Method for detecting activity of double-strand break generation reagent
A double-strand break and reagent technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, measurement devices, biological material analysis, etc., can solve difficult PCR amplification products to distinguish from original templates, cannot effectively quantitatively analyze cutting efficiency, and increase gene editing. risks, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0078] Materials and methods
[0079] PEM-seq procedure and data analysis
[0080] 1. Primer extension
[0081] All biotin-labeled primers (see Table 2 for sequences) (Sangon, Shanghai) were set within 100 bp from the cleavage site. Repeated annealing and denaturation of the primers and 20 μg of sonicated genomic DNA (0.3-2 kb), the specific conditions are as follows: 95°C for 3 minutes; 95°C for 2 minutes, annealing at the annealing temperature Ta for 3 minutes, 5 cycles ( See Table 1 for details); annealed at Ta for 3 minutes. Bst polymerase 3.0 (NEB) was then added for primer extension: 10 minutes at 65°C, 5 minutes at 80°C. After that, 1.2×AxyPrep Mag PCR Clean Up bead (Axygen, USA) was added to remove excess biotinylated primers. The purified product was heated to 95°C for 5 minutes, then rapidly cooled on ice for 5 minutes to denature the DNA. Finally using Dynabeads TM MyOne TM Sterptavidin C1 (Thermo Fisher) enriches for biotin-labeled extension products.
...
Embodiment 2
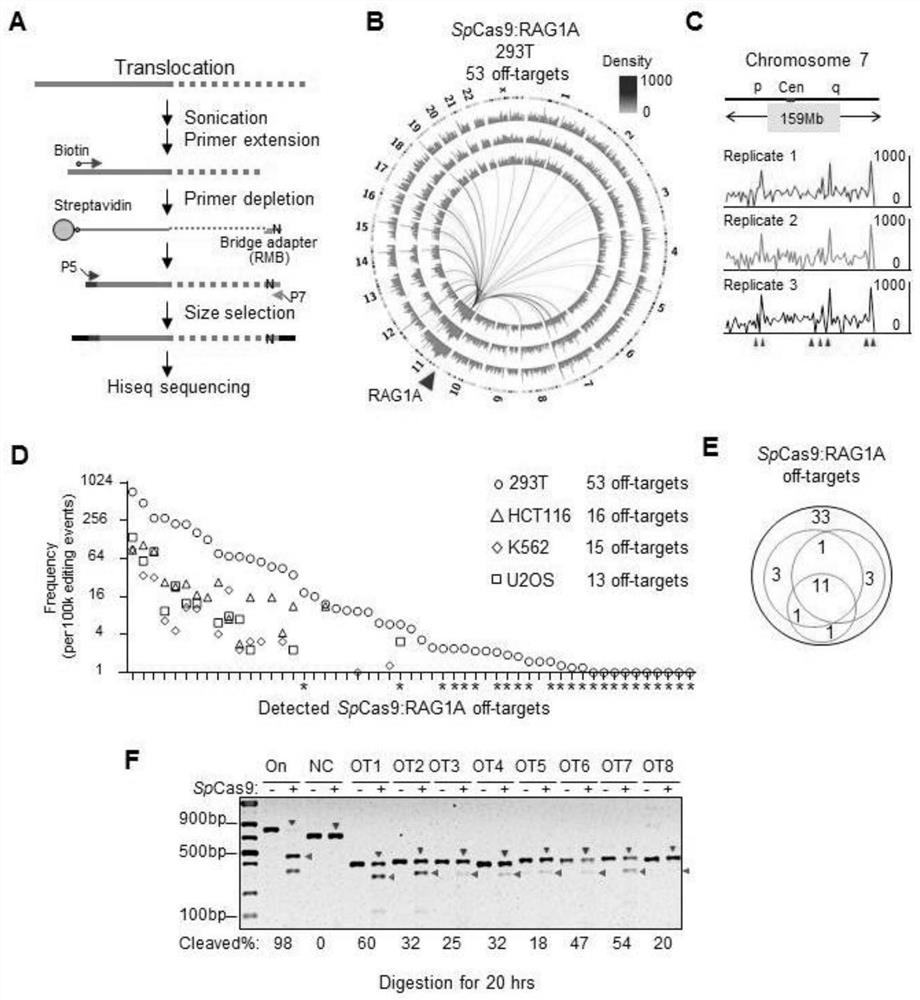
[0134] Example 2 PEM-seq can detect off-target hotspots of CRISPR / Cas9 very sensitively
[0135] This example compares with the LAM-HTGTS method, which identified 33 off-target sites in HEK293T cells using SpCas9 targeting the RAG1A site (Frock et al., 2015). Each PEM-seq library was constructed using about 20 μg of CRISPR / Cas9-treated genomic DNA, and the extension primers were designed to be within 200 bp of the target cleavage site. Experiments were repeated three times for hotspot analysis of translocation junctions ( figure 1 B and 1C); hotspots with a high sequence similarity to the target site and / or defined PAMs occurring in at least two replicates were considered off-target sites (Frock et al., 2015).
[0136] A total of 53 off-target sites were identified by PEM-seq, including 24 new sites not identified by LAM-HTGTS, while 4 weak sites identified by LAM-HTGTS were lost ( figure 1 B-D and Table S2). In order to verify the authenticity of these off-target sites, 8 ...
Embodiment 3
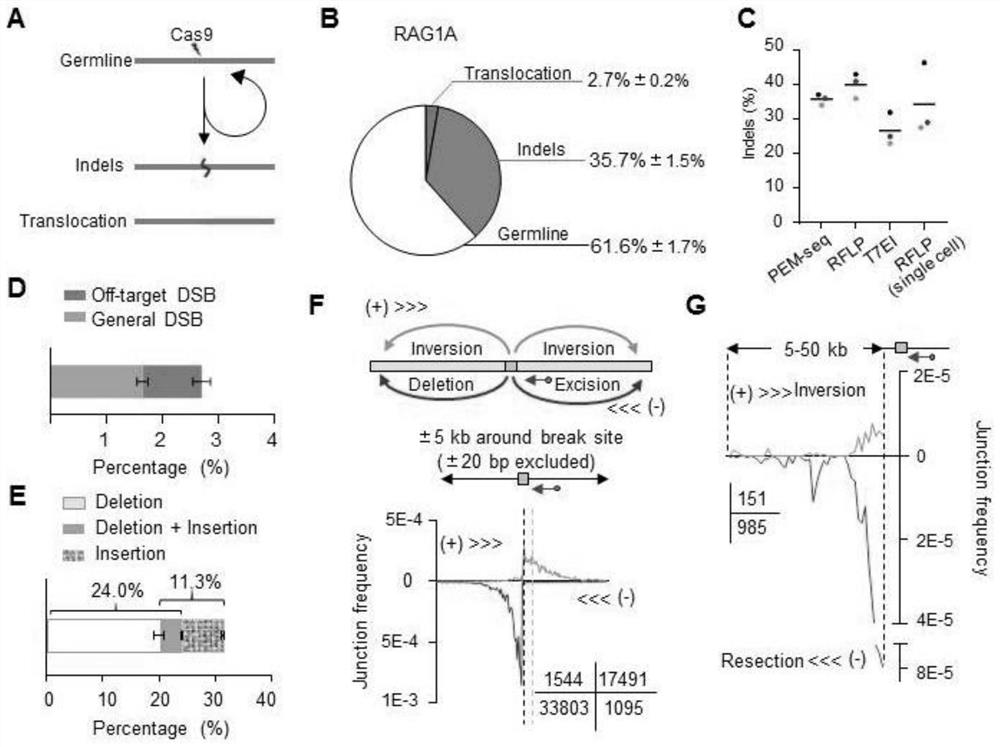
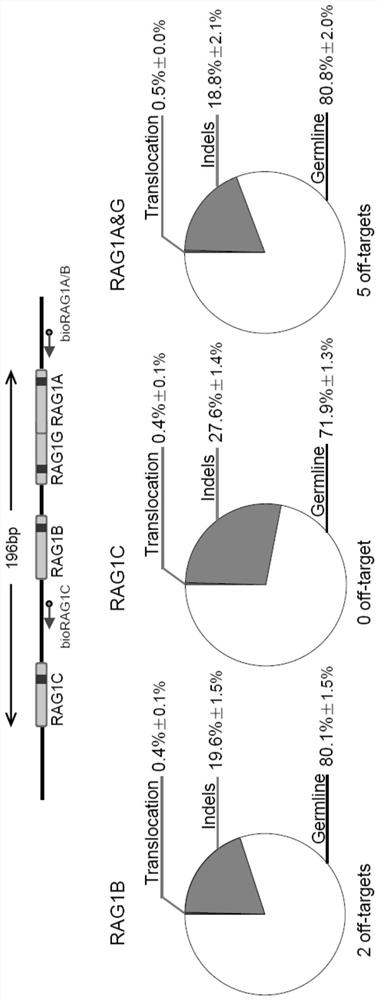
[0138] Example 3 PEM-seq can quantitatively analyze the editing ability of CRISPR / Cas9
[0139] This example tests the ability of PEM-seq to analyze all gene editing events, especially the quantitative analysis. The events generated after gene editing can be divided into: chromosomal translocation, insertion and deletion (indel) and germline (germline). Chromatin translocation is the joining of two independent double-strand breaks (DSBs), such as those that occur between a target DSB and a DSB cleaved off-target by Cas9, or with a basal level of DSB naturally present in the genome; indels are detected by Cas9 The cleaved ends are reconnected through the in vivo DNA repair mechanism, but due to incomplete repair, the repaired sequence is different from the original sequence, resulting in insertion or deletion of the sequence ( figure 2 A). The so-called "germline" is that the target fragment is not cut or completely repaired after cutting. In the case of complete repair, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com