Methods for Treating Osteogenesis Imperfecta
A technology for osteogenesis imperfecta and uses, which can be used in antibody medical components, chemical instruments and methods, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., and can solve problems such as reduced life expectancy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
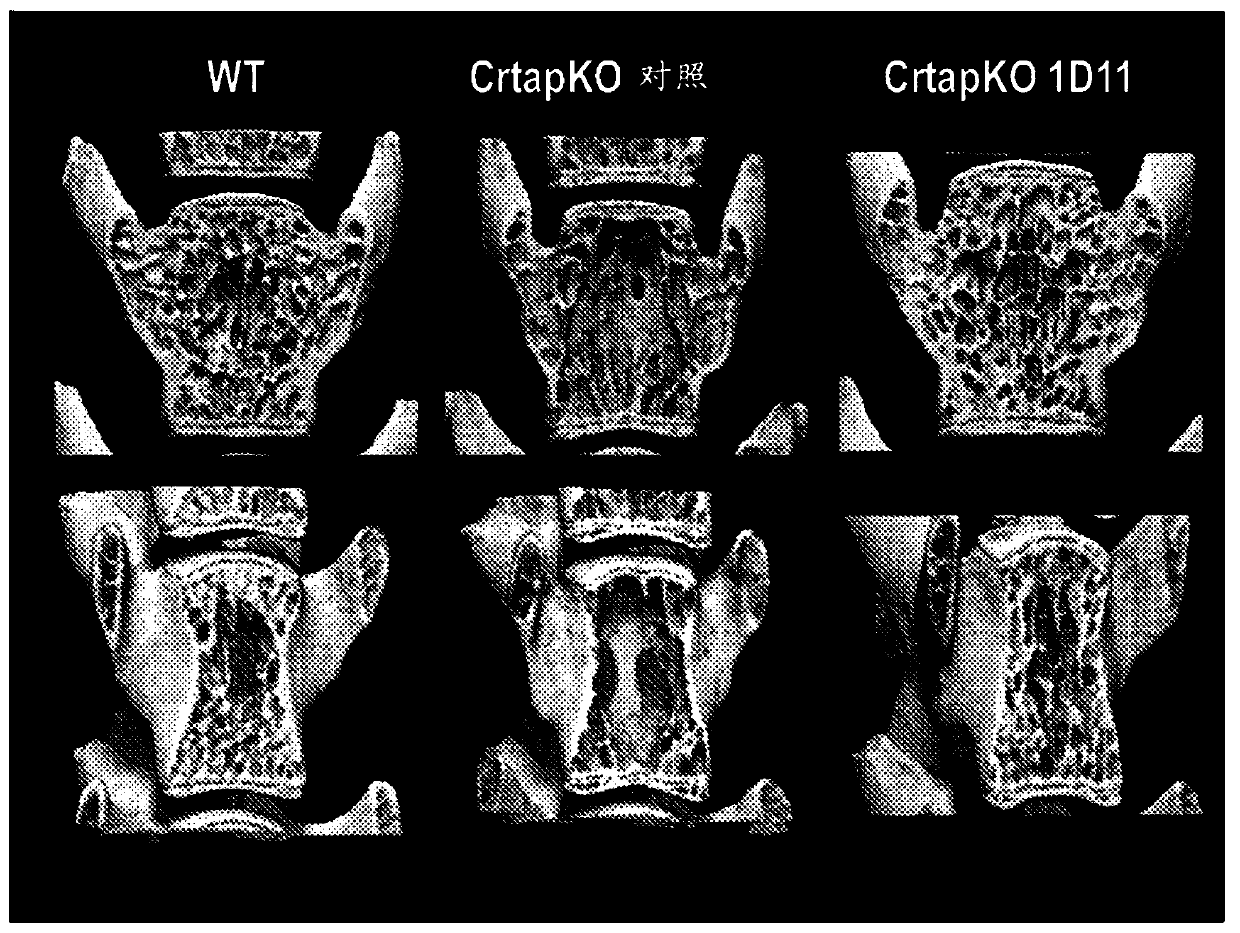
[0114] Several methods can be used to measure and characterize bone structure, density and quality, including histology and histomorphometry, atomic force microscopy, confocal Raman microscopy, nanoindentation, three-point bending test, X-ray Imaging and micro-computed tomography (μ-CT). In an exemplary embodiment, bone is measured and characterized by at least one of these methods.
[0115] The term "bone volume density" refers to the fraction of a given volume of bone (total volume or TV) that contains calcified material (bone volume or BV). Therefore, bone volume density was calculated as BV / TV and reported as a percentage. The term "specific bone surface area" refers to the total bone surface area (BS) per given bone volume. Therefore, the specific bone surface area was calculated as BS / TV. Other common bone measurements include: bone area (B.Ar), trabecular number (Tb.N); trabecular space (Tb.Sp); N.Oc (number of osteoclasts); Oc.S (osteoclast surface area ); Oc.S / BS;...
Embodiment 1
[0233] Example 1: Crtap - / - Altered TGFβ signaling in the calvaria
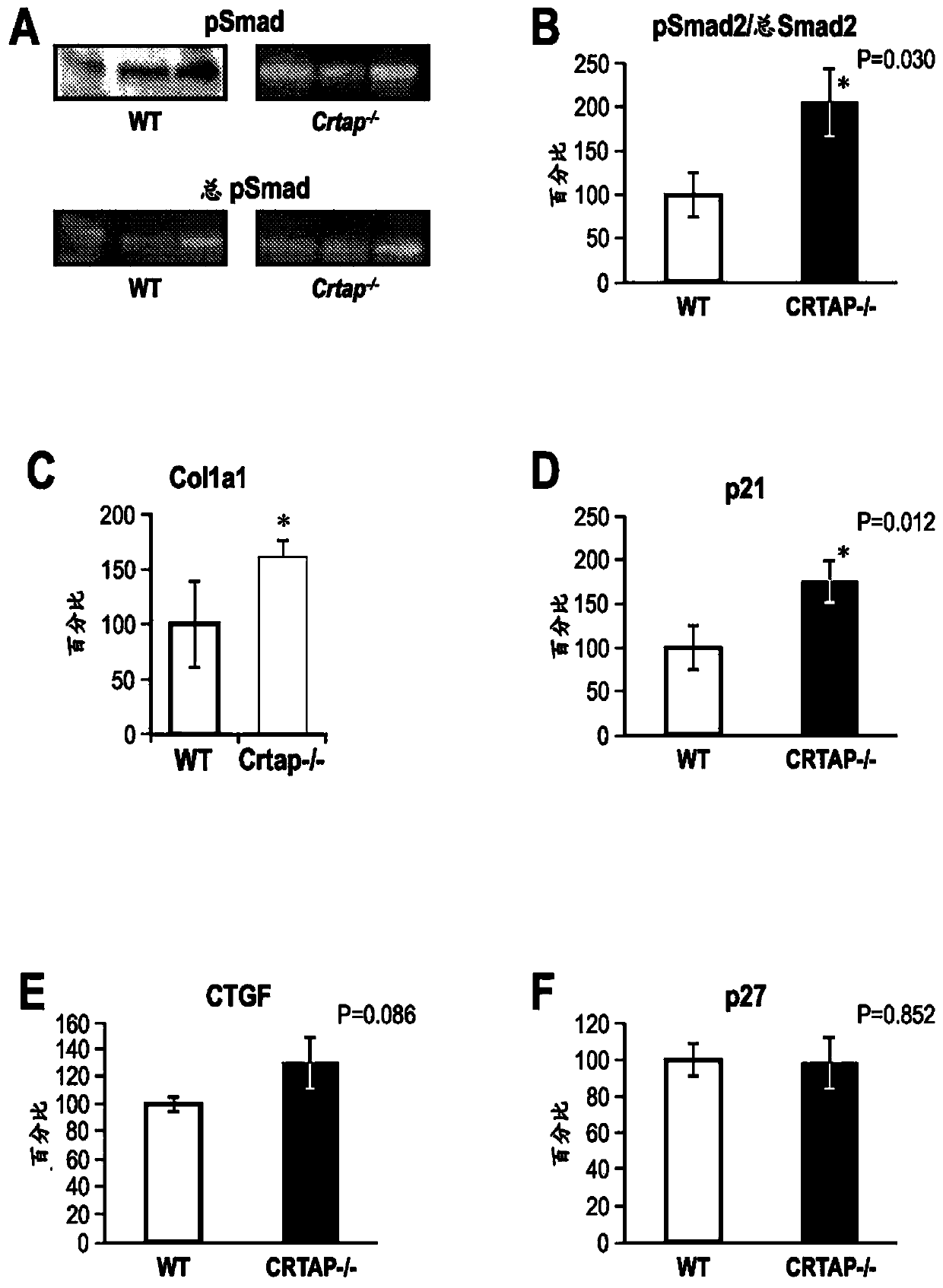
[0234] Analyze Crtap - / - Activation of pSmad2, a member of the TGFβ signaling pathway, and expression of other downstream targets of TGFβ in mice and age-matched littermate wild-type (WT) controls. The calvaria was excised and RNA and protein were extracted and analyzed by real-time-PCR and Western blot, respectively. as seen in figure 1 A and 1B, Crtap compared with wild-type mice - / - Mice had a 100% high ratio of pSmad2 to total Smad2, as determined by Western blot and quantified by densitometry, indicating that TGFβ signaling in Crtap - / - was elevated in mice. Transcriptional targets of TGFβ, such as Col1a1 and p21, are elevated compared to WT controls, as measured by RT-PCR and described respectively in figure 1 C and figure 1 d. measured the fibrillar ECM protein connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and found that compared to WT controls, in Crtap - / - Approximately 50% higher in mice as determ...
Embodiment 2
[0235] Example 2: In Crtap - / - mice in vivo and in crtap - / - Increased TGFb activity in osteoblasts
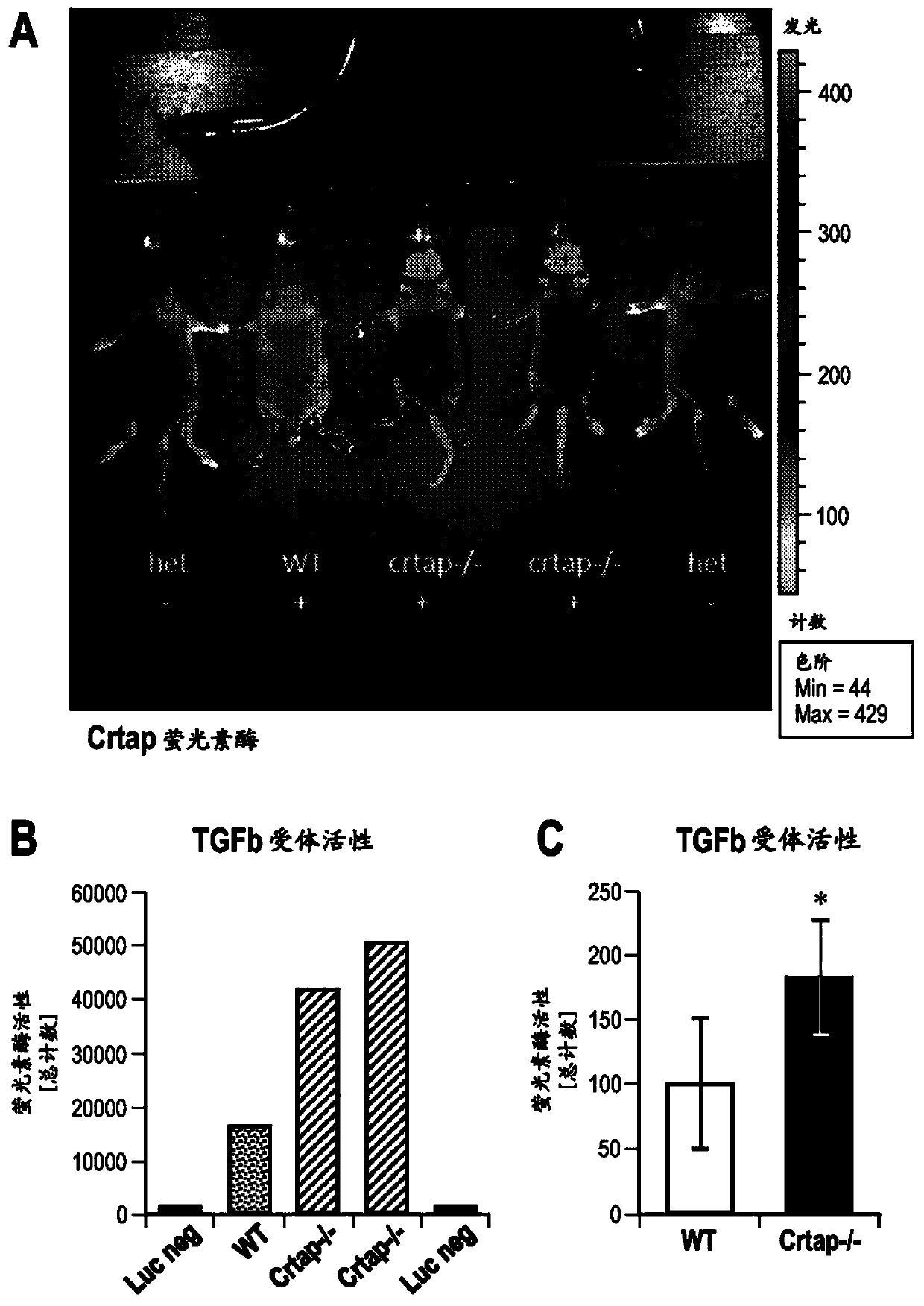
[0236] Crtap - / - Mice were crossed with TGF[beta] reporter mice (Jackson Laboratory; B6.Cg-Tg(SBE / TK-luc)7Twc / J) expressing luciferase in response to activation of TGF[beta] signaling. P9 mice were injected 10 minutes before imaging with the substrate D-luciferin (150 mg / kg). Such as figure 2 As shown in A, compared with WT control, Crtap - / - Mice have much higher fluorescence in their tail, long bones and calvaria, indicating that crtap - / - Increased TGFb activity in mice. figure 2 B, Quantification of luciferase activity at the calvaria.
[0237] Bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) were isolated from Crtap - / - Mice and WT mice, cultured ex vivo under osteogenic conditions, and conditioned medium were analyzed for TGFβ activity using a cell line expressing luciferase in response to activation of TGFβ signaling. Such as figure 2 Shown in C, compared with BMSCs from W...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com