Method and device for measuring heat conductivity coefficient and thermal diffusion coefficient of film material under strains
A technology of thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity, which is applied in the field of heat transfer, can solve the problems of large thermal conductivity error, limitations, and heavy workload, so as to reduce the impact, improve accuracy and convenience, and facilitate operation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046]The invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
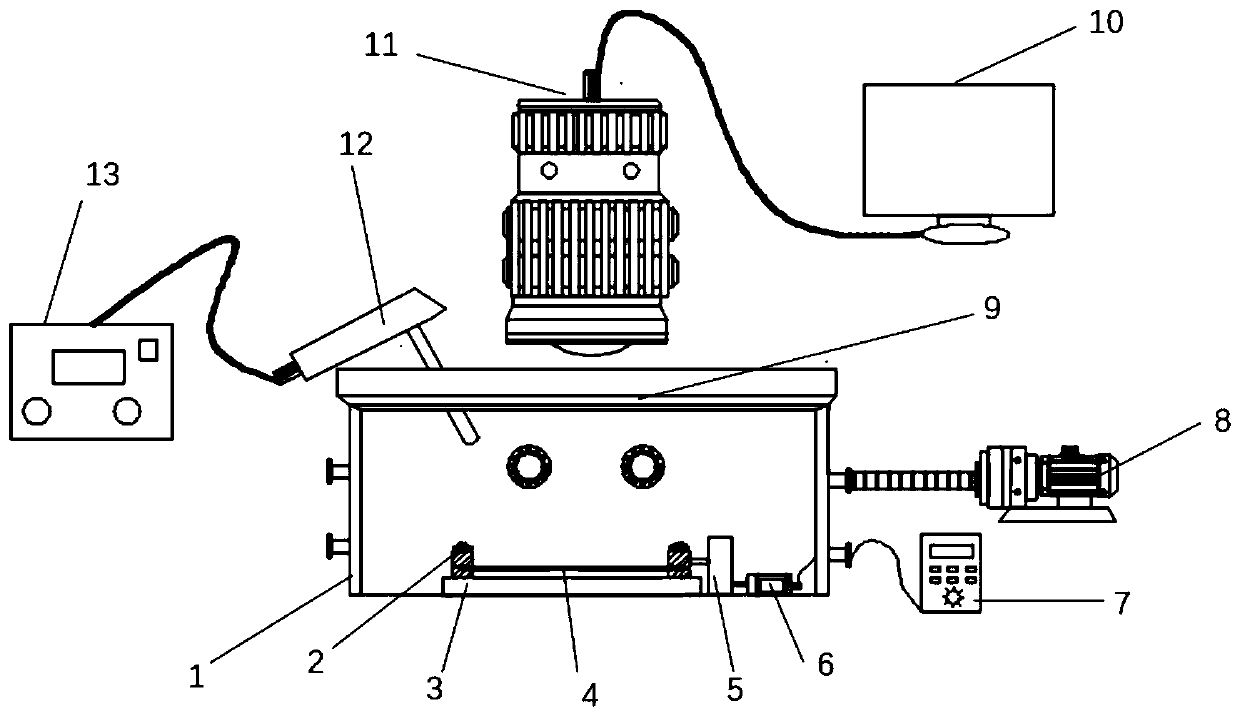
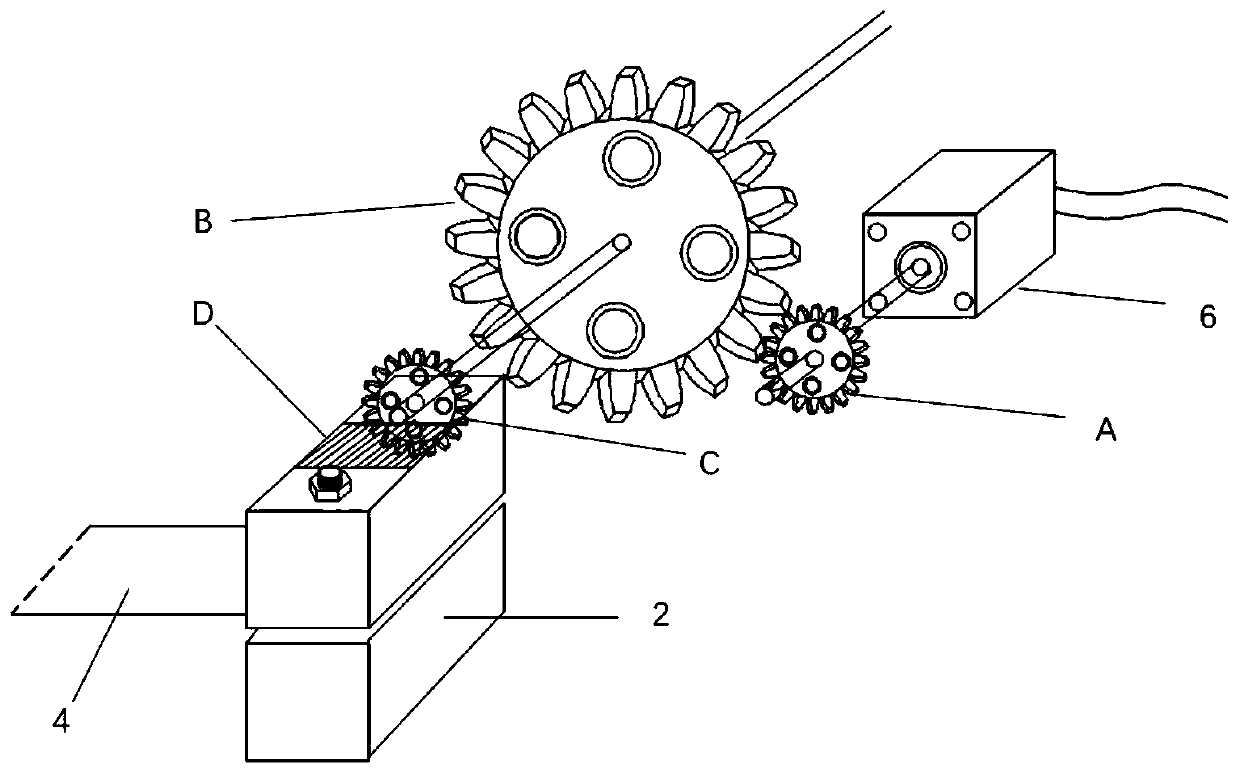
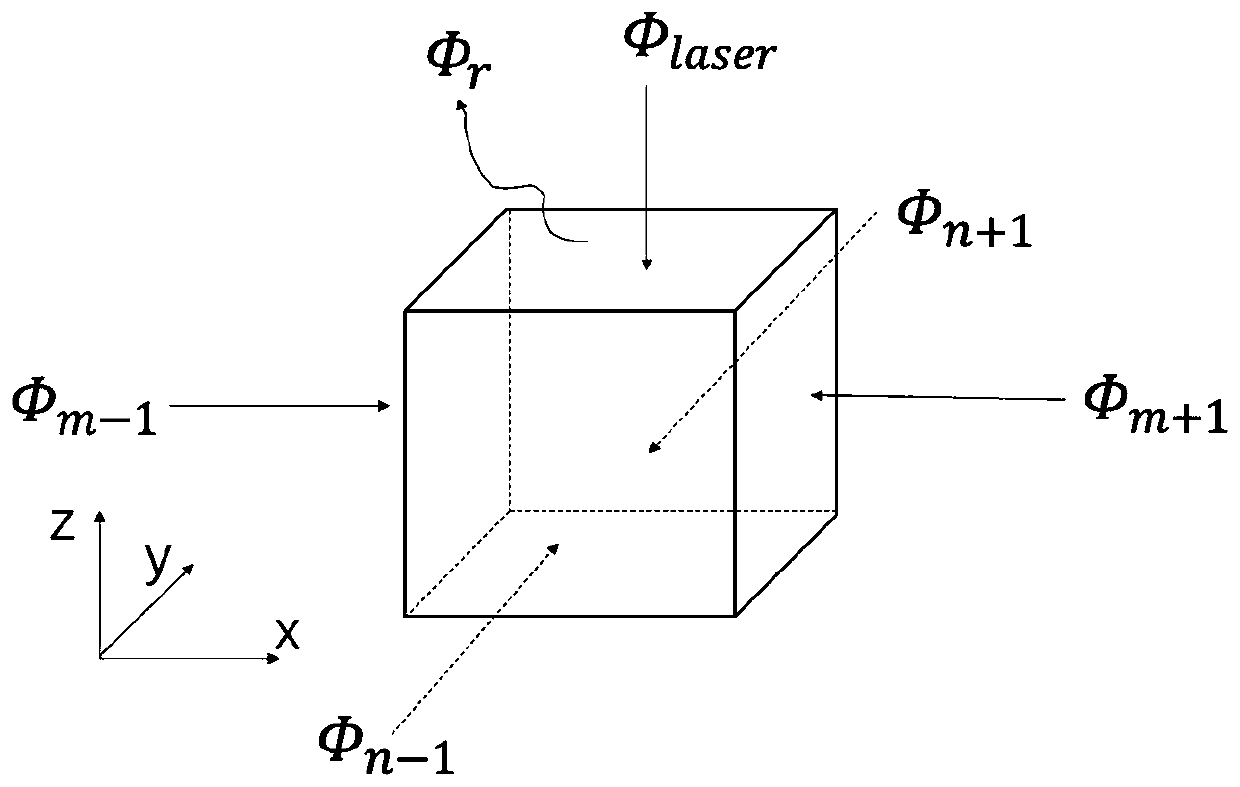
[0047] like figure 1 As shown, a device for measuring the thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity of thin film materials under strain includes a vacuum cavity 1 with a light-transmitting window, a laser probe 12 sealed and extended into the vacuum cavity 1, a laser 13 connected to the laser probe 12, The air pump 8 for evacuating the vacuum chamber 1, the infrared camera 11 for photographing the sample in the vacuum chamber 1 facing the light-transmitting window (the infrared camera 11 is installed and fixed by the support frame), and the data processing module connected with the infrared camera 11 (computer 10 ) and a tensioning mechanism and a driving mechanism located in the vacuum chamber 1, the tensioning mechanism is used for tensioning both ends of the sample 4, and the driving mechanism is used for driving the tensioning mechanism to contr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com