Method for curing of an ink or toner layer and printing system with curing unit
A printing system and ink technology, which is applied to the equipment, ink, and printing of the electrical recording process using charge graphics, which can solve the problems of expensive ink, ink yellowing, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing odor, less migration, and improving surface curing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
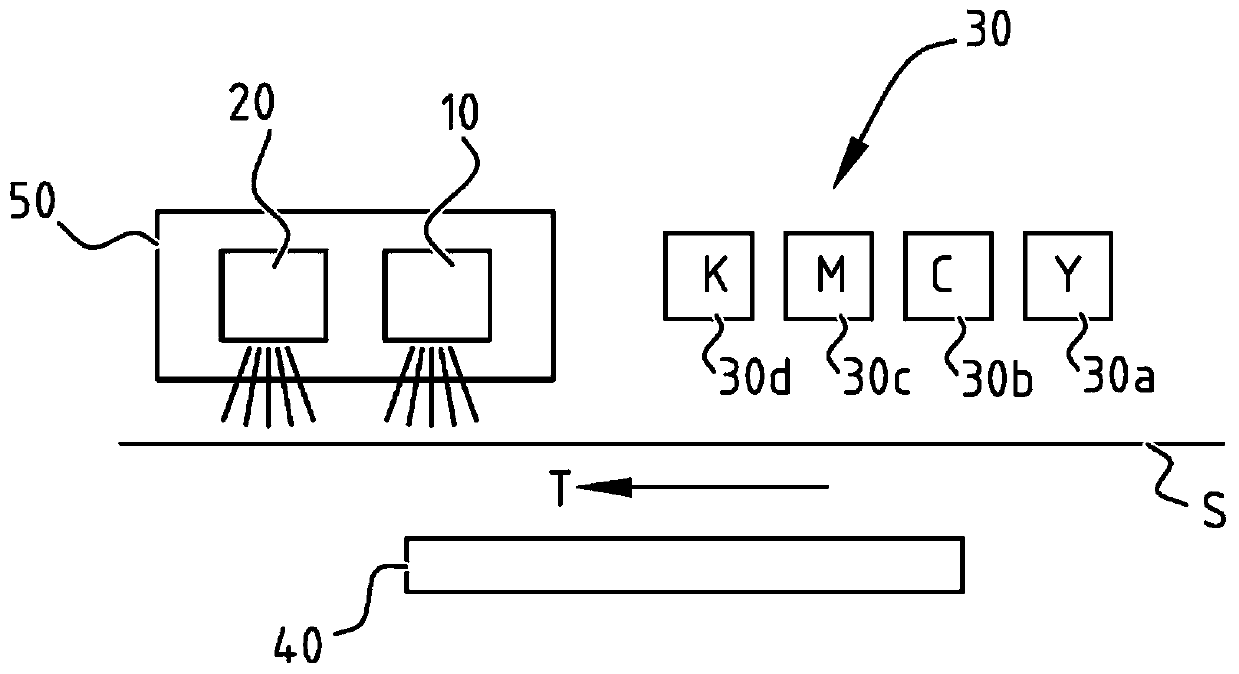
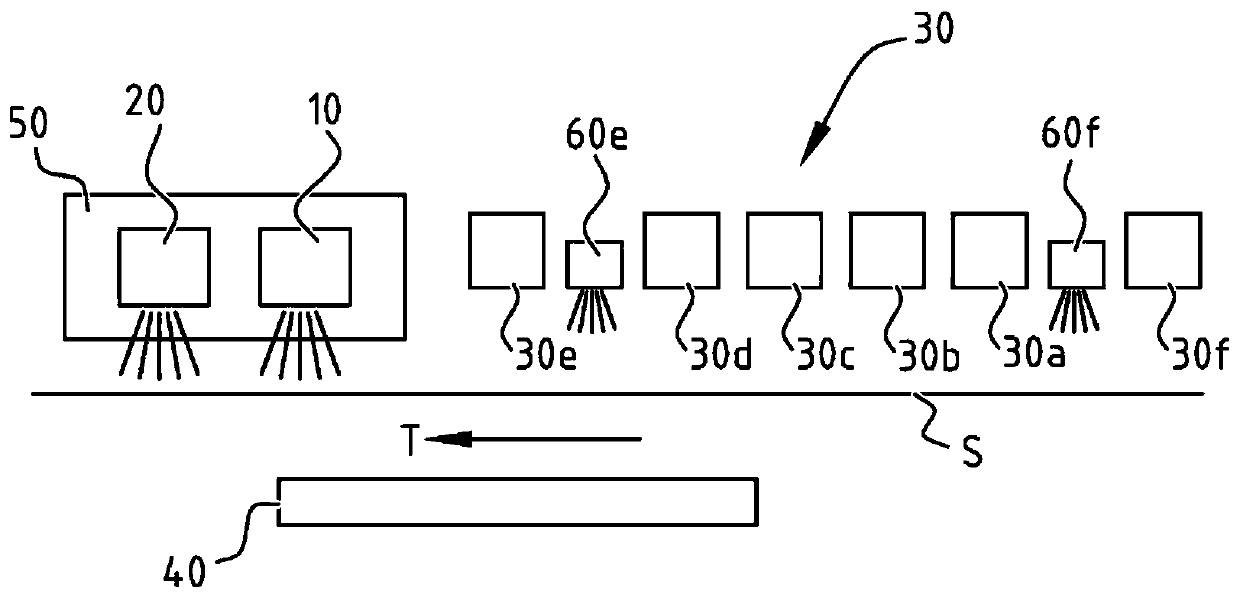
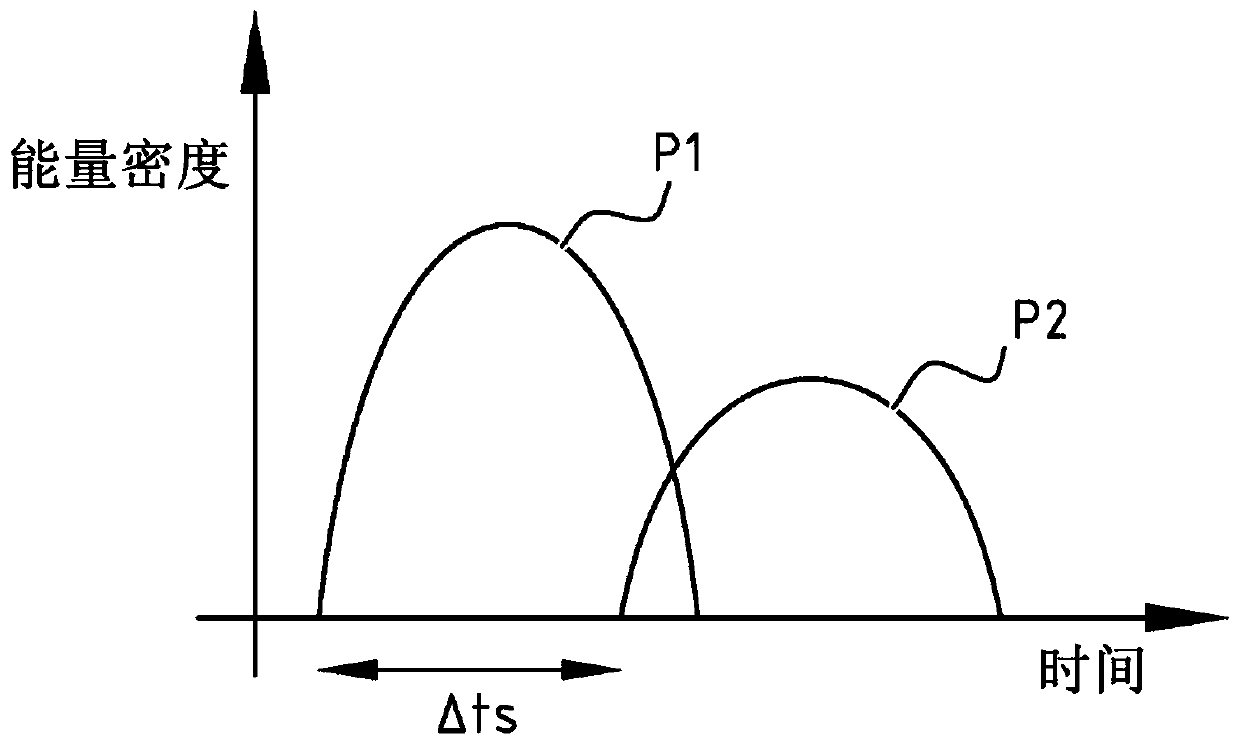
[0112]The samples were printed on a Fasson PP white substrate with UV curable cyan, magenta, yellow and black inks using a web based print engine at a speed of 50 m / min. After depositing the ink, a curing unit is placed with a first curing device emitting a first radiation dose D1 in the range of 320nm to 445nm, followed by a second curing device emitting in the range of 200 to 319nm The second radiation dose D2 within.
[0113] For samples 1 to 6, use a maximum power density of 24W / cm from ITL 2 A Solidcure 2HD unit from ® was used as the first curing unit, and a 140W / cm GEW mercury bulb was used as the second curing unit.
[0114] In samples 7, 8 and 10 a maximum power density of 24W / cm from ITL was used 2 A Solidcure 2HD device was used as the first curing device, and a 140W / cm GEW mercury bulb was used as the second curing device.
[0115] In sample 9 the cure speed was 25m / min instead of 50m / min and 140W / cm was used 2 GEW iron-doped light bulbs.
[0116] After the cu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com