Recombinant lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strain and preparation method thereof
A technology of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and engineering strains, applied in the field of recombinant Lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strains and its preparation, to achieve the effect of improving antioxidant capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
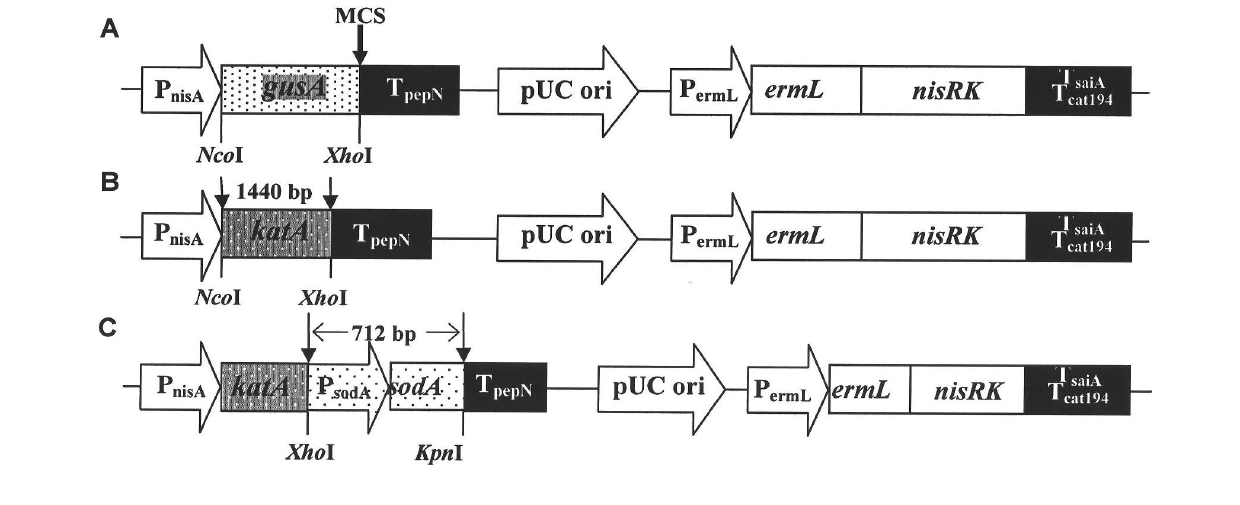
[0025] Embodiment 1 The construction of the plasmid vector carrying the target gene katA
[0026] 1.1 Lactobacillus sake genomic DNA extraction
[0027] The genome was extracted using a bacterial genome DNA extraction kit (Tiangen Biochemical Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd.), as follows:
[0028] (1) Take 5ml of Lactobacillus sake cultured to the logarithmic phase, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 minute, discard the supernatant, add 200 μl of TES to resuspend once, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 minute, and aspirate the supernatant as much as possible;
[0029] (2) Add 180 μl of lysozyme (20 mg / ml), and treat in a water bath at 37°C for 1 hour;
[0030] (3) Add 20 μl RNase (10 mg / ml), shake slightly for 15 seconds, and place at room temperature for 5 minutes;
[0031] (4) Add 20 μl proteinase K solution and mix gently;
[0032] (5) Add 220 μl of buffer GB, shake for 15 seconds, treat in a water bath at 70°C for 10 minutes, and briefly centrifuge to remove water beads on the c...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Embodiment 2 The construction of the plasmid vector carrying the target genes katA and sodA
[0081] 2.1 Extraction of genomic DNA from Streptococcus thermophilus
[0082] The method is the same as in Example 1.
[0083] 2.2 PCR amplification of catalase gene fragment sodA
[0084] Upstream primer: 5'-CCG CTCGAG CAAGATTTTGTAAG-3’
[0085] Downstream primer: 5'-GG GGTACC TGAGGATGATTCTAGAC-3'.
[0086] Xho I and Kpn I restriction sites were introduced into the upstream and downstream primers respectively, that is, the underlined part in the sequence.
[0087] The PCR procedure is as follows:
[0088]
[0089] Component Addition (unit: μl)
[0090]
[0091] The genomic DNA of Streptococcus thermophilus 1
[0092] Upstream primer (10μM) 0.5
[0093] Downstream primer (10μM) 0.5
[0094] dNTPs (10mM) 0.5
[0095] Ex Taq enzyme 0.5
[0096] 10× Reaction Buffer 2 ...
Embodiment 3
[0117] Example 3 Preparation of recombinant Lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strain
[0118] 3.1 Preparation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus competent
[0119] Lactobacillus rhamnosus was cultured in MRSS (MRS, 0.3M sucrose, 1% glycine (W / W)) medium and grown to OD 600 =0.4~0.6, take 10ml of bacterial liquid, centrifuge at 6000rpm, 4℃ for 8min, collect the bacteria; add 2ml of rinse solution (0.3M sucrose, 1mM MgCl) 2 ) for 2 times, centrifuge at 6000 rpm for 8 min at 4°C, discard the supernatant; add 2 ml of 30% (W / W) PEG-1500 to resuspend the cells, centrifuge at 6000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C, discard the supernatant, and use 200 μl of 30% Use after resuspending in PEG-1500.
[0120] 3.2 Electrotransformation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus with recombinant plasmids
[0121] Take 40 μl of Lactobacillus rhamnosus competent cells, mix with 2 μl of recombinant plasmid pSIPCS, transfer it to a 2mm electroporation cup, use Bio-Rad Gene Pulser Xcell TM Type electrotransformer, electroco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com