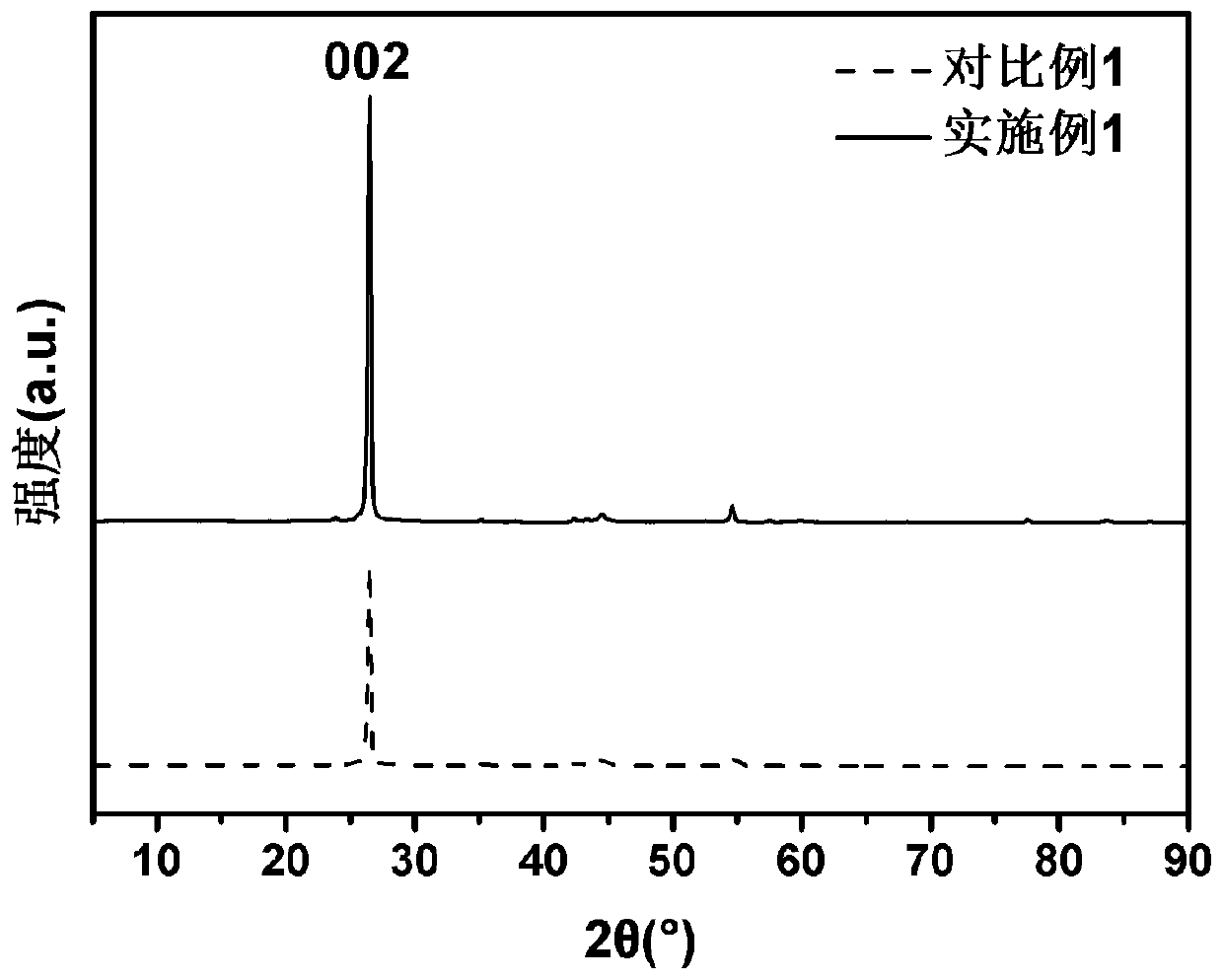
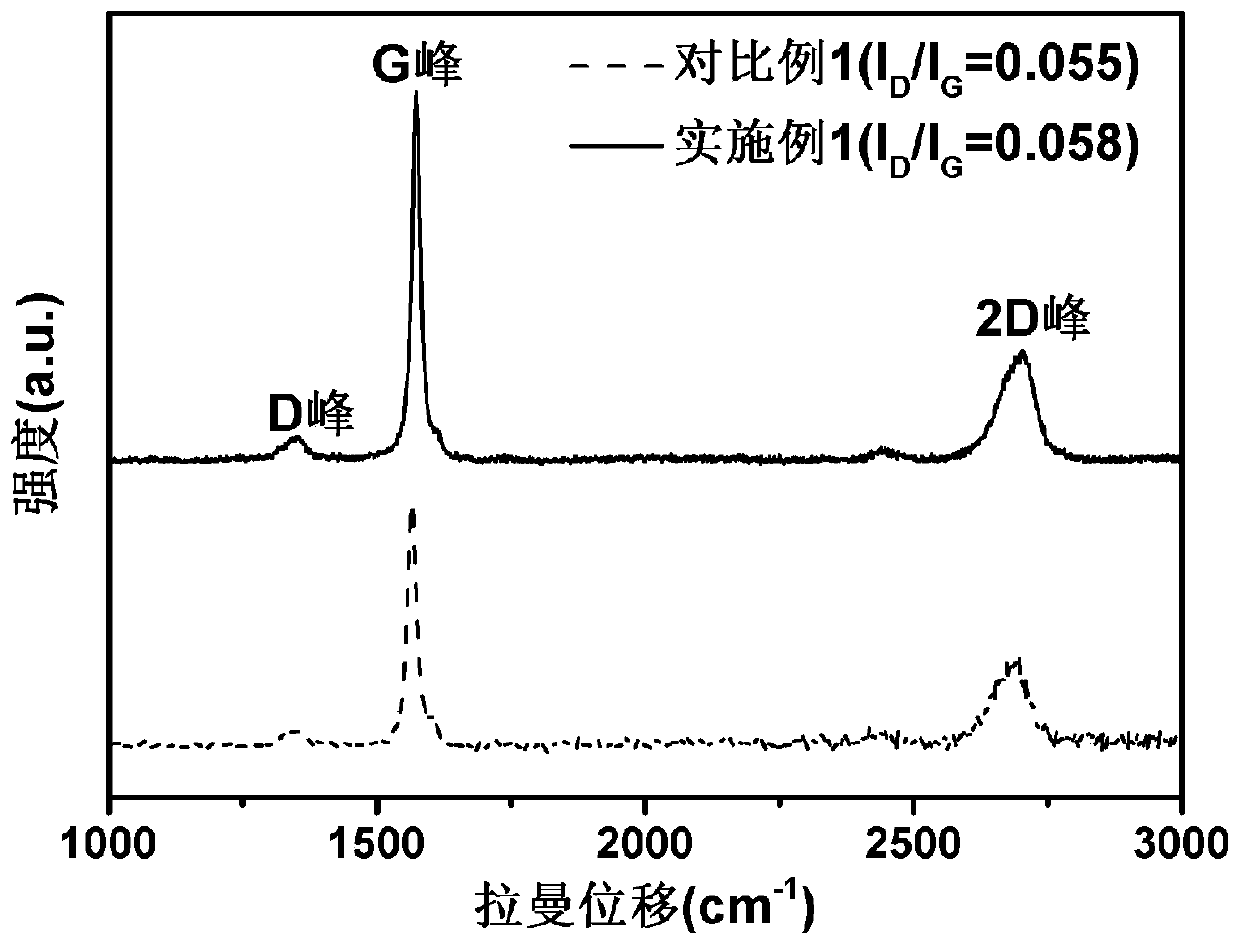
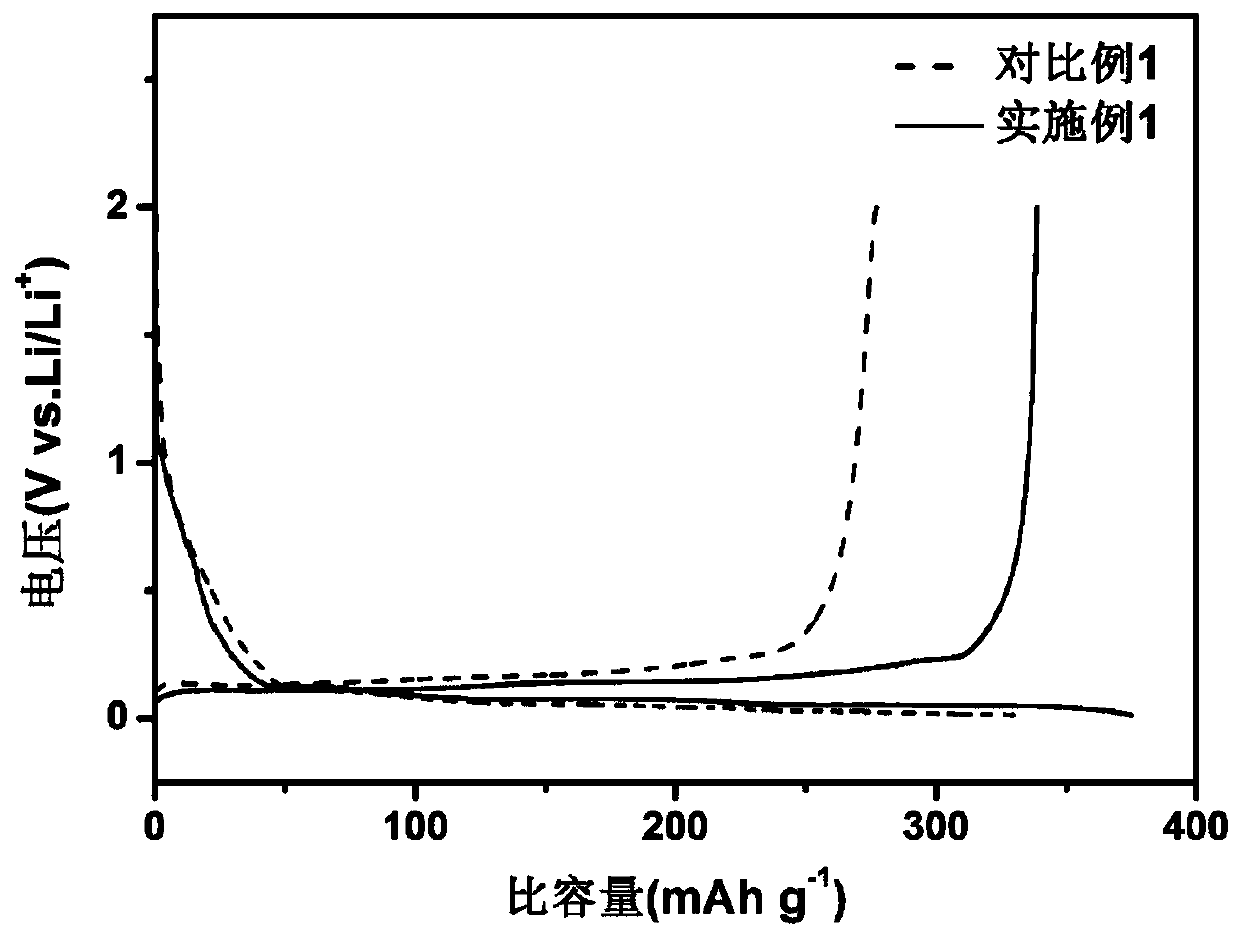
Regeneration method of lithium ion battery negative electrode graphite
A lithium-ion battery and graphite technology, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, battery recycling, etc., to achieve the effects of easy operation, easy promotion and application, and good structural integrity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A regeneration method for lithium-ion battery negative electrode graphite, comprising the following steps:
[0036] (1) Discharging, crushing, hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy are performed on the negative electrode of the waste battery to obtain graphite slag;
[0037] (2) Put the graphite slag into an oven and dry at 50°C for 24 hours, pass through a 400-mesh sieve, and then keep the graphite slag in air at 360°C for 12 hours;
[0038] (3) Put the graphite slag treated in step (2) into 0.1mol / L sulfuric acid solution for soaking, ultrasonic treatment for 2h, to obtain solution A;
[0039] (4) The solution A was subjected to solid-liquid separation, the precipitate was collected, the pH was adjusted to 7 after adding deionized water, and 0.01mol / LEDTA was added to obtain the solution B;
[0040] (5) The solution B is subjected to solid-liquid separation, the precipitate is collected, and the precipitate is repeatedly washed with deionized water and absolute ethanol ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] A regeneration method for lithium-ion battery negative electrode graphite, comprising the following steps:
[0043] (1) Discharging, crushing, hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy are performed on the negative electrode of the waste battery to obtain graphite slag;
[0044] (2) Put the graphite slag into an oven and dry it at 50°C for 24 hours, pass through a 400-mesh sieve, and then keep the graphite slag in air at 480°C for 12 hours;
[0045] (3) Put the graphite slag treated in step (2) into 0.1mol / L sulfuric acid solution for soaking, ultrasonic treatment for 2h, to obtain solution A;
[0046] (4) The solution A was subjected to solid-liquid separation, the precipitate was collected, the pH was adjusted to 7 after adding deionized water, and 0.01mol / LEDTA was added to obtain the solution B;
[0047] (5) The solution B is subjected to solid-liquid separation, the precipitate is collected, and the precipitate is repeatedly washed with deionized water and absolute ethan...
Embodiment 3
[0049] A regeneration method for lithium-ion battery negative electrode graphite, comprising the following steps:
[0050] (1) Discharging, crushing, hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy are performed on the negative electrode of the waste battery to obtain graphite slag;
[0051] (2) Put the graphite slag into an oven and dry at 50°C for 24 hours, pass through a 400-mesh sieve, and then keep the graphite slag in air at 360°C for 12 hours;
[0052] (3) Put the graphite slag processed in step (2) into 5mol / L sulfuric acid solution for soaking, and ultrasonically treat for 2h to obtain solution A;
[0053] (4) The solution A was subjected to solid-liquid separation, the precipitate was collected, the pH was adjusted to 7 after adding deionized water, and 0.01mol / LEDTA was added to obtain the solution B;
[0054](5) The solution B is subjected to solid-liquid separation, the precipitate is collected, and the precipitate is repeatedly washed with deionized water and absolute ethano...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com