Large primer PCR site-specific mutagenesis method
A technology of site-directed mutation and flanking primers, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems that the mutation efficiency cannot reach 100%, and the mutation success rate is not high, and achieve the effect of shortening the annealing time and increasing the mutation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
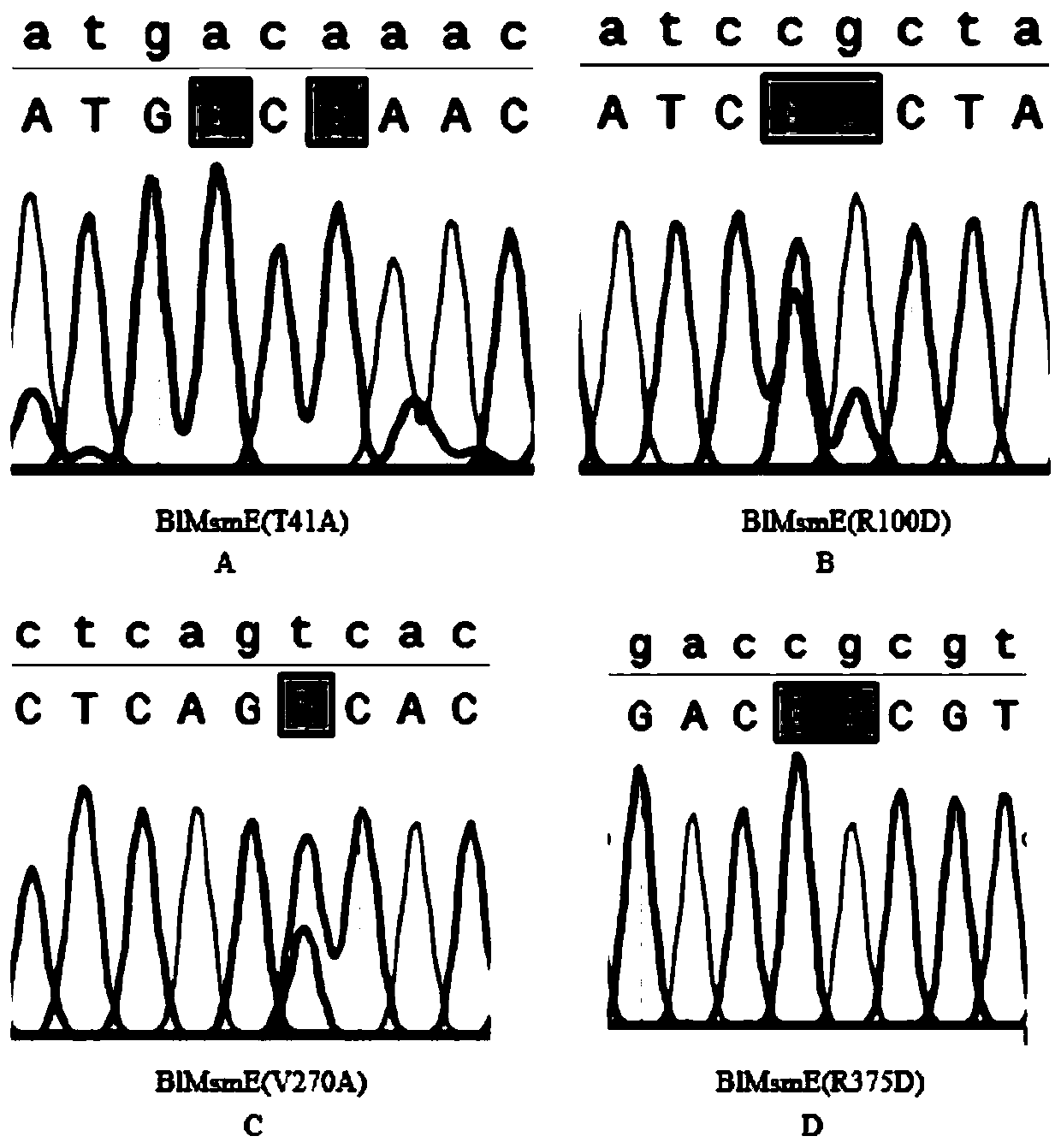
[0025] Search and download the B1MsmE gene of Bacillus licheniformis ABC transporter through the NCBI database, and its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO. The lower flanking primer sequences are SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.3 respectively, and then it is determined that the site to be mutated is located in the first half of the target gene, and Snapgene is used to design a mutation primer 1SEQ ID NO.4 centered on the mutation site, The specific primer sequences are shown in Table 1, wherein gcagctg in the upper flanking primer sequence is a protective base, and the restriction enzyme cleavage site of the upper flanking primer is CATATG; cgac in the lower flanking primer sequence is a protective base, and the restriction enzyme cleavage site is GGATCC; the underlined portion in Table 1 represents the mutated base.
[0026] Table 1 Primer sequences
[0027]
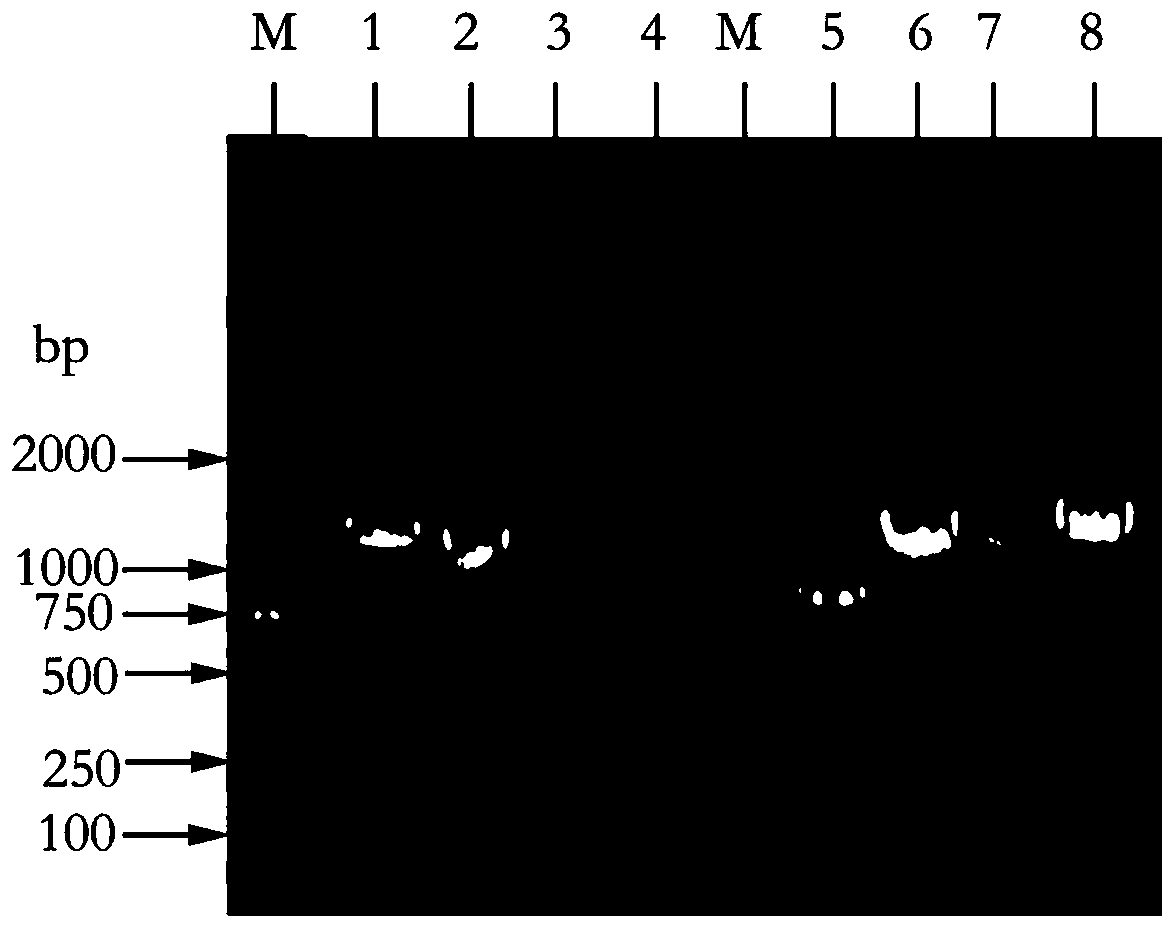
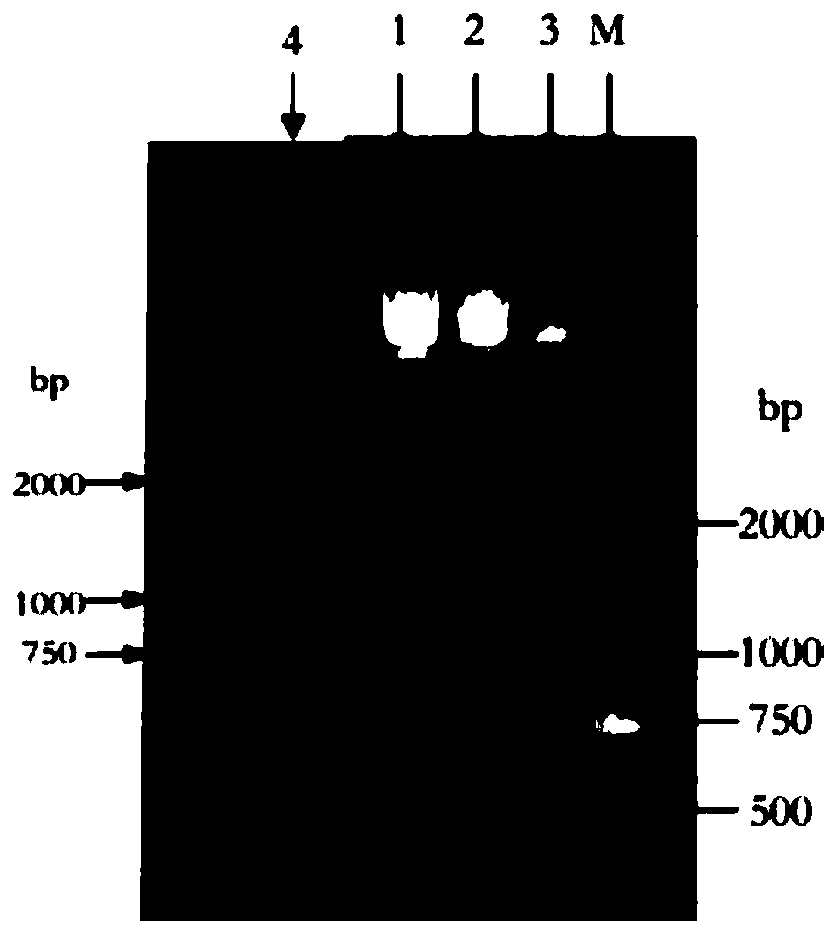
[0028] Carry out the first round of PCR reaction according to the above mutation primers and lower flanking prim...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Search and download the B1MsmE gene of Bacillus licheniformis ABC transporter through the NCBI database, and its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO. The lower flanking primer sequences are SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.3 respectively, and then it is determined that the site to be mutated is located in the first half of the target gene, and Snapgene is used to design a mutation primer 2SEQ ID NO.7 centered on the mutation site, The specific primer sequences are shown in Table 1, wherein gcagctg in the upper flanking primer sequence is a protective base, and the restriction enzyme cleavage site of the upper flanking primer is CATATG; cgac in the lower flanking primer sequence is a protective base, and the restriction enzyme cleavage site is GGATCC; the underlined portion in Table 1 represents the mutated base.
[0044] Table 2 Primer sequences
[0045]
[0046] Carry out the first round of PCR reaction according to the above mutation primers and lower flanking prim...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Search and download the B1MsmE gene of Bacillus licheniformis ABC transporter through the NCBI database, and its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO. The lower flanking primer sequences are SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.3 respectively, then determine that the site to be mutated is located in the first half of the target gene, and use Snapgene to design a mutation primer 3SEQ ID NO.10 centered on the mutation site, The specific primer sequences are shown in Table 1, wherein gcagctg in the upper flanking primer sequence is a protective base, and the restriction enzyme cleavage site of the upper flanking primer is CATATG; cgac in the lower flanking primer sequence is a protective base, and the restriction enzyme cleavage site is GGATCC; the underlined portion in Table 1 represents the mutated base.
[0062] Table 3 Primer sequences
[0063]
[0064] Carry out the first round of PCR reaction according to the above mutation primers and lower flanking primers, wherein t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com