A low-carbon control method for power systems containing gas-coal-fired-wind turbines
A technology of wind turbines and power systems, applied in the field of power systems, can solve the problems of less research on low-carbon operation strategies of power systems, and achieve the effects of improving wind power utilization, promoting wind power consumption, and reducing the cost of carbon emissions on the load side
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
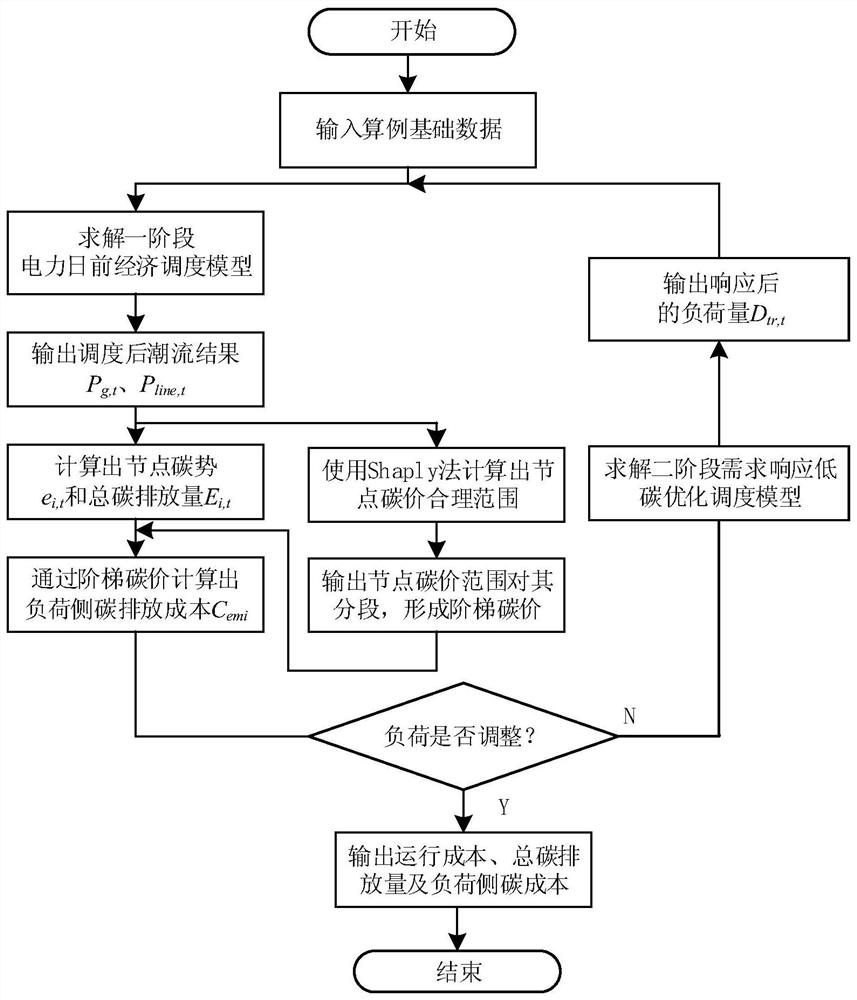
[0051]The embodiment of the present invention establishes a low-carbon control method for a power system including gas-coal-fired-wind turbines, transfers the responsibility of carbon emissions from the power generation side to the load side for accounting, and flexibly adjusts the load during dispatching through the demand response capability of the load side The distribution within the cycle can effectively reduce the total carbon emissions of the system and the cost of carbon emissions on the load side, and provide a more feasible reference for the power control method under the low-carbon background, including the following steps:
[0052] 101: Based on the carbon emission flow theory, assign the carbon emission responsibility of the power generation side to the load side, and calculate the carbon potential and total carbon emission of each node on the load side when there is no response;
[0053] 102: Introduce the Shapley value to share the responsibility of carbon emissi...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Combine below figure 1 , Table 1 and the specific calculation formula are further introduced to the scheme in Example 1, see the description for details:
[0060] 201: An overview of the theory of carbon emission flow in the power system:
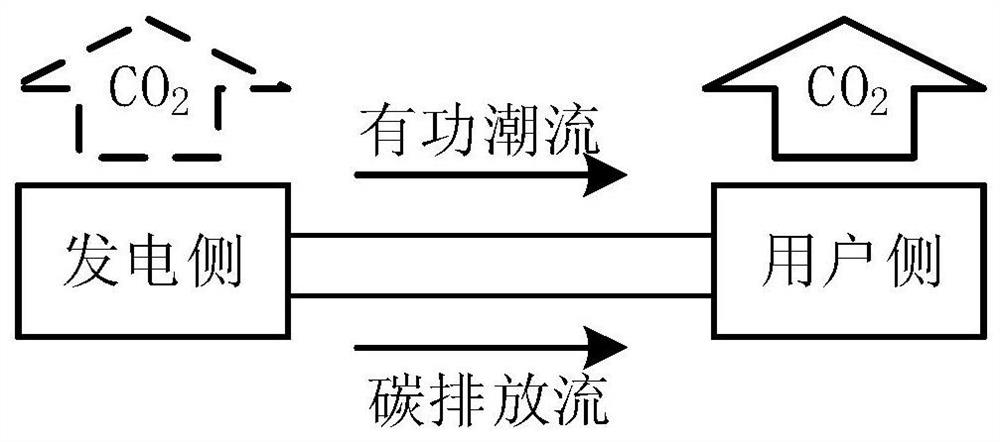
[0061] When fossil fuels are used to generate electricity, a large amount of carbon dioxide is produced after combustion, resulting in carbon emissions. Due to the dependence between carbon emissions and currents, such as figure 1 As shown, carbon emission data labels can be added to the power flow data to form the basis of the carbon emission flow theory.
[0062] The theoretical concepts and indicators of carbon emission flow in the power system are shown in Table 1:
[0063] Table 1 Basic concepts and indicators of carbon emission theory
[0064]
[0065] According to the principle of proportional sharing, any branch of the outgoing power flow has a component of each incoming power flow, let N + and N - is the set of bran...
Embodiment 3
[0145] The following is a combination of specific examples, Figure 3-8 , and table 1-6 carry out feasibility verification to the scheme in embodiment 1 and 2, see below for details:
[0146] 301: PJM-5 Node Test System
[0147] Table 1 Unit parameters
[0148]
[0149]
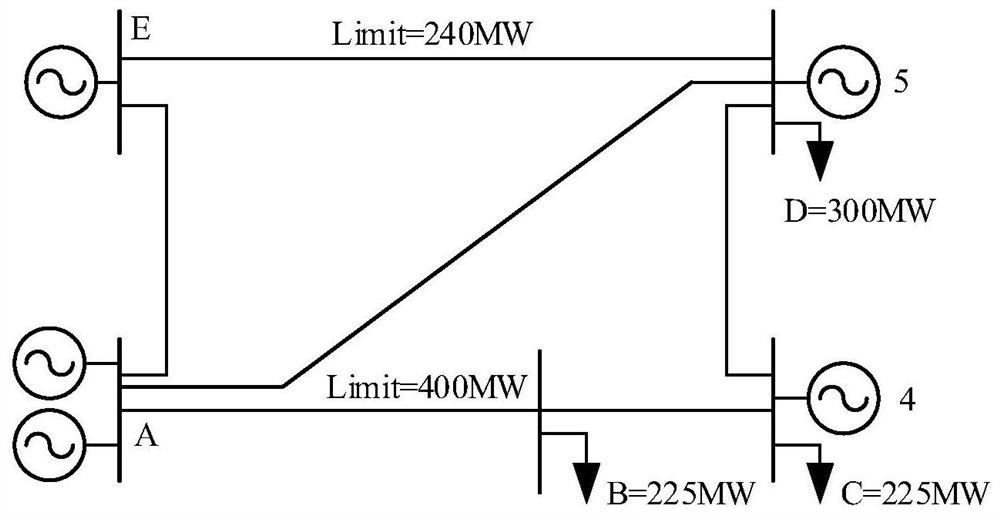
[0150] This example takes the PJM-5 node system as an example for analysis and verification. image 3 Take the PJM-5 node system as an example for analysis. The system includes 5 generator nodes, 6 transmission lines and 3 load nodes B, C, and D. The specific system parameters are shown in Table 1.
[0151] Figure 4 Predict the total load and forecast wind power output for the system within 24 hours. The predicted hourly total load is evenly distributed to load nodes B, C, and D, and the load value of each node in each period is obtained. Establish a two-stage low-carbon economic dispatch model for the PJM-5 node full thermal power scenario and the scenario with wind turbines, and calculate the re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com