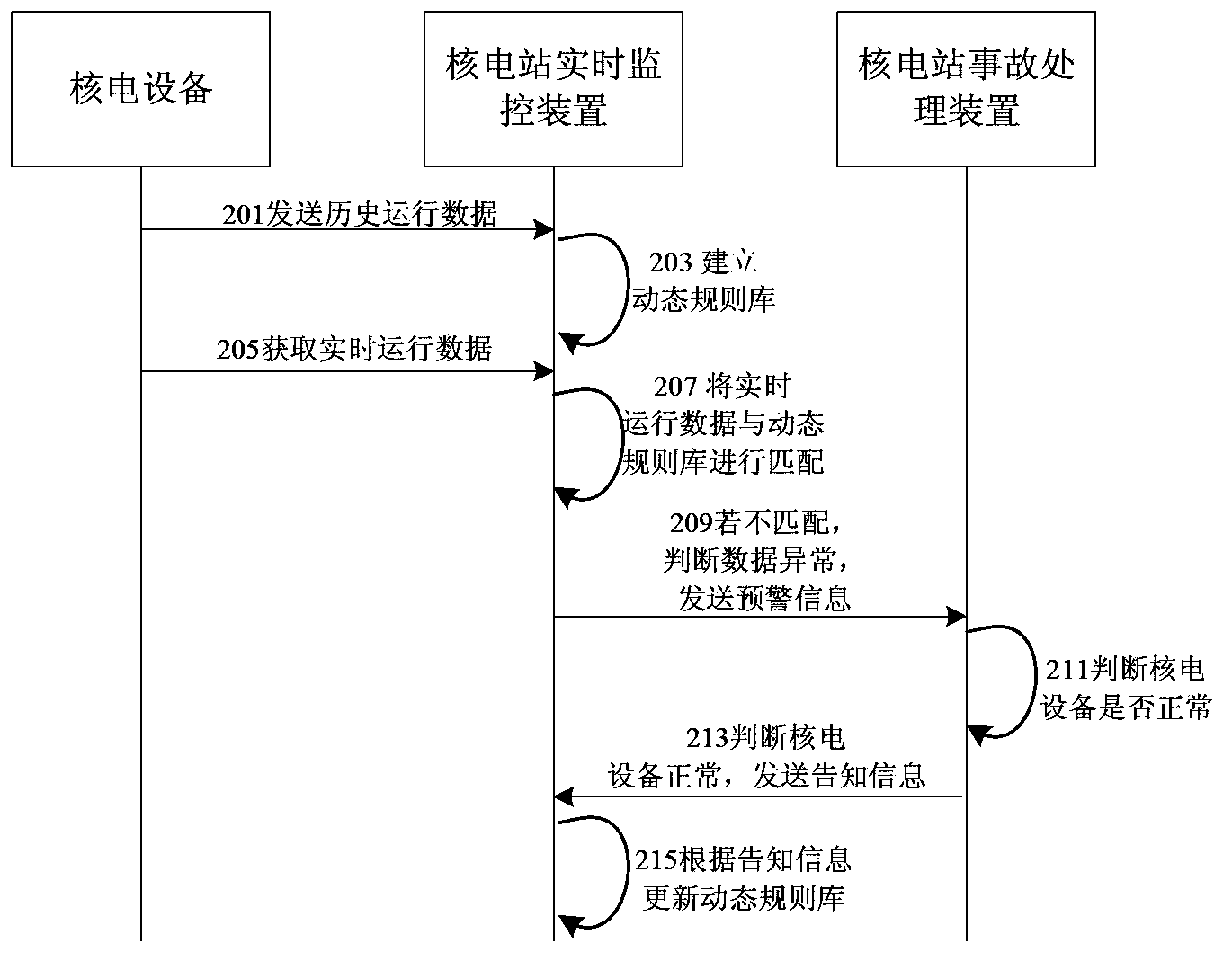
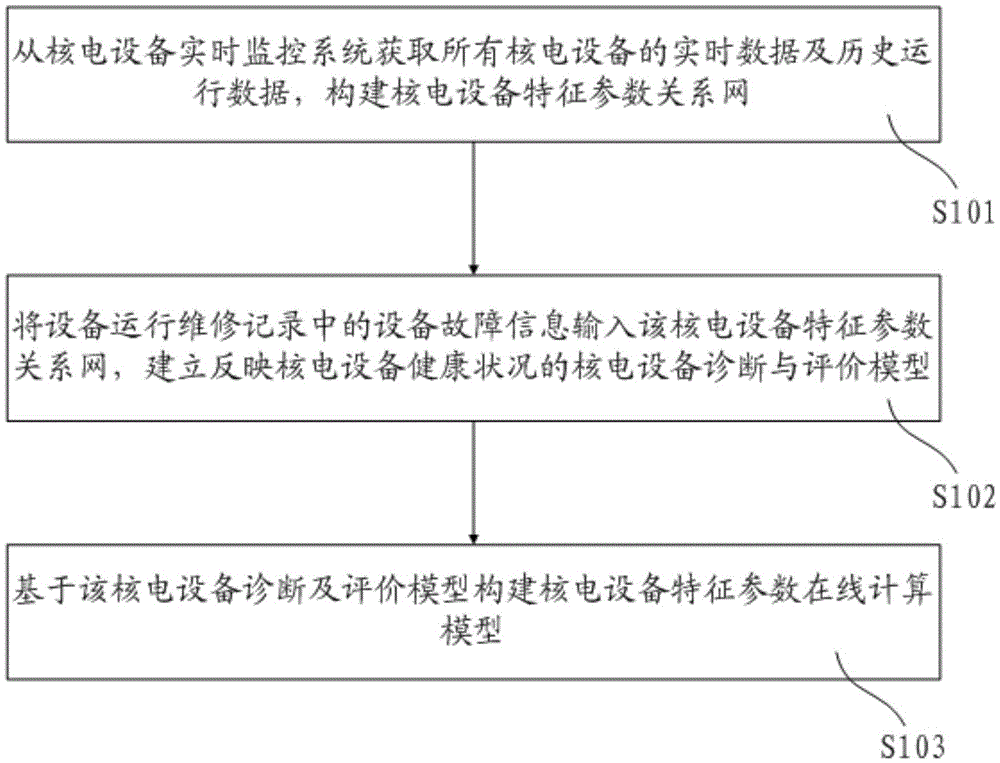
Method, device and system for monitoring running state of nuclear power plant
ActiveCN104299659AThe problem of realizing effective judgment in real timeAvoid false alarmsPower plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationNon real timeNuclear power
A method for monitoring running status of a nuclear power plant comprises: a nuclear power plant real-time monitoring apparatus establishing a dynamic rule base according to historical data of nuclear power equipment in normal running status; the nuclear power plant real-time monitoring apparatus acquiring, in real time, an online running status parameter of the nuclear power equipment; and if the online running status parameter does not match the dynamic rule base, the nuclear power plant real-time monitoring apparatus determining that the online running status parameter is abnormal. In the method for monitoring running status of a nuclear power plant, non-real-time running data and real-time running data of a nuclear power plant system are input in a simulation model to perform a simulation test, thereby implementing effective real-time monitoring on running of equipment of the nuclear power plant. Moreover, further disclosed are an apparatus and a system for monitoring running status of a nuclear power plant.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +2
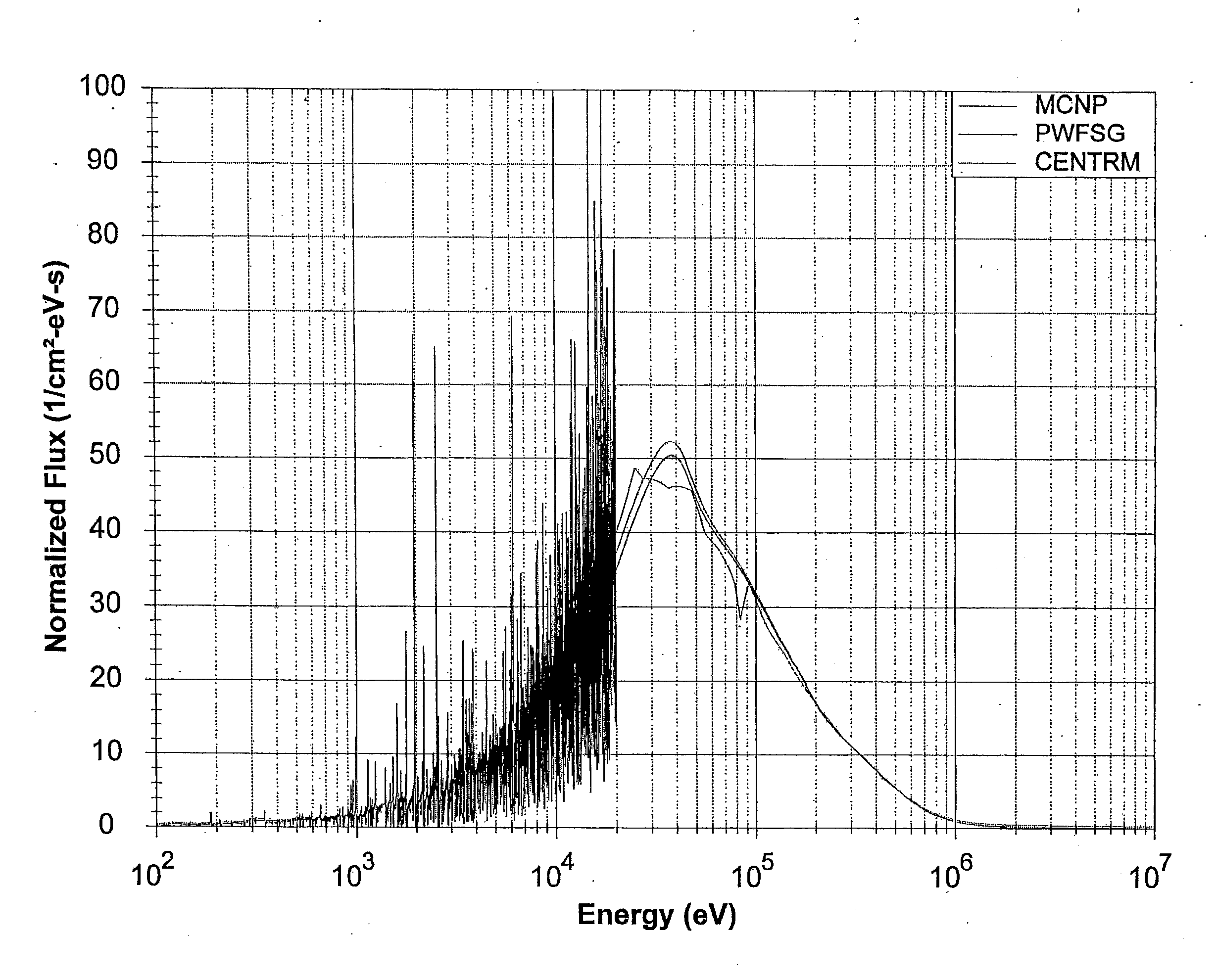
Methods, systems, and computer program products for generating fast neutron spectra
ActiveUS20130166223A1Nuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringTelecommunications linkCommunication link
Methods implemented by at least one electronic processor for generating pointwise fast neutron spectra may include receiving composition data; receiving source data or calculating the source data; receiving nuclear data; and calculating the pointwise fast neutron spectrum based on numerical integration using the composition, source, and nuclear data. Systems for generating pointwise fast neutron spectra may include a bus; at least one electronic processor connected to the bus; an input device connected to the bus; and a communication link connected to the bus. The at least one electronic processor may be configured to receive composition data from the input device via the bus, to receive source data from the input device via the bus or to calculate the source data, to receive nuclear data from the communication link via the bus, and to calculate the pointwise fast neutron spectrum based on numerical integration using the composition, source, and nuclear data.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
Method and apparatus for evaluating robustness of proposed solution to constraint problem and considering robustness in developing a constraint problem solution
ActiveUS7461038B2Nuclear energy generationAnalogue computers for electric apparatusGraphicsGraphical user interface
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
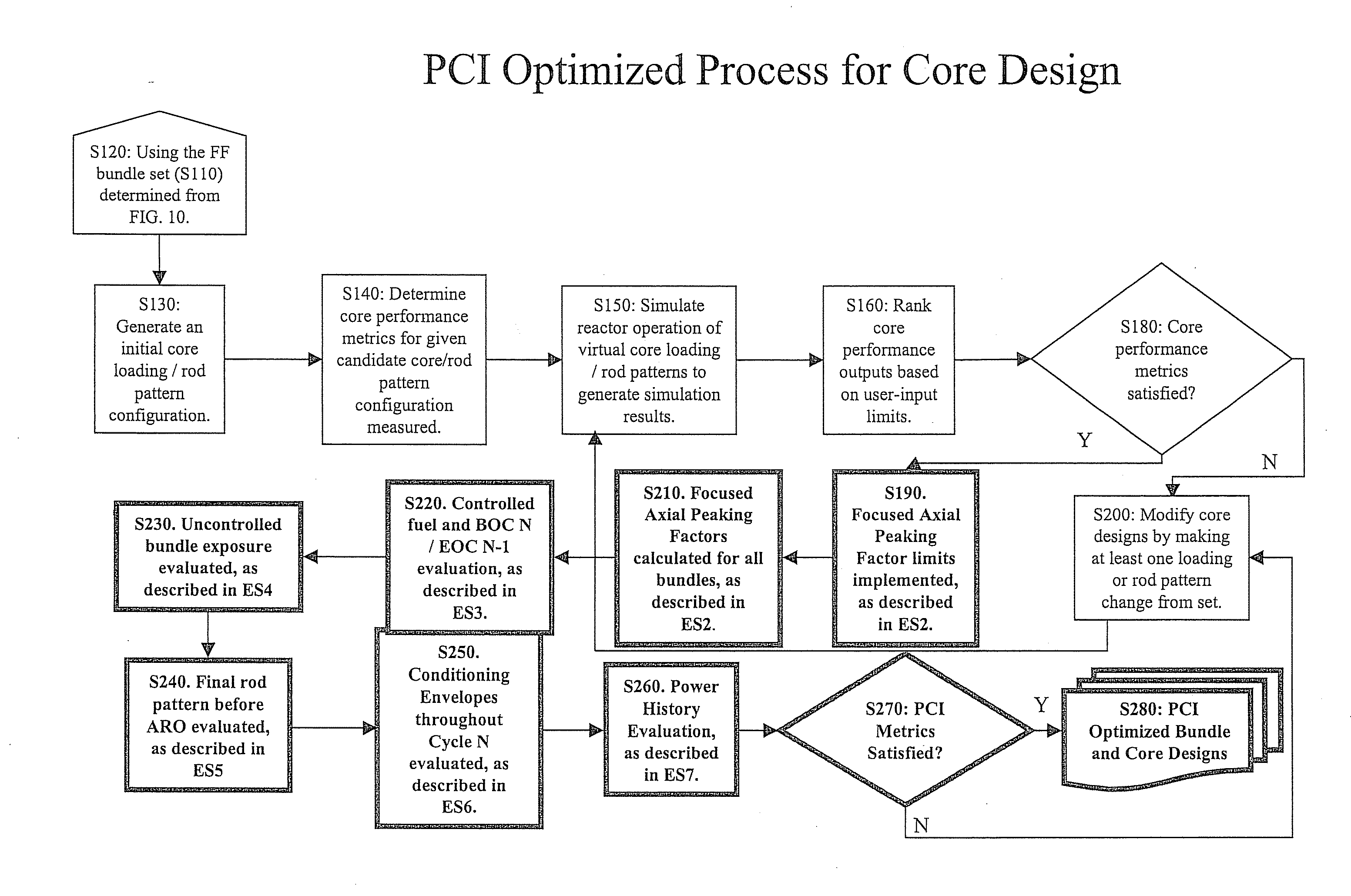
Method for pellet cladding interaction (PCI) evaluation and mitigation during bundle and core design process and operation
InactiveUS20110246153A1More reliabilityMaximize plant performanceNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactorNuclear power plant
Example embodiments are directed to a method of fuel bundle design, core design, or combined fuel and core design, to ensure Pellet Cladding Interaction (PCI) related fuel failures are mitigated. More specifically, example embodiments provide fuel and / or core designs that may be determined prior to operation of a nuclear power plant, or prior to production of fresh fuel bundles. The PCI optimized fuel / core designs may include some or all of seven PCI Evaluation Methods which may be incorporated into existing nuclear reactor simulation programs. PCI optimized fuel and / or core design enhances fuel reliability, allows faster beginning-of-cycle (BOC) startups and faster middle-of-cycle (MOC) sequence exchanges to maximize plant performance, and minimizes ramping restrictions, thereby maximizing nuclear power plant performance.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
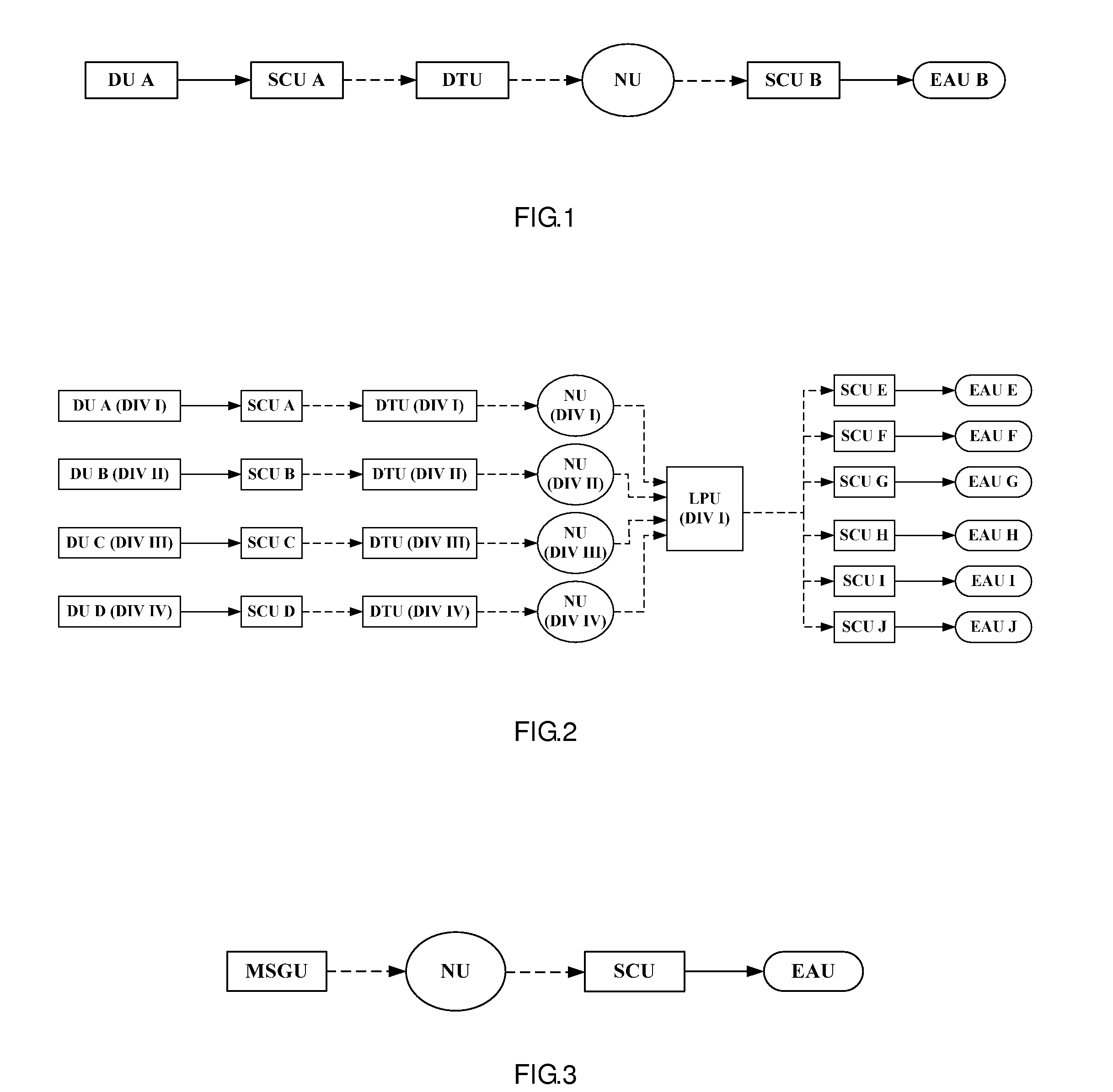
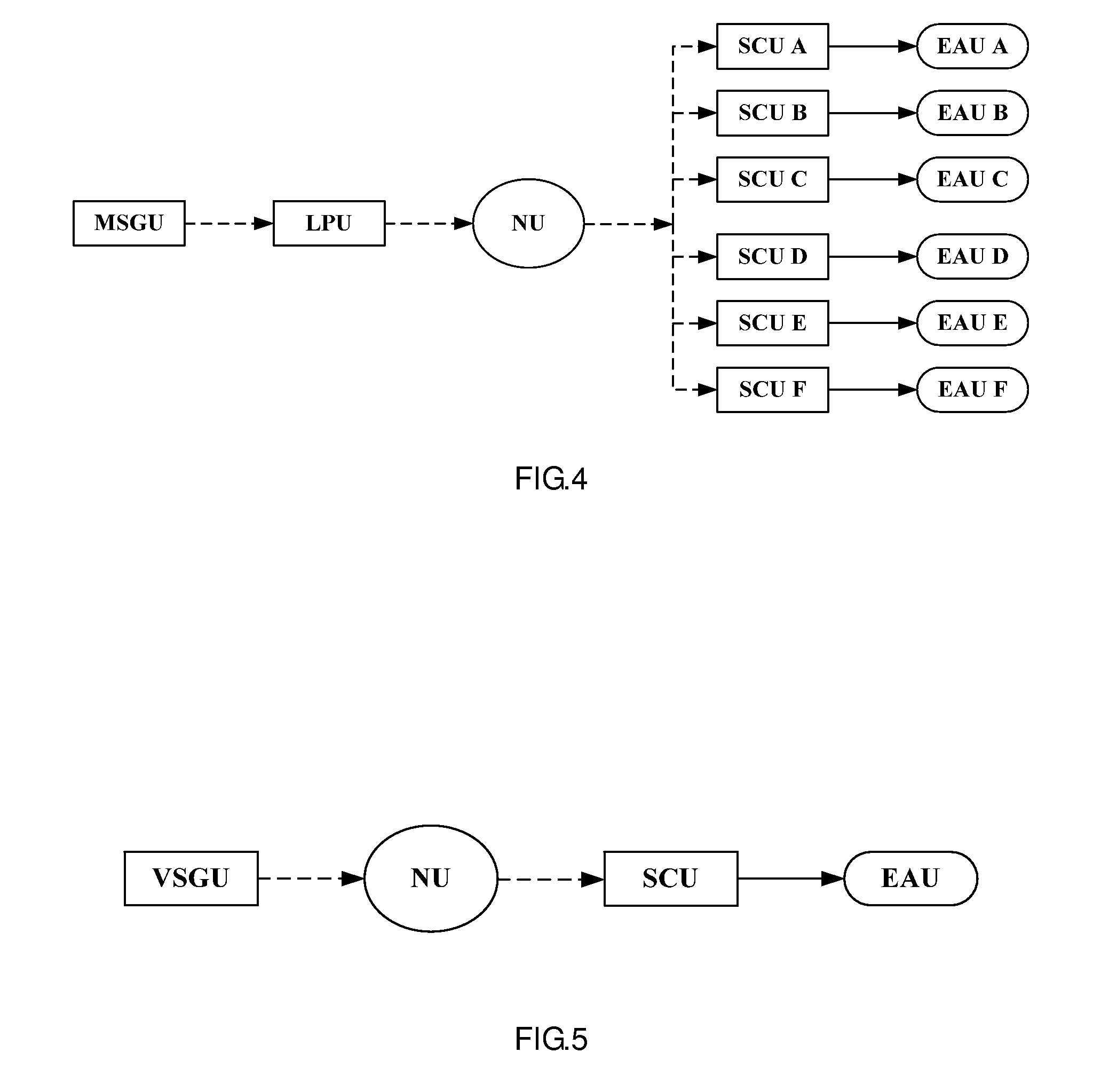
Method, arrangement and computer program for determining standardized rod types for nuclear reactors
ActiveUS20040243370A1Fuel element assembliesAnalogue computers for electric apparatusNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A method, arrangement and computer program is described for determining a set of standardized rod types for use in a nuclear reactor core. The method may include defining a set of rod type-related limits, and determining, based on the limits, an initial population of rod types to be evaluated for use in cores of a selected number of nuclear reactor plants. Based on the initial population of rod types a database of selectable fresh fuel bundle designs applicable to the one or more cores may be generated. Bundle data related to at least a subset of the selectable fresh fuel bundle designs may be retrieved from the database, and a target number of rod types may be selected from the initial population based on the retrieved bundle data as the set of standardized rod types.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
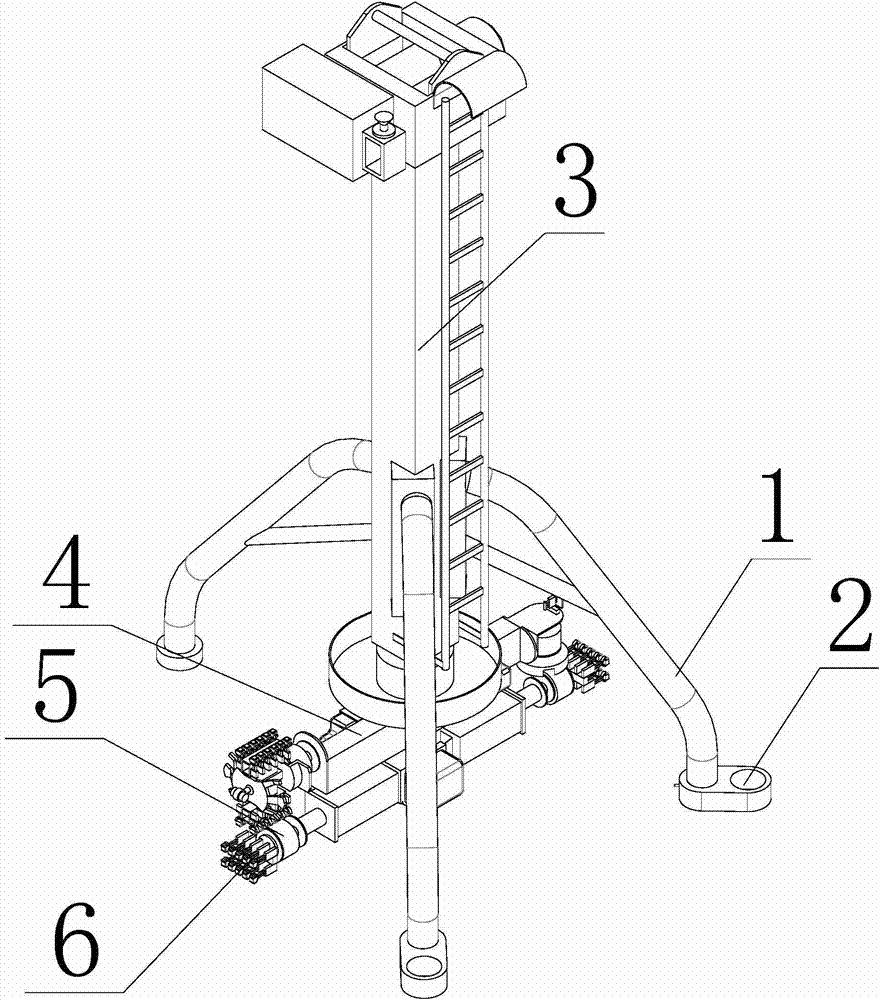
Nondestructive testing robot intelligent testing method based on virtual reality technology
ActiveCN103761996ARealize synchronized motionImprove control efficiencyNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringReactor pressure vesselSimulation
The invention discloses a nondestructive testing robot intelligent testing method based on a virtual reality technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a nondestructive testing robot for nondestructive testing is mounted at a predetermined position in a to-be-tested reactor pressure vessel; (2) freedom degree kinematic axes of the nondestructive testing robot are each restored to an initial state, then the freedom degree kinematic axes are each subjected to position calibration, and a global coordinate system and axis coordinate systems of the freedom degree kinematic axes are constructed; (3) corresponding relationships are established between simulation models and real devices; and (4) the simulation model of the nondestructive testing robot performs position attitude transformation, virtually displays and controls synchronous movement of the nondestructive test robot to perform nondestructive testing in a three-dimensional virtual environment according to real-timely acquired position attitude information feedback values of the freedom degree kinematic axes of the nondestructive testing robot. The method realizes the omni-directional three-dimensional WYSIWYG display control mode, greatly improves the security of on-site project implementation, and improves the project implementation efficiency.
Owner:CGNPC INSPECTION TECH +3
Method of calibrating excore detectors in a nuclear reactor
InactiveUS20110268239A1Improve accuracyImprove excore detector calibrationPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreNODAL
A method of calibrating excore detectors for a pressurized water reactor (PWR) includes: measuring peripheral core flux signals using excore detectors disposed at a plurality of locations spaced about the periphery of the core, and using the measured power distribution from either a core monitoring system or in-core flux measurement. Calibration of the excore detectors is broken into two parts: (1) the relation between the excore detector signal and weighted peripheral assembly axial offset, and (2) the relation between weighted peripheral assembly axial offset and core average axial offset. Relation (2) can be determined by a representative neutronics model. Accuracy of the neutronics solution is improved by applying nodal calibration factors, which represent the ratio of the measured three-dimensional power distribution to the nodal predicted three-dimensional power distribution and correct the neutronic results to match what would be measured if predictive scenarios were actually performed in the actual reactor core.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
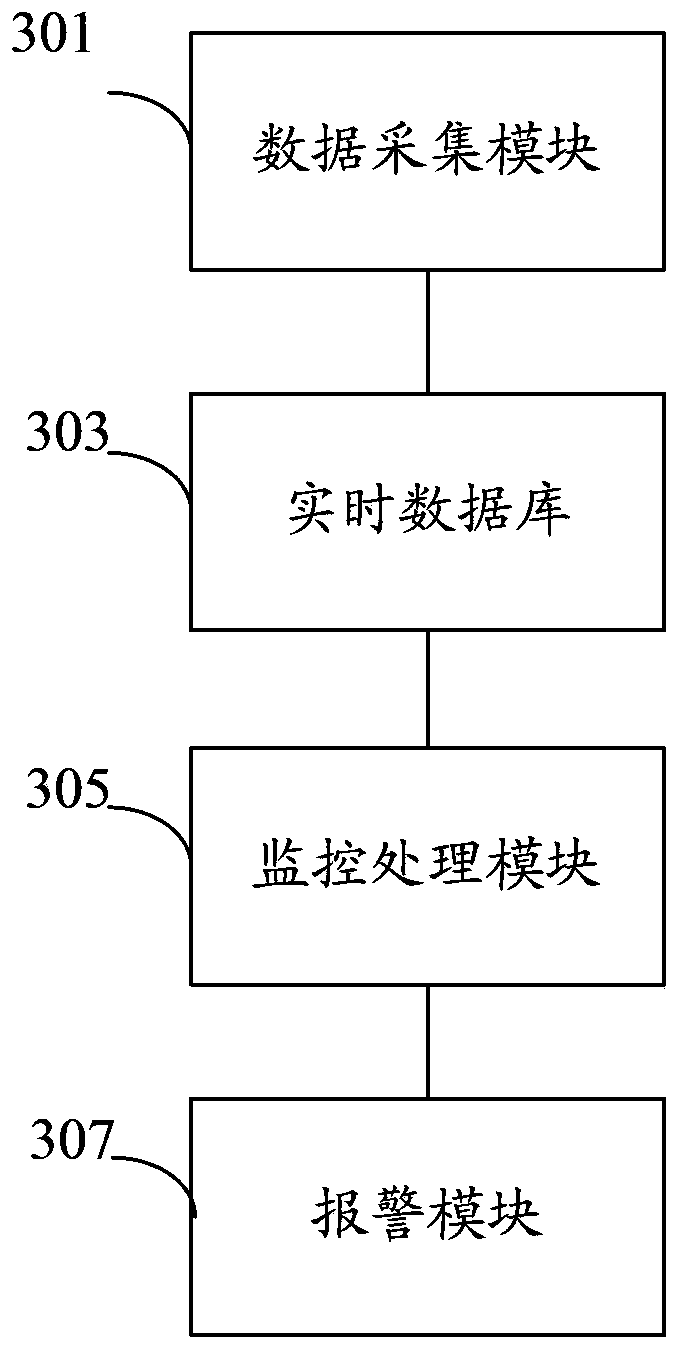
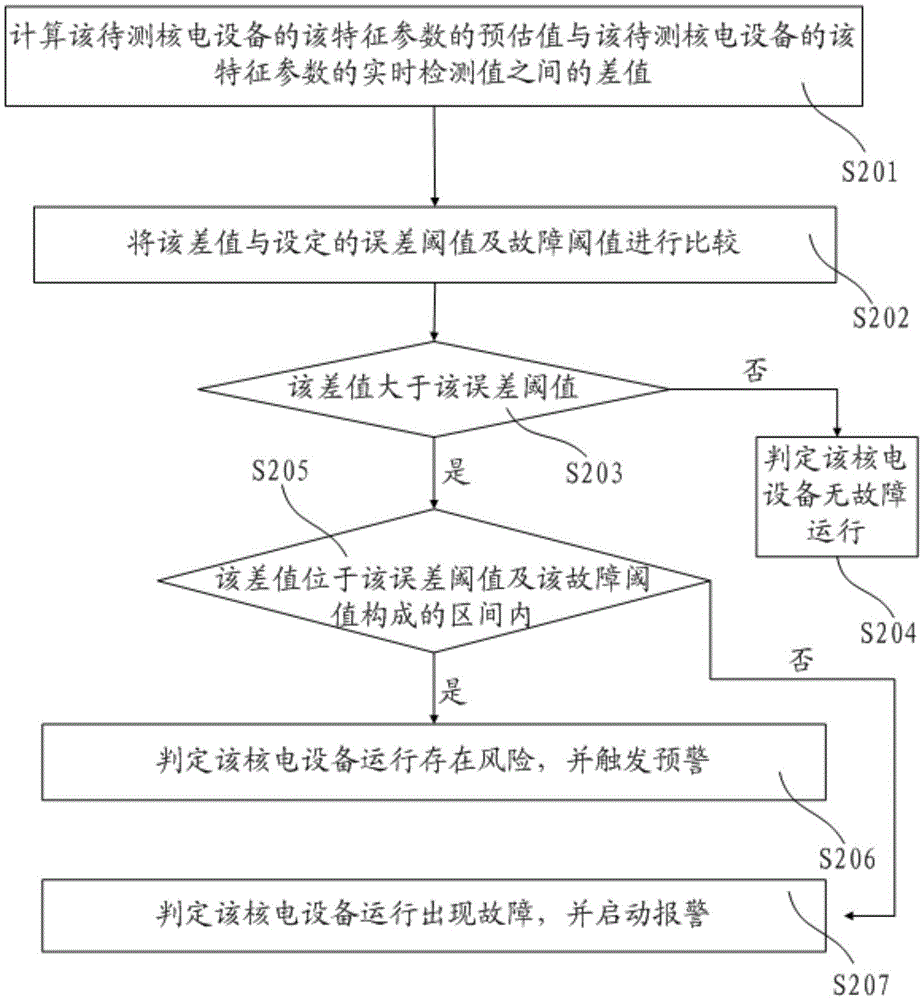
Method and system for on-line monitoring of running state of nuclear power equipment
ActiveCN105551549AAccurate online monitoring resultsImprove operational safetyPower plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationNuclear powerNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a method and system for on-line monitoring of the running state of nuclear power equipment. The system includes a nuclear power equipment database; a model building module used for building a nuclear power equipment characteristic parameter on-line calculation model according to the nuclear power equipment database; and a nuclear power equipment running state diagnosis module used for analog calculation of a characteristic parameter predicted value of nuclear power equipment to be tested of the previous moment before the current moment according to the nuclear power equipment characteristic parameter calculation model, a contrastive analysis of the characteristic parameter predicted value and a real-time detection value of the characteristic parameter of the nuclear power equipment is made, and an on-line monitoring result of the running state of the nuclear power equipment is obtained according to the contrastive analysis. A nuclear power plant manager can discriminate abnormal or fault equipment among numerous nuclear power equipment according to the monitoring result, thereby providing a scientific basis for guiding equipment maintenance or replacement work, and improving operation safety and stability of the nuclear power plant.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
Method and arrangement for determining nuclear reactor core designs
ActiveUS7200541B2Fuel element assembliesAnalogue computers for electric apparatusNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
In the method, a set of limits are defined and a reference core design is generated based on the limits, and includes an initial loading pattern of current fresh fuel bundles arranged in a plurality of fuel locations. A unique subset of fresh fuel bundles is selected for evaluation as the reference core design is subjected to an iterative improvement process. The iterative process includes replacing, at each fuel location, at least one of the current fresh fuel bundles with at least one of the selected fresh fuel bundles, and simulating reactor operation on the reference core design to obtain a plurality of outputs. The outputs may be ranked based on the defined set of limits, and the highest ranked output may be selected as an accepted core design for the nuclear reactor.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
System and method for determining fluctuating pressure loading on a component in a reactor steam dome
ActiveUS20060078081A1Accurate estimateAccurate measurementTesting/calibration apparatusFlow propertiesSound sourcesEngineering
A system and method for accurately estimating the fluctuating pressure loads on components, such as steam dryers, within a BWR steam dome using pressure time history measurements made on components of the BWR facility external to the steam dome. The method uses existing sensors to obtain the pressure time histories. An accurate determination of the fluctuating pressure loads within the steam dome may be obtained by modeling and analyzing the steam delivery system external to the steam dome, including all possible acoustic sources, using acoustic circuit methodology and pressure time histories, and then coupling these results, essentially as part of the boundary conditions, to the solutions for Helmholtz equation within the steam dome.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Long period fuel management method of pressurized water reactor core
ActiveCN103871528AEasy to flatten power distributionReduce power crest factorNuclear energy generationReactor fuel elementsNuclear reactor coreNuclear power
The invention relates to the technical field of nuclear power, and specifically discloses a long period fuel management method of a pressurized water reactor core. According to the method, the first cycle reactor core adopts a high leakage loading mode, wherein the high enrichment degree assembly and the low enrichment degree assembly in the reactor core are mutually matched and combined, and the highest enrichment degree fuel assembly is placed on the outermost circle of the reactor core; and in the subsequent cycle, the reactor core adopts a low leakage loading mode, wherein the new fuel assemblies updated every time are placed inside the reactor core, and are matched with the burned-up old component, and the burned-up old component is placed on the outermost circle of the reactor core. According to the present invention, the long period fuel change design from the first cycle to the cycle balance is directly achieved, the availability and the load factor of the power plant are increased, and the economic benefits of the power plant are enhanced.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
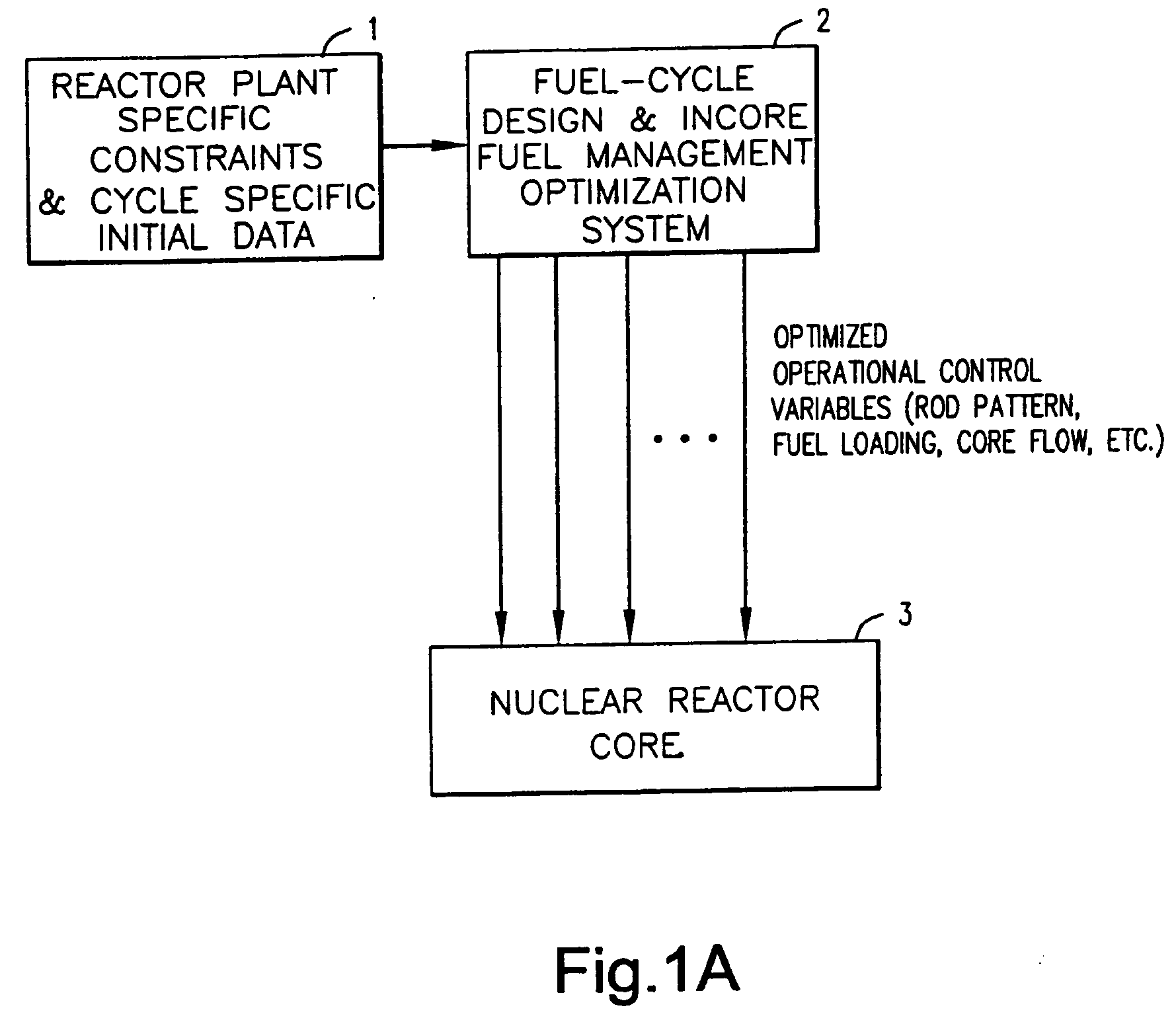
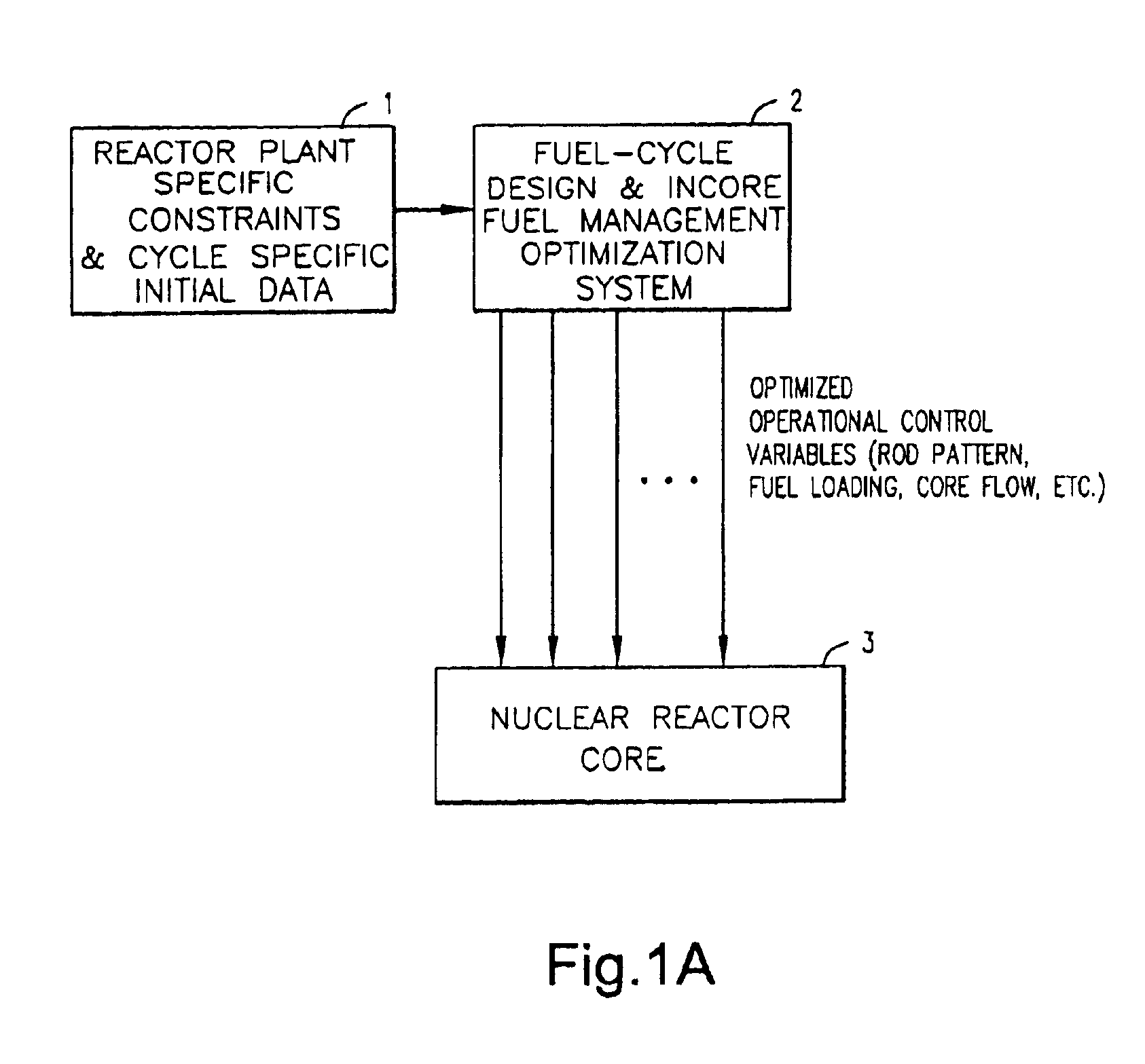
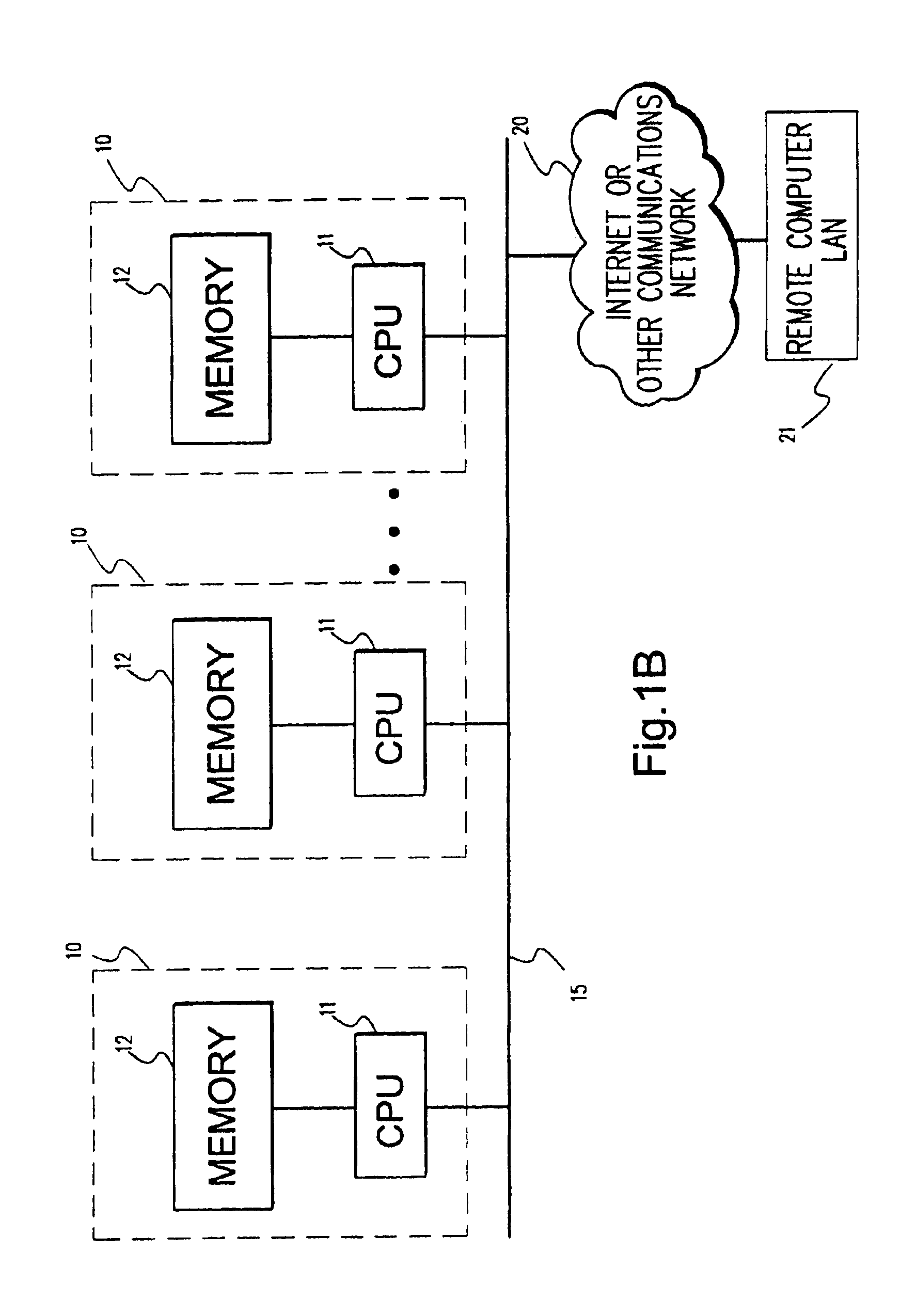
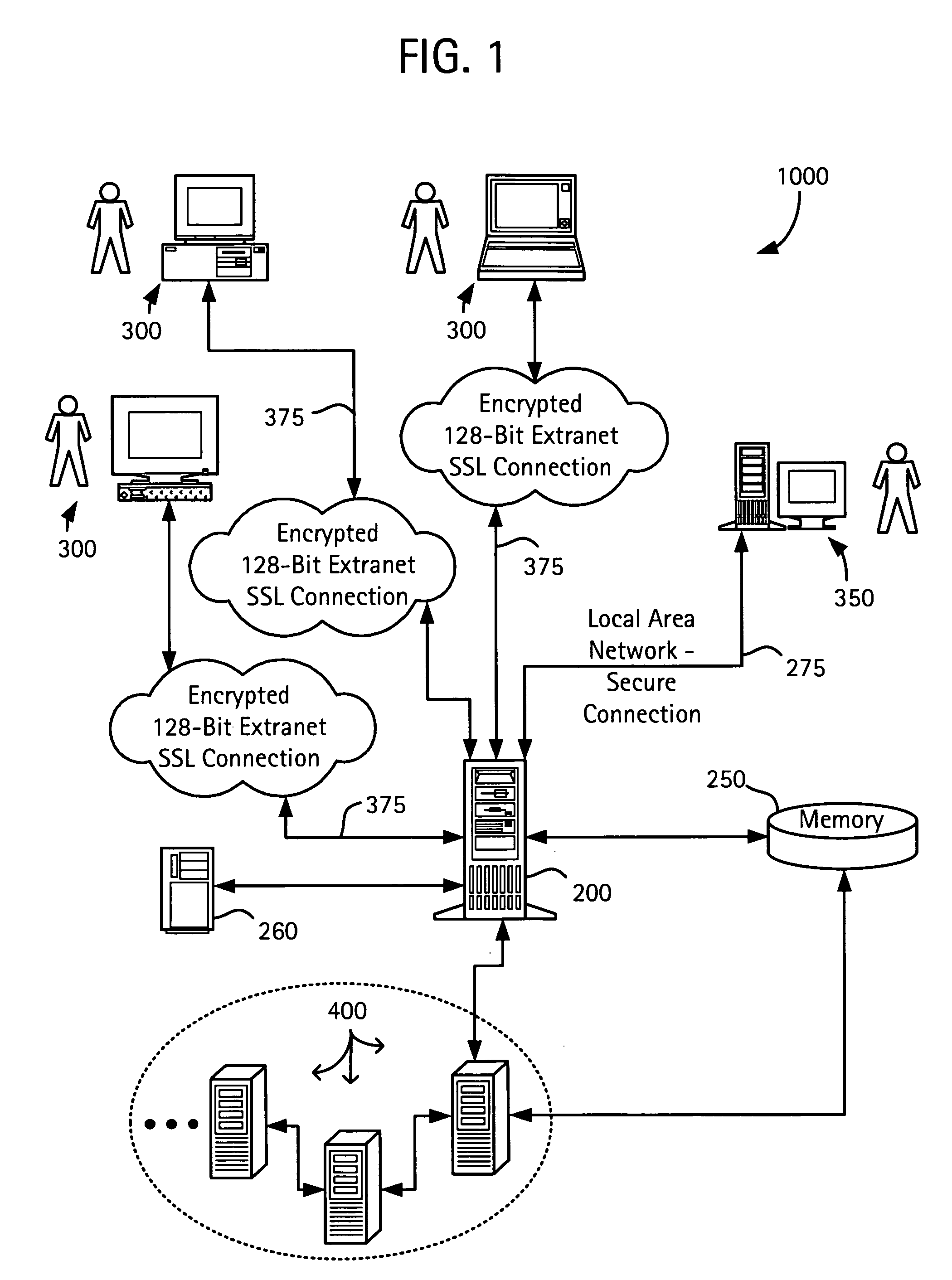
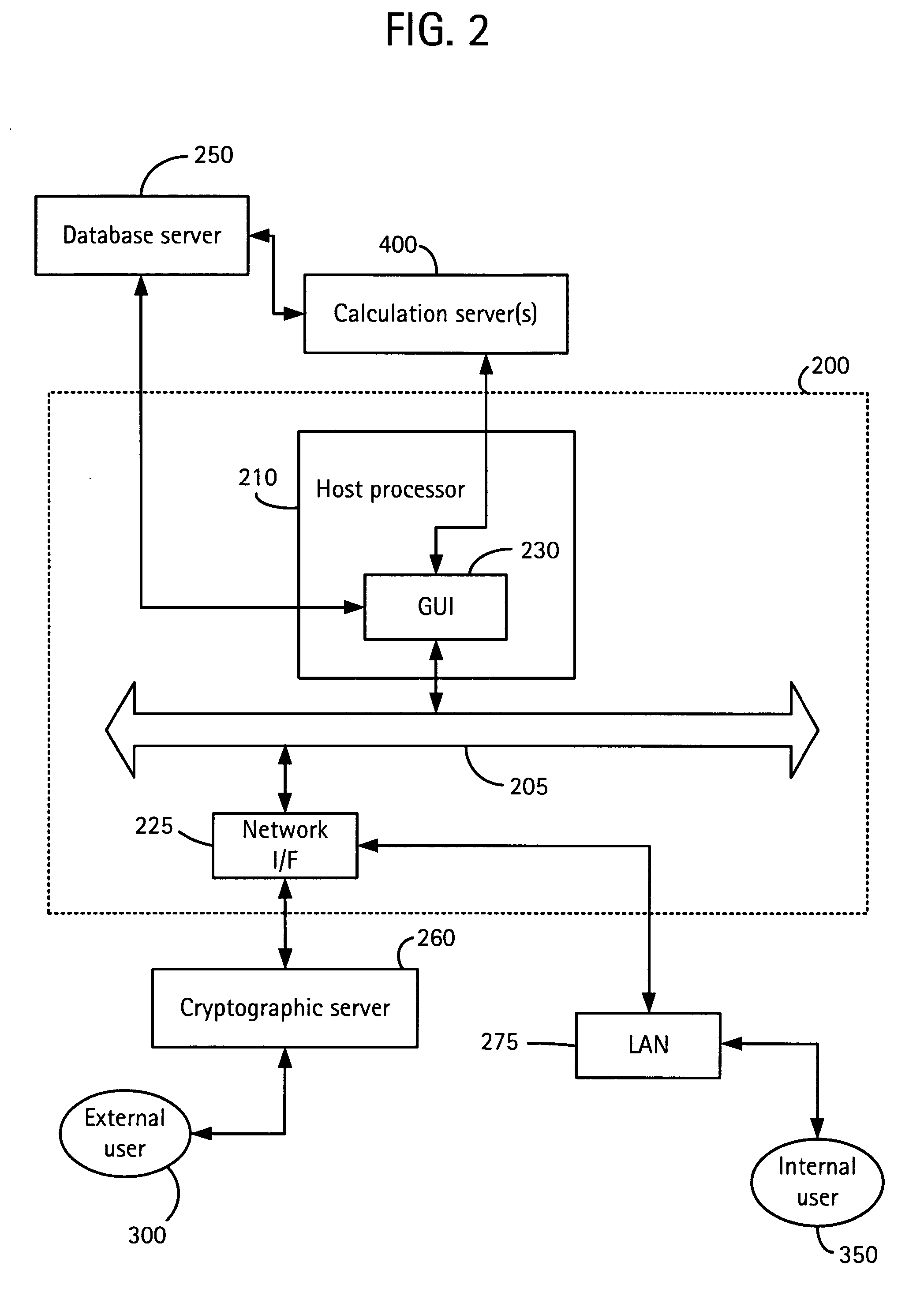
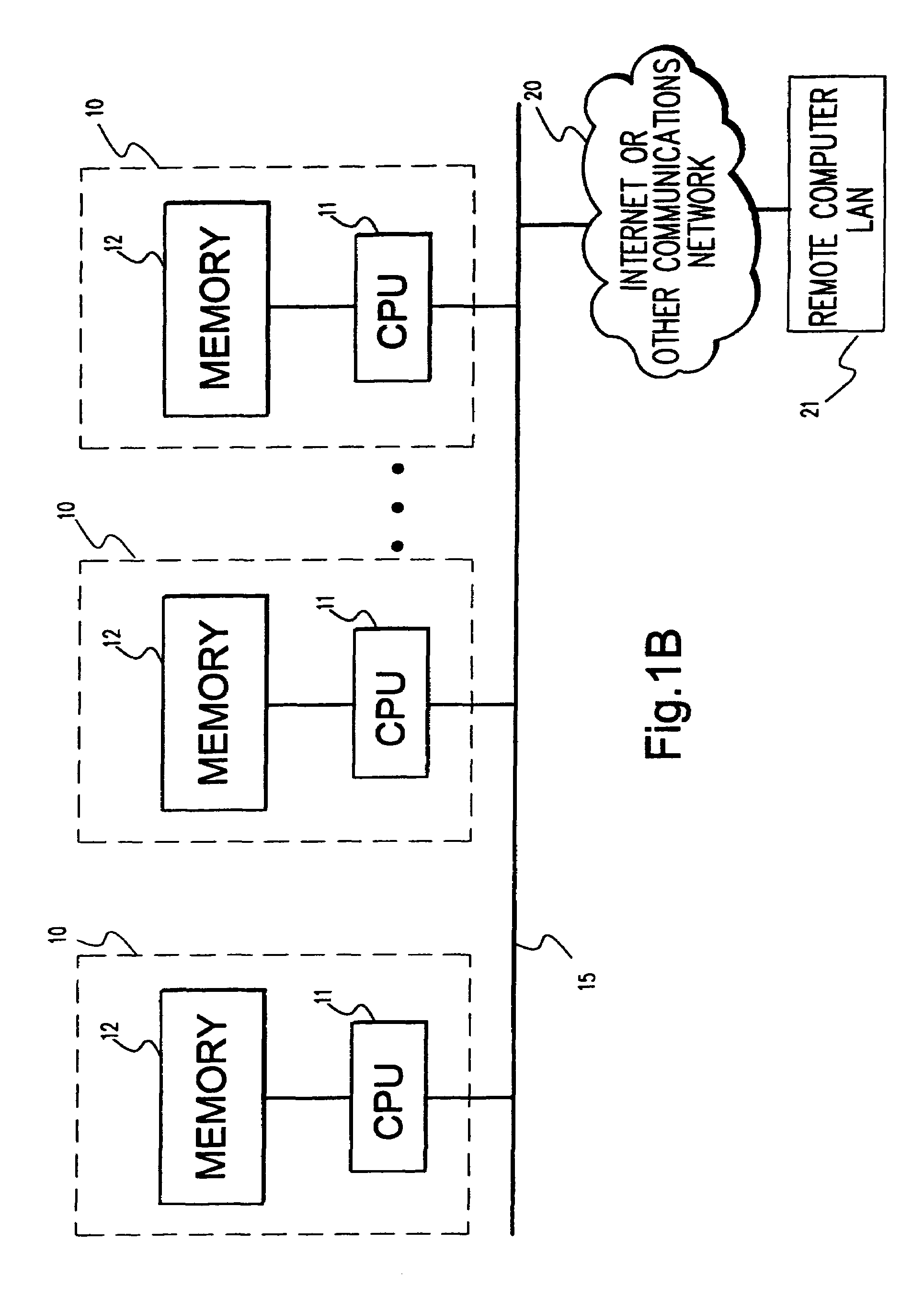
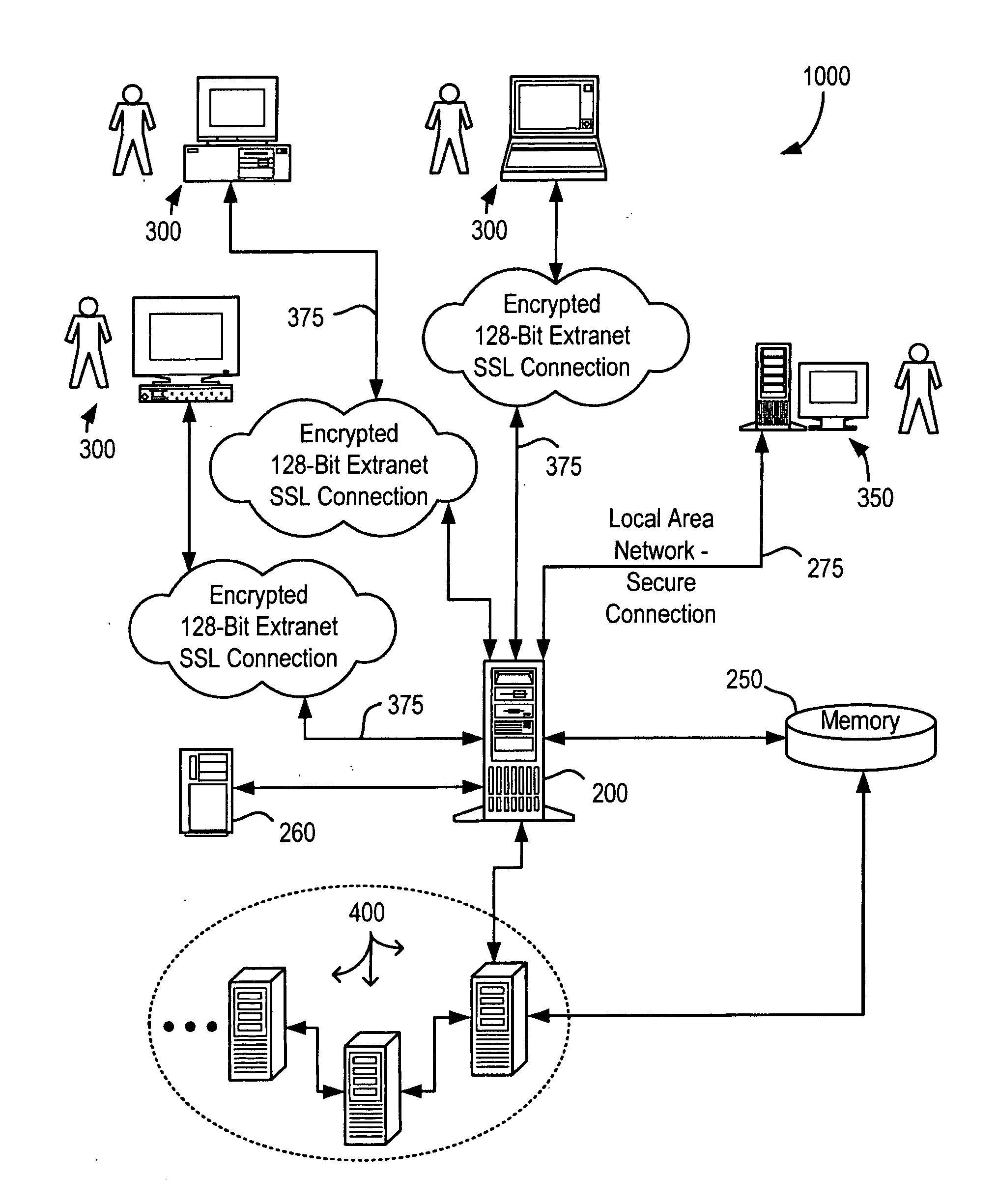
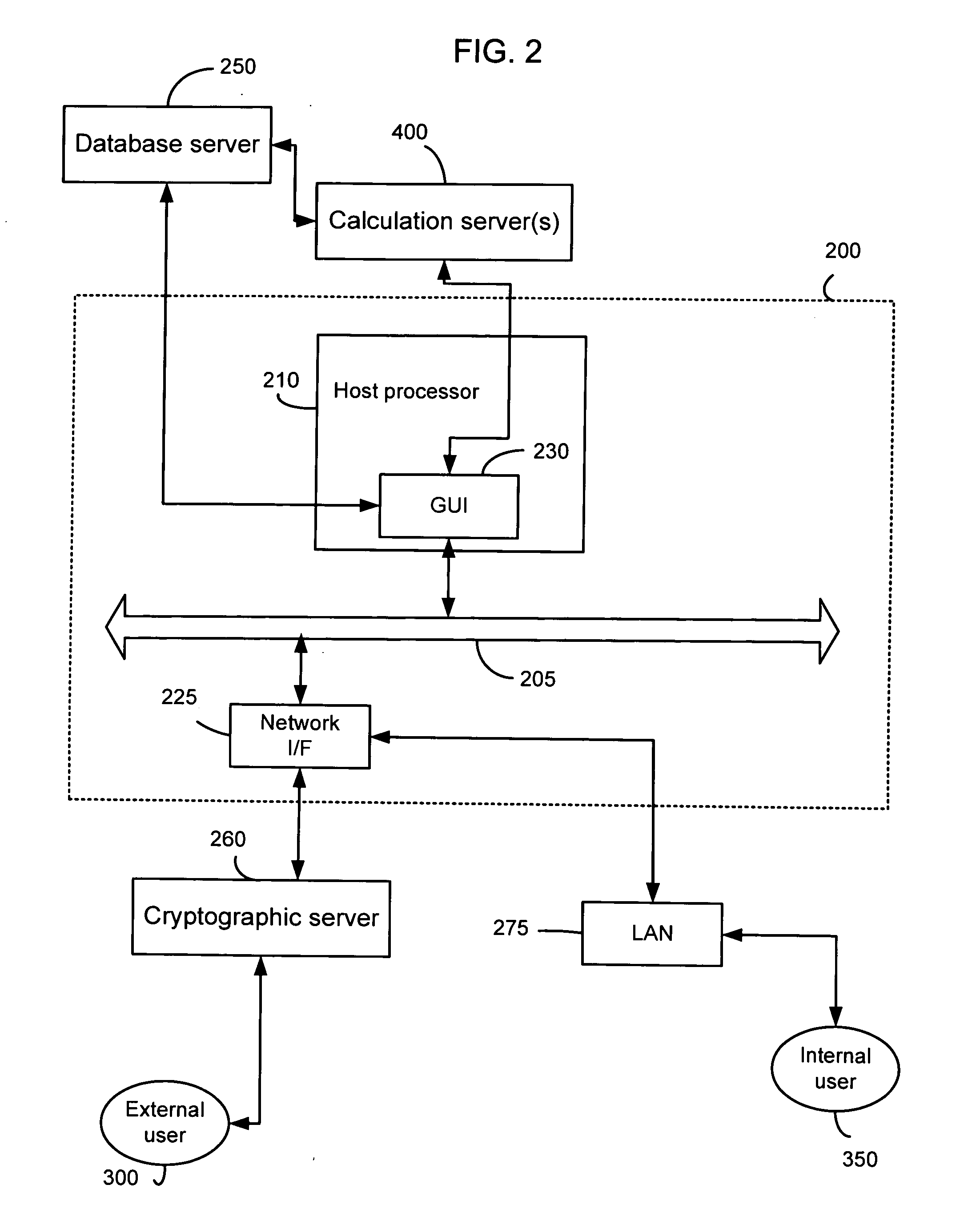
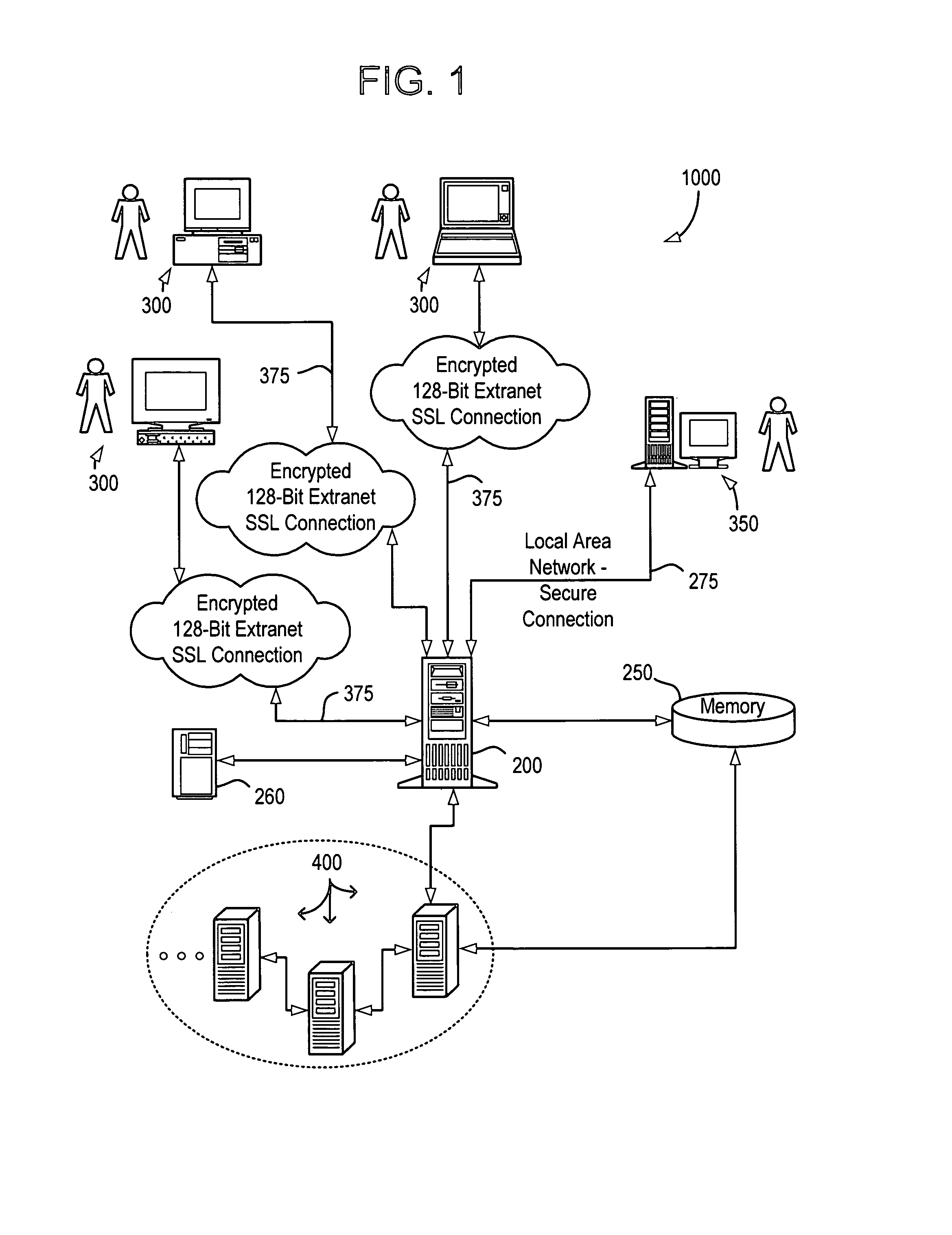
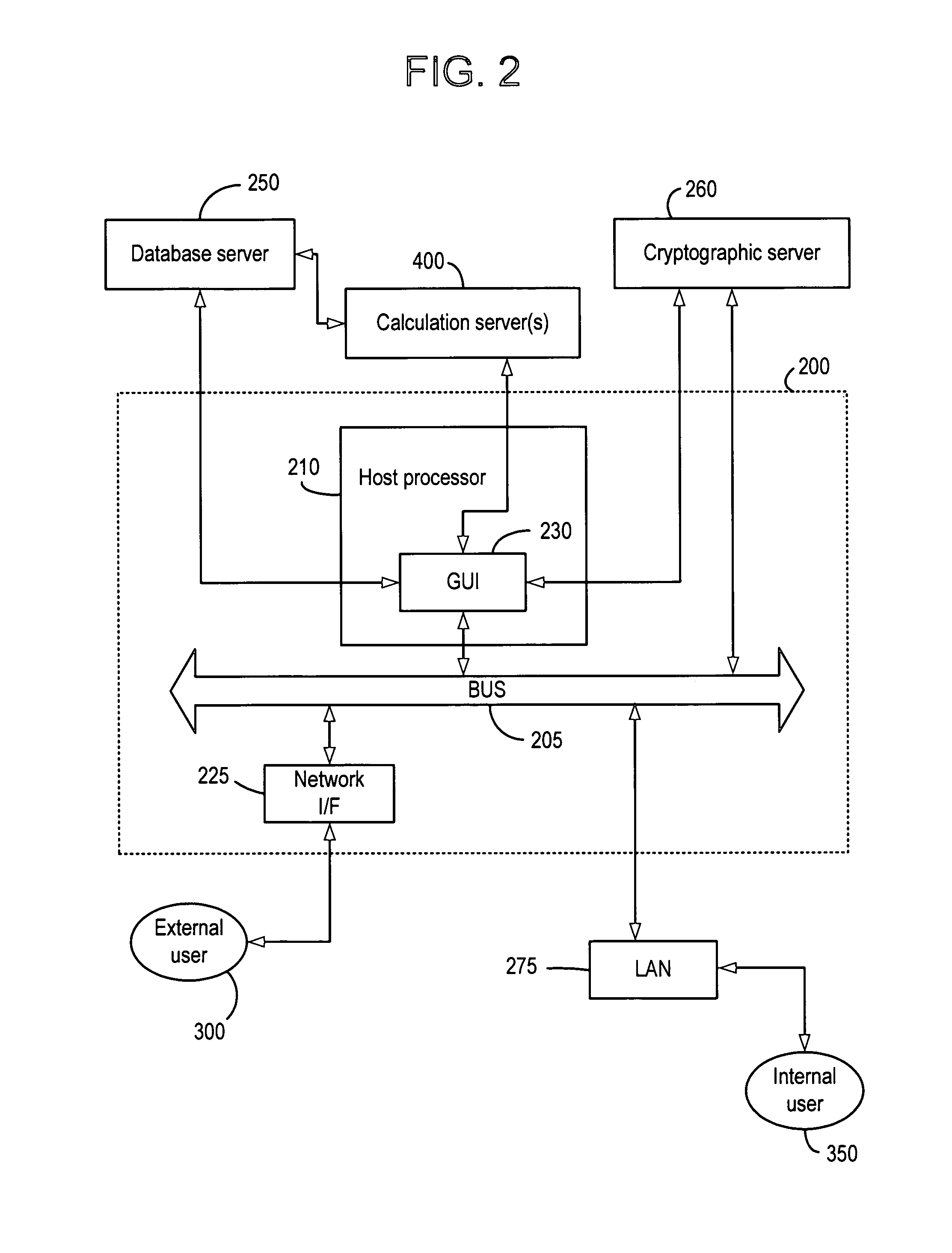
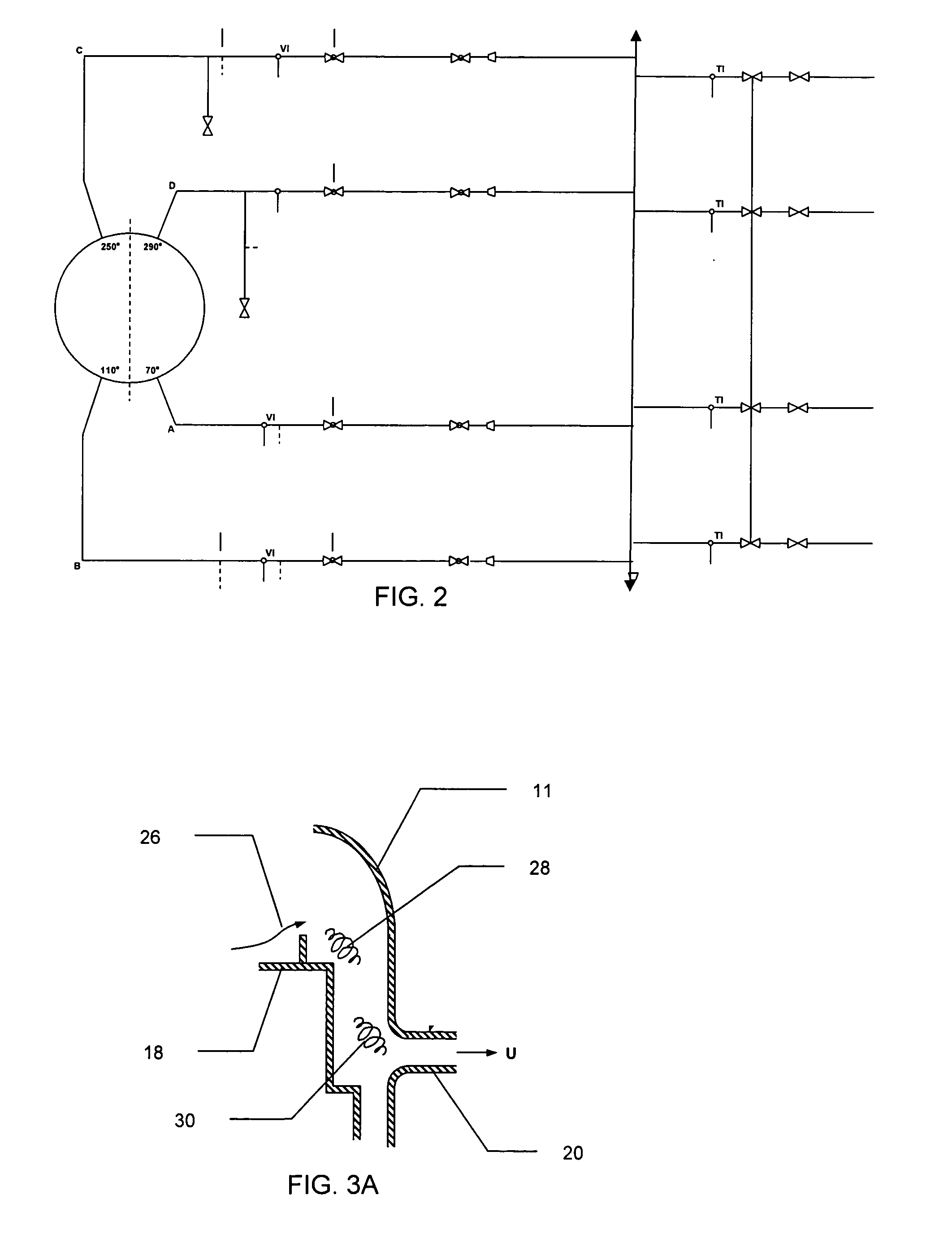
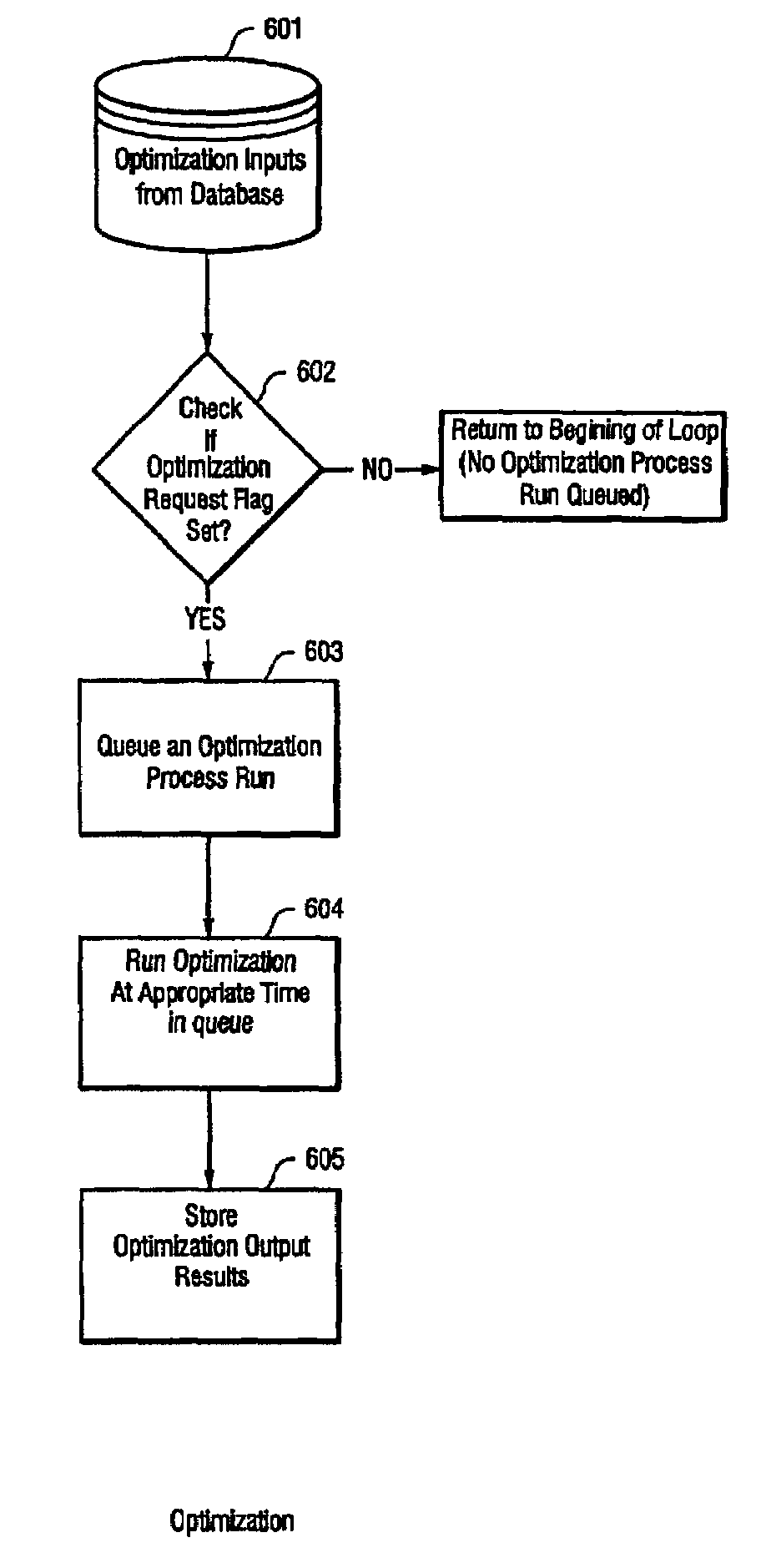
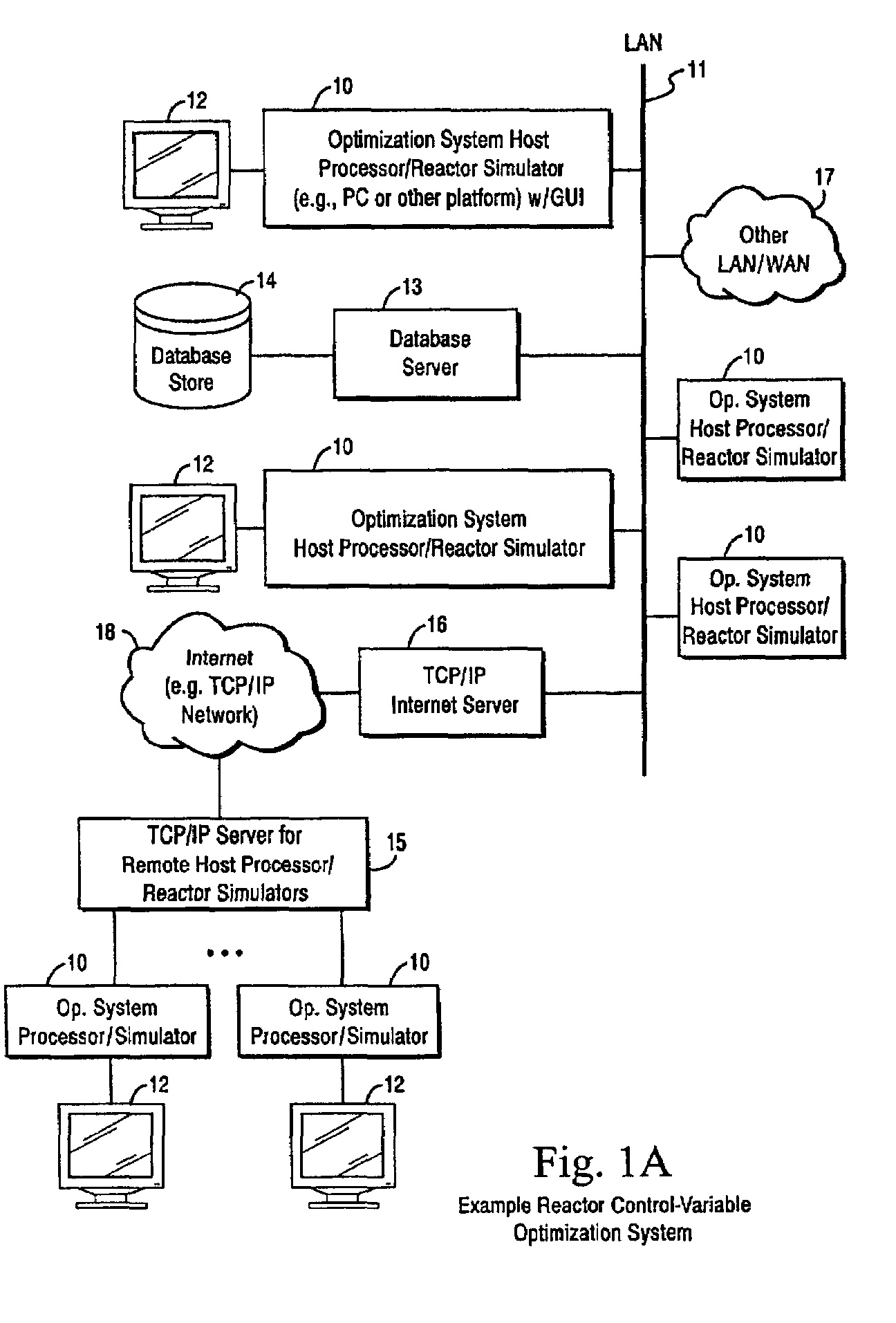
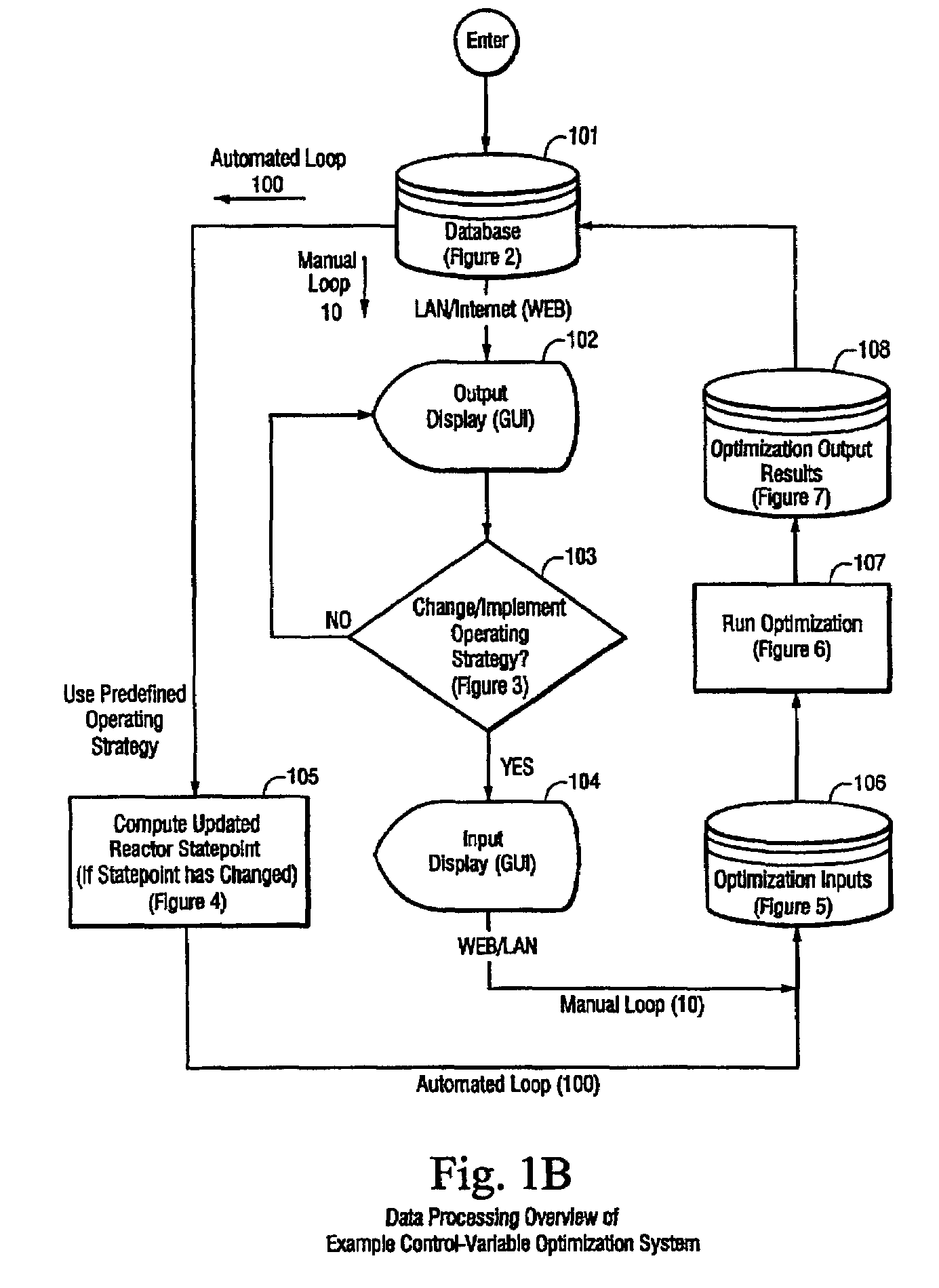
System and method for continuous optimization of control-variables during operation of a nuclear reactor
InactiveUS7555092B2Flexible and economical and safe manner of operationFlexible and economical and safe mannerPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A system and method is provided for a continual updating of the optimization of multiple operational control-variables during the operation of a nuclear reactor over a plurality of fuel cycles. A networked computer system includes one or more hosts programmed to execute an optimization process to identify and make changes in quantitative values of operational control-variables that result in improved efficiency and operational flexibility. Optimization and updating of operational control-variables may proceed selectively under manual control for inputting specific optimization constraints and reactor state-point information or may proceed autonomously through a repetitive performing of the optimization process based upon a predetermined user-defined strategy stored on the network. Communications between users and networked processors is facilitated by use of a TCP / IP server connected to the Internet so that portions of the optimization process may be conducted contemporaneously at remote locations and / or the results made accessible to users via conventional browser enabled computers.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com