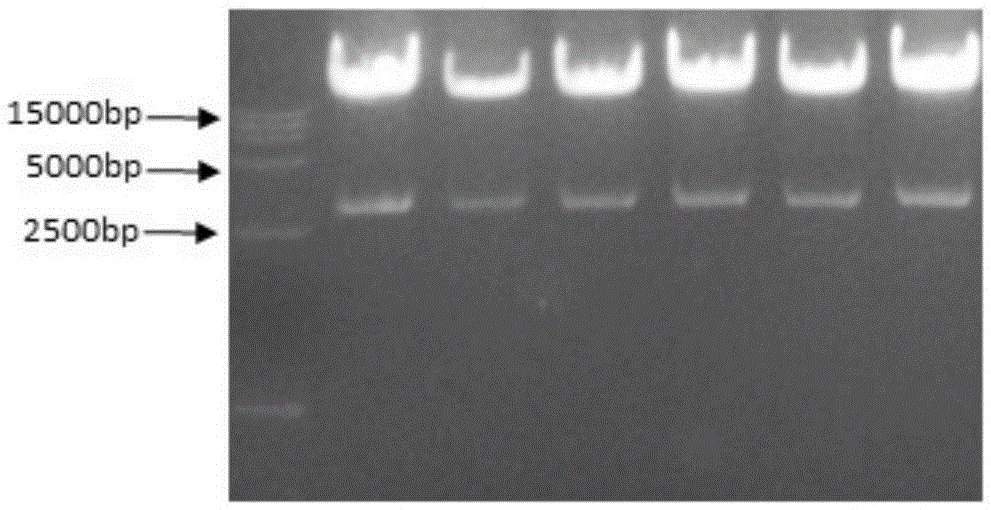
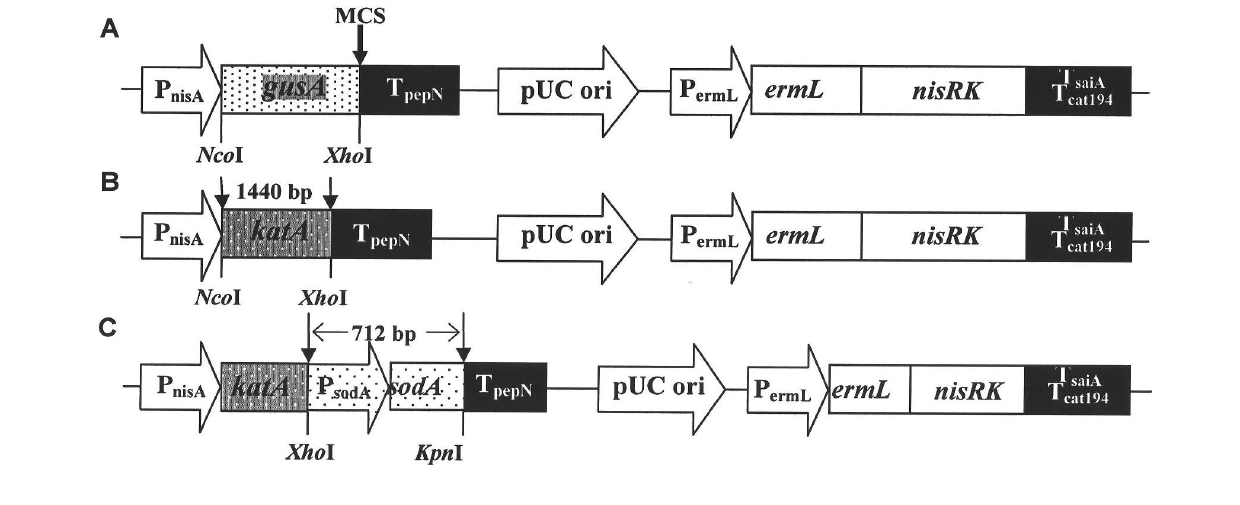
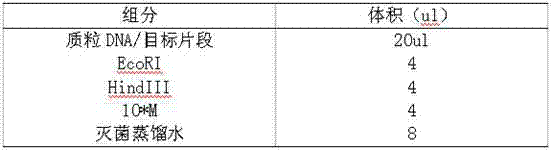
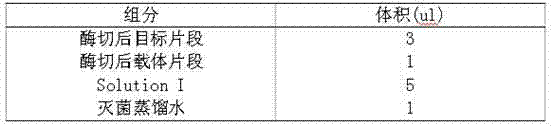
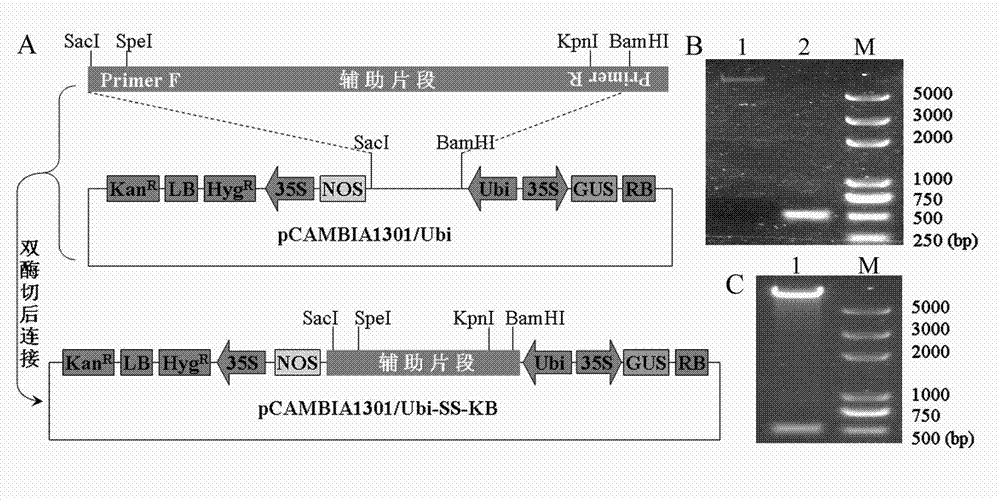
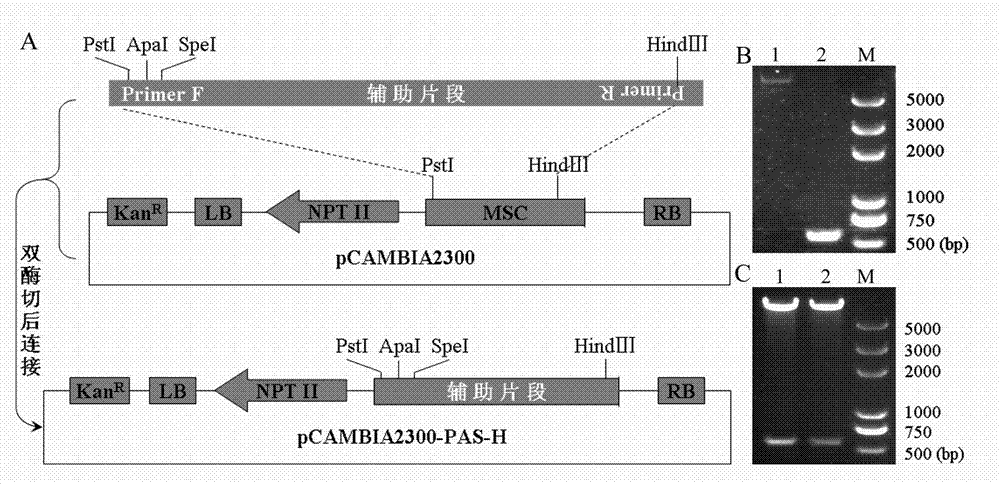
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Restriction Enzyme Cleavage Site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The specific DNA base that is cut by a specific restriction enzyme.
Sequencing method
InactiveUS20100311602A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAdaptor moleculeRestriction Enzyme Cleavage Site
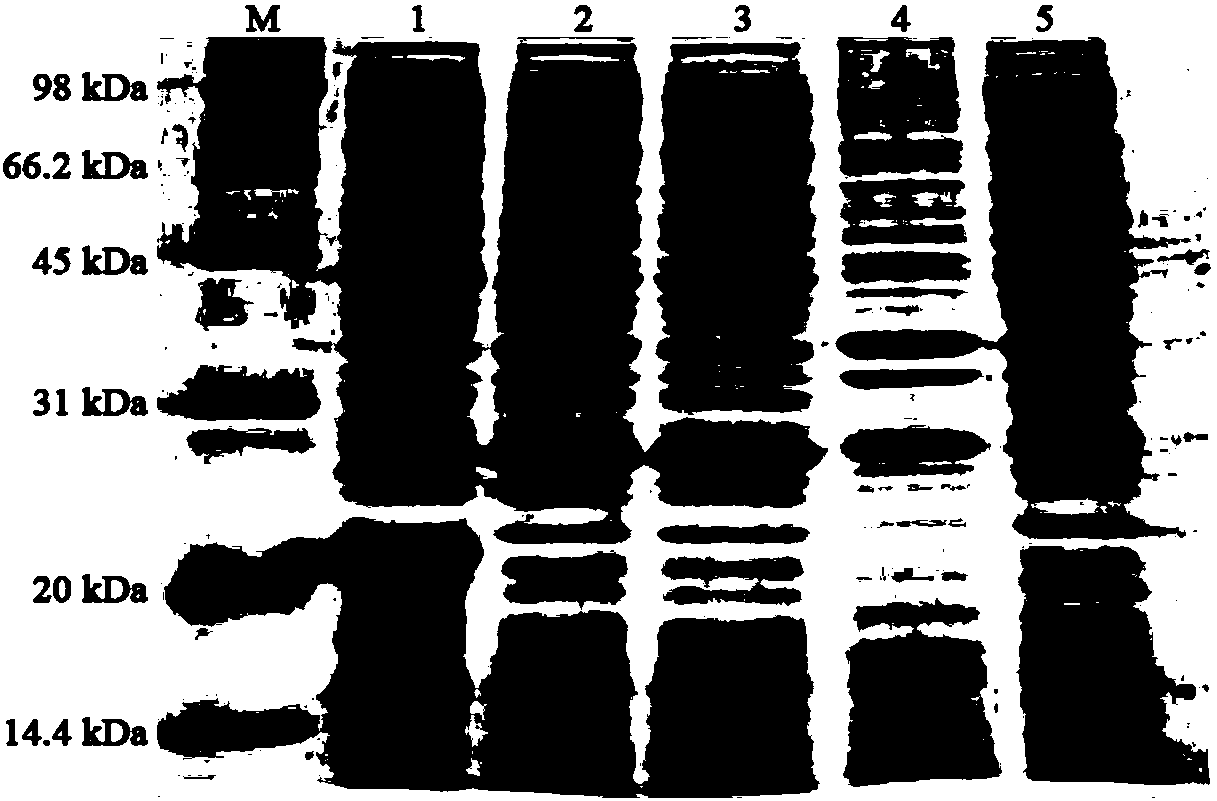
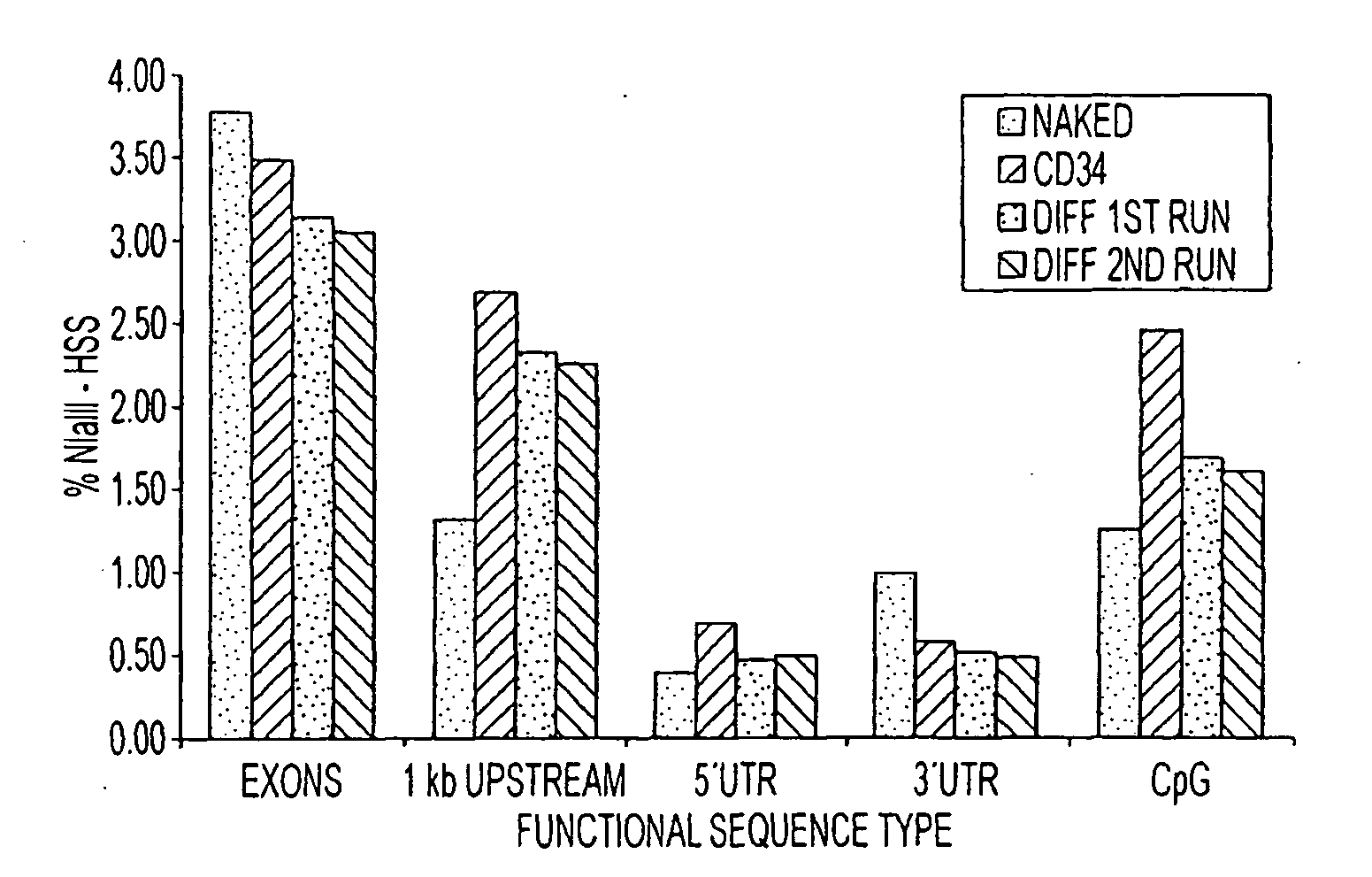
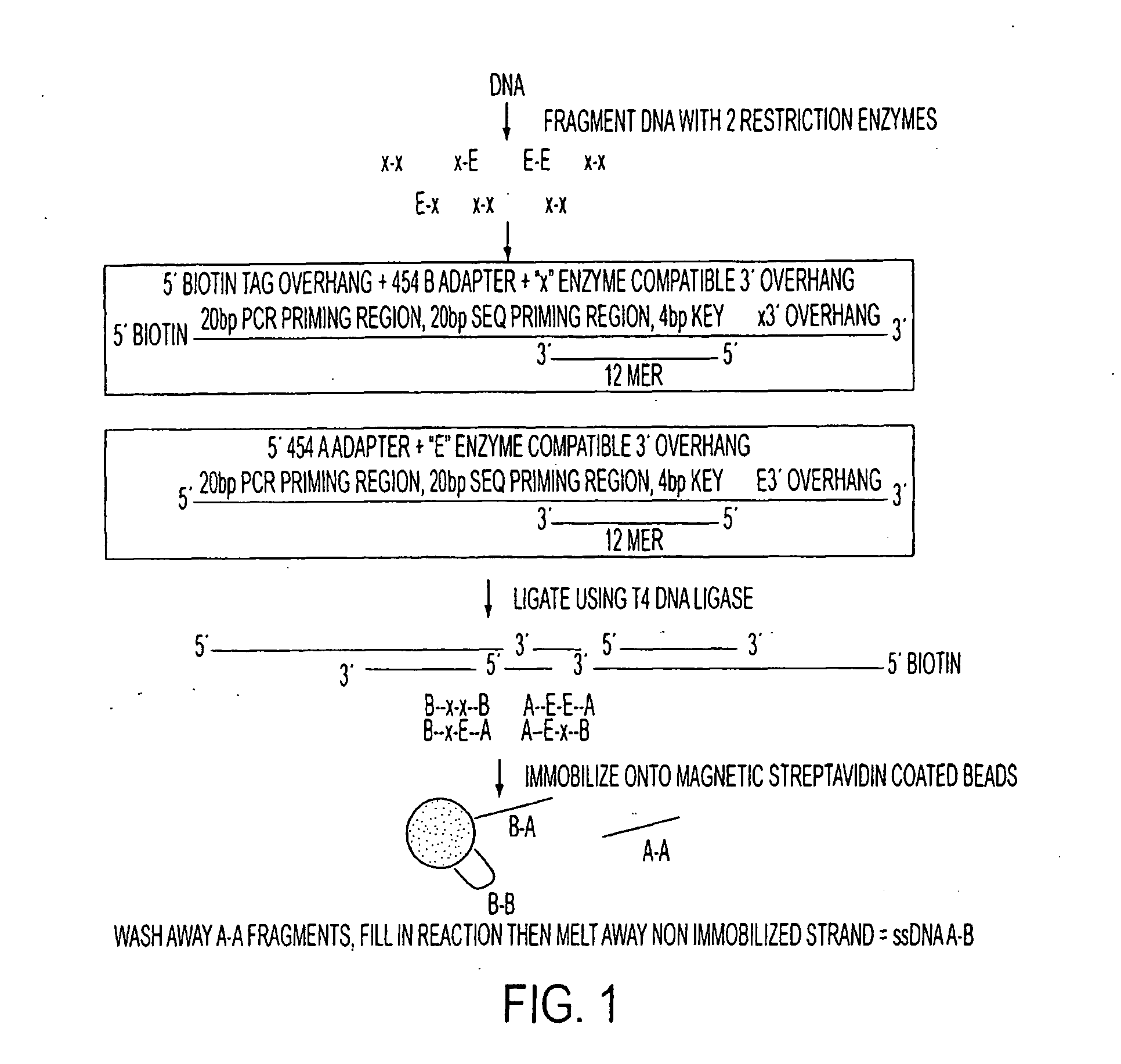
The present invention relates, e.g., to a method for isolating a DNA molecule of interest in a form suitable for sequencing at least a portion of the DNA by a high throughput sequencing method, comprising (a) digesting a double-stranded (ds) DNA molecule with two different restriction enzymes, A and B, to generate a ds form of the DNA molecule of interest, which is bounded by the two restriction enzyme cleavage products, and (b) attaching to each end of the DNA molecule of interest an adaptor molecule which comprises at one end a restriction enzyme cleavage site that is compatible with the restriction enzyme A or the restriction enzyme B cleavage product, and which also comprises a sequence and / or element that allows the DNA of interest to be sequenced with a high throughput sequencing apparatus. The method can be adapted for sequencing DNA with a variety of high throughput sequencing apparatuses, including machines manufactured by the 454, Illumina (Solexa Sequencing technology) and ABI (SOLiD™ Sequencing technology) companies. A method is also described for sequencing regulatory elements within a cell, comprising subjecting a collection of ds DNA molecules that are enriched for regulatory elements and that are generated by digestion with two restriction enzymes, A and B, which generate sticky ends, to an isolation method of the invention, and sequencing the collection of ds DNA molecules with a high throughput sequencing apparatus.
Owner:J CRAIG VENTER INST
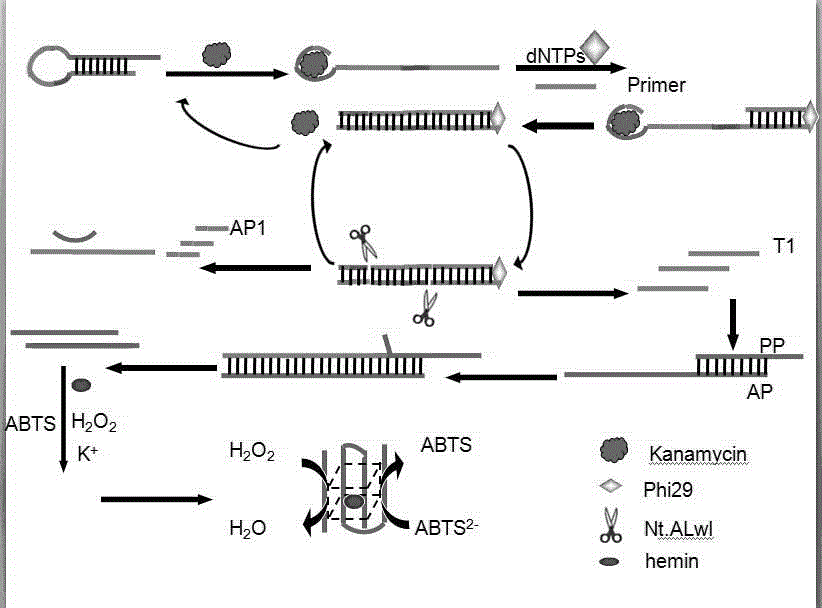
Method for detecting kanamycin
InactiveCN105925699AAchieve high sensitivityAchieve improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementKanamycinSpecific detection
The invention provides a method for detecting kanamycin. The kanamycin is detected by using double restriction enzyme cleavage sites and color change caused by G-tetrad. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps: carrying out specific binding on a hair pin and kanamycin; adding a color developing agent into a homogeneous phase reaction mixed liquor for display detection. According to the method, high specific detection for the target object kanamycin is realized by using the oxidability of the G-tetrad; the effect of signal amplification is reached by using nucleic acid tool enzymes.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
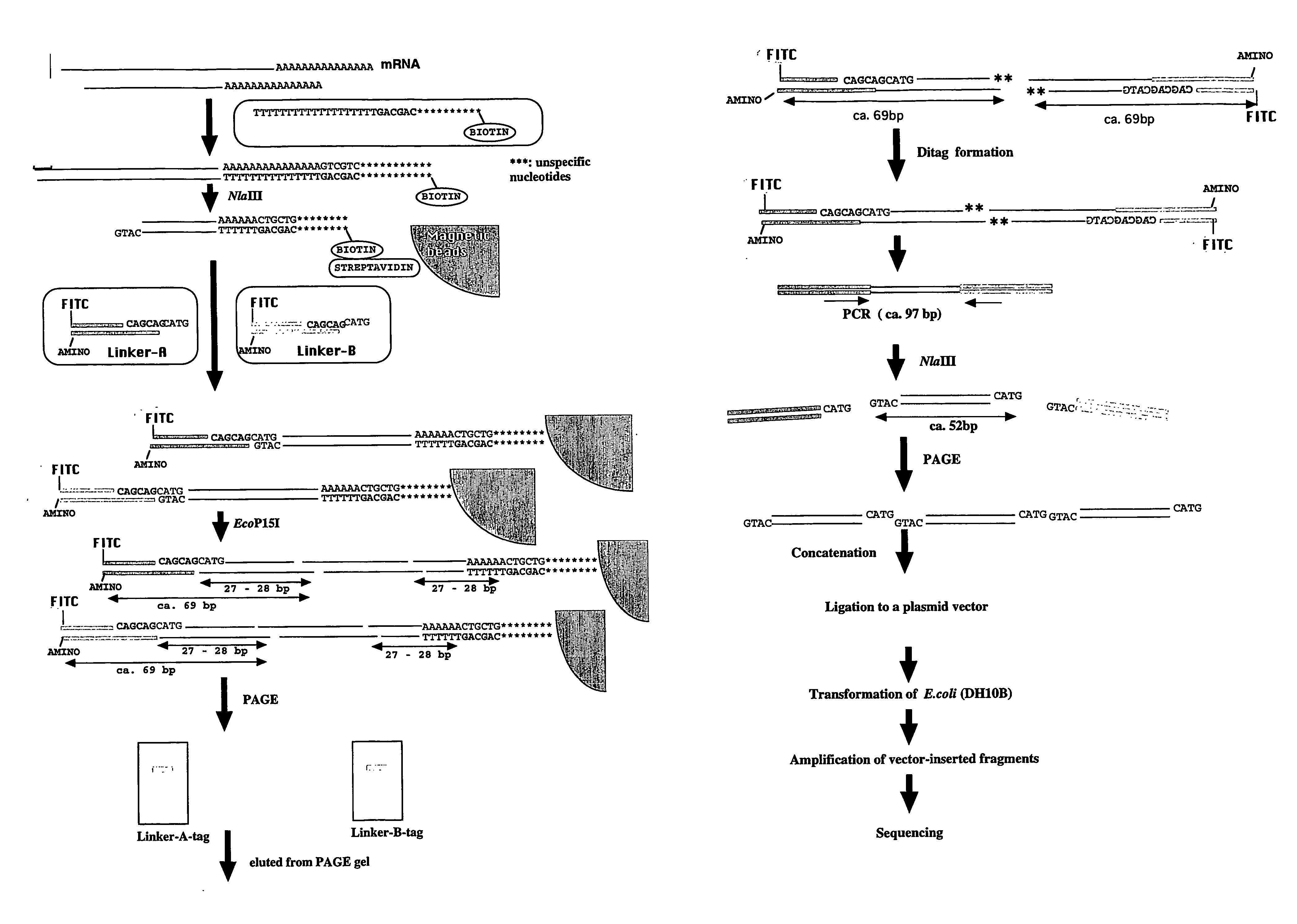
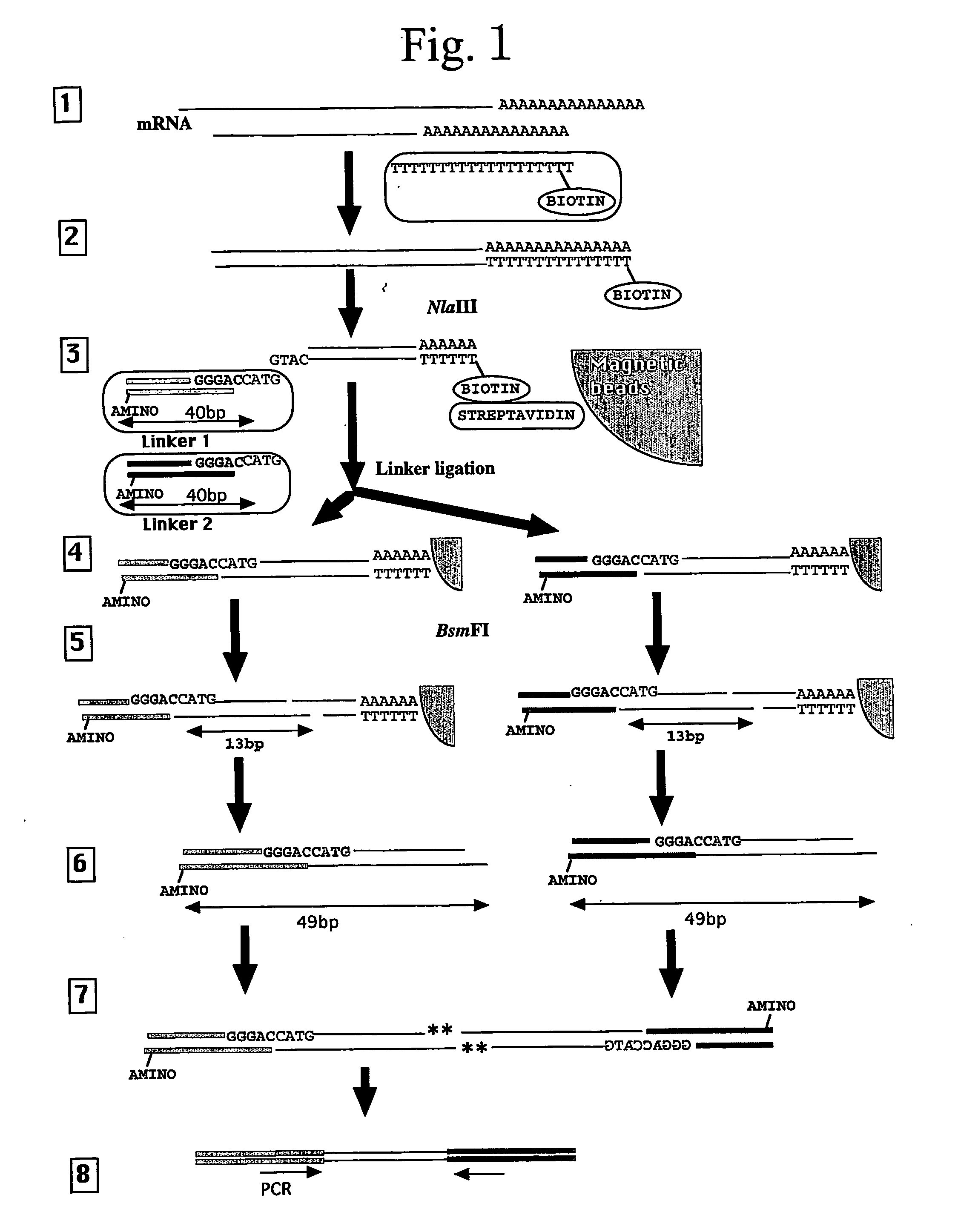
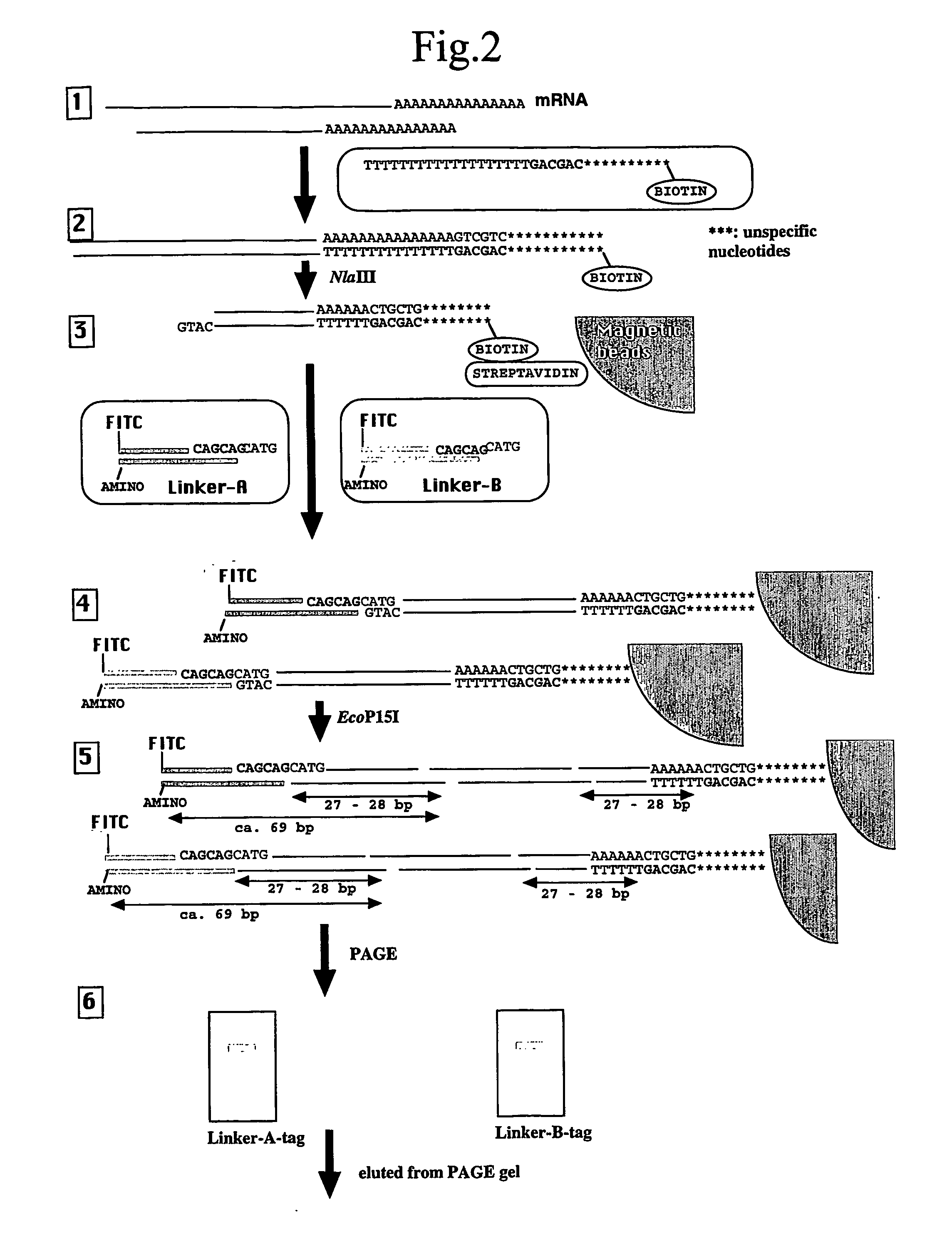
Use Of A Type III Restriction Enzyme To Isolate Identification Tags Comprising More Than 25 Nucleotides
InactiveUS20080008993A1Improve efficiencyAccurate identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideRestriction Enzyme Cleavage Site
The type III restriction enzyme EcoP15I is used to isolate from cDNA of an expressed gene a tag comprising more than 25 nucleotides and capable of identifying the expressed gene, wherein the 3′ end of the tag is defined by a cleavage site of the type III restriction enzyme and the 5′ end of the tag is defined by the cleavage site of another restriction enzyme that is closest to the 3′ end of the cDNA of the expressed gene. The tag of the invention allows accurate quantitative gene expression analysis and rapid gene expression profiling in any organism for which no expressed sequence tag (EST) database is available.
Owner:IWATE PREFECTUAL GOVERNMENT +1
Tumor acidity responsive autophagy-induced polypeptide as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107686523AEasy to manufactureHigh yieldPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaEscherichia coliChemical synthesis
The invention provides tumor acidity responsive autophagy-induced polypeptide as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: chemicallysynthesizing gene sequences of pH low insertion peptide (pHLIP) and Beclin 1 active fragments and connecting the sequences to a pET-32a expression vector through a restriction enzyme cutting site to obtain a recombinant plasmid; converting the recombinant plasmid to escherichia coli BL-21(DE3) and obtaining engineering bacteria pET-32a-pHLIP-Beclin 1 / BL21(DE3) through screening; performing IPTG induced expression on the engineering bacteria, collecting thalli and obtaining target proteins through separation and purification. The tumor acidity responsive autophagy-induced polypeptide provided by the invention can be positioned to a tumor acidic microenvironment through pHLIP; the Beclin 1 active fragment is conveyed to tumor cells in a targeted manner, so that the tumor cells are induced togenerate autophagic death; the tumor acidity responsive autophagy-induced polypeptide can be applied to the preparation of a targeted anti-cancer drug.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
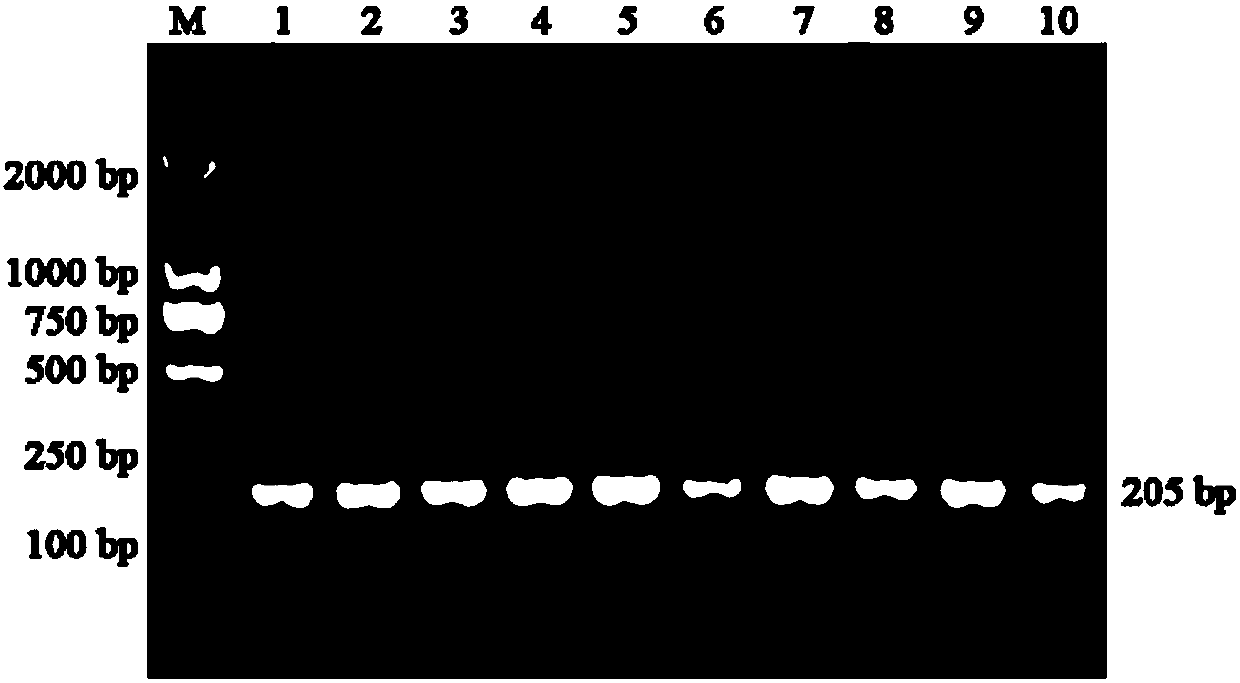
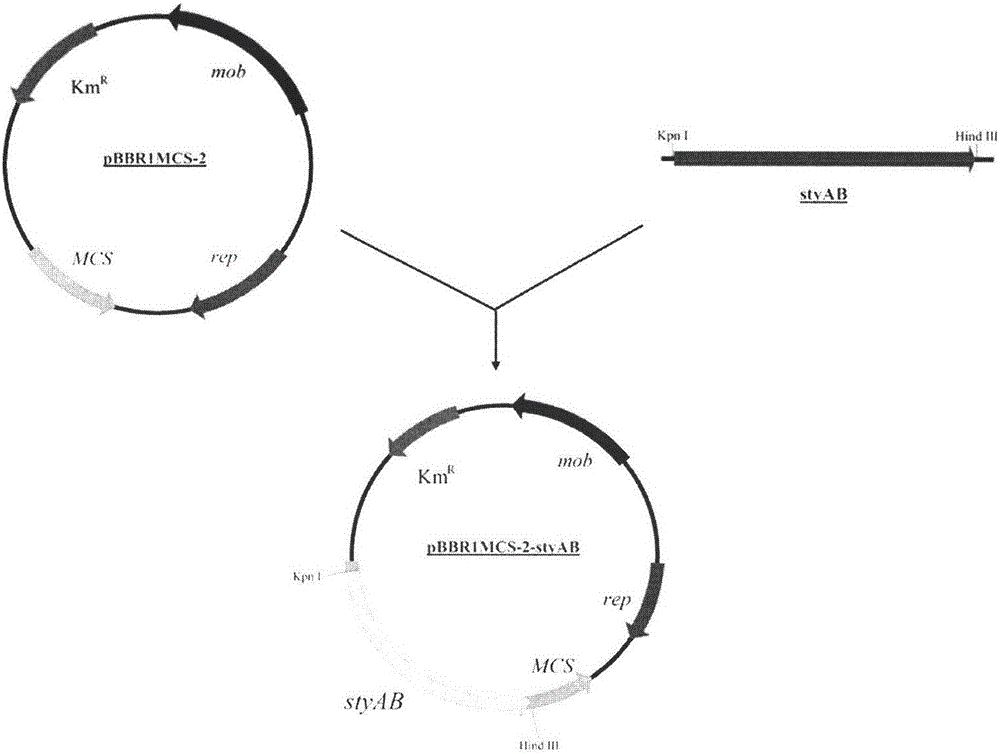
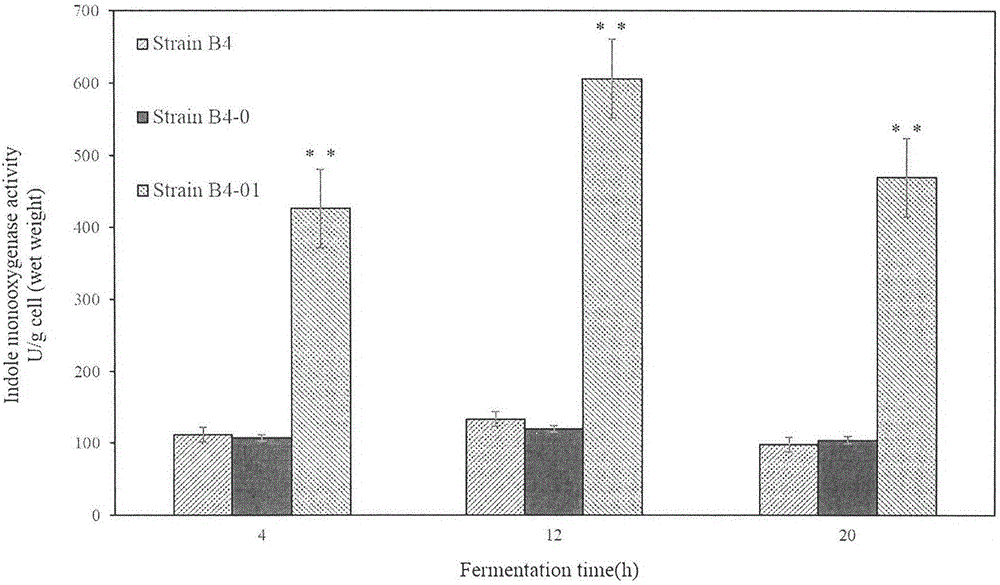
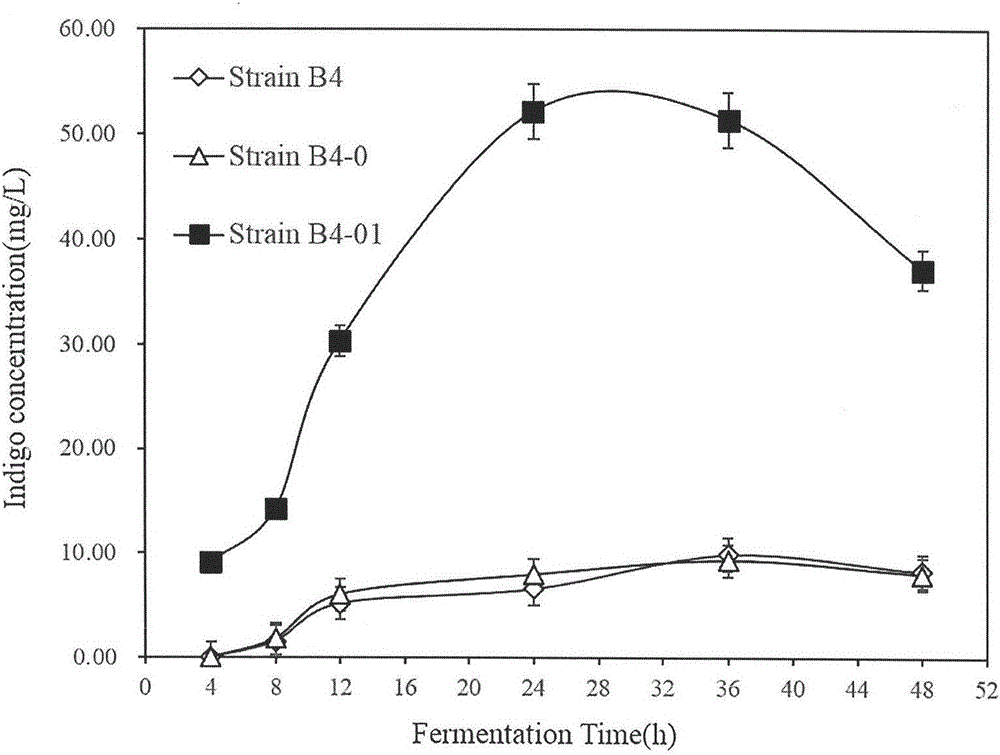
Construction method and application of genetically engineering strain capable of producing indigo pigment
InactiveCN105802986ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesStyrene monooxygenaseRestriction enzyme digestion
The invention relates to a recombinant genetically engineering strain Pseudomonas putida and a preparation method thereof. The engineering strain carries an expression vector with overexpressed endogenous styrene monooxygenase genes styAB. The preparation method of the engineering strain comprises the following steps: 1) endogenous styrene monooxygenase genes styAB fragments are amplified in a Pseudomonas putida genome with a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method; 2) a specific restriction enzyme digestion site is designed and constructed onto a Pseudomonas plasmid vector pBBR1MCS-2; 3) a recombinant plasmid is transformed into Pseudomonas putida with an electroporation method. The recombinant genetically engineering strain Pseudomonas putida prepared with the method can remarkably increase the synthetic amount of the natural pigment indigo and can be applied to industries such as food, medicine, daily chemicals and the like.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Multi-copy beefy meaty peptide expression gene and carrier, and recombination Pichia pastoris construction
InactiveCN101148669AHigh expressionHigh selectivityFungiMicroorganism based processesDelicious peptideRestriction Enzyme Cleavage Site
The present invention is multicopy beefy meaty peptide (BMP) and its expression gene, vector and construction process in recombinant Pichia pastoris, and relates to molecular biotechnology. Based on the codon partiality expressed and translated with Pichia pastoris, are designed a 4 copy BMP expressing gene sequence and essential limiting cleavage sites, 6His and a termination codon. Through in vitro operation, the copy number is increased to 16, the BMP is inserted to expression vector pPIC9, and after linearization of pPIC9, the 16 copy BMP expressing gene as the target segment is recombined onto the Pichia pastoris genome by means of electric transformation. BMP is obtained in high yield through fermentation and methanol induction of Pichia pastoris, and is separated and purified in 6His affiliated Ni column.
Owner:TIANJIN CHUNFA BIO TECH GRP +1
Ultra-binary vector as well as construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN103255166AEasy to filterSelf-segregationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionRestriction Enzyme Cut Site3-deoxyribose
The invention relates to an ultra-binary vector as well as a construction method and an application thereof. The ultra-binary vector is characterized in that a framework vector of the ultra-binary vector is pCMBIA1301-hpt<->, and Xba I-RB-LB-Sal I is inserted between restriction enzyme cutting sites Xba I and Sal I of the framework vector, thereby forming two T-DNA (transferred-deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) regions together with original left and right border sequences; and hpt II is connected into a T-DNA2 region through the restriction enzyme cutting sites, so as to acquire the ultra-binary vector pDT1301 containing the hpt II. The pDT1301 disclosed by the invention contains the hpt II and is convenient for screening callus-resistant and transgenic regenerated plants; and exogenous target genes of the hpt II are not in the same T-DNA region, so that the self-fertilization and separation of transgenic descendants are facilitated, the safe transgenic plants which do not contain selective marker genes are acquired, and obstacles for the safe release of the transgenic plants are cleared.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
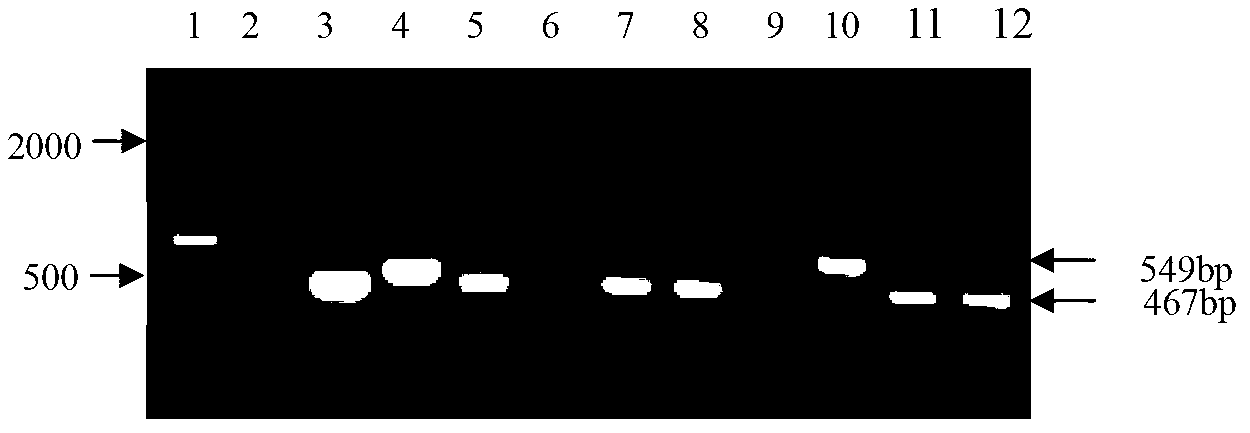
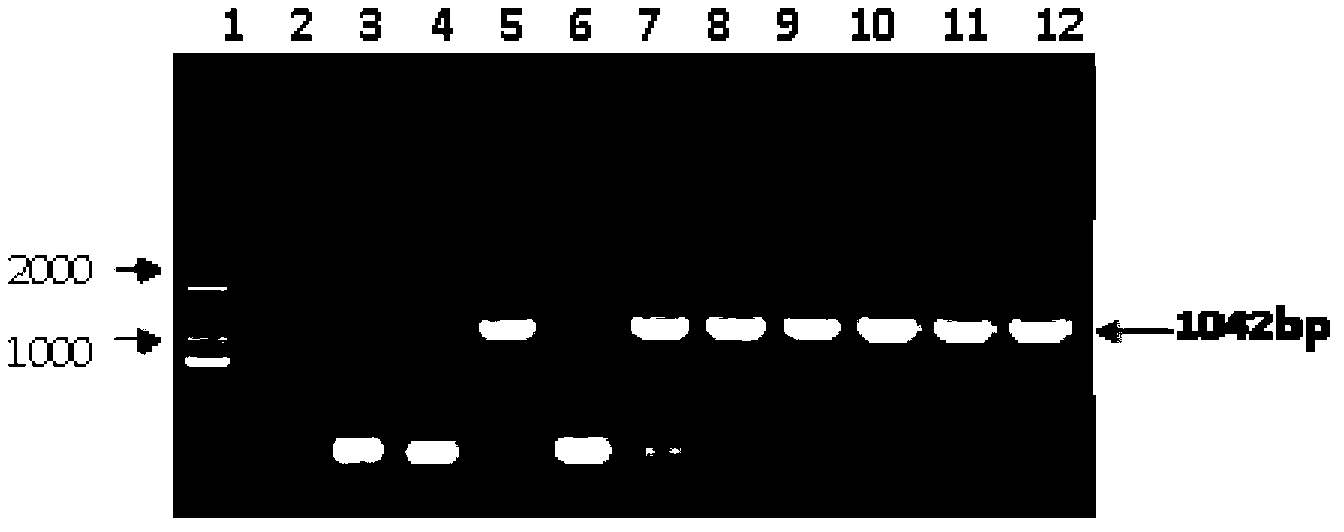
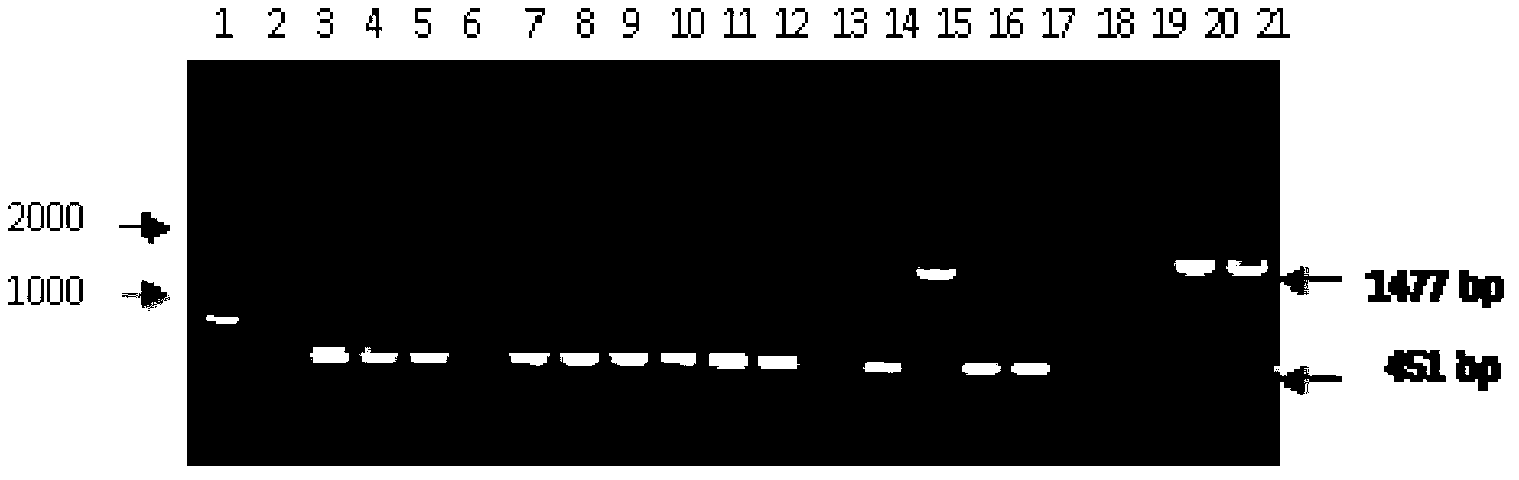
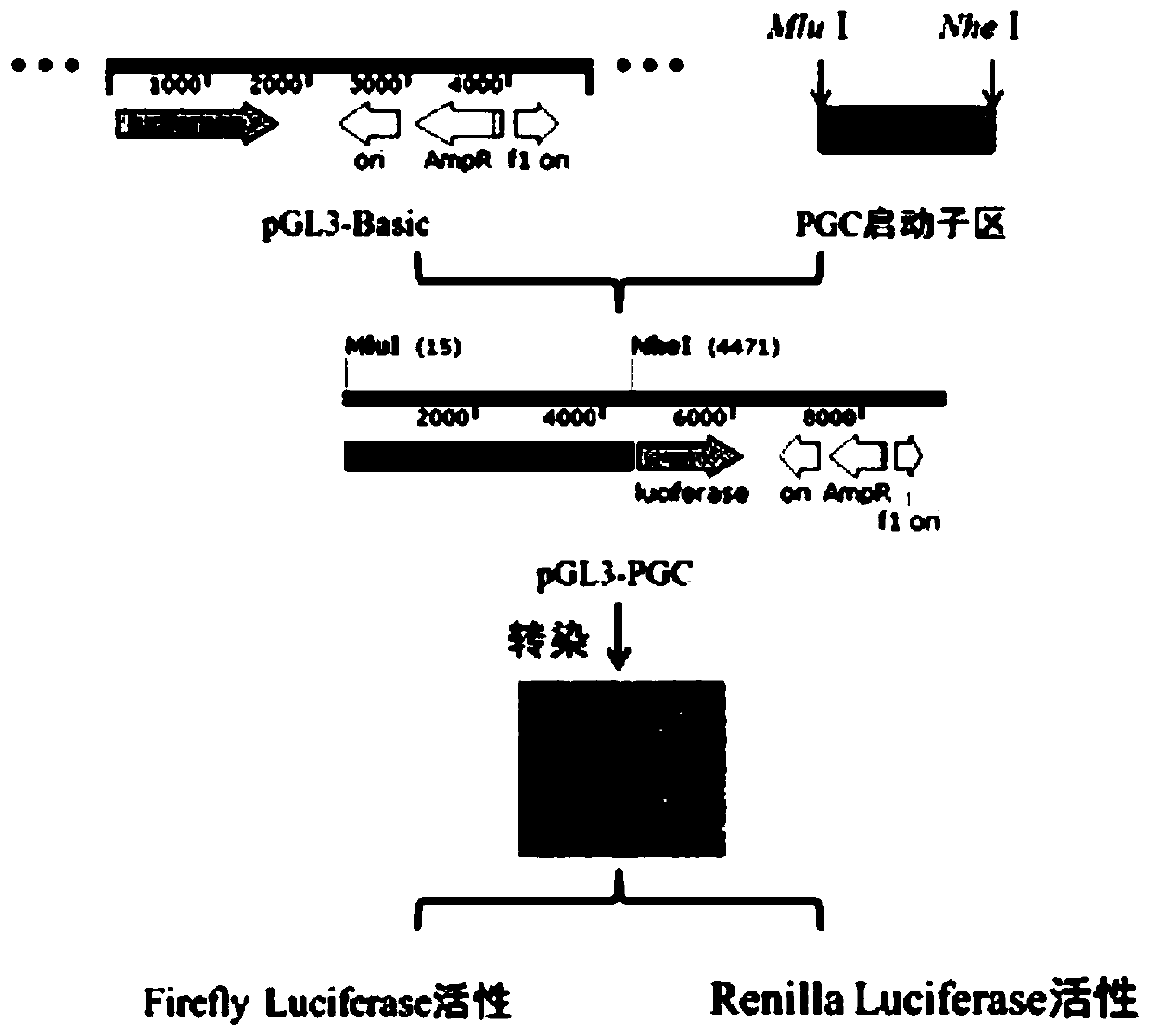
PGC promoter of porcine small intestinal epithelial cell expression and application thereof
ActiveCN110004144AEasy constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorChemical synthesisEscherichia coli
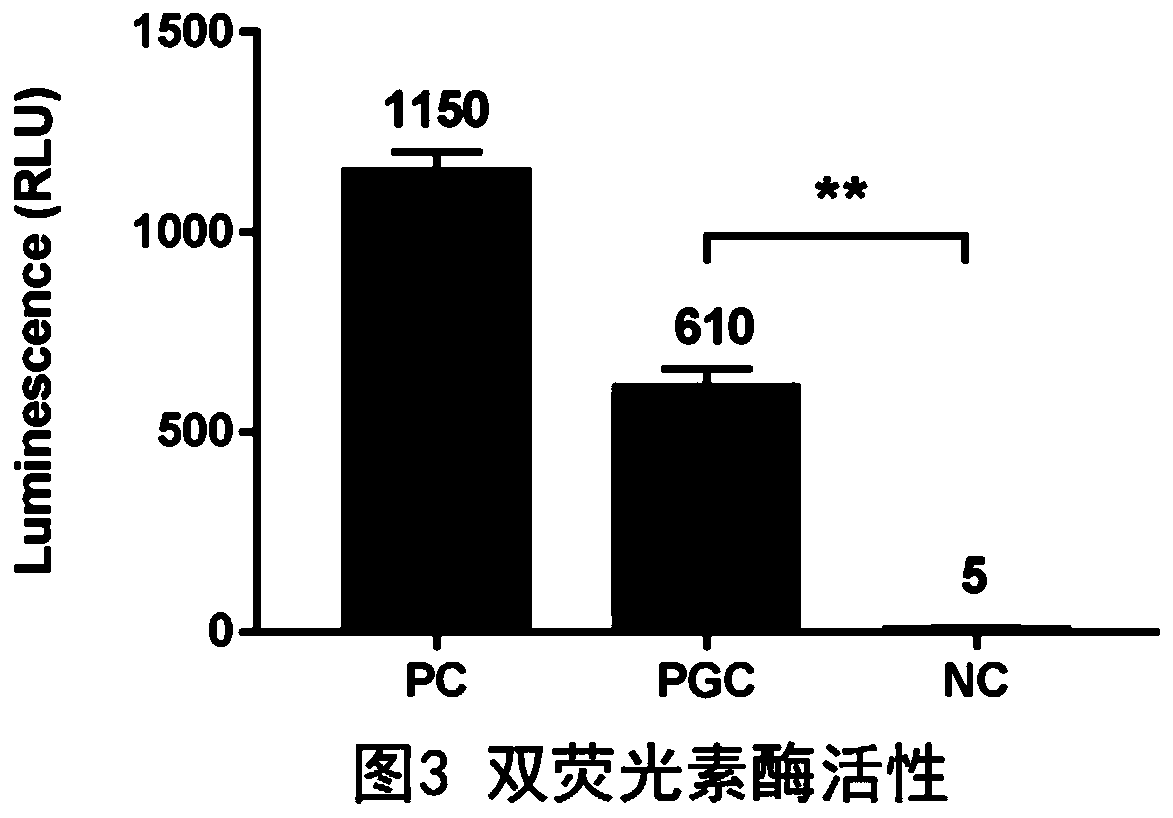
The invention provides a PGC promoter of porcine small intestinal epithelial cell expression and application thereof. The PGC promoter has the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1. A PGC reliablepromoter area is predicted through an online website; a primer is synthesized through a chemical synthesizing method; a PGC promoter sequence is inserted in a pGL3-Basic carrier through restriction enzyme cutting sites MluI and NheI to obtain a PGC-dual-luciferase recombinant plasmid; the plasmid is transfected into escherichia coli to be amplified, the plasmid is extracted, and sequencing and verifying are conducted; the plasmid is transfected into a porcine small intestinal epithelial cell, it is found that the porcine PGC promoter can promote the dual-luciferase gene expression in the porcine small intestinal epithelial cell, it is shown that the promoter can regulate and control the expression of a downstream gene in the porcine small intestinal epithelial cell, a stable and efficientsmall intestinal transfection regulation and control element can be easily established, and the PGC promoter has application value in the research on the transgenic animal preparation and the small intestinal disease gene therapy.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Brucella three-gene recombinant plasmid, construction method thereof and expression and application thereof in escherichia coli
ActiveCN109486846AAvoid infectionPrevent proliferationAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a brucella three-gene recombinant plasmid, a construction method thereof and expression and application thereof in escherichia coli, belonging to the technical field of geneticengineering. According to the technical scheme, a pET-28a(+) plasmid is taken as as a carrier, and a synthetic full-length gene Omp10-Omp28-L7 / L12 is inserted between pET-28a(+) restriction enzyme cutting sites BamHI and XhoI so as to establish a pET-28a(+)recombinant plasmid containing an Omp10-Omp28-L7 / L12 gene segment and a kanamycin screening label, namely pET-28a(+)-Omp10-Omp28-L7 / L12 recombinant plasmid. The brucella three-gene recombinant plasmid has the beneficial effects that brucella Omp10-Omp28-L7 / L12 is successfully cloned and is linked and converted to the recombinant plasmid, sothat the efficient soluble expression of the recombinant plasmid in an escherichia coli expression system is realized, an expressed protein is capable of inhibiting the infection, proliferation and transfer capabilities of brucella in the body fluid and cell levels, promoting the level of an antibody in a mouse and prolonging the immune time, and a novel treatment through is provided for the treatment of brucella diseases.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
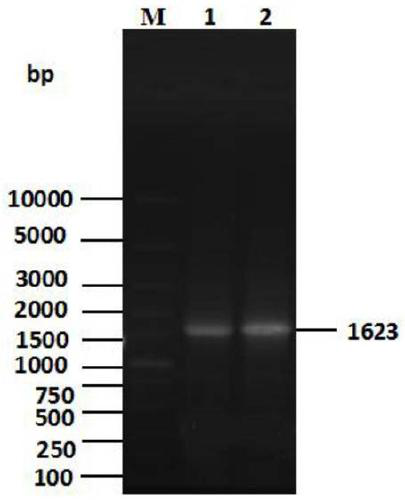
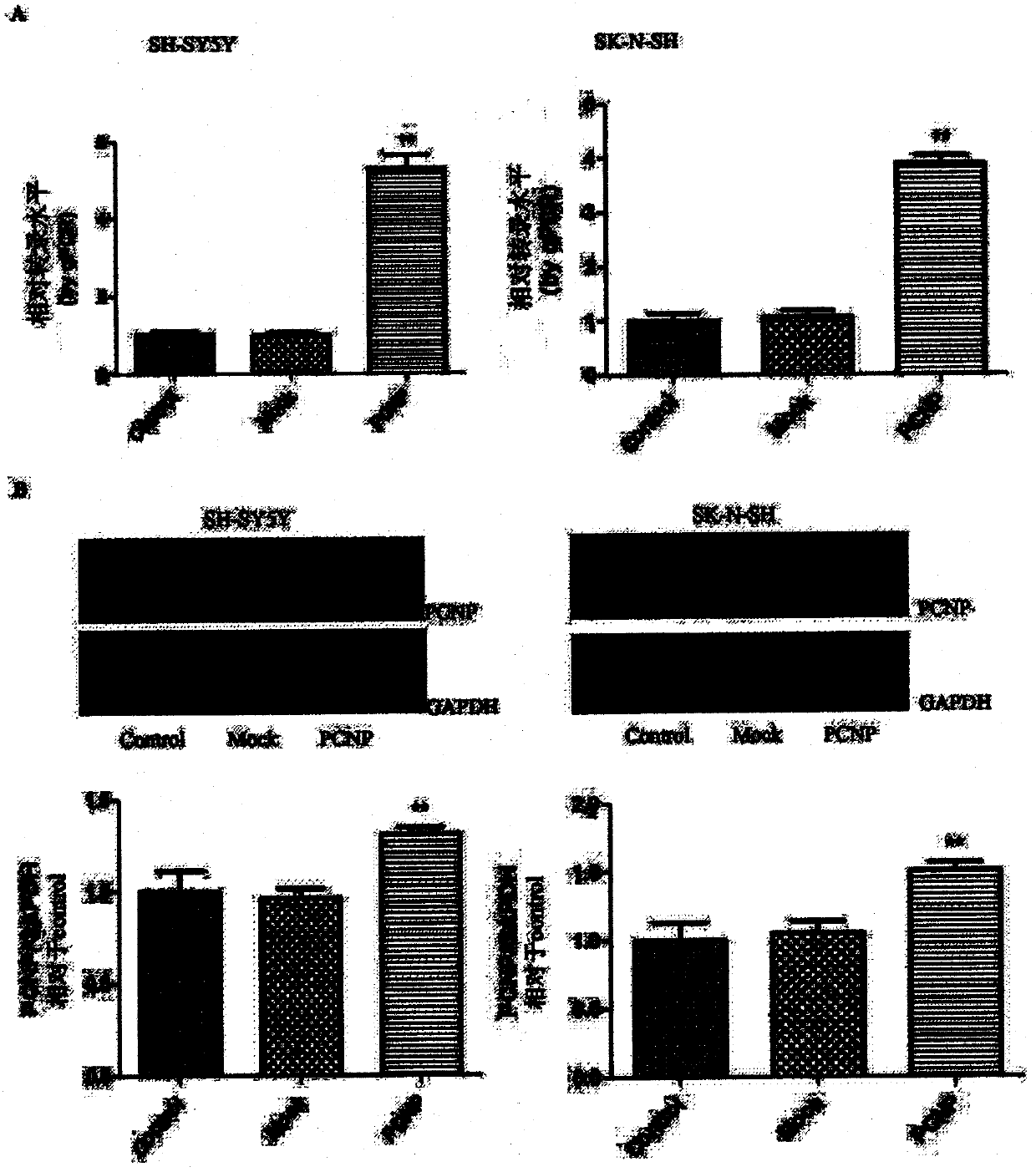
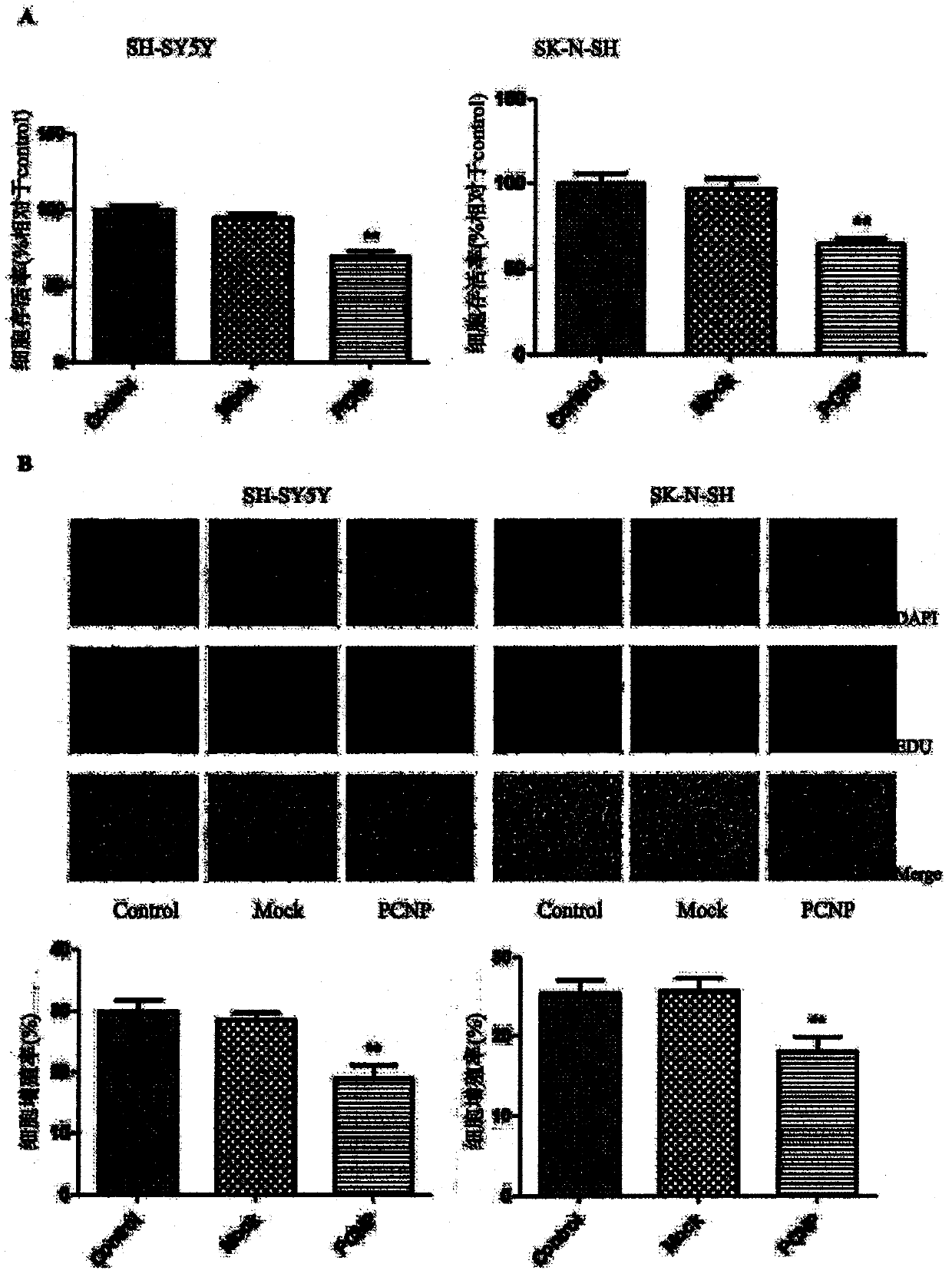
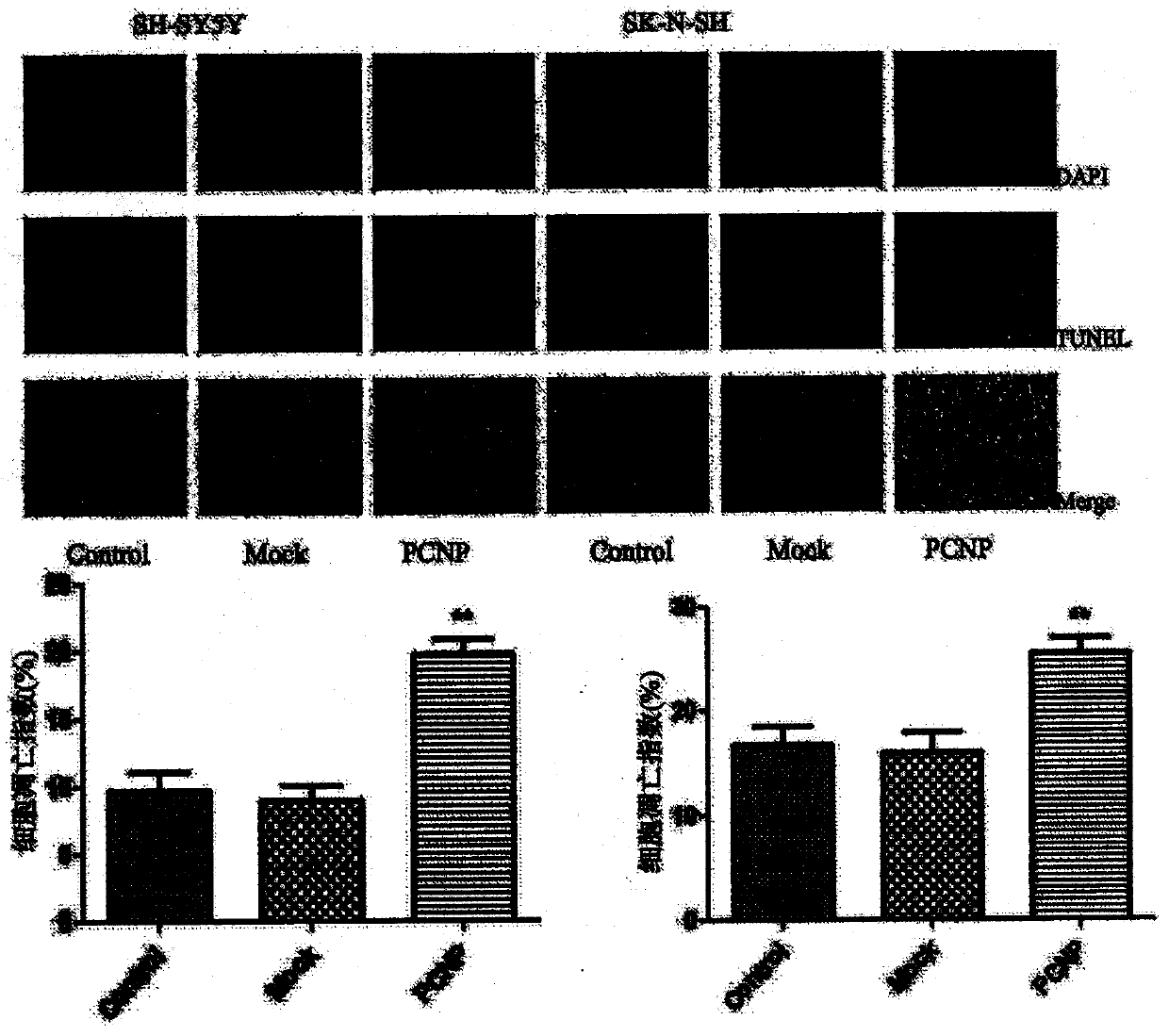
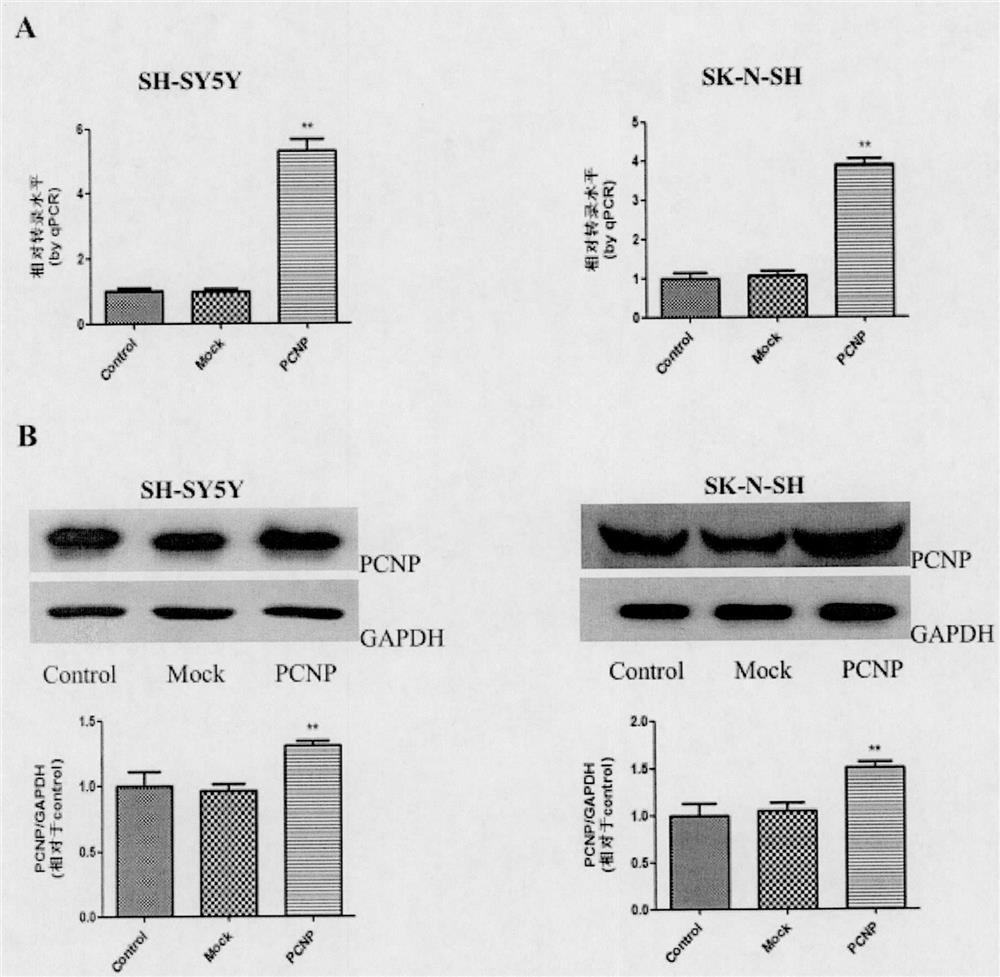
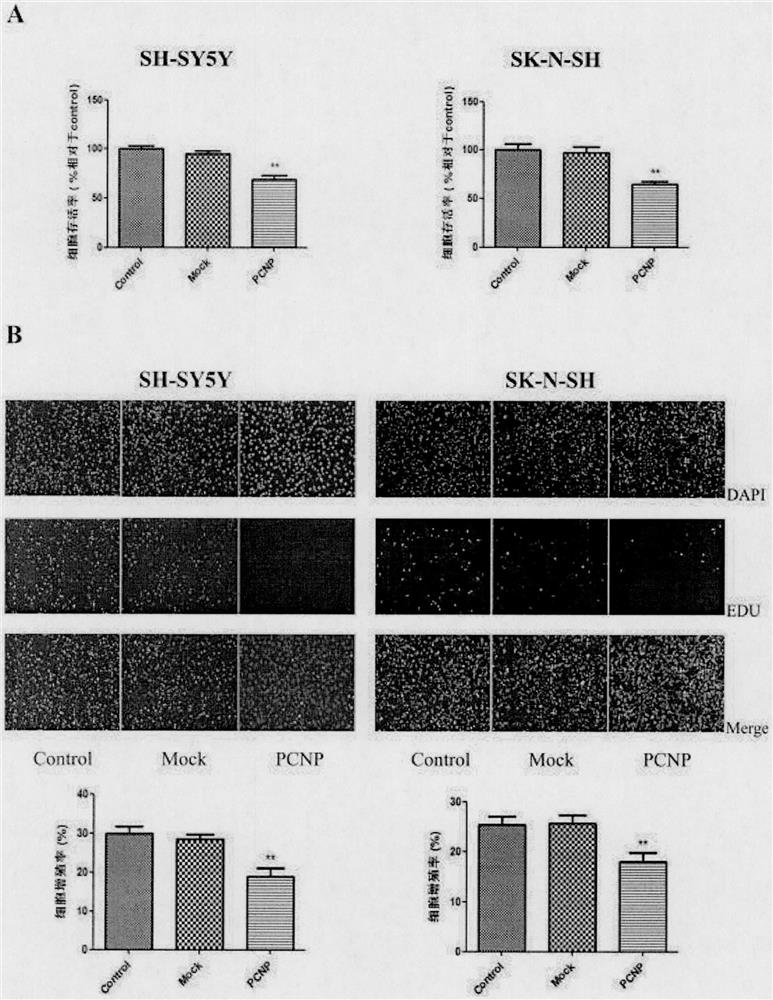
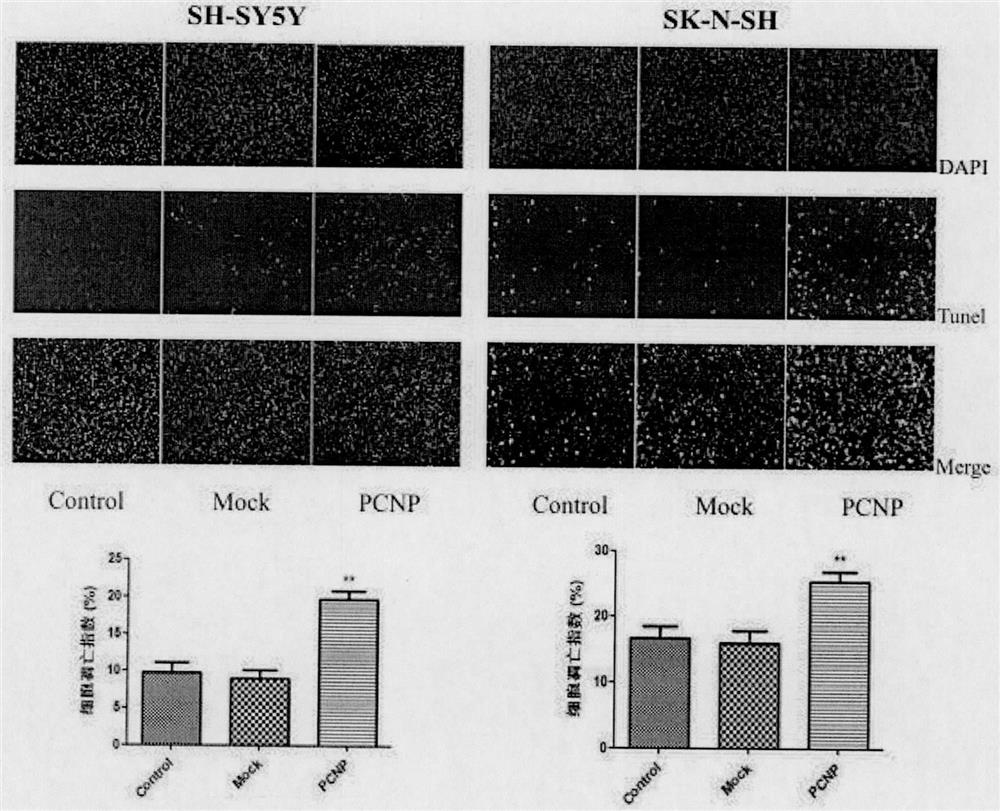
Preparation method and use of medicine over-expressing PCNP gene
ActiveCN107630027AGrowth inhibitionPromote apoptosisGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsEnzyme digestionRestriction enzyme digestion
The invention provides a preparation method and a use of a medicine over-expressing a PCNP gene. The medicine includes a plasmid over-expressing the PCNP gene and a PCNP protein obtained through the over-expression of the PCNP gene. The construction method of the plasmid over-expressing the PCNP gene comprises the following steps: designing a primer according to the sequence of the PCNP gene, andcarrying out PCR amplification on a target gene; carrying out enzyme digestion on restriction enzyme digestion sites Xho I and Kpn I in a GV230 vector to form a linearized GV230 vector; and connectingthe target gene with the linearized GV230 vector to construct a GV230-PCNP vector which is the plasmid over-expressing the PCNP gene. When the medicine over-expressing the PCNP gene is used in humanneuroblastoma cells, the overexpression of the PCNP gene in the human neuroblastoma cells can promote apoptosis, inhibit cell growth, inhibit cell migration and inhibit the growth of human neuroblastomas.
Owner:吴东栋 +8
Construction method and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae genetically engineered bacterium with high yield of 3-methylthio-propanol
InactiveCN104745491AIncrease synthesisEfficient productionFungiTransferasesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
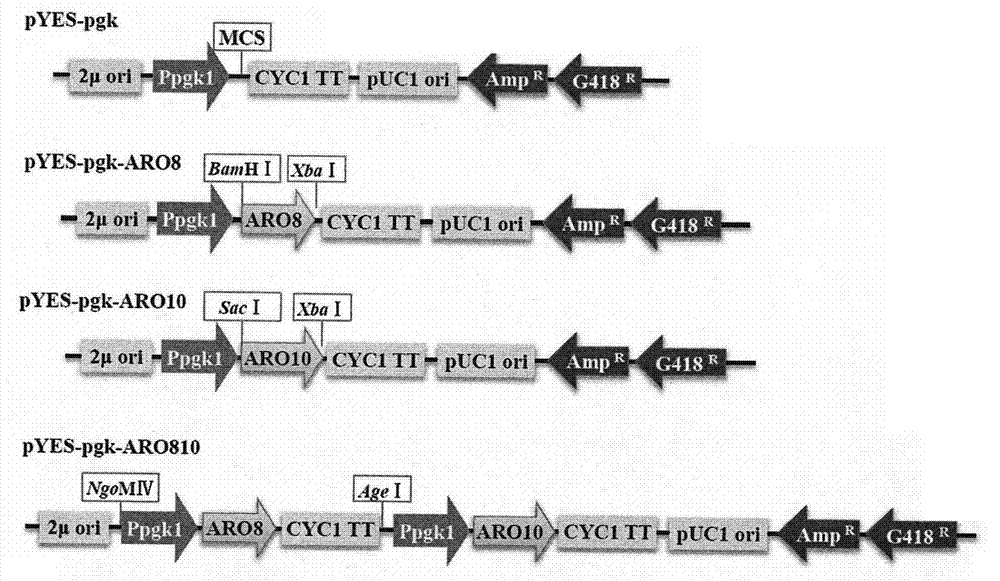
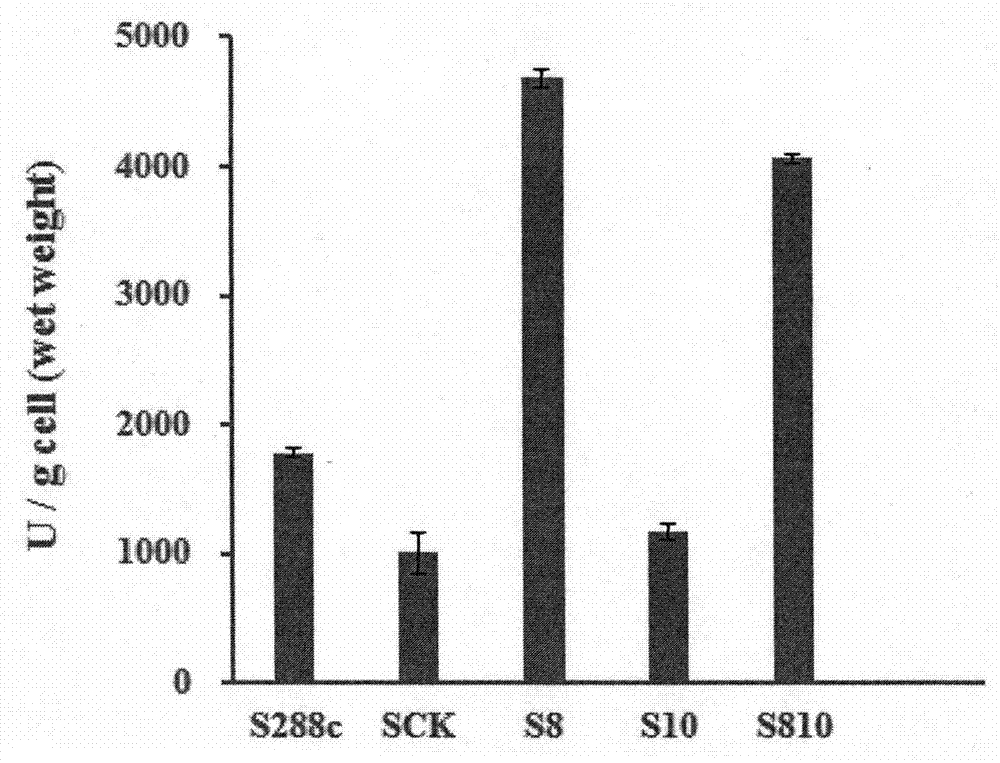
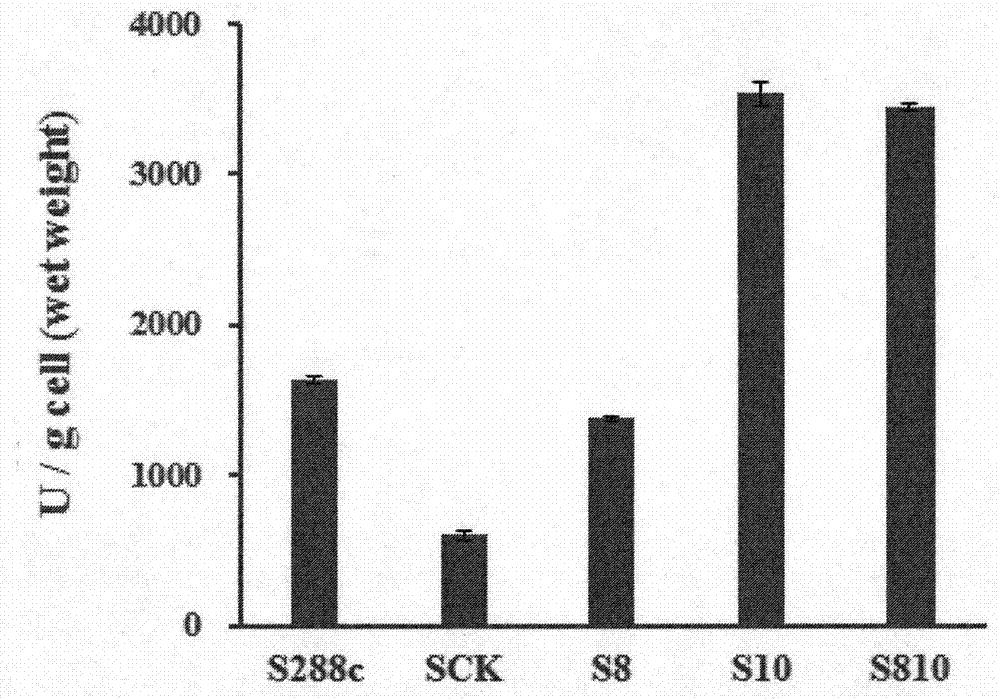
The invention relates to a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain and a preparation method thereof. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain carries a transaminase gene expression carrier and a decarboxylase gene expression carrier which are connected in series. The preparation method of the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain comprises the following steps: 1) respectively amplifying a transaminase gene fragment and a decarboxylase gene fragment from a saccharomyces cerevisiae genome; 2) designing a specific restriction enzyme digestion site, and connecting the specific restriction enzyme digestion site on escherichia coli-saccharomyces cerevisiae shuttle plasmid vector pYES-pgk in series; and 3) transforming recombinant plasmid into saccharomyces cerevisiae by adopting a PEG / LiAc method. The prepared recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain can be used for obviously increasing synthetic amount of a flavour component 3-methylthio-propanol and can be applied to the industries of food, medicines and daily chemicals.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
CRICPR-Cas9-based method for in-vitro modifying adenovirus vectors
The invention discloses a CRICPR-Cas9-based method for in-vitro modifying adenovirus vectors and further provides a molecular cloning method suitable for modifying large plasmid vectors. The CRICPR-Cas9-based method includes: designing proper sgRNA according to a to-be-modified site of a starting plasmid; adopting Cas9 protein and the sgRNA to in-vitro cut the starting plasmid; connecting the starting plasmid which is cut with a target gene on the basis of a homologous recombination method to complete modifying. By using the CRICPR-Cas9-based method, the problem that proper restriction enzyme cutting sites are difficult to find for modifying the large plasmid vectors through conventional molecular biologic means is solved effectively. The method is an improvement of a site mutation kit which generally includes site mutation of target protein and building of truncation with deleted structural domain. By the method, the technical problem that secondary mutation (random mutation caused by PCR enzyme fidelity) is easy to be caused when the site mutation kit is used for mutation of large vectors exceeding 10kb is solved effectively.
Owner:BEIJING PROTEOME RES CENT
Support for fixing nucleotide and process for producing the same
InactiveCN1396954AEffective generationEasy to fixSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideRestriction site
A support for fixing a nucleotide which contributes to the efficient clarification of DNA without damaging the terminal parts of the DNA and, therefore, is useful in the fields of molecular biology, biochemistry and the like. This support for fixing a nucleotide is a chemically modified substrate on which oligonucleotides are immobilized characterized in that the oligonucleotides have a restriction enzyme cleavage site. This support is produced by chemically modifying the substrate, immobilizing a single-stranded oligonucleotide thereon, then hybridizing the single-stranded oligonucleotide with another single-stranded oligonucleotide having a base sequence complementary thereto, and ligating an oligonucleotide having a restriction enzyme site at the end thereof.
Owner:TOYO KOHAN CO LTD
Recombinant lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strain and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101948856AImprove survival rateImprove antioxidant capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDismutase
The invention relates to a recombinant lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strain and a preparation method thereof. The lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strain carries expression vectors of a catalase gene and a superoxide dismutase gene which are connected in series. The method for preparing the engineering strain comprises the following steps of: 1) amplifying catalase gene segments and superoxide dismutase gene segments from genomes of lactobacillus sake and streptococcus thermophiles by a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method; 2) designing a specific restriction enzyme site, wherein the restriction enzyme site is connected in series with an escherichia coli-lactobacillus shuttle plasmid vector pSIP502; and 3) transforming a recombinant plasmid into lactobacillus rhamnosus by an electroporation method. The recombinant lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strain prepared by the method can remarkably enhance oxidation resistance and can be applied to the fermented food industry.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
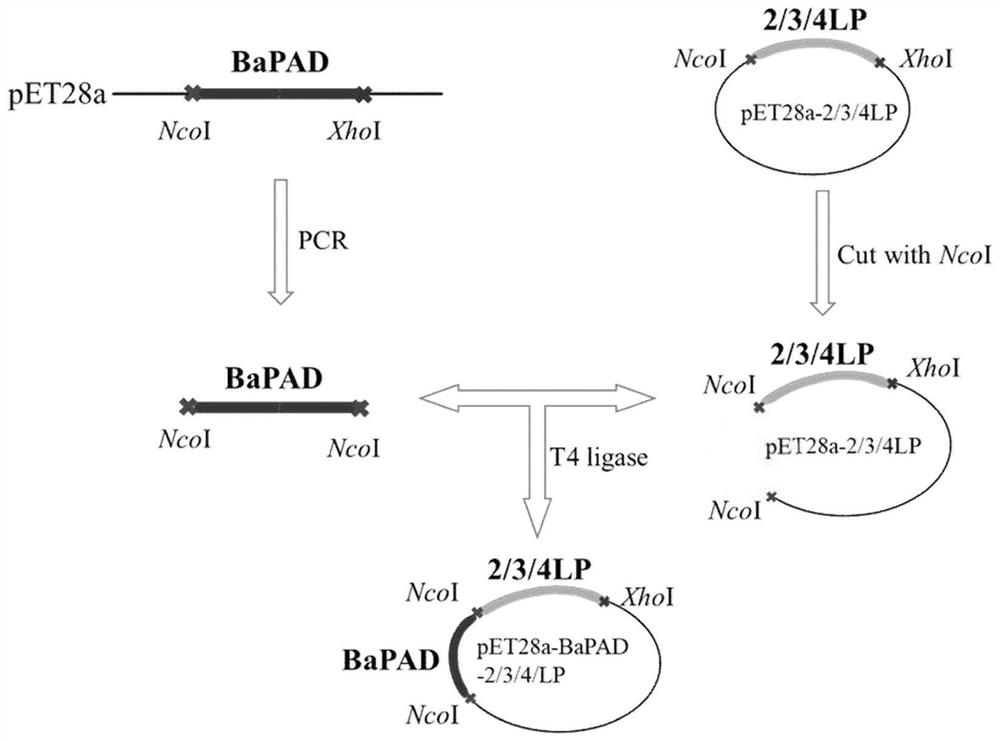
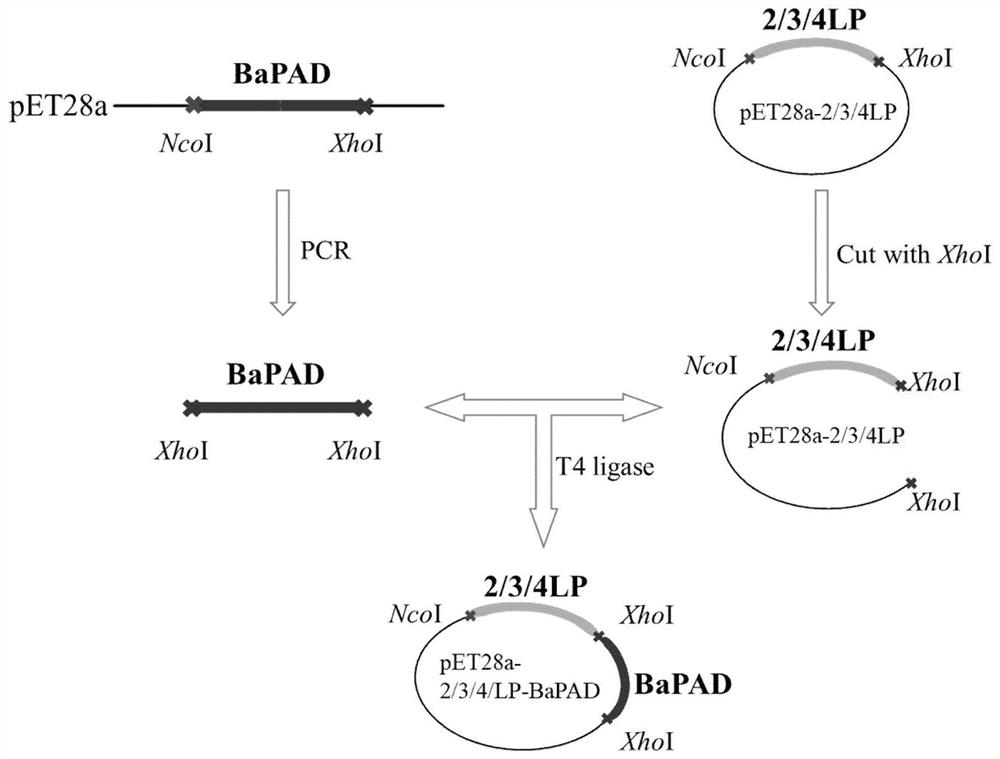
Linker peptide mediated enzyme immobilized BaPAD catalyst, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111662899ARealize the needs of industrialized productionEasy to useFermentationOn/in inorganic carrierPtru catalystPhenolic acid decarboxylase
The invention discloses a linker peptide mediated enzyme immobilized BaPAD catalyst, and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of preparation and application of catalysts. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, inserting linker peptide, which specifically adsorbs zeolite, into a plasmid pET28a-bapad vector containing an encoded phenolic acid decarboxylase BaPAD gene through an Nco I / Xho I restriction enzyme cutting site, and then, immobilizing to obtain the enzyme immobilized BaPAD catalyst on a pre-treated Na-Y zeolite carrier through fusion enzyme, wherein the phenolic acid decarboxylase BaPAD is from bacillus atrophaeus. The biocatalyst prepared by the invention is used for catalyzing FA to produce 4-VG; compared with a method for catalyzing FA to produce 4-VG in a whole-cell manner, the concentration and productivity of 4-VG are improved to 1.97 M and 22.8 g / L / h under the same condition; and the catalyst has good reusability, and canmeet industrial production requirements of 4-VG.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Recombinant plasmid of expression L-lysine transportprotein and engineering bacteria and application
InactiveCN103695454AReduce concentrationReduce feedback inhibitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRestriction Enzyme Cleavage SiteEcoRI
The invention discloses a recombinant plasmid of expression L-lysine transportprotein and engineering bacteria and application. The gene is from corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032, and amplified from a glutamate corynebacterium genome by polymerase chain reaction (PCR); EcoRI and HindIII restriction enzyme cutting sites are respectively added to two ends of the L-lysine transportprotein gene; pKk223-3 connection and transformation after digestion are carried out by using the same restriction enzyme; plasmids are screened and extracted, and electrically converted into the corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032; multiplication of the transportprotein in the corynebacterium glutamicum is realized; the molecular weight of the expression product L-lysine transportprotein is 25081.9Da. By adopting the recombinant L-lysine transportprotein or engineering bacteria of expressing the recombinant transportprotein, the L-lysine can be transferred to the outside from inside of the cell, and the recombinant plasmid has the advantages of high transport efficiency and high transfer speed, and the yield of the L-lysine is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG SHOUGUANG JUNENG GOLDEN CORN CO LTD
Method for remaking multiple cloning sites of known vector
InactiveCN103194474AImprove efficiencyIncrease flexibilityMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliPlasmid Vector
The invention discloses a method for remaking multiple cloning sites of a known vector, namely an adapter primer-PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method. The method comprises the following steps of: amplifying the known DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) fragment of any species by applying an adapter primer which respectively adds multiple restriction enzyme cutting sites to a 5' tail end; carrying out double enzyme cutting by using restriction enzymes positioned on both ends of the amplified fragment, and connecting to the multiple cloning sites of a vector to be remade by using a T4DNA joining enzyme; transforming a connected product into competent escherichia coli; and selecting positive clone, extracting plasmids, verifying whether the remade vector is carried with new enzyme cutting sites or not through enzyme cutting, and retaining a correct plasmid vector. The method disclosed by the invention can meet the requirements of a specific experiment by fast and conveniently adding the new enzyme cutting sites to the multiple cloning sites of the known vector, is low in cost and high in flexibility and can be applied to remaking the multiple cloning sites of the known vector.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Rabies viruses CTN strain complete genome infectious cDNA cloning, and preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101475943BPreserve weak toxicitySafeMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsRabies virus strainCdna cloning
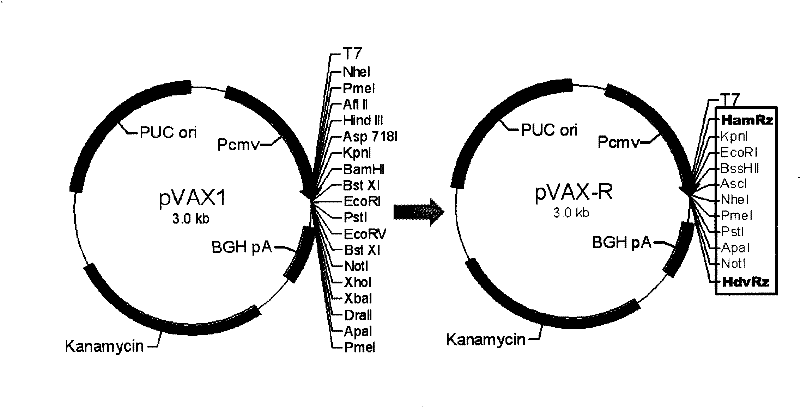
The present invention provides a rabies virus CTN strain whole genome cDNA infectious clone, as well as a method of using reverse genetics technology to save the active rabies virus. The present inventive method includes: using the single restriction enzyme sites in the CTN strain of rabies virus full-length genome to divide the full-length virus into four segments to amplify, simultaneously using the green fluorescent protein gene to substitute 423bp base at the pseudo-gene point, cloning in the pVAX-R expression vector, to construct a recombinant full-length plasmid of the virus genome; performing PCR amplification of nucleoprotein, phosphoprotein, glycoprotein and transcription large protein gene sequence of the CTN strain of the rabies virus, and cloning the amplified fragment into a vector pVAX1, to constitute four auxiliary plasmids in the reverse heredity system; and then using the five plasmids to jointly transfect cells, to rescue the rabies virus. The present invention successfully saves the rabies virus, and has a great significance in the study of the pathogenic mechanism of rabies virus, development of new vaccines, viral vectors and the like areas.
Owner:STATION OF VIRUS PREVENTION & CONTROL CHINA DISEASES PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
A method for building a library and a method for SNP typing
ActiveCN108300764BReduce design difficultyEnsure consistencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationEnzyme actionRestriction Enzyme Cleavage Site
The invention provides a method for building a library, comprising: A, using a specific amplification primer set to perform PCR amplification on a sample to be sequenced containing a SNP site to be tested to obtain an amplification product; at least one of the primer sets Contain IIS type restriction endonuclease recognition sequence on the kind of primer, contain IIS type restriction endonuclease cleavage site on the described amplified product, described IIS type restriction endonuclease cleavage site and described SNP to be tested The distance between the sites is 0 to 5 bases; B. The amplified product is digested with an IIS type restriction endonuclease to obtain the first nucleic acid fragment containing the SNP site to be detected, and the first The first end is formed by enzymatic cleavage on the nucleic acid fragment; C. Under the action of ligase, the first nucleic acid fragment is connected to a sequencing adapter at the first end to obtain library molecules. The invention also provides a SNP typing method. The invention shortens the site detection time, improves the detection accuracy, and unifies the sequencing primers for multiple site detection in the same system.
Owner:WUHAN CONSIDERIN GENE & HEALTH TECH CO LTD
Monkey type 1 adenovirus (SAdV-1) vector system and application thereof
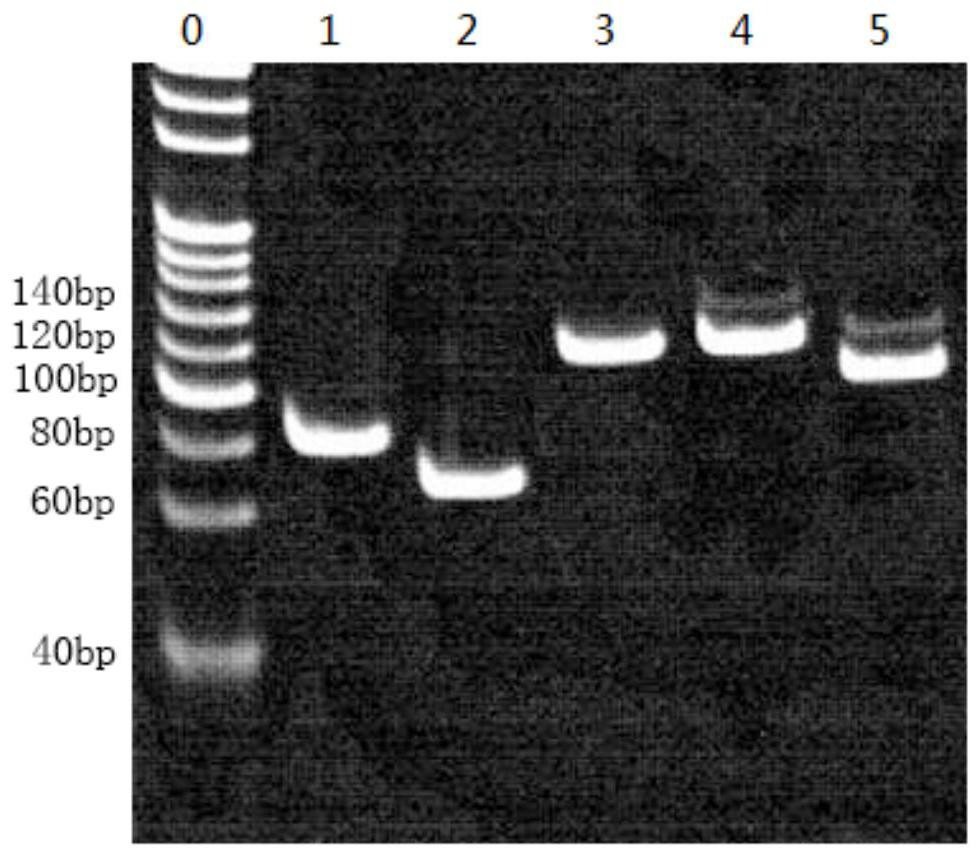
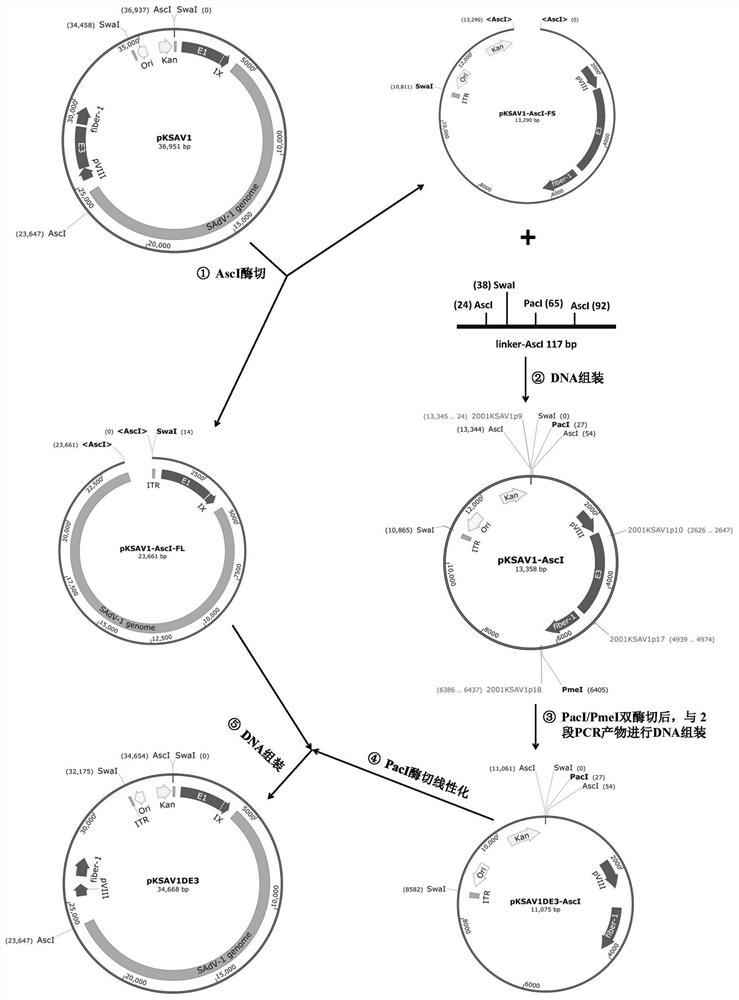
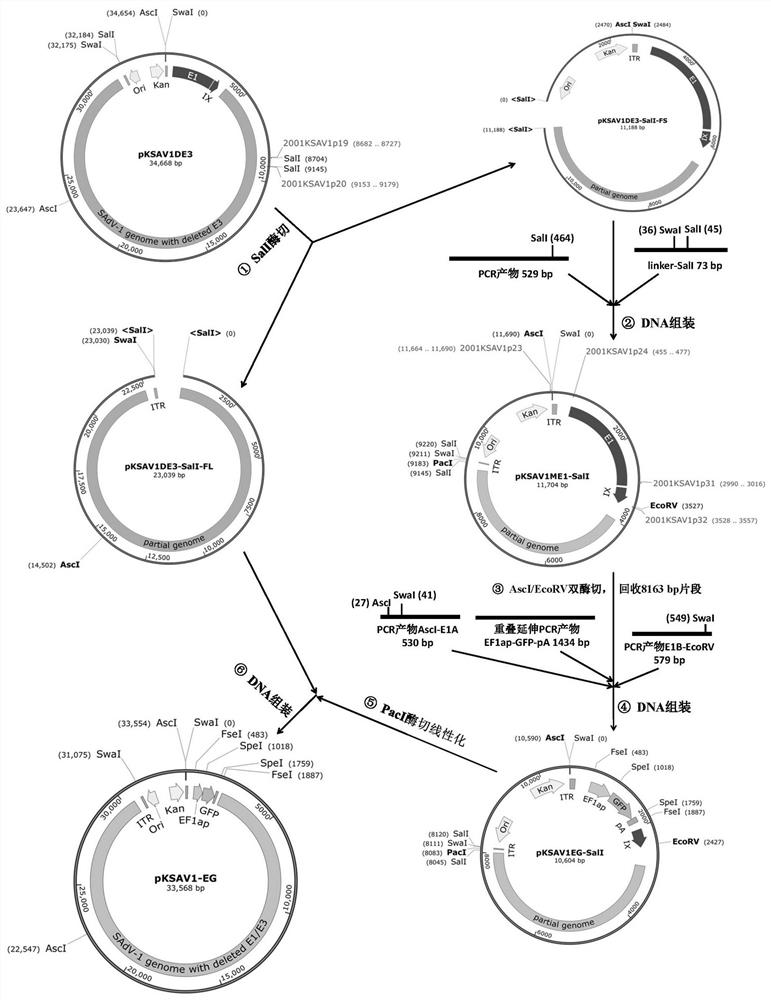
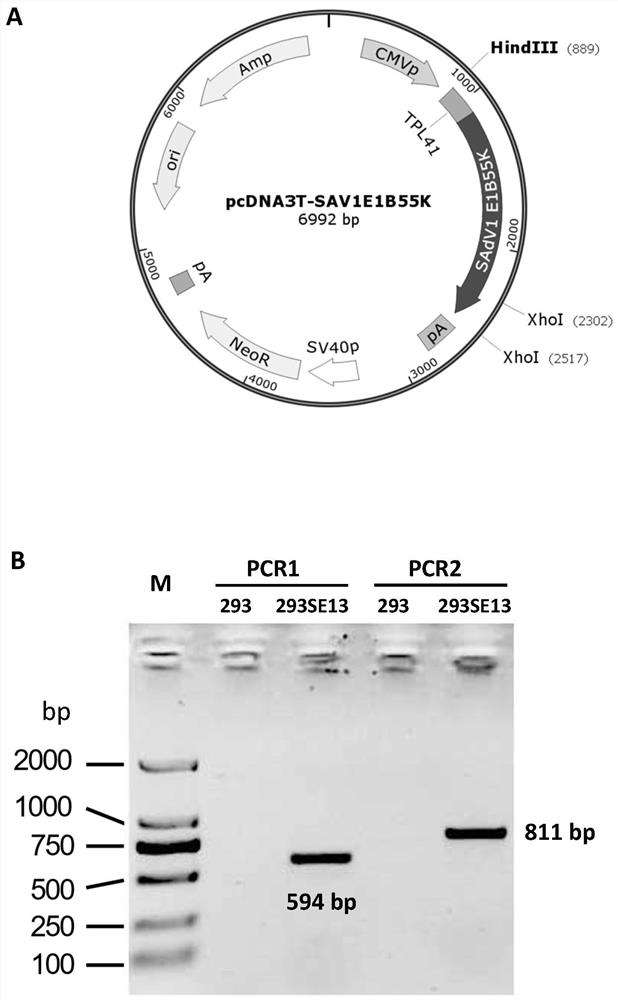
PendingCN113637705AGenetically modified cellsNucleic acid vectorVector vaccineRestriction Enzyme Cleavage Site
The invention provides a monkey type 1 adenovirus SAdV-1 vector system. The monkey type 1 adenovirus SAdV-1 vector system comprises an adenovirus plasmid pKSAV1-EG and a packaging cell line 293SE13. A target gene coding sequence can be inserted into a SpeI restriction enzyme cleavage site of the pKSAV1-EG plasmid through DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) assembly or restriction enzyme cleavage-ligation cloning to generate an adenovirus plasmid carrying the target gene; and an exogenous gene expression cassette containing an expression regulatory sequence can be similarly inserted into an FseI site of pKSAV1-EG, and an adenovirus plasmid carrying the exogenous gene expression cassette is generated. By transfecting a 293SE13 cell with the adenovirus plasmid subjected to SwaI linearization, and a recombinant virus is rescued; and the 293SE13 is also used for amplifying the recombinant virus. The generated SADV-1 virus genome is deleted in an E1 / E3 part, and the SADV-1 virus is a replication-defective virus. The human lacks the pre-stored immunity to the SADV-1, and the target cells of the SADV-1 are different from those of a common HAdV-5 vector, so that the vector system is predicted to have a wide application prospect in the fields of gene therapy and vector vaccines.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所
Preparation and application of a drug for overexpressing PCNP gene
ActiveCN107630027BGrowth inhibitionPromote apoptosisGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsApoptosisRestriction Enzyme Cleavage Site
The invention provides the preparation and use of a drug overexpressing PCNP gene. The medicine includes a plasmid overexpressing PCNP gene and PCNP protein obtained by overexpressing PCNP gene. The construction method of the plasmid overexpressing PCNP gene, which comprises the following steps: according to the PCNP gene sequence, design primers, PCR amplify the target gene; carry out restriction enzyme cutting site Xho I and Kpn I in the GV230 vector. , to form a linearized GV230 vector; the target gene is connected with the linearized GV230 vector to construct a GV230-PCNP vector, which is a plasmid that overexpresses the PCNP gene. When the drug overexpressing PCNP gene is used in human neuroblastoma, the overexpression of PCNP gene in human neuroblastoma can promote cell apoptosis, inhibit cell growth, inhibit cell migration, and inhibit the growth of human neuroblastoma. grow.
Owner:吴东栋 +8
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method for eliminating genes
InactiveCN102604932BGood repeatabilityShort experiment cycleDNA preparationRestriction Enzyme Cleavage SiteBase Pair Mismatch
The invention discloses a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method for eliminating genes, which can eliminate non-target genes in a mixed gene population. The key points of the technology disclosed by the invention are as follows: making or artificially synthesizing the non-target genes into short-sequence gene eliminating primers, performing enzyme cutting on the mixed gene population containing target genes, adding a restriction enzyme cutting site with a base pair mismatch and a joint with Poly (dA), purifying, using the mixed gene population as a template, restoring the correct enzyme cutting site through the gene eliminating primers and annealing extension of the template in the PCR, and then using the heat-resistant restriction enzyme cutting site to eliminate the joint of the non-target genes so as to prevent amplification of the non-target genes. The reaction is cycled by utilizing a PCR instrument: 30s at the temperature of 94 DEG C, 40s at the temperature of 60 DEG C, 8min at the temperature of 75 DEG C, 12-18 cycles are performed for enriching the target genes, and then the conventional PCR is adopted for further amplifying the target genes. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high efficiency, high speed, simplicity and convenience in operation, low cost, high repeatability, good separation effect and low false positive rate.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Ultra-binary vector as well as construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN103255166BFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyRestriction Enzyme Cleavage Site
The invention relates to an ultra-binary vector as well as a construction method and an application thereof. The ultra-binary vector is characterized in that a framework vector of the ultra-binary vector is pCMBIA1301-hpt<->, and Xba I-RB-LB-Sal I is inserted between restriction enzyme cutting sites Xba I and Sal I of the framework vector, thereby forming two T-DNA (transferred-deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) regions together with original left and right border sequences; and hpt II is connected into a T-DNA2 region through the restriction enzyme cutting sites, so as to acquire the ultra-binary vector pDT1301 containing the hpt II. The pDT1301 disclosed by the invention contains the hpt II and is convenient for screening callus-resistant and transgenic regenerated plants; and exogenous target genes of the hpt II are not in the same T-DNA region, so that the self-fertilization and separation of transgenic descendants are facilitated, the safe transgenic plants which do not contain selective marker genes are acquired, and obstacles for the safe release of the transgenic plants are cleared.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
pcr-rflp primers and methods for identifying mycoplasma goat subspecies and other members of the mycoplasma cluster
ActiveCN108950036BIdentification method is simpleIdentification methods are cheapMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDistinctinRestriction Enzyme Cleavage Site
The present invention provides PCR-RFLP primers and methods for identifying Mycoplasma mycoplasma goat subspecies and other members of Mycoplasma mycoplasma cluster, the upstream primer P1: 5'-ACAAAAAATATTAGCATTCAAACTT-3', the downstream primer P2: 5'-GGTGTTATTTTTGATTTAG ATGGAG-3' , the method is to use the differences in the enzyme cutting sites contained in the pgmb protein gene coding region of mycoplasma goat subspecies and other members of the mycoplasma cluster to distinguish, including DNA extraction, PCR amplification to obtain the corresponding target fragment RFLP analysis was performed after HindⅢ digestion. The identification method of the invention has simple operation and high accuracy.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
A method for detecting kanamycin
InactiveCN105925699BAchieve recyclingEnhanced detection signalMicrobiological testing/measurementKanamycinSpecific detection
The invention provides a method for detecting kanamycin. The kanamycin is detected by using double restriction enzyme cleavage sites and color change caused by G-tetrad. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps: carrying out specific binding on a hair pin and kanamycin; adding a color developing agent into a homogeneous phase reaction mixed liquor for display detection. According to the method, high specific detection for the target object kanamycin is realized by using the oxidability of the G-tetrad; the effect of signal amplification is reached by using nucleic acid tool enzymes.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
A method for detecting mutation and methylation of tumor-specific genes in ctDNA
ActiveCN112176419BEffective filteringReduced sample size requirementsNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementInsertion deletionRestriction Enzyme Cleavage Site
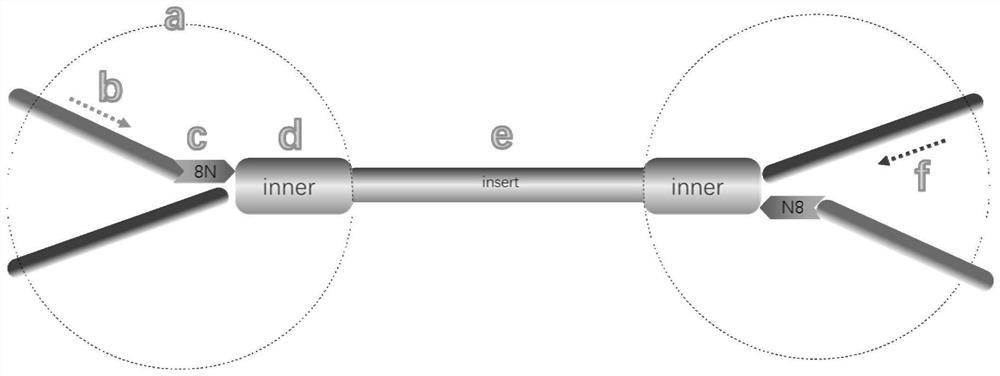
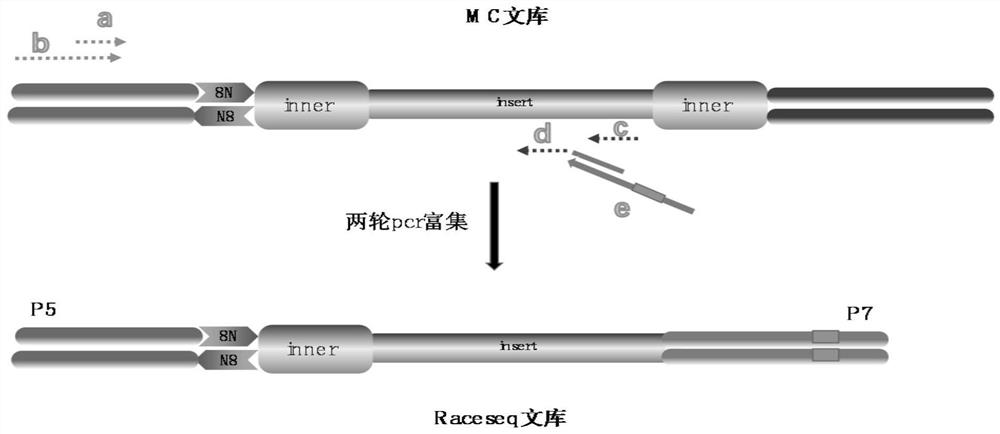
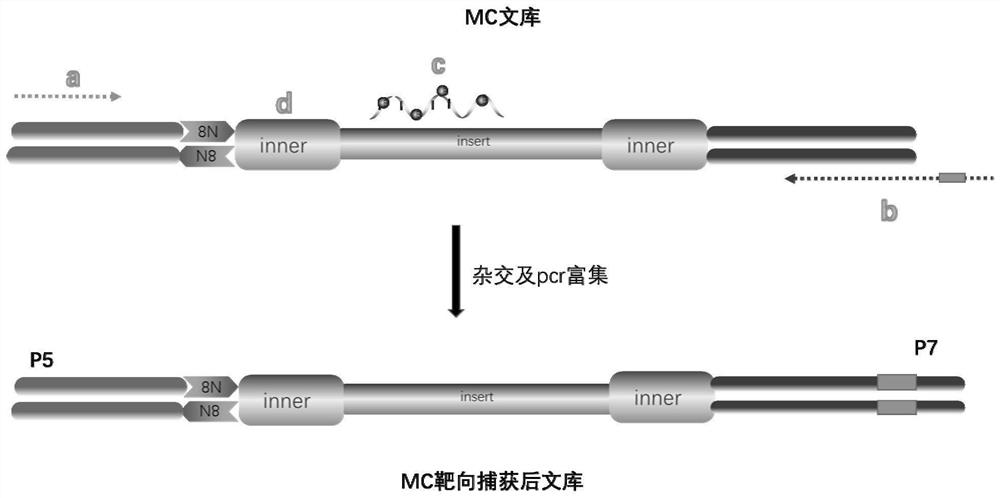
The invention discloses a method for detecting the variation and methylation of tumor-specific genes in ctDNA. The method can simultaneously detect the variation of tumor-specific genes in ctDNA (including point mutations, insertion-deletion mutations, and HBV integration) in one sample. and / or methylation method, not only the sample size requirement is low, but also the MC library prepared by this method can support 10‑20 follow-up detections, and the results of each detection can represent all original ctDNA samples The mutation status and the methylation modification of the region covered by the restriction site will not cause a decrease in sensitivity and specificity. The invention has important clinical significance for early tumor screening, disease tracking, curative effect evaluation, prognosis prediction, etc., and has great application value.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI +1
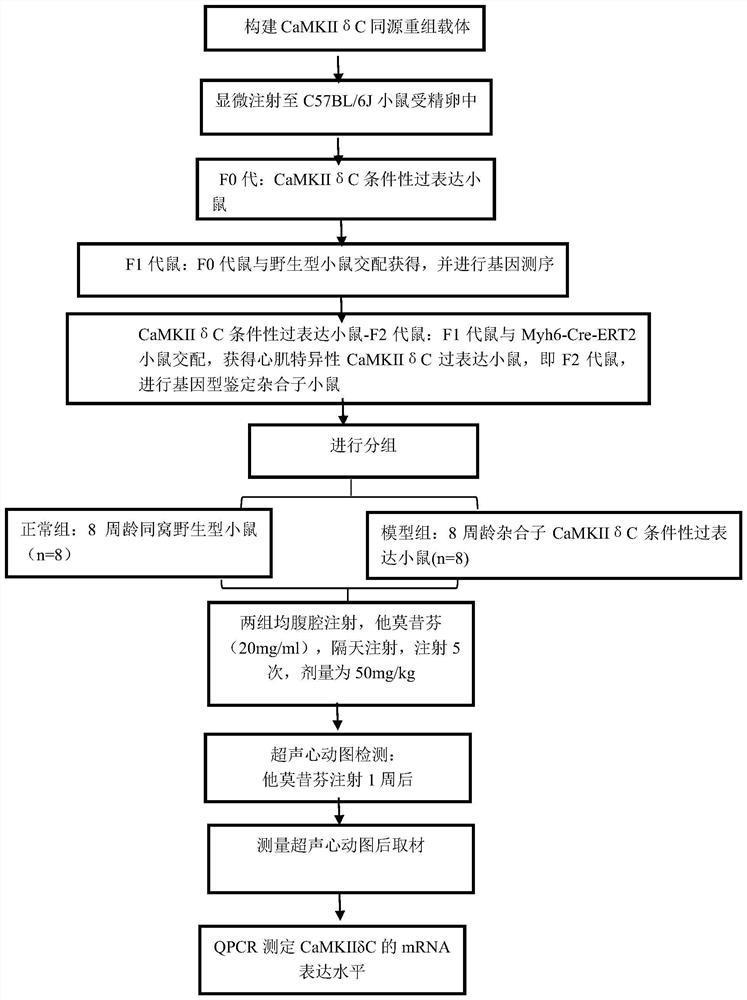
Construction method for CamkIIdeltaC gene overexpression induced ejection fraction reduction type heart failure
PendingCN114657211ALow costImprove efficiencyHydrolasesTransferasesMedicineRestriction Enzyme Cleavage Site
The invention discloses a construction method for CamkII delta C gene overexpression induced ejection fraction reduction type heart failure, which comprises the following steps: constructing a CaMKII delta C gene overexpression mouse by using a Crisp-cas9 transgenic technology; tamoxifen is injected every other day, CaMKII delta C gene overexpression is induced, and the heart failure phenotype with reduced ejection fraction appears in the mouse after one week. Meanwhile, by using a conventional CRISPR-Cas9 in-vitro transcription technology, the effect of improving the error-tolerant rate is achieved, meanwhile, the transcription efficiency is improved, the transcription cost is reduced, and compared with common methods such as TA cloning, restriction enzyme cutting cloning and smooth end cloning, the method has the defects that the connection efficiency is low, specific restriction enzyme cutting sites are needed, and consumed time is long; according to the invention, any DNA fragment can be cloned into any linearized vector by adopting the In-Fusion Cloning method, and after the PCR reaction is carried out, the high fidelity of the target gene is fully ensured.
Owner:DONGFANG HOSPITAL BEIJING UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
A drug conjugate for targeted traceless release and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN109908363BTargetedWith syntheticPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAptamerCyclic peptide
The invention relates to a drug conjugate for targeted traceless release, a preparation method and application thereof. Specifically disclosed is a targeted traceless release drug conjugate, the structure of which is T-L-D, T represents a targeting group, L represents a linker, and D represents an active ingredient, wherein T is selected from RGD peptide, cyclic RGD Peptides, RGD peptide derivatives, RGD cyclic peptide derivatives, folic acid, membrane-penetrating peptides, nucleic acid aptamers, fluorescent dyes; D is a pharmaceutical active ingredient with a tertiary amino group, preferably coyba peptide A, coyba peptide A Derivatives; L is A-BC-E, BC represents the enzyme cleavage site. The present invention uses cyclic RGD which has targeting effect and is easy to synthesize and modify instead of expensive and difficult-to-synthesize antibody as the targeting molecule, which is simpler to prepare and achieves high specific targeting effect. Under the action, through the self-elimination of p-aminobenzyl quaternary ammonium salt, the traceless release of the active ingredient of the drug is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
A dna molecular labeling method based on single primer amplification reaction
InactiveCN104946742BConvenient assisted selection breedingOvercome the disadvantage of being prone to false positivesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBinding siteGenomic DNA
The invention discloses an SPAR (single primer amplification reaction) based DNA molecular marking method, which belongs to the field of biotechnology. The method comprises the following steps: designing and synthesizing a single primer, extracting a sample genomic DNA as a template, carrying out PCR amplification in a conventional PCR reaction system and a conventional reaction procedure by using the single primer and the sample DNA template, and after an amplified product is subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis separation, detecting the polymorphism between two binding sites in a genomic gene exon area, wherein the sequence length of the single primer is 17 bp, six base filling sequences at a 5' terminal are AT-base-rich restriction enzyme cleavage site sequences, a mid-core area sequence is randomly composed of 8 GC bases, and 3 selective bases are arranged at the last 3' terminal. The primer in the invention is good in universality, and the DNA molecular marking method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple operation, high stability, good repeatability, number abundance, high specificity, high polymorphism, reliable results, and the like.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院经济作物研究所
High-density fermentation and purification process for recombination high temperature-resistant hyperoxide dismutase
InactiveCN101275144BAvoid pollutionSimple purification processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
The present invention provides a high density fermentation and a purification process of a recombination high temperature resistance superoxide dismutase, the construction method of the invention includes: using gene coded for SOD in a thermophilic bacteria as a template, designing specific primer amplification target gene having restriction enzyme sites, after double digestion, connecting to plasmid vector pET28a after the same double digestion, constructing a recombinant plasmid, named for pSOD, transforming plasmid pSOD to competence escherichia coli BL21(DE3) by chemical transformation method, obtaining strain having high SOD yield after screening, completing the construction of SOD engineering bacteria; the fermentation process includes four steps of first order seed culture, secondary order feed culture, batch fermentation and induced expression, fermentation product SOD is finally obtained; the fermentation process realizes high level expression of SOD, the expression of the target protein is more than 60% of the bacterial protein total; SOD has excellent thermal stability and heat resistance, the expression product accounts for more than 60% of the whole proteins, and fully soluble protein, avoiding any trouble in the course of inclusion body renaturation; the purification process is simple, having high yield, lower cost, the final product SOD has high purification, high activity and strength stability.
Owner:YANGTZE DELTA REGION INST OF TSINGHUA UNIV ZHEJIANG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com