Renewable electrochemical sensor for detecting trace kanamycin, and preparation method and application thereof
A kanamycin and biosensor technology, applied in the field of biosensors, can solve the problems of low specificity, sensitivity, and high cost, and achieve the effects of high specificity, low detection limit, and fast detection speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] A preparation method of the electrochemical biosensor of the present invention:
[0064] a. The gold electrode is first polished in 0.3 and 0.05 µm alumina slurry until it becomes a mirror surface, and then rinsed repeatedly with PBS and secondary water;
[0065] b. Add 10 μL of 10 μM H3 dropwise to the electrode surface, incubate at 37 °C for 2 h, and wash.
[0066] So far, the modification process of the electrode has come to an end. The following describes the reaction in the homogeneous solution and the main steps in the homogeneous reaction:
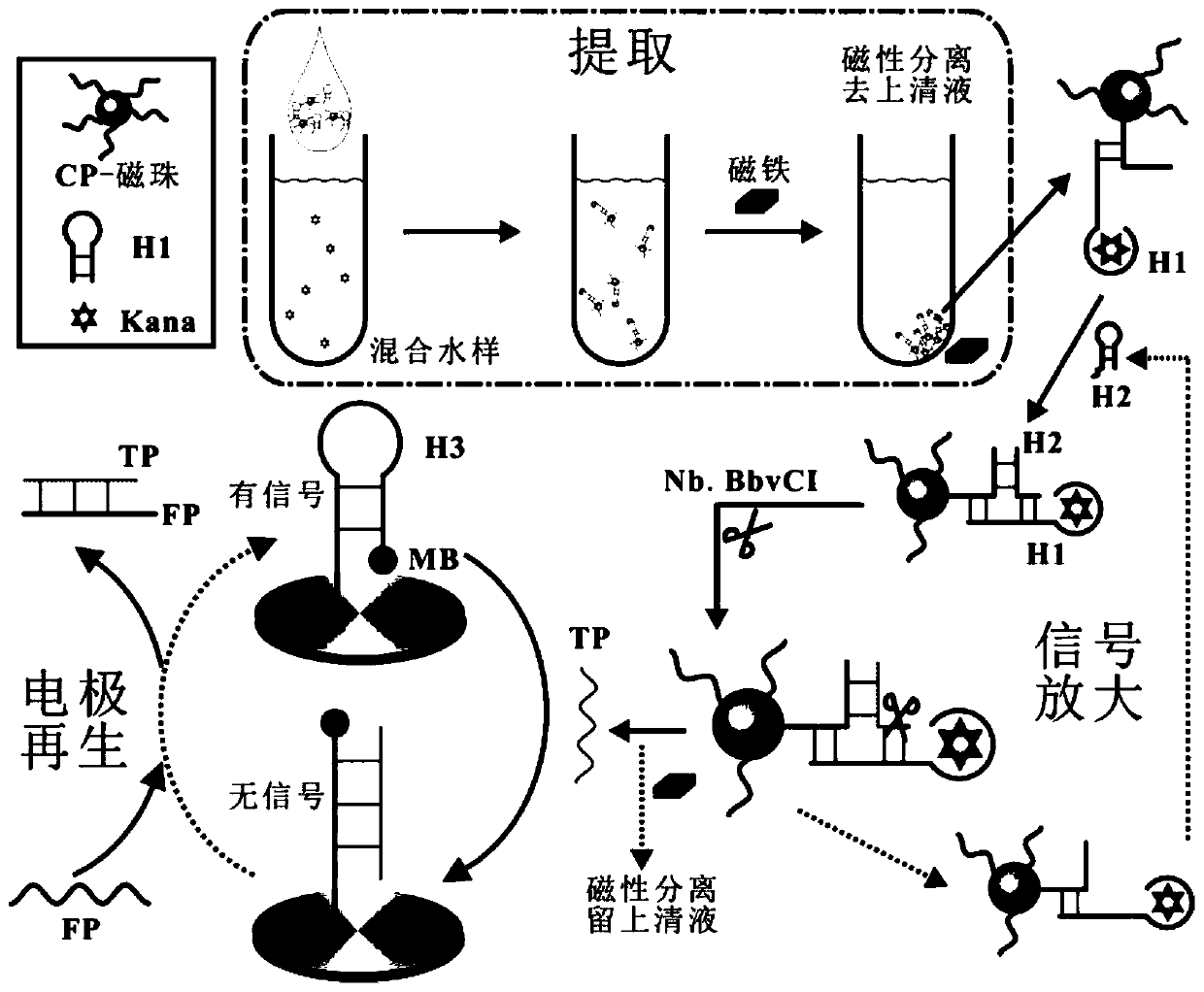
[0067] a. Add 200 μL 0.5 μM magnetic beads-CP (based on CP) and 200 μL 0.5 μM H1 into 4.6 mL water sample to be tested (Kana concentration is 100 pM), shake for 30 s, and place in a constant temperature of 37 ℃ Incubate in the box for 30 min; then, use a magnet to remove the supernatant through magnetic separation to obtain magnetic beads-CP / H1 / Kana, which are dispersed in 20 μL of ultrapure water;
[0068] b. Take 20 μL ma...
Embodiment 2
[0075] A preparation method of the electrochemical biosensor of the present invention:
[0076] a. The gold electrode is first polished in 0.3 and 0.05 µm alumina slurry until it becomes a mirror surface, and then rinsed repeatedly with PBS and secondary water;
[0077] b. Add 10 μL of 10 μM H3 dropwise to the electrode surface, incubate at 37 °C for 2 h, and wash.
[0078] So far, the modification process of the electrode has come to an end. The following describes the reaction in the homogeneous solution and the main steps in the homogeneous reaction:
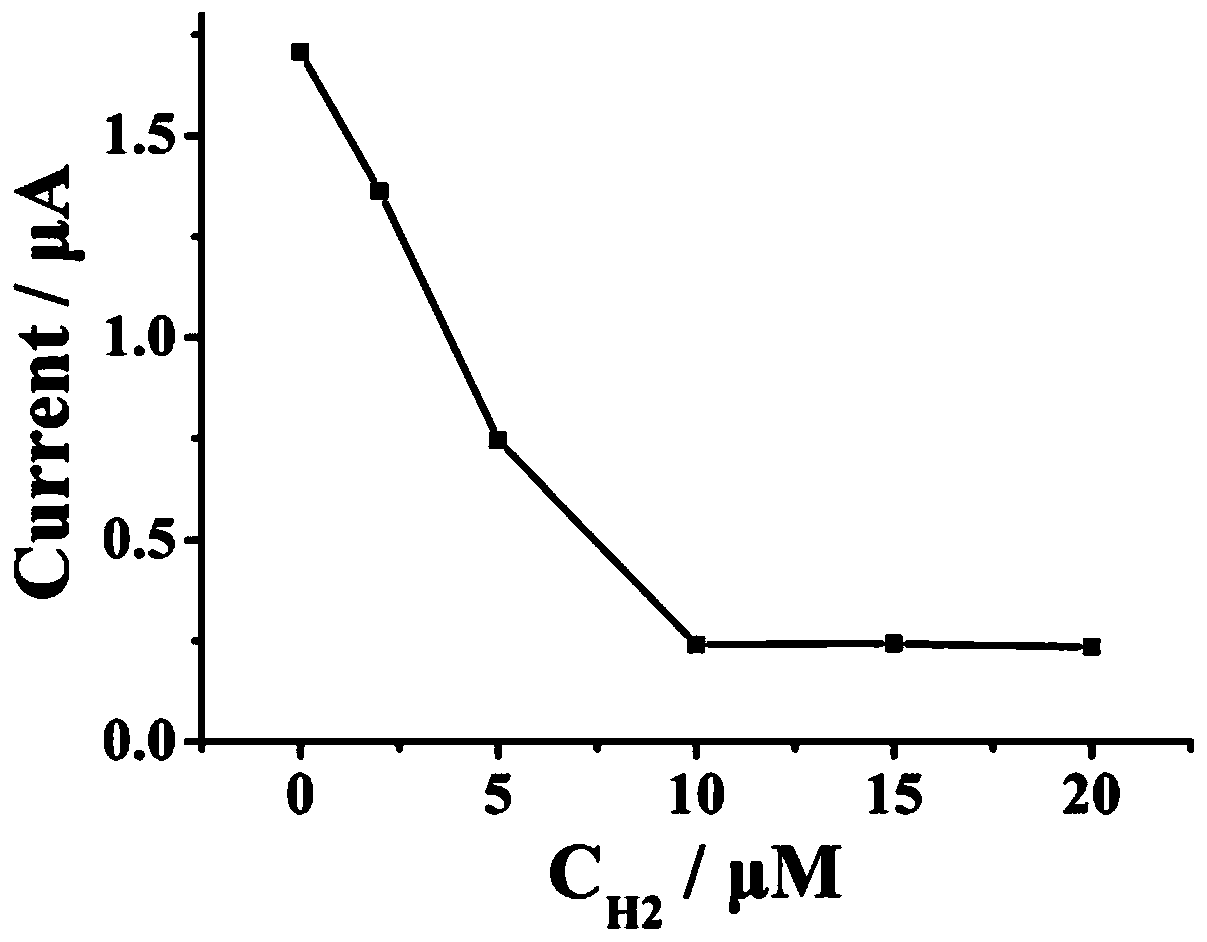
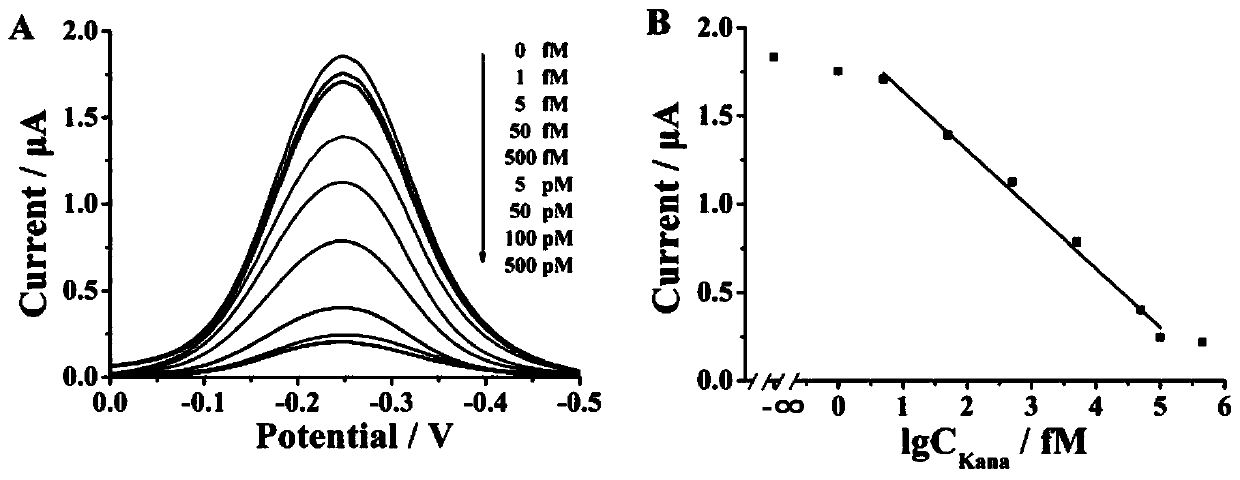
[0079] a. Add 200 μL 0.5 μM magnetic beads-CP (based on CP), 200 μL 0.5 μM H1 to 4.6 mL water sample to be tested (Kana concentration: 0, 1 fM, 5 fM, 50 fM, 500 fM, 5 pM, 50 pM, 100 pM, 500 pM), shaken for 30 s, and incubated in a 37 °C incubator for 30 min; then, the supernatant was removed by magnetic separation with a magnet to obtain magnetic beads-CP / H1 / Kana, dispersed in 20 μL ultrapure water;
[0080] b. Take 20 μL...
Embodiment 3
[0086] A preparation method of the electrochemical biosensor of the present invention:
[0087] a. The gold electrode is first polished in 0.3 and 0.05 µm alumina slurry until it becomes a mirror surface, and then rinsed repeatedly with PBS and secondary water;
[0088] b. Add 10 μL of 10 μM H3 dropwise to the electrode surface, incubate at 37 °C for 2 h, and wash.
[0089] So far, the modification process of the electrode has come to an end. The following describes the reaction in the homogeneous solution and the main steps in the homogeneous reaction:
[0090] e. Add 200 μL of 0.5 μM magnetic beads-CP (based on CP) and 200 μL of 0.5 μM H1 into 4.6 mL of the water sample to be tested (Kana concentration is 100 pM), shake for 30 s, and place in a constant temperature of 37 °C Incubate in the box for 30 min; then, use a magnet to remove the supernatant through magnetic separation to obtain magnetic beads-CP / H1 / Kana, which are dispersed in 20 μL of ultrapure water;
[0091] f....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com