Metal additive manufacturing method and additive manufacturing material
A metal additive and manufacturing method technology, applied in the field of 3D printing, can solve problems such as uneven expansion and contraction, accelerated metal component failure, damage to structural integrity, etc., to reduce deformation, long service life, and reduce tensile residuals. effect of stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] This embodiment provides a metal additive manufacturing material, and the metal additive manufacturing material has a volume expansion characteristic during cooling. Specifically, the metal additive manufacturing material in this embodiment is martensitic steel, including the following percentage components: Ni 6-20%, Cr 5-16%, Mn<20%, Cu<10%, Mo 0- 2%, Si<2%, C<0.4, and the balance is Fe.
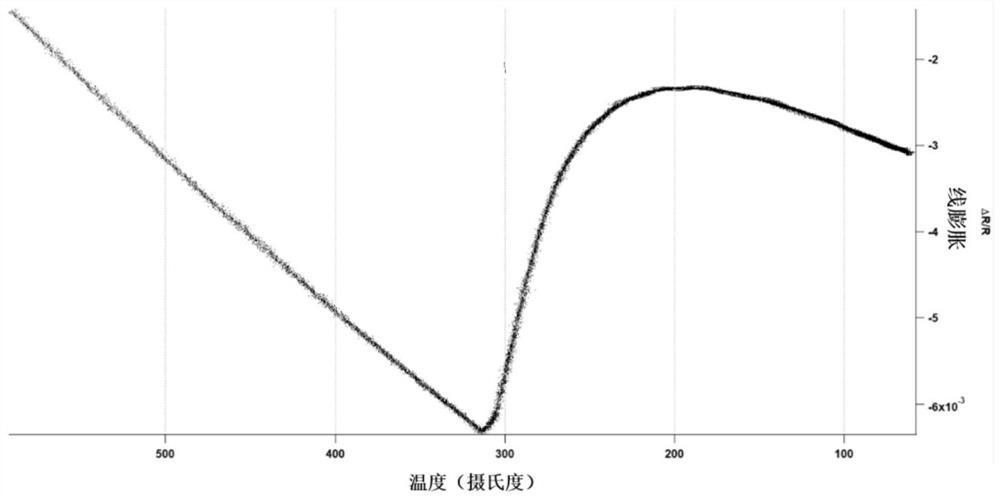
[0033] The martensitic steel of this embodiment has volume expansion characteristics in allotropic transformation, and its expansion curve is as follows figure 1 as shown, figure 1 The expansion curves in are measured by dilatation method.
[0034] From figure 1 It can be seen that the martensitic transformation initiation temperature ranges from 25 to 800°C, and the martensite transformation begins at close to 220°C (martensite transformation initiation temperature, Ms), and the volume expansion reaches the maximum at about 50°C. It means that cooling to this temperature has th...
Embodiment 2
[0041]In order to reduce the tensile residual stress or / and deformation generated during the additive manufacturing process, this embodiment provides a metal additive manufacturing method. In this embodiment, materials with volume expansion characteristics during the cooling process are selected for additive manufacturing. Specifically, in this embodiment, martensitic steel is selected for additive manufacturing.
[0042] During the cooling process of martensitic steel, high-temperature austenite transforms into low-temperature phases, such as ferrite, bainite, and martensite, or these low-temperature phases of ferrite, bainite, and martensite are in steel mixture, and leads to volume expansion, which can counteract high tensile residual stress and deformation; the effectiveness of counteracting high tensile residual stress and deformation depends on the degree of volume expansion and the temperature range in which the allotropic phase transition occurs, Martens Formation of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com