A Genetically Engineered Strain of Rhodosporidium Saccharomyces Producing Astaxanthin
A technology for genetically engineered strains and Rhodosporidium spores, applied in the field of biotechnology, can solve problems such as high price and achieve good growth effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: Construction of recombinant plasmid pRHcrtW-crtZ by seamless cloning
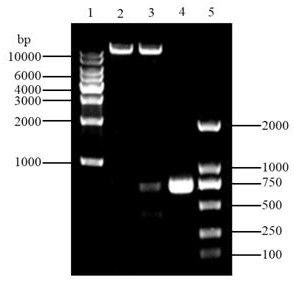
[0021] Using Vazyme's ClonExpress ® II One Step Cloning Kit kit for the construction of recombinant plasmid pRHcrtW-crtZ; designed for seamless cloning according to the instructions crtW, crtZ Gene-specific primers, using the target fragment synthesized by Shuoqing Biotechnology Co., Ltd. as a template, perform PCR amplification on a PCR instrument (BIOER company). The primers, components and amplification conditions used in the reaction are as follows:
[0022] pRHcrtW-F: 5'- ACAACACCAGATCACTCA CCATGG ATGAGCGCACATGCC -3', underlined as Nco I restriction site;
[0023] pRHcrtW-R: 5'-ATCCCGGTCGGCATCTAC GATATC TCATGCGGTGTCCCC -3' , underlined as EcoR V restriction site;
[0024] pRHcrtZ-F: 5'-ATACATTATACGAAC GGTACC TGTACAGTGACCGGT -3', underlined Kpn Ⅰ Restriction site;
[0025] pRHcrtZ-R: 5'-CTGATCCAAGCTCAAGCT AAGCTT GCATGCCTGCAG -3', underlined Hind Ⅲ Restriction site; ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: Construction of Rhodosporidium genetically engineered strains and synthesis of astaxanthin and carotenoids in Rhodosporidium yeast
[0030] 1. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Rhodosporidium YM25235
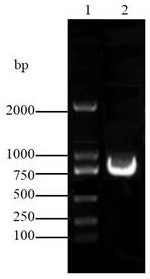
[0031] The recombinant plasmid pRHcrtW-crtZ was transformed into Rhodosporidium YM25235 by the Agrobacterium-mediated method, and the transformants were selected with the YPD medium containing the final concentration of Hygromycin B (Hygromycin B) at a final concentration of 150 µg / mL. Genomic DNA of yeast transformants was extracted according to the steps in the instructions of the DNA extraction kit of Bioengineering Co., Ltd., and then verified by PCR. The results are as follows: Image 6 shown;
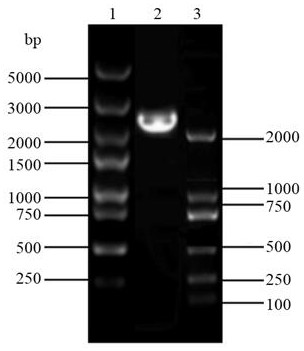
[0032] 2. Analysis of astaxanthin and carotenoid synthesis content in Rhodosporidium yeast after transformation of recombinant plasmid pRHcrtW-crtZ by HPLC
[0033] The strain transformed with the recombinant plasmid pRHcrtW-crtZ was cultured at 28°C for 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com